> 寫給初生牛犢不怕虎的童鞋們,大佬可隨意摘看
> 本章基于PHP Laravel
# 前言
經常會有人問
- 目錄如何設計比較好?
- 代碼如何分布好?
- 怎么寫一個可維護的項目?
“爛”項目我也沒少寫,以下是參考互聯網各大佬的文章總結及個人開發經驗而來.
# Controller
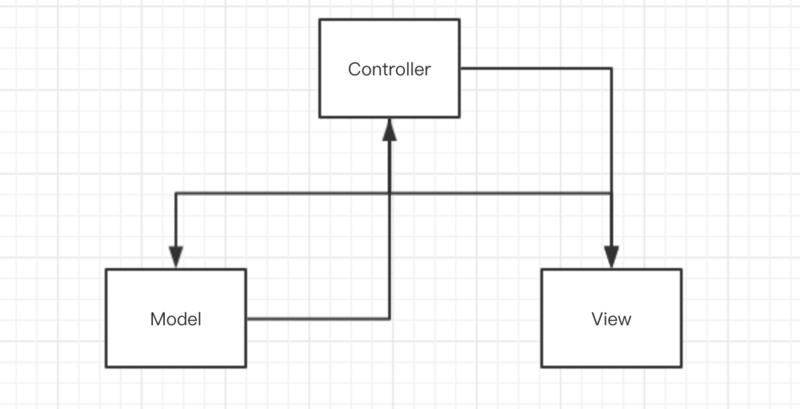
Controller顧名思義是控制器,在入門PHP的時候,就知道Controller代表MVC中的C層,MVC本身的概念就代碼分離,教你如何如何將業務分開,但面臨著業務的不斷發展,代碼的復雜度也隨之提高,功能與功能之間的鏈接錯綜復雜,最后你的MVC就變成了下圖,所以僅僅依托MVC的設計思想已經無法支撐不斷發展的業務。
現在我們將Controller的任務和能力重新定義,控制器僅僅控制Http Reqeust的請求,這樣就符合了SOLID 單一功能原則.
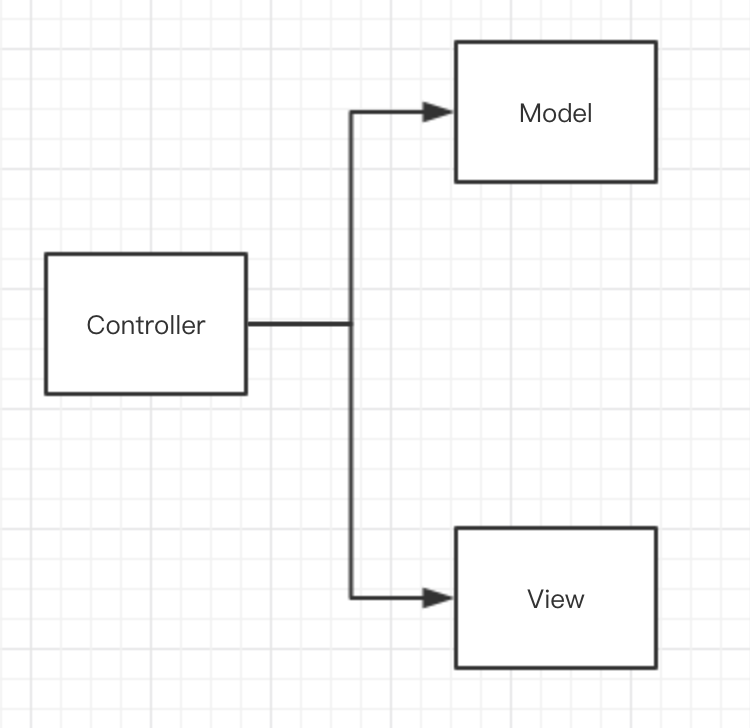
直接將業務代碼寫在Controller中,會使得代碼及其臃腫,不易于維護和擴展
```
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controller;
class UserController extends Controller{
public function register(Request $request){
$user = new User();
$user->username = $request->input('username');
$user->password = $request->input('password');
$result = $user->save();
return $result;
}
}
```
這時就應該思考如何分離業務代碼,我們引入Service的概念
# Service
Service本身譯為服務
- 將外部方法,公共方法注入到Service
- 將Service注入到控制器
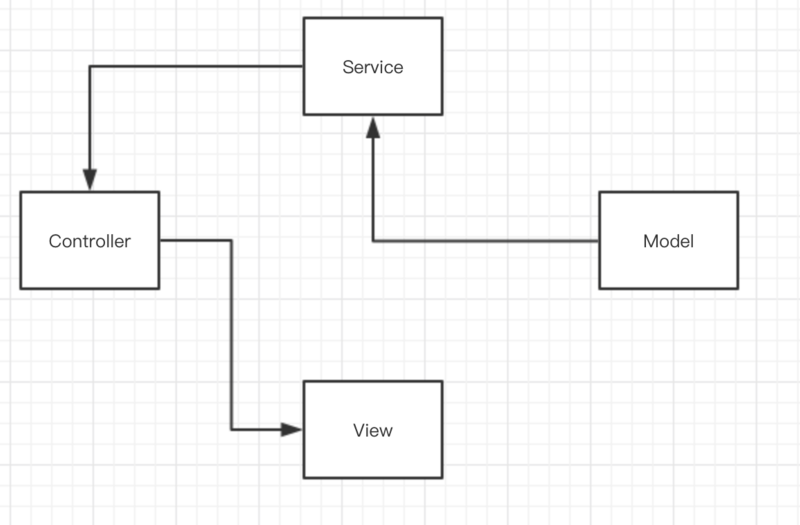
像上圖這樣
### UserController
```
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controller;
class UserController extends Controller{
public $request;
protected $userService;
public function __construct(Request $request, UserService $userService)
{
$this->request = $request;
$this->userService = $userService;
}
public function register()
{
//... validation
return $this->userService->register ($this->request->all());
}
}
```
### UserService
```
<?php
namespace App\Service;
class UserService{
public function register($data)
{
$username = $data['username'];
$password = $data['password'];
