[TOC]
## 概述
* 基于哈希表的實現的Map接口
* 無序
* 允許一個null鍵
* HashMap不是線程同步的。在多線程環境下使用HashMap,并且有寫操作的話,必須要自己實現線程之間的同步,或者使用其他同步容器。
* iterator方法返回的迭代器是快速失敗的。在創建迭代器之后的任何修改,除非是通過迭代器自身的remove方法對列表進行修改,否則迭代器都會拋出ConcurrentModificationException。
## HashMap的數據結構
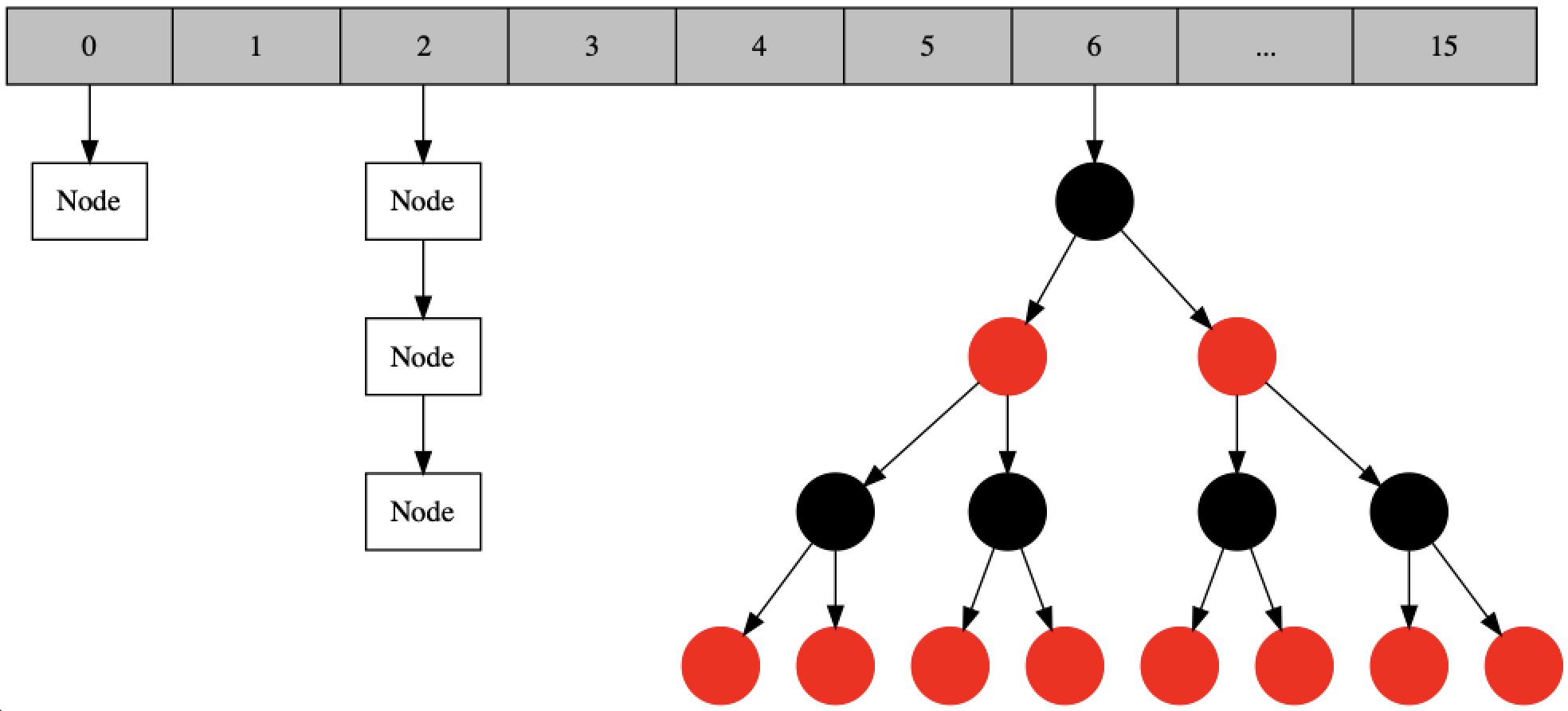
jdk8中HashMap的實現是 數組 + 鏈表 + 紅黑樹。
1. 新key-value進來時,首先按key的hash值計算數組中存放的下標,并放入數組中;
2. 如果hash沖突,那么多個節點組成鏈表。
3. 當鏈表長度過長時,會轉成紅黑樹。
### 鏈表Node
~~~
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash; // key的hash值
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next; // 下一個節點
~~~
### 紅黑樹TreeNode
這里不展開講紅黑樹了,有興趣的可以看【數據結構-紅黑樹詳解】。
~~~
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {
TreeNode<K,V> parent; // 父節點
TreeNode<K,V> left; // 左子節點
TreeNode<K,V> right; // 右子節點
TreeNode<K,V> prev; // 前置節點,刪除節點的時候解除鏈接
boolean red; // 節點顏色,紅黑
~~~
## HashMap的實現
### 類定義
~~~
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable {
~~~
### 默認配置
~~~
// Node數組的默認初始容量16
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4;
// Node數組的最大容量
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
// 默認加載因子0.75
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
// 當鏈表長度大于此值時,轉換為紅黑樹
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
// Node數組大小超過64才使用紅黑樹
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
~~~
### 關鍵屬性
~~~
// 哈希表
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
// MapEntry集合
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
// 鍵值對數量
transient int size;
// HashMap修改次數,用于判斷迭代器使用過程中是否快速失敗。
transient int modCount;
// 數組大小 * 加載因子,對于給定初始容量或已知key大小的情況,第一次賦值是數組大小,后續變成數組大小 * 加載因子
int threshold;
// 加載因子
final float loadFactor;
~~~
### 構造函數
~~~
// 默認構造器,加載因子=0.75
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
}
// 構造一個指定初始容量(真實容量會擴展到2^n次方)和加載因子的HashMap實例
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
// 將cap增加到2^m次方(不寫n次方是為了與下面的變量n區分)
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1; // 減1是針對cap=2^m的情況,最后的計算結果還是cap原值,不會增大
// 下面的操作是對n的所有二進制位都置為1,n = 2^m - 1。
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1; // n + 1 = 2^m
}
// 構造一個指定初始容量(真實容量會擴展到2^n次方)的HashMap實例
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
// 用已有Map實例構造一個HashMap實例,導入所有鍵值對
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
putMapEntries(m, false); // 把m的所有鍵值對導入新HashMap中,具體實現放到后面講
}
~~~
### 關鍵操作
#### 添加key-value
~~~
// 新增鍵值對,若已存在則覆蓋。
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
// 如果數組為空,先擴容,resize后面講
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// 計算key在數組中的存放位置i,i跟數組大小和 key 的 hash 值有關
// 如果i位置上還沒有數據,就把key和value存放到這個位置上。
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) // key已存在,并且是鏈表頭結點或紅黑樹根節點
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
// 將key-value節點添加到紅黑樹,若已存在,直接返回已存在的key-value節點
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
// 遍歷鏈表,查找key對應的node
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
// 遍歷結束,key不存在,把key-value節點添加到鏈表中
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // 鏈表長度超過8,試圖轉成紅黑樹
