# MyBatis進階
[TOC]
## 導學
在之前的學習中,我們使用MyBatis進行了數據的CRUD操作,而且還學習了它里面一些開發小技巧。那么在本節課程中,我們將要學習MyBatis的一些高級特性。
## MyBatis日志管理
### 日志接口jar包及其實現jar包
什么是日志?這個問題其實很簡單,日志是對生活和工作的記錄。
那么MyBatis的日志,實際上就是對MyBatis工作的記錄,就如同飛機的黑匣子會記錄飛機飛行產生的一切數據一樣。我們可以使用MyBatis的日志,來記錄和分析,應用程序使用過程中對數據庫的操作及其影響,也是我們診斷問題和理解系統活動的重要依據。
通常日志是記錄和保存在日志文件中的,同學們其實也接觸過日志,就是我們在Tomcat使用過程中控制臺所顯示的那些內容。
其實,在Java中也可以通過第三方的日志的接口模塊創建日志記錄和文件,再由不同的jar包實現對應的接口模塊,比如常用的有`Comms-Logging=>log4j`和`SLF4J=>logback`等。
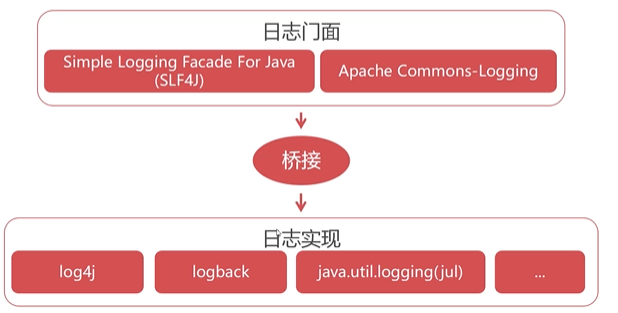
從目前的趨勢來看,越來越多的開源項目從Commons-Logging加Log4j轉向了SLF4J加logback。**我們在使用日志記錄的時候,需要注意項目中使用的是Commons-Logging還是SLF4J,雖然切換日志實現不會造成什么影響。比如SLF4J還是Commons-Logging,都可以使用logBack作為日志實現,但是它們的接口方法的定義還是不同的。**
### logback
早期的Java項目中,基本都是使用的log4j。但是,在本教程中我們將針對logback做著重的講解。
因為log4j和logback是近親,這兩個日志管理實現都是由一個人開發的。英文log4j雖然經過多次更新迭代,仍然有些問題積重難返,所以作者另起爐灶開發了另一款日志管理實現logback,而且logback的性能要好的多。在MyBatis底層可以通過SLF4J支持logback!
**代碼實現:**
1. pom.xml增加依賴
~~~
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
~~~
其實此時,如果我們運行測試類中方法,就會發現在控制臺中就會打印日志信息了。
2. 對日志管理進行自定義設置
在resources目錄下新增logback.xml文件。注意,必須叫這個名字!