$password = encrypt ($password);
$user = new User();
$user->username = $username;
$user->password = $password;
$result = $user->save();
return $result;
}
}
```
到現在為止,我們至少將業務與請求徹底分開了。但還是不如人意,如果把所有的業務及CURD全部寫在Service中,那只不過是將Controller的臃腫轉移到了Service,那Service就沒有什么存在意義了。
所以我們需要繼續分割Service,將對數據庫的R操作獨立出來,因為CUD的操作基本是一貫不變的,而R操作根據業務的復雜度則變的多姿多彩。所以獨立R操作。這個時候我們引用Repository的概念。
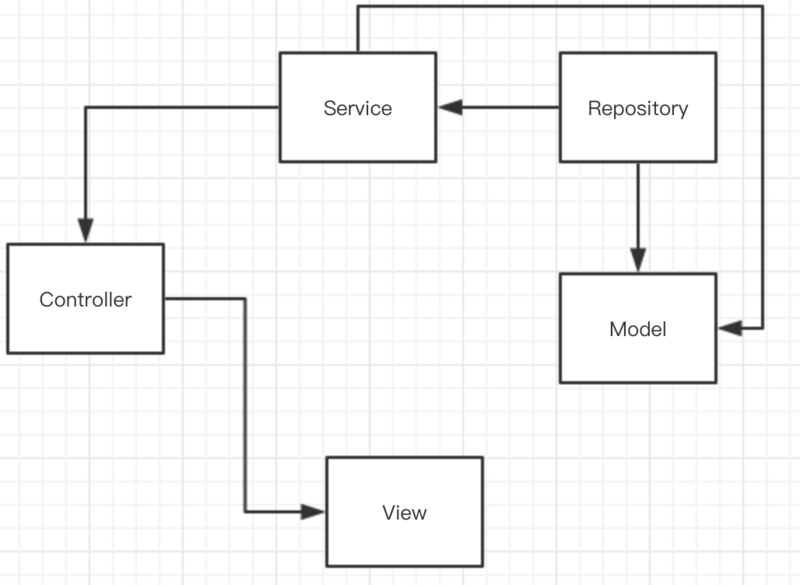
# Repository
我們使用Repository輔助Model,將相關的查詢邏輯封裝到不同的repository中,方便邏輯代碼的維護
- 符合SOLID的單一原則
- 符合SOLID的依賴反轉
### UserController
```
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controller;
class UserController extends Controller{
public $request;
protected $userService;
public function __construct(Request $request, UserService $userService)
{
$this->request = $request;
$this->userService = $userService;
}
public function getUserInfo()
{
//... validation
return $this->userService->getUserInfo ($this->request->all());
}
}
```
### UserService
```
<?php
namespace App\Service;
class UserService{
public $userRepository;
public function __construct(UserRepository $userRepository){
$this->userRepository = $userRepository;
}
public function getUserInfo()
{
return $this->userRepository->getUserInfo($data);
}
}
```
### UserRepository
```
<?php
namespace App\Repository;
class UserRepository{
public function getUserInfo($data)
{
$userId = $data['user_id'];
$result = User::where('id',$userId)->first();
return $result;
}
}
```
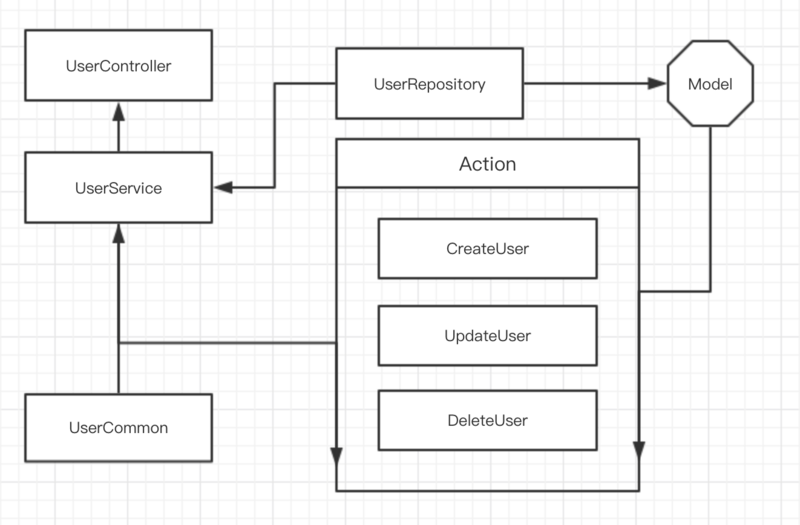
解決了R的問題,有人就問了,難道因為CUD比較統一簡單就可以放在一起了嗎?答案是NO,我們引用一個新的名詞Action。
