# 3.2 散列表
map 由運行時實現,編譯器輔助進行布局,其本質為散列表。我們可以通過圖 1 展示的測試結果看出使用 map 的容量(無大量碰撞)。
**圖1: cgo/Go/C/net 包 在網絡 I/O 場景下的性能對比,圖取自github.com/changkun/cgo-benchmarks**
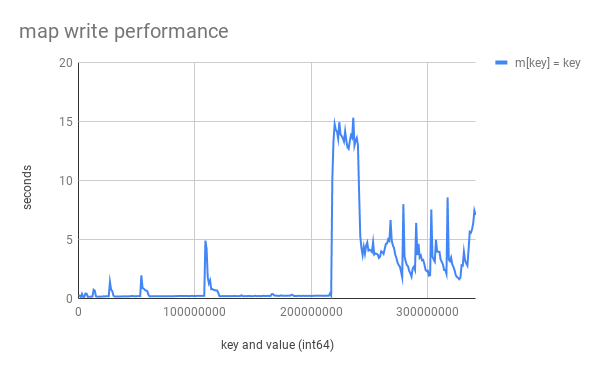
**圖1: map\[int64\]int64 寫入性能,其中`key==value`且 key 從 1 開始增長。從 218000000 個 key 后開始出現比較嚴重的碰撞。**
我們就 int64 這種情況來看看具體 Go map 的運行時機制:
```
func write() {
var step int64 = 1000000
var t1 time.Time
m := map[int64]int64{}
for i := int64(0); ; i += step {
t1 = time.Now()
for j := int64(0); j < step; j++ {
m[i+j] = i + j
}
fmt.Printf("%d done, time: %v\n", i, time.Since(t1).Seconds())
}
}
```
上面這段代碼中涉及 map 的匯編結果為:
```
TEXT main.write(SB) /Users/changkun/dev/go-under-the-hood/demo/7-lang/map/main.go
(...)
main.go:10 0x109386a 0f118c2450010000 MOVUPS X1, 0x150(SP)
main.go:11 0x1093872 0f57c9 XORPS X1, X1
main.go:11 0x1093875 0f118c2498010000 MOVUPS X1, 0x198(SP)
main.go:11 0x109387d 0f57c9 XORPS X1, X1
main.go:11 0x1093880 0f118c24a8010000 MOVUPS X1, 0x1a8(SP)
main.go:11 0x1093888 0f57c9 XORPS X1, X1
main.go:11 0x109388b 0f118c24b8010000 MOVUPS X1, 0x1b8(SP)
main.go:11 0x1093893 488d7c2478 LEAQ 0x78(SP), DI
main.go:11 0x1093898 0f57c0 XORPS X0, X0
main.go:11 0x109389b 488d7fd0 LEAQ -0x30(DI), DI
main.go:11 0x109389f 48896c24f0 MOVQ BP, -0x10(SP)
main.go:11 0x10938a4 488d6c24f0 LEAQ -0x10(SP), BP
main.go:11 0x10938a9 e824dffbff CALL 0x10517d2
main.go:11 0x10938ae 488b6d00 MOVQ 0(BP), BP
main.go:11 0x10938b2 488d842498010000 LEAQ 0x198(SP), AX
main.go:11 0x10938ba 8400 TESTB AL, 0(AX)
main.go:11 0x10938bc 488d442478 LEAQ 0x78(SP), AX
main.go:11 0x10938c1 48898424a8010000 MOVQ AX, 0x1a8(SP)
main.go:11 0x10938c9 488d842498010000 LEAQ 0x198(SP), AX
main.go:11 0x10938d1 4889842420010000 MOVQ AX, 0x120(SP)
main.go:11 0x10938d9 e8e2c3faff CALL runtime.fastrand(SB)
main.go:11 0x10938de 488b842420010000 MOVQ 0x120(SP), AX
main.go:11 0x10938e6 8400 TESTB AL, 0(AX)
main.go:11 0x10938e8 8b0c24 MOVL 0(SP), CX
main.go:11 0x10938eb 89480c MOVL CX, 0xc(AX)
main.go:11 0x10938ee 488d842498010000 LEAQ 0x198(SP), AX
main.go:11 0x10938f6 4889842408010000 MOVQ AX, 0x108(SP)
main.go:12 0x10938fe 48c744245000000000 MOVQ $0x0, 0x50(SP)
(...)