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) // 找到key,遍歷結束
break;
p = e;
}
}
// 對于已存在的key,更新value,并返回舊value
if (e != null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) // 判斷是否覆蓋
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e); // 回調函數,在LinkedHashMap中使用
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount; // 修改次數加1
// 如果key數量超過threshold,則擴容
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict); // 回調函數,在LinkedHashMap中使用
return null;
}
final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) {
int n, index; Node<K,V> e;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
resize(); // 數組大小不超過MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY,不使用紅黑樹,先擴容一次
else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
do {
TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null); // 鏈表Node實例都轉成TreeNode實例,只是類型轉換,還不是樹
if (tl == null)
hd = p;
else {
p.prev = tl;
tl.next = p;
}
tl = p;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
if ((tab[index] = hd) != null)
hd.treeify(tab); // 轉成紅黑樹結構
}
}
~~~
#### 批量添加key-value
~~~
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
putMapEntries(m, true);
}
final void putMapEntries(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m, boolean evict) {
int s = m.size();
if (s > 0) {
// 如果數組為空,根據key數量計算數組大小。第一次put的時候才真正的創建數組
if (table == null) {
float ft = ((float)s / loadFactor) + 1.0F; // 為什么+1?從結果來看,對于s / loadFactor = 2^n次方的情況,+1后再調用tableSizeFor的計算結果是2^(n+1)次方,就是提前擴容了。
int t = ((ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : MAXIMUM_CAPACITY);
if (t > threshold)
threshold = tableSizeFor(t); // 增加到2^n次方
}
else if (s > threshold)
resize();
// 循環導入key-value
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet()) {
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, evict);
}
}
}
~~~
#### 擴容
~~~
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { // 已達最大容量,threshold設置為Integer.MAX_VALUE,不會再觸發擴容
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
// 數組大小擴容兩倍
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY & oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // 擴容閾值也增加2倍。oldCap < DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY時,threshold值是DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY,不能直接2倍,需要按公式 數組大小 * 加載因子 重新計算
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap]; // 新建數組
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
// 遍歷舊數組,把原來的數據復制到新數組
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
// 如果是單個節點,計算新下標,并放入新數組中
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
// 如果是紅黑樹,調用split
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
// 如果是鏈表,按e.hash & oldCap == 0拆分成兩個鏈表,一個存放到原來的位置j,另一個存放到位置j+oldCap
else { // preserve order
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
~~~
#### 刪除key
~~~
public V remove(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ?
null : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value, boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v;