~~~
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<configuration>
<!-- 指定在控制臺中輸出日志 -->
<!-- name屬性可以隨意,如果要在控制臺輸出,一般稱之為console -->
<!-- class屬性指定何處打印輸出 -->
<appender name="console" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<!-- 編碼節點 -->
<encoder>
<!--
%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS}:輸出時間格式,精確到毫秒
[%thread]:當前操作的線程
%-5level:以5個字符右對齊以及級別
%logger{36}:具體哪個類的日志(只顯示36個字符)
%msg:日志信息
%n:換行
這些表達式在logback官網上都有詳細說明
-->
<pattern>%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!--
日志輸出級別(優先級高到低):
error: 錯誤 - 系統的故障日志
warn: 警告 - 存在風險或使用不當的日志
info: 一般性消息
debug: 程序內部用于調試信息
trace: 程序運行的跟蹤信息
下方root標簽表示日志的最低輸出級別為debug,即debug級別以下的信息不進行輸出
-->
<root level="debug">
<appender-ref ref="console"></appender-ref>
</root>
</configuration>
~~~
## MyBatis的動態SQL
在我們使用SQL語句時,有的時候參數是不固定的。比如用戶可以指定多個檢索條件,也可能單獨只指定一個檢索條件。在這個時候,我們無法確定條件參數的數量,只能使用動態SQL完成。在實際的開發中,動態SQL的使用非常普遍。
>[success]動態SQL是指根據參數數據動態組織SQL的技術,它有些類似于對SQL執行拼接。
可以使用`<where>`標簽和`<if>`組合使用,或是單獨使用`<if>`標簽來實現動態SQL。
~~~
<select id="dynamicSQL" parameterType="java.util.Map" resultType="com.dodoke.mybatis.entity.Goods">
select * from t_goods
<!-- 不需要寫where關鍵字,只需要利用where標簽智能判斷and是否要添加 -->
<where>
<!-- 針對map中的key進行判斷對應的value值是否為null和空 -->
<if test="categoryId != null and categoryId!=''">
and category_id = #{categoryId}
</if>
<if test="currentPrice != null and categoryId!=''">
and current_price < #{currentPrice}
</if>
</where>
</select>
~~~
~~~
/**
* 動態SQL語句
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testDynamicSQL() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = null;
try{
session = MyBatisUtils.openSqlSession();
Map param = new HashMap();
param.put("categoryId", 44);
param.put("currentPrice", 500);
//查詢條件
List<Goods> list = session.selectList("com.dodoke.mybatis.resources.mappers.GoodsMapper.delete.dynamicSQL", param);
for(Goods g:list){
System.out.println(g.getTitle() + ":" +
g.getCategoryId() + ":" + g.getCurrentPrice());
}
}catch (Exception e){
throw e;
}finally {
MyBatisUtils.closeSqlSession(session);
}
}
~~~
## MyBatis的緩存機制
在一個項目中,查詢數據庫中的操作算是一個非常常用的操作,但是有些數據會被經常性的查詢,而每一次都去數據庫中查詢這些重復的數據,會很消耗數據庫的資源,同時使得查詢效率也很低。
而 MyBatis 中就通過緩存技術來解決這樣的問題,也就是說:將一些經常查詢,并且不經常改變的,以及數據的正確對最后的結果影響不大的數據,放置在一個緩存容器中,當用戶再次查詢這些數據的時候,就不必再去數據庫中查詢,直接在緩存中提取就可以了。
>[info]注:緩存可以簡單理解為存在于內存中的臨時數據
在MyBatis中,存在一級緩存和二級緩存,一級緩存的效果,可以體現為同一個`sqlSession`對象操作同一條SQL時,只要參數相同就不會再去進行數據庫查詢,一級緩存默認開啟。二級緩存需要手動開啟。
關于如何使用二級緩存,可以參考如下文章,這里不再贅述,各位同學自由補充。
**參考文檔:**
[https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/106258135](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/106258135)
## MyBatis多表級聯查詢
MyBatis多表級聯查詢和之前學習的MyBatis多表關聯查詢不一樣。
* 多表關聯查詢:兩個表通過主外鍵在一條SQL中完成所有數據的提取。
* 多表級聯查詢:通過一個對象來獲取與它關聯的另外一個對象,執行的SQL語句分為多條。
**確定對象之間的關系是雙向的:**
雙向的一對多,應該變成多對多,在進行數據庫設計的時候需要單獨抽象出一張中間表來!!!