main.go:14 0x109394d eb63 JMP 0x10939b2
main.go:15 0x109394f 488b442450 MOVQ 0x50(SP), AX
main.go:15 0x1093954 4803442448 ADDQ 0x48(SP), AX
main.go:15 0x1093959 4889442470 MOVQ AX, 0x70(SP)
main.go:15 0x109395e 488d05fb6d0100 LEAQ runtime.rodata+92544(SB), AX
main.go:15 0x1093965 48890424 MOVQ AX, 0(SP)
main.go:15 0x1093969 488b8c2408010000 MOVQ 0x108(SP), CX
main.go:15 0x1093971 48894c2408 MOVQ CX, 0x8(SP)
main.go:15 0x1093976 488b4c2450 MOVQ 0x50(SP), CX
main.go:15 0x109397b 48034c2448 ADDQ 0x48(SP), CX
main.go:15 0x1093980 48894c2410 MOVQ CX, 0x10(SP)
main.go:15 0x1093985 e846b0f7ff CALL runtime.mapassign_fast64(SB)
main.go:15 0x109398a 488b442418 MOVQ 0x18(SP), AX
main.go:15 0x109398f 4889842418010000 MOVQ AX, 0x118(SP)
main.go:15 0x1093997 8400 TESTB AL, 0(AX)
main.go:15 0x1093999 488b4c2470 MOVQ 0x70(SP), CX
main.go:15 0x109399e 488908 MOVQ CX, 0(AX)
main.go:15 0x10939a1 eb00 JMP 0x10939a3
(...)
```
可以看到運行時通過`runtime.mapassign_fast64`來給一個 map 進行賦值。那么我們就來仔細看一看這個函數。
TODO:`runtime.extendRandom`
## 運行時算法初始化
```
// src/runtime/proc.go
func schedinit() {
(...)
cpuinit() // 必須在 alginit 之前運行
alginit() // maps 不能在此調用之前使用,從 CPU 指令集初始化散列算法
(...)
}
```
運行時初始化過程中的,`alginit`來根據`cpuinit`解析得到的 CPU 指令集的支持情況, 進而初始化合適的 hash 算法,用于對 Go 的`map`結構進行支持。
```
func alginit() {
// 如果需要的指令存在則安裝 AES 散列算法
if (GOARCH == "386" || GOARCH == "amd64") &&
GOOS != "nacl" &&
cpu.X86.HasAES && // AESENC
cpu.X86.HasSSSE3 && // PSHUFB
cpu.X86.HasSSE41 { // PINSR{D,Q}
initAlgAES()
return
}
if GOARCH == "arm64" && cpu.ARM64.HasAES {
initAlgAES()
return
}
getRandomData((*[len(hashkey) * sys.PtrSize]byte)(unsafe.Pointer(&hashkey))[:])
hashkey[0] |= 1 // 確保這些數字為奇數
hashkey[1] |= 1
hashkey[2] |= 1
hashkey[3] |= 1
}
```
可以看到,在指令集支持良好的情況下,amd64 平臺會調用`initAlgAES`來使用 AES 散列算法。
```
var useAeshash bool
func initAlgAES() {
useAeshash = true
algarray[alg_MEM32].hash = aeshash32
algarray[alg_MEM64].hash = aeshash64
algarray[alg_STRING].hash = aeshashstr
// 使用隨機數據初始化,從而使散列值的碰撞攻擊變得困難。
getRandomData(aeskeysched[:])
}
// typeAlg 還用于 reflect/type.go,保持同步
type typeAlg struct {
// 函數用于對此類型的對象求 hash,(指向對象的指針, 種子) --> hash
hash func(unsafe.Pointer, uintptr) uintptr
// 函數用于比較此類型的對象,(指向對象 A 的指針, 指向對象 B 的指針) --> ==?
equal func(unsafe.Pointer, unsafe.Pointer) bool
}
// 類型算法 - 編譯器知曉
const (
alg_NOEQ = iota
alg_MEM0
(...)
)
var algarray = [alg_max]typeAlg{
alg_NOEQ: {nil, nil},
alg_MEM0: {memhash0, memequal0},
(...)