if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) // key節點是鏈表頭部或樹的根節點
node = p;
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {
if (p instanceof TreeNode) // 如果是紅黑樹,在樹上查找key節點
node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else { // 如果是鏈表,遍歷鏈表查找key節點
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
p = e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value || (value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
// 如果是紅黑樹,從樹上刪除 key節點
if (node instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);
// 如果是鏈表,從鏈表上刪除 key節點
else if (node == p)
tab[index] = node.next;
else
p.next = node.next;
++modCount;
--size;
afterNodeRemoval(node); // 回調函數,在LinkedHashMap中使用
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
~~~
#### 獲取key-value
~~~
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first.hash == hash && ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) // key節點是鏈表頭部或樹的根節點
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode) // 如果是紅黑樹,在樹上查找key節點
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do { // 如果是鏈表,遍歷鏈表查找key節點
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
~~~
### 迭代器Iterator
~~~
abstract class HashIterator {
Node<K,V> next; // 下一個返回的節點
Node<K,V> current; // 當前節點
int expectedModCount; // 用于快速失敗
int index; // 當前位置
HashIterator() {
expectedModCount = modCount; // 初始化為map當前修改次數
Node<K,V>[] t = table;
current = next = null;
index = 0;
// 遍歷數組與鏈表,找到第一個不為空的節點
if (t != null && size > 0) {
do {} while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null);
}
}
public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
final Node<K,V> nextNode() {
Node<K,V>[] t;
Node<K,V> e = next;
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
// 從當前位置開始,遍歷數組與鏈表,找到下一個不為空的節點
if ((next = (current = e).next) == null && (t = table) != null) {
do {} while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null);
}
return e;
}
public final void remove() {
Node<K,V> p = current;
if (p == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
current = null;
K key = p.key;
// 刪除當前節點
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, false);
expectedModCount = modCount; // 更新expectedModCount,通過迭代器刪除,不會快速失敗
}
}
final class KeyIterator extends HashIterator
implements Iterator<K> {
public final K next() { return nextNode().key; }
}
final class ValueIterator extends HashIterator
implements Iterator<V> {
public final V next() { return nextNode().value; }
}
final class EntryIterator extends HashIterator
implements Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public final Map.Entry<K,V> next() { return nextNode(); }
}
~~~
### 并發迭代器Spliterator
~~~
static class HashMapSpliterator<K,V> {
final HashMap<K,V> map;
Node<K,V> current; // 當前節點
int index; // 當前位置,trySplit、tryAdvance時變化
int fence; // 初始值-1
int est; // 預估數量
int expectedModCount; // 用于快速失敗
HashMapSpliterator(HashMap<K,V> m, int origin,
int fence, int est,
int expectedModCount) {
this.map = m;
this.index = origin;
this.fence = fence;
this.est = est;