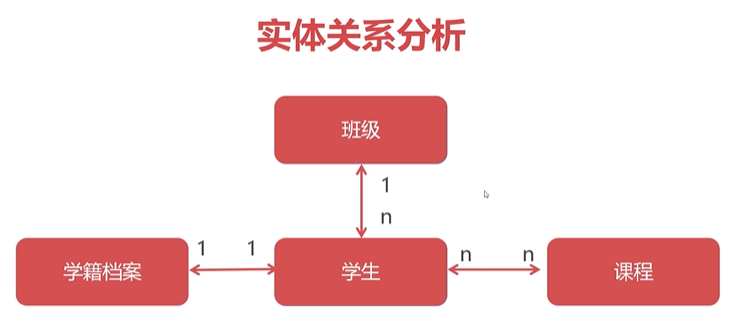
### 一對多關聯查詢
案例:要求查詢某件商品的詳細信息
1. 新建實體類
~~~
package com.dodoke.mybatis.entity;
public class GoodsDetail {
private Integer gdId;
private Integer goodsId;
private String gdPicUrl;
private Integer gdOrder;
public Integer getGdId() {
return gdId;
}
public void setGdId(Integer gdId) {
this.gdId = gdId;
}
public Integer getGoodsId() {
return goodsId;
}
public void setGoodsId(Integer goodsId) {
this.goodsId = goodsId;
}
public String getGdPicUrl() {
return gdPicUrl;
}
public void setGdPicUrl(String gdPicUrl) {
this.gdPicUrl = gdPicUrl;
}
public Integer getGdOrder() {
return gdOrder;
}
public void setGdOrder(Integer gdOrder) {
this.gdOrder = gdOrder;
}
}
~~~
2. 新建mapper xml文件 `GoodsDetailMapper.xml`
~~~
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="goodsDetail">
<select id="selectByGoodsId" parameterType="Integer"
resultType="com.dodoke.mybatis.entity.GoodsDetail">
select * from t_goods_detail where goods_id = #{value}
</select>
</mapper>
~~~
3. 修改Goods類,為體現一對多的關系,新增一個屬性
~~~
/**
* 數據庫t_goods表對應映射的實體類
*/
public class Goods {
private Integer goodsId;//商品編號
private String title;//標題
private String subTitle;//子標題
private Float originalCost;//原始價格
private Float currentPrice;//當前價格
private Float discount;//折扣率
private Integer isFreeDelivery;//是否包郵 ,1-包郵 0-不包郵
private Integer categoryId;//分類編號
private List<GoodsDetail> goodsDetails;
public List<GoodsDetail> getGoodsDetails() {
return goodsDetails;
}
public void setGoodsDetails(List<GoodsDetail> goodsDetails) {
this.goodsDetails = goodsDetails;
}
public Integer getGoodsId() {
return goodsId;
}
public void setGoodsId(Integer goodsId) {
this.goodsId = goodsId;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getSubTitle() {
return subTitle;
}
public void setSubTitle(String subTitle) {
this.subTitle = subTitle;
}
public Float getOriginalCost() {
return originalCost;
}
public void setOriginalCost(Float originalCost) {
this.originalCost = originalCost;
}
public Float getCurrentPrice() {
return currentPrice;
}
public void setCurrentPrice(Float currentPrice) {
this.currentPrice = currentPrice;
}
public Float getDiscount() {
return discount;
}
public void setDiscount(Float discount) {
this.discount = discount;
}
public Integer getIsFreeDelivery() {
return isFreeDelivery;
}
public void setIsFreeDelivery(Integer isFreeDelivery) {
this.isFreeDelivery = isFreeDelivery;
}
public Integer getCategoryId() {
return categoryId;
}
public void setCategoryId(Integer categoryId) {
this.categoryId = categoryId;
}
}
~~~
4. 利用resultMap實現一對多映射,GoodsMapper.xml
~~~
<!--
resultMap可用于說明一對多或者多對一的映射邏輯
id 是resultMap屬性引用的標志
type 指向One的實體(Goods)
-->
<resultMap id="rmGoods1" type="com.dodoke.mybatis.entity.Goods">
<!-- 映射goods對象的主鍵到goods_id字段 -->
<id column="goods_id" property="goodsId"></id>
<!--
collection的含義是,在
select * from t_goods limit 0,10 得到結果后,對所有Goods對象遍歷得到goods_id字段值,
并代入到goodsDetail命名空間的findByGoodsId的SQL中執行查詢,
將得到的"商品詳情"集合賦值給goodsDetails List對象.