}
```
其中`algarray`是一個用于保存 hash 函數的數組。
否則在 Linux 上,會根據程序引導一章中提到的輔助向量提供的隨機數據來初始化 hashkey:
```
func getRandomData(r []byte) {
if startupRandomData != nil {
n := copy(r, startupRandomData)
extendRandom(r, n)
return
}
fd := open(&urandom_dev[0], 0 /* O_RDONLY */, 0)
n := read(fd, unsafe.Pointer(&r[0]), int32(len(r)))
closefd(fd)
extendRandom(r, int(n))
}
```
或在 darwin 中,通過讀取`/dev/urandom\x00`的內容來獲取隨機值:
```
var urandom_dev = []byte("/dev/urandom\x00")
//go:nosplit
func getRandomData(r []byte) {
fd := open(&urandom_dev[0], 0 /* O_RDONLY */, 0)
n := read(fd, unsafe.Pointer(&r[0]), int32(len(r)))
closefd(fd)
extendRandom(r, int(n))
}
```
這里我們粗略的看了一下運行時 map 類型使用的 hash 算法以及隨機 key 的初始化, 具體的`runtime.extendRandom`,和下列函數:
```
func aeshash32(p unsafe.Pointer, h uintptr) uintptr
func aeshash64(p unsafe.Pointer, h uintptr) uintptr
func aeshashstr(p unsafe.Pointer, h uintptr) uintptr
```
## CPU 相關信息的初始化
初始化過程中,會根據當前運行程序的 CPU 初始化一些與 CPU 相關的值, 獲取 CPU 指令集相關支持,并支持對 CPU 指令集的調試,例如禁用部分指令集。
> 位于 runtime/proc.go
// cpuinit 會提取環境變量 GODEBUGCPU,如果 GOEXPERIMENT debugcpu 被設置,
// 則還會調用 internal/cpu.initialize
func cpuinit() {
const prefix = "GODEBUG="
var env string
cpu.DebugOptions = true
// 類似于 goenv_unix 但為 GODEBUG 直接提取了環境變量
// TODO(moehrmann): remove when general goenvs() can be called before cpuinit()
n := int32(0)
for argv_index(argv, argc+1+n) != nil {
n++
}
for i := int32(0); i < n; i++ {
p := argv_index(argv, argc+1+i)
s := *(*string)(unsafe.Pointer(&stringStruct{unsafe.Pointer(p), findnull(p)}))
if hasprefix(s, prefix) {
env = gostring(p)[len(prefix):]
break
}
}
cpu.Initialize(env)
// 支持 CPU 特性的變量由編譯器生成的代碼來阻止指令的執行,從而不能假設總是支持的
x86HasPOPCNT = cpu.X86.HasPOPCNT
x86HasSSE41 = cpu.X86.HasSSE41
arm64HasATOMICS = cpu.ARM64.HasATOMICS
}
其中,`cpu.Initialize(env)`會調用`internal/cpu/cpu.go`中的函數:
```
// Initialize 檢查處理器并設置上面的相關變量。
// 該函數在程序初始化的早期由運行時包調用,在運行正常的 init 函數之前。
// 如果 go 是使用 GODEBUG 編譯的,則 env 在 Linux/Darwin 上由運行時設置
func Initialize(env string) {
doinit()
processOptions(env)
}
```
而`doinit`會根據 CPU 架構的不同,存在不同的實現,在 amd64 上:
```
// options 包含可在 GODEBUG 中使用的 cpu 調試選項。
// options 取決于架構,并由架構特定的 doinit 函數添加。
// 不應將特定 GOARCH 必需的功能添加到選項中(例如 amd64 上的 SSE2)。
var options []option
// Option 名稱應為小寫。 例如 avx 而不是 AVX。
type option struct {
Name string
Feature *bool
Specified bool // whether feature value was specified in GODEBUG
Enable bool // whether feature should be enabled
Required bool // whether feature is mandatory and can not be disabled
}
const (
// edx bits
cpuid_SSE2 = 1 << 26
// ecx bits
cpuid_SSE3 = 1 << 0
cpuid_PCLMULQDQ = 1 << 1
(...)
// ebx bits
cpuid_BMI1 = 1 << 3
(...)
)
func doinit() {
options = []option{
{Name: "adx", Feature: &X86.HasADX},
{Name: "aes", Feature: &X86.HasAES},
(...)