this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;
}
final int getFence() { // initialize fence and size on first use
int hi;
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
HashMap<K,V> m = map;
est = m.size; // 預估數量=map元素數量
expectedModCount = m.modCount;
Node<K,V>[] tab = m.table;
hi = fence = (tab == null) ? 0 : tab.length; // fence設置成數組長度
}
return hi;
}
public final long estimateSize() {
getFence(); // force init
return (long) est;
}
}
static final class KeySpliterator<K,V>
extends HashMapSpliterator<K,V>
implements Spliterator<K> {
KeySpliterator(HashMap<K,V> m, int origin, int fence, int est,
int expectedModCount) {
super(m, origin, fence, est, expectedModCount);
}
// 每次將數組切一半出去,新建一個KeySpliterator實例。
public KeySpliterator<K,V> trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
return (lo >= mid || current != null) ? null :
new KeySpliterator<>(map, lo, index = mid, est >>>= 1, // 當前位置index變成剩余一半的開始位置,預估大小減半
expectedModCount);
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super K> action) {
int i, hi, mc;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
HashMap<K,V> m = map;
Node<K,V>[] tab = m.table;
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
mc = expectedModCount = m.modCount;
hi = fence = (tab == null) ? 0 : tab.length;
}
else
mc = expectedModCount;
// 遍歷所有節點,執行action操作
if (tab != null && tab.length >= hi &&
(i = index) >= 0 && (i < (index = hi) || current != null)) {
Node<K,V> p = current;
current = null;
do {
if (p == null)
p = tab[i++];
else {
action.accept(p.key);
p = p.next;
}
} while (p != null || i < hi);
if (m.modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
// 嘗試對下一個節點執行action操作
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super K> action) {
int hi;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Node<K,V>[] tab = map.table;
if (tab != null && tab.length >= (hi = getFence()) && index >= 0) {
while (current != null || index < hi) {
if (current == null)
current = tab[index++];
else {
K k = current.key;
current = current.next;
action.accept(k);
if (map.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public int characteristics() {
return (fence < 0 || est == map.size ? Spliterator.SIZED : 0) |
Spliterator.DISTINCT;
}
}
~~~
ValueSpliterator 與 EntrySpliterator 的實現與KeySpliterator類似,這里不再贅述。
- 概要
- JDK源碼解讀系列
- 容器類
- ArrayList源碼解讀
- LinkedList源碼解讀
- HashSet源碼解讀
- LinkedHashSet源碼解讀
- TreeSet源碼解讀
- HashMap源碼解讀
- LinkedHashMap源碼解讀
- 數據結構
- 紅黑樹詳解
- 設計模式
- 設計模式的7個基本原則
- 單一職責原則
- 開閉原則
- 里氏替換原則
- 依賴倒置原則
- 接口隔離原則
- 迪米特法則
- 合成復用原則
- GoF的23種設計模式
- 創建型模式
- 單例模式
- 原型模式
- 工廠方法模式
- 抽象工廠模式
- 建造者模式
- 結構型模式
- 代理模式
- 適配器模式
- 裝飾器模式
- 行為型模式
- 模板方法模式
- 策略模式
- 命令模式
- 責任鏈模式
- 觀察者模式
- Mybatis技術內幕
- 第一章 Mybatis整體架構
- 第二章 基礎支持層
- 2.1 解析器模塊
- 2.2 反射工具箱
- 2.3 類型轉換
- 2.4 日志模塊
- 2.5 資源加載
- 2.6 數據源DataSource
- 2.7 事務Trasaction
- 2.8 Binding模塊
- 2.9 緩存模塊
- 第三章 核心處理層
- 3.1 MyBatis初始化
- 3.2 SqlNode&SqlSource
- 3.3 ResultSetHandler
- 3.4 KeyGenerator
- 3.5 StatementHandler
- 3.6 Executor
- 3.7 SqlSession