-->
<collection property="goodsDetails" select="goodsDetail.selectByGoodsId"
column="goods_id"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectOneToMany" resultMap="rmGoods1">
select * from t_goods limit 0,10
</select>
~~~
5. 編寫測試方法
~~~
/**
* 一對多對象關聯查詢
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testOneToMany() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = null;
try {
session = MyBatisUtils.openSqlSession();
List<Goods> list = session.selectList("com.dodoke.mybatis.resources.mappers.GoodsMapper.selectOneToMany");
for(Goods goods:list) {
System.out.println(goods.getTitle() + ":" + goods.getGoodsDetails().size());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw e;
} finally {
MyBatisUtils.closeSqlSession(session);
}
}
~~~
### 多對一關聯查詢
當多對一的時候,只需要在多的一方實體類中,持有一的一方的實體!
即:
~~~
package com.dodoke.mybatis.entity;
public class GoodsDetail {
private Integer gdId;
private Integer goodsId;
private String gdPicUrl;
private Integer gdOrder;
private Goods goods;//添加goods類屬性
public Integer getGdId() {
return gdId;
}
public void setGdId(Integer gdId) {
this.gdId = gdId;
}
public Integer getGoodsId() {
return goodsId;
}
public void setGoodsId(Integer goodsId) {
this.goodsId = goodsId;
}
public String getGdPicUrl() {
return gdPicUrl;
}
public void setGdPicUrl(String gdPicUrl) {
this.gdPicUrl = gdPicUrl;
}
public Integer getGdOrder() {
return gdOrder;
}
public void setGdOrder(Integer gdOrder) {
this.gdOrder = gdOrder;
}
public Goods getGoods() {
return goods;
}
public void setGoods(Goods goods) {
this.goods = goods;
}
}
~~~
修改GoodsDetailMapper.xml
~~~
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="goodsDetail">
<select id="selectByGoodsId" parameterType="Integer"
resultType="com.dodoke.mybatis.entity.GoodsDetail">
select * from t_goods_detail where goods_id = #{value}
</select>
<resultMap id="rmGoodsDetail" type="com.dodoke.mybatis.entity.GoodsDetail">
<!-- 除了id,只有其它的屬性符合駝峰命名規則就不需要填寫大量的result標簽 -->
<id column="gd_id" property="gdId"/>
<!-- 因為在下方使用了goods屬性,導致goods_id沒有對goodsId進行正確賦值,所以需要進行手動賦值 -->
<result column="goods_id" property="goodsId"/>
<!-- 該標簽表示從多的一方關聯到一的一方 -->
<association property="goods" select="com.dodoke.mybatis.resources.mappers.GoodsMapper.selectById" column="goods_id"></association>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectManyToOne" resultMap="rmGoodsDetail">
select * from t_goods_detail limit 0,20
</select>
</mapper>
~~~
## MyBatis整合C3P0連接池
在之前的課程中,我們就使用過連接池。而且在mybatis-config.xml文件中也設置了使用數據庫連接池,但是這個數據庫連接池是使用的MyBatis自帶的數據庫連接池。我們希望使用更好的數據庫連接池,可以采用C3P0連接池替換掉自帶連接池。
pom.xml中添加依賴
~~~
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mchange</groupId>
<artifactId>c3p0</artifactId>
<version>0.9.5.2</version>
</dependency>
~~~
新增一個C3P0DataSourceFactory擴展類
~~~
package com.dodoke.mybatis.datasources;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
import org.apache.ibatis.datasource.unpooled.UnpooledDataSourceFactory;
/**
* C3P0與MyBatis兼容使用的數據源工廠類
* 繼承UnpooledDataSourceFactory類實現C3P0的遷入工作。
*/
public class C3P0DataSourceFactory extends UnpooledDataSourceFactory {