// 下面這些特性必須總是在 amd64 上啟用
{Name: "sse2", Feature: &X86.HasSSE2, Required: GOARCH == "amd64"},
}
maxID, _, _, _ := cpuid(0, 0)
if maxID < 1 {
return
}
_, _, ecx1, edx1 := cpuid(1, 0)
X86.HasSSE2 = isSet(edx1, cpuid_SSE2)
X86.HasSSE3 = isSet(ecx1, cpuid_SSE3)
(...)
osSupportsAVX := false
// 對于 XGETBV,OSXSAVE 位是必需且足夠的。
if X86.HasOSXSAVE {
eax, _ := xgetbv()
// 檢查 XMM 和 YMM 寄存器是否支持。
osSupportsAVX = isSet(eax, 1<<1) && isSet(eax, 1<<2)
}
X86.HasAVX = isSet(ecx1, cpuid_AVX) && osSupportsAVX
if maxID < 7 {
return
}
_, ebx7, _, _ := cpuid(7, 0)
X86.HasBMI1 = isSet(ebx7, cpuid_BMI1)
X86.HasAVX2 = isSet(ebx7, cpuid_AVX2) && osSupportsAVX
(...)
}
func isSet(hwc uint32, value uint32) bool {
return hwc&value != 0
}
其中`X86`變量為`x86`類型:
````
```
var X86 x86
// CacheLinePad 用于填補結構體進而避免 false sharing
type CacheLinePad struct{ _ [CacheLinePadSize]byte }
// CacheLineSize 是 CPU 的假設的緩存行大小
// 當前沒有對實際的緩存行大小在運行時檢測,因此我們使用針對每個 GOARCH 的 CacheLinePadSize 進行估計
var CacheLineSize uintptr = CacheLinePadSize
// x86 中的布爾值包含相應命名的 cpuid 功能位。
// 僅當操作系統支持 XMM 和 YMM 寄存器時,才設置 HasAVX 和 HasAVX2
type x86 struct {
_ CacheLinePad
HasAES bool
(...)
HasSSE42 bool
_ CacheLinePad
}
```
而`cpu.cpuid`和`cpu.xgetbv`的實現則由匯編完成:
```
func cpuid(eaxArg, ecxArg uint32) (eax, ebx, ecx, edx uint32)
func xgetbv() (eax, edx uint32)
```
本質上就是去調用 CPUID 和 XGETBV 這兩個指令:
```
// internal/cpu/cpu_x86.s
// func cpuid(eaxArg, ecxArg uint32) (eax, ebx, ecx, edx uint32)
TEXT ·cpuid(SB), NOSPLIT, $0-24
MOVL eaxArg+0(FP), AX
MOVL ecxArg+4(FP), CX
CPUID
MOVL AX, eax+8(FP)
MOVL BX, ebx+12(FP)
MOVL CX, ecx+16(FP)
MOVL DX, edx+20(FP)
RET
// func xgetbv() (eax, edx uint32)
TEXT ·xgetbv(SB),NOSPLIT,$0-8
#ifdef GOOS_nacl
// nacl 不支持 XGETBV.
MOVL $0, eax+0(FP)
MOVL $0, edx+4(FP)
#else
MOVL $0, CX
XGETBV
MOVL AX, eax+0(FP)
MOVL DX, edx+4(FP)
#endif
RET
```
`cpu.doinit`結束后,會處理解析而來的 option,從而達到禁用某些 CPU 指令集的目的:
```
// processOptions 根據解析的 env 字符串來禁用 CPU 功能值。
// env 字符串應該是 cpu.feature1=value1,cpu.feature2=value2... 格式
// 其中功能名稱是存儲在其中的體系結構特定列表之一 cpu 包選項變量,且這些值要么是 'on' 要么是 'off'。
// 如果 env 包含 cpu.all=off 則所有功能通過 options 變量引用被禁用。其他功能名稱和值將導致警告消息。
func processOptions(env string) {
field:
for env != "" {
field := ""
i := indexByte(env, ',')
if i < 0 {
field, env = env, ""
} else {
field, env = env[:i], env[i+1:]
}
if len(field) < 4 || field[:4] != "cpu." {
continue
}
i = indexByte(field, '=')
if i < 0 {