# Action
> 這是看了@Charlie_Jade的文章才學到的
獨立每個操作文件,例如CreateUser,DeleteUser,UpdateUser
- 符合SOLID的單一原則

### UserController
```
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controller;
class UserController extends Controller{
public $request;
protected $userService;
public function __construct(Request $request, UserService $userService)
{
$this->request = $request;
$this->userService = $userService;
}
public function register(){
//... validation
return $this->userService->register($this->request->all());
}
public function getUserInfo()
{
return $this->userService->getUserInfo ($this->request->all());
}
}
```
### UserService
```
<?php
namespace App\Service;
class UserService{
public function getUserInfo(UserRepository $userRepository)
{
return $this->userRepository->getUserInfo($data);
}
public function register(){
$result = (new CreateUser())->execute($this->request->all());
return $result;
}
}
```
### UserRepository
```
<?php
namespace App\Repository;
class UserRepository{
public function getUserInfo($data)
{
$userId = $data['user_id'];
$result = User::where('id',$userId)->first();
return $result;
}
}
```
### CreateUser
```
<?php
namespace App\Action;
use App\Model\Member;
class CreateUser extends CreateUserWallet
{
public function execute(array $data)
{
$models = new Member();
$models->tel = $data['tel'];
$models->password = $data['password'];
$result = $models->save ();
return $result;
}
}
```
以上代碼邏輯見下圖
除模版(V)等HTML,JS等,還需要一些其他的規則,或者說是方式去實現一些代碼的解耦合,以下不再提供代碼案例。
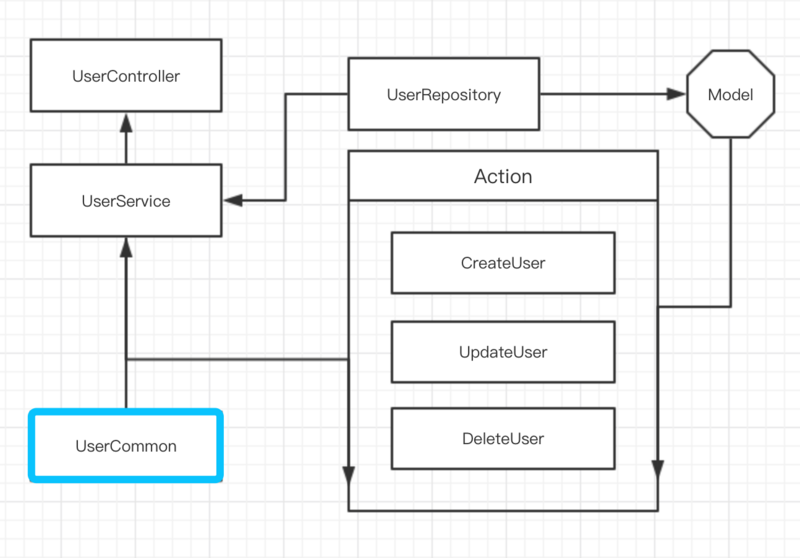