public C3P0DataSourceFactory(){
//指UnpooledDataSourceFactory類的數據源由C3P0提供
this.dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
}
}
~~~
修改mybatis-config.xml,type改成指向新增的類:C3P0DataSourceFactory
修改C3P0屬性值
~~~
<!--<dataSource type="POOLED">-->
<dataSource type="com.dodoke.mybatis.datasources.C3P0DataSourceFactory">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/babytun?serverTimezone=UTC&characterEncoding=UTF-8"/>
<property name="user" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
<property name="initialPoolSize" value="5"/>
<property name="maxPoolSize" value="20"/>
<property name="minPoolSize" value="5"/>
</dataSource>
~~~
## MyBatis的批量處理
MyBatis的批量處理實際上就是通過循環實現SQL的批量執行
~~~
<!--INSERT INTO table-->
<!--VALUES ("a" , "a1" , "a2"),("b" , "b1" , "b2"),(....)-->
<insert id="batchInsert" parameterType="java.util.List">
INSERT INTO t_goods(title, sub_title, original_cost, current_price, discount, is_free_delivery, category_id)
VALUES
<foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index" separator=",">
(#{item.title},#{item.subTitle}, #{item.originalCost}, #{item.currentPrice}, #{item.discount}, #{item.isFreeDelivery}, #{item.categoryId})
</foreach>
</insert>
<!--in (1901,1902)-->
<delete id="batchDelete" parameterType="java.util.List">
DELETE FROM t_goods WHERE goods_id in
<foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index" open="(" close=")" separator=",">
#{item}
</foreach>
</delete>
~~~
* collection="list"代表迭代的數據源從哪來,一般情況下書寫list,指代從外側傳來的List集合,這個名字是mybatis強制要求不能隨意修改
* item="item" 循環中的迭代遍歷
* indx="index" 循環的索引,當前是第幾次循環
* separator="," 分割器,生成文本時(("a","a1","a2"),("b","b1","b2"),...),每個記錄用逗號分割
* 批量刪除中傳入的list中包含的是每一個要刪除的數據的編號,foreach標簽中要加入open="(" close=")"
~~~
/**
* 批量插入測試
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testBatchInsert() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = null;
try {
long st = new Date().getTime();
session = MyBatisUtils.openSqlSession();
List list = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
Goods goods = new Goods();
goods.setTitle("測試商品");
goods.setSubTitle("測試子標題");
goods.setOriginalCost(200f);
goods.setCurrentPrice(100f);
goods.setDiscount(0.5f);
goods.setIsFreeDelivery(1);
goods.setCategoryId(43);
//insert()方法返回值代表本次成功插入的記錄總數
list.add(goods);
}
session.insert("goods.batchInsert", list);
session.commit();//提交事務數據
long et = new Date().getTime();
System.out.println("執行時間:" + (et - st) + "毫秒");
// System.out.println(goods.getGoodsId());
} catch (Exception e) {
if (session != null) {
session.rollback();//回滾事務
}
throw e;
} finally {
MyBatisUtils.closeSqlSession(session);
}
}
/**
* 10000次數據插入對比測試用例
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testInsert1() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = null;
try{
long st = new Date().getTime();
session = MyBatisUtils.openSqlSession();
List list = new ArrayList();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i++) {
Goods goods = new Goods();
goods.setTitle("測試商品");
goods.setSubTitle("測試子標題");
goods.setOriginalCost(200f);
goods.setCurrentPrice(100f);
goods.setDiscount(0.5f);