print("GODEBUG: no value specified for \"", field, "\"\n")
continue
}
key, value := field[4:i], field[i+1:] // e.g. "SSE2", "on"
var enable bool
switch value {
case "on":
enable = true
case "off":
enable = false
default:
print("GODEBUG: value \"", value, "\" not supported for cpu option \"", key, "\"\n")
continue field
}
if key == "all" {
for i := range options {
options[i].Specified = true
options[i].Enable = enable || options[i].Required
}
continue field
}
for i := range options {
if options[i].Name == key {
options[i].Specified = true
options[i].Enable = enable
continue field
}
}
print("GODEBUG: unknown cpu feature \"", key, "\"\n")
}
for _, o := range options {
if !o.Specified {
continue
}
if o.Enable && !*o.Feature {
print("GODEBUG: can not enable \"", o.Name, "\", missing CPU support\n")
continue
}
if !o.Enable && o.Required {
print("GODEBUG: can not disable \"", o.Name, "\", required CPU feature\n")
continue
}
*o.Feature = o.Enable
}
}
```
- 第一部分 :基礎篇
- 第1章 Go語言的前世今生
- 1.2 Go語言綜述
- 1.3 順序進程通訊
- 1.4 Plan9匯編語言
- 第2章 程序生命周期
- 2.1 從go命令談起
- 2.2 Go程序編譯流程
- 2.3 Go 程序啟動引導
- 2.4 主Goroutine的生與死
- 第3 章 語言核心
- 3.1 數組.切片與字符串
- 3.2 散列表
- 3.3 函數調用
- 3.4 延遲語句
- 3.5 恐慌與恢復內建函數
- 3.6 通信原語
- 3.7 接口
- 3.8 運行時類型系統
- 3.9 類型別名
- 3.10 進一步閱讀的參考文獻
- 第4章 錯誤
- 4.1 問題的演化
- 4.2 錯誤值檢查
- 4.3 錯誤格式與上下文
- 4.4 錯誤語義
- 4.5 錯誤處理的未來
- 4.6 進一步閱讀的參考文獻
- 第5章 同步模式
- 5.1 共享內存式同步模式
- 5.2 互斥鎖
- 5.3 原子操作
- 5.4 條件變量
- 5.5 同步組
- 5.6 緩存池
- 5.7 并發安全散列表
- 5.8 上下文
- 5.9 內存一致模型
- 5.10 進一步閱讀的文獻參考
- 第二部分 運行時篇
- 第6章 并發調度
- 6.1 隨機調度的基本概念
- 6.2 工作竊取式調度
- 6.3 MPG模型與并發調度單
- 6.4 調度循環
- 6.5 線程管理
- 6.6 信號處理機制
- 6.7 執行棧管理
- 6.8 協作與搶占
- 6.9 系統監控
- 6.10 網絡輪詢器
- 6.11 計時器
- 6.12 非均勻訪存下的調度模型
- 6.13 進一步閱讀的參考文獻
- 第7章 內存分配
- 7.1 設計原則
- 7.2 組件
- 7.3 初始化
- 7.4 大對象分配
- 7.5 小對象分配
- 7.6 微對象分配
- 7.7 頁分配器
- 7.8 內存統計
- 第8章 垃圾回收
- 8.1 垃圾回收的基本想法
- 8.2 寫屏幕技術
- 8.3 調步模型與強弱觸發邊界
- 8.4 掃描標記與標記輔助
- 8.5 免清掃式位圖技術
- 8.6 前進保障與終止檢測
- 8.7 安全點分析
- 8.8 分代假設與代際回收
- 8.9 請求假設與實務制導回收
- 8.10 終結器
- 8.11 過去,現在與未來
- 8.12 垃圾回收統一理論
- 8.13 進一步閱讀的參考文獻
- 第三部分 工具鏈篇
- 第9章 代碼分析
- 9.1 死鎖檢測
- 9.2 競爭檢測
- 9.3 性能追蹤
- 9.4 代碼測試
- 9.5 基準測試
- 9.6 運行時統計量
- 9.7 語言服務協議
- 第10章 依賴管理
- 10.1 依賴管理的難點
- 10.2 語義化版本管理
- 10.3 最小版本選擇算法
- 10.4 Vgo 與dep之爭
- 第12章 泛型
- 12.1 泛型設計的演進
- 12.2 基于合約的泛型
- 12.3 類型檢查技術
- 12.4 泛型的未來
- 12.5 進一步閱讀的的參考文獻
- 第13章 編譯技術
- 13.1 詞法與文法
- 13.2 中間表示
- 13.3 優化器
- 13.4 指針檢查器
- 13.5 逃逸分析
- 13.6 自舉
- 13.7 鏈接器
- 13.8 匯編器
- 13.9 調用規約
- 13.10 cgo與系統調用
- 結束語: Go去向何方?