# Common
譯為公共的,常用的,再部分開發中,你可能需要一些公共的方法(并非公共的類,例如郵件發送等,用他并不合適),比如查詢用戶余額,查詢用戶是否注冊或者是否在線,生成訂單號等。使用Common更要簡單。他更像一個公共函數庫的樣子
# Event
不關心執行結果時可以選使用,不過Event的Listen也是提供了隊列。
# Exception
不要將你的所有錯誤提示都使用Return返回,很多時候你的返回未必是你的返回
# 致謝
感謝各位同學看完這篇文章,如果你有新的想法歡迎在評論區討論.
# 參考文章
Laravel 的中大型專案架構:http://oomusou.io/laravel/architecture/#Service
Laravel 程序架構設計思路使用動作類 : https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000015208089
如何使用 Service 模式? : http://oomusou.io/laravel/service/
面向對象設計的SOLID原則 : https://www.cnblogs.com/shanyou/archive/2009/09/21/1570716.html
- 前言
- 服務治理架構
- PHP程序員如何簡單的開展服務治理架構(一)
- PHP程序員如何簡單的開展服務治理架構(二)
- PHP程序員如何簡單的開展服務治理架構(三)
- 遷移重構相關
- 老項目的遷移手記
- 老項目重構手記之用戶系統
- PHP其他
- PHP GD庫解析一張簡單圖片并輸出
- 初中級PHP面試基礎匯總
- 一道看似簡單的面試題
- 運行/調試你的PHP代碼
- 取代PHP原生函數的一些擴展包
- Laravel相關
- 五分鐘入門 Dingo API
- Laravel-Action 對代碼的改造
- Laravel源碼解析之反射的使用
- Laravel源碼解析之從入口開始
- Laravel源碼解析之路由的使用
- Laravel源碼解析之Model
- 你可能需要了解下Laravel集合
- Nignx相關
- NGINX日志配置總結
- NGINX宏觀手記
- 暴力解說之首次部署NGINX
- 電商相關設計
- 電商系統設計之用戶系統
- 電商系統設計之購物車
- 電商系統設計之商品 (上)
- 電商系統設計之商品 (中)
- 電商系統設計之商品 (下)
- 電商系統設計之訂單
- 電商系統設計之商品接口
- 電商系統設計之商品[番外篇]
- Go相關
- PHP To Go 轉型手記 (一)
- PHP To Go 轉型手記 (二)
- PHP To Go 轉型手記 (三)
- PHP To Go 轉型手記 (終)
- [積德篇] 如何少寫PHP "爛"代碼
- [還魂篇] 初來乍到如何致人于死地
- 舉槍消滅"爛代碼"的實戰案例
- PHP程序員必備工具
- PHP程序員必須知道的兩種日志
- RabbitMQ 初體驗
- 冷門PHP函數匯總
- MySQL常用函數匯總
- 不一樣的PHP基礎知識匯總
- 程序員自省錄
- 淺談架構是為了什么 (上)
- 淺談架構是為了什么 (下)
- XDEBUG 從入門到精通
- MySQL SQL模式特點匯總
- “生于憂患,死于安樂”之程序員人生
- Supervisor 從入門到放棄
- Docker構建程序員的日常
- 基于業務設計數據表的總結
- 不要被集成環境束縛住你前進的腳步
- 論某教育機構考試系統設計
- 淺談重構造成的災難性毀滅