goods.setIsFreeDelivery(1);
goods.setCategoryId(43);
//insert()方法返回值代表本次成功插入的記錄總數
session.insert("goods.insert" , goods);
}
session.commit();//提交事務數據
long et = new Date().getTime();
System.out.println("執行時間:" + (et-st) + "毫秒");
// System.out.println(goods.getGoodsId());
}catch (Exception e){
if(session != null){
session.rollback();//回滾事務
}
throw e;
}finally {
MyBatisUtils.closeSqlSession(session);
}
}
/**
* 批量刪除測試
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testBatchDelete() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = null;
try {
long st = new Date().getTime();
session = MyBatisUtils.openSqlSession();
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(1920);
list.add(1921);
list.add(1922);
session.delete("goods.batchDelete", list);
session.commit();//提交事務數據
long et = new Date().getTime();
System.out.println("執行時間:" + (et - st) + "毫秒");
// System.out.println(goods.getGoodsId());
} catch (Exception e) {
if (session != null) {
session.rollback();//回滾事務
}
throw e;
} finally {
MyBatisUtils.closeSqlSession(session);
}
}
~~~
**批量插入數據的局限,需要通過壓力測試來調整**
1. 無法獲得插入的數據id
2. 批量生成的SQL太長,可能會被服務器拒絕。
## 對MyBatis中使用到的類起別名
之前,我們在 mapper xml 文件中的引用實體類時,需要寫上實體類的全類名(包名+類名),每次都寫這么一長串內容挺麻煩的,而我們希望能夠采用一種簡寫的形式。比如寫成這種形式就挺舒服的。
~~~
<select id="selectAll" resultType="_Goods">
select * from t_goods order by goods_id desc limit 10
</select>
~~~
可以在mybatis-config.xml標簽中添加`typeAliases`,注意添加位置。

~~~
<settings>
<!-- 駝峰命名轉化設置 -->
<!-- 該設置表示將數據庫中表的字段,比如goods_id => goodsId -->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias type="com.dodoke.mybatis.entity.Goods" alias="_Goods"/>
</typeAliases>
~~~
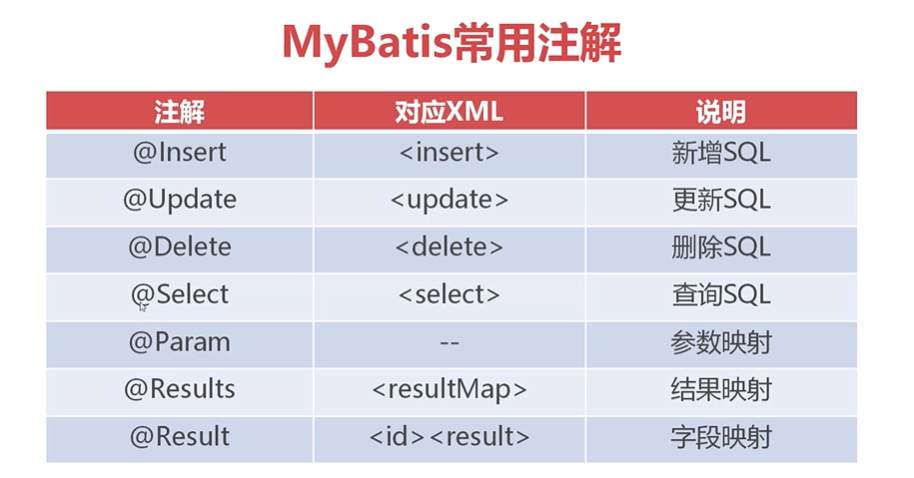
## Mybatis使用注解進行開發
對于Mybatis而言,它提供了一種使用注解的開發方式,這種開發方式與使用xml進行開發比較,它更適合使用在一些小型敏捷的項目中。
在之前的項目基礎上新建一個項目:(pom.xml中依賴不變,工具類不變,logback自定義文件不變)

**mybatis-config.xml**
~~~
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<!-- 官網復制DTD約束 -->
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<!-- 設置根節點 -->
<configuration>
<settings>
<!-- 駝峰命名轉化設置 -->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
<environments default="dev">
<environment id="dev">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<!-- 數據源節點,設置type="POOLED"采用數據庫連接池的方式管理數據庫連接 -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/babytun?serverTimezone=UTC&characterEncoding=UTF-8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<!-- mybatis如果使用注解開發,需要將接口當做mapper xml 進行注冊-->
<!--<mapper class="com.dodoke.mybatisannotation.dao.GoodsDao"/>-->
<!-- 可以通過package標簽將該包中接口全部注冊 -->
<package name="com.dodoke.mybatisannotation.dao"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
~~~
**實體類**
~~~
public class Goods {
private Integer goodsId;//商品編號
private String title;//標題
private String subTitle;//子標題
private Float originalCost;//原始價格
private Float currentPrice;//當前價格
private Float discount;//折扣率
private Integer isFreeDelivery;//是否包郵 ,1-包郵 0-不包郵
private Integer categoryId;//分類編號
public Integer getGoodsId() {
return goodsId;
}
public void setGoodsId(Integer goodsId) {
this.goodsId = goodsId;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getSubTitle() {
return subTitle;
}
public void setSubTitle(String subTitle) {
this.subTitle = subTitle;
}
public Float getOriginalCost() {
return originalCost;
}
public void setOriginalCost(Float originalCost) {
this.originalCost = originalCost;
}
public Float getCurrentPrice() {
return currentPrice;
}
public void setCurrentPrice(Float currentPrice) {
this.currentPrice = currentPrice;
}
public Float getDiscount() {
return discount;
}
public void setDiscount(Float discount) {
this.discount = discount;
}
public Integer getIsFreeDelivery() {
return isFreeDelivery;
}
public void setIsFreeDelivery(Integer isFreeDelivery) {
this.isFreeDelivery = isFreeDelivery;
}
public Integer getCategoryId() {
return categoryId;
}
public void setCategoryId(Integer categoryId) {
this.categoryId = categoryId;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Goods{" +
"goodsId=" + goodsId +
", title='" + title + '\'' +
", subTitle='" + subTitle + '\'' +
", originalCost=" + originalCost +
", currentPrice=" + currentPrice +
", discount=" + discount +
", isFreeDelivery=" + isFreeDelivery +
", categoryId=" + categoryId +
'}';
}
}
~~~
**數據傳輸類**
~~~
package com.dodoke.mybatisannotation.dto;
public class GoodsDTO {
private int goodsId;
private String title;
private String subTitle;
public int getGoodsId() {
return goodsId;
}
public void setGoodsId(int goodsId) {
this.goodsId = goodsId;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getSubTitle() {
return subTitle;
}
public void setSubTitle(String subTitle) {
this.subTitle = subTitle;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "GoodsDTO{" +
"goodsId=" + goodsId +
", title='" + title + '\'' +
", subTitle='" + subTitle + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
~~~
**接口注解開發-接口**
~~~
package com.dodoke.mybatisannotation.dao;
import com.dodoke.mybatisannotation.dto.GoodsDTO;
import com.dodoke.mybatisannotation.entity.Goods;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 該接口用操作數據庫
*/
public interface GoodsDao {
@Select("select * from t_goods where current_price between #{min} and #{max} order by current_price limit 0,#{limt}")
public List<Goods> selectByPriceRange(@Param("min") Float min, @Param("max") Float max, @Param("limt") Integer limt);
/**
* 對于注解開發來說,新增和刪除,以及修改方法的返回值都要是int類型
* @param goods
* @return
*/
@Insert("INSERT INTO t_goods(title, sub_title, original_cost, current_price, discount, is_free_delivery, category_id) VALUES (#{title} , #{subTitle} , #{originalCost}, #{currentPrice}, #{discount}, #{isFreeDelivery}, #{categoryId})")
@SelectKey(statement = "select last_insert_id()" ,before=false,keyProperty = "goodsId" ,resultType = Integer.class)
public int insert(Goods goods);
@Select(" select * from t_goods order by goods_id desc limit 10")
//如果沒有設置駝峰命令轉換或者要設置數據轉換類,或者多對一,一對多的時候,可以利用results注解
@Results({
//設置id=true,明確指示id屬性
@Result(column = "goods_id",property = "goodsId" , id=true),
@Result(column = "title",property = "title" ),
@Result(column = "sub_title",property = "subTitle" ),
})
public List<GoodsDTO> selectLimit();
}
~~~
