[toc]
# 一、collection概述
collection是一個接口類,其有兩個主要的子接口List和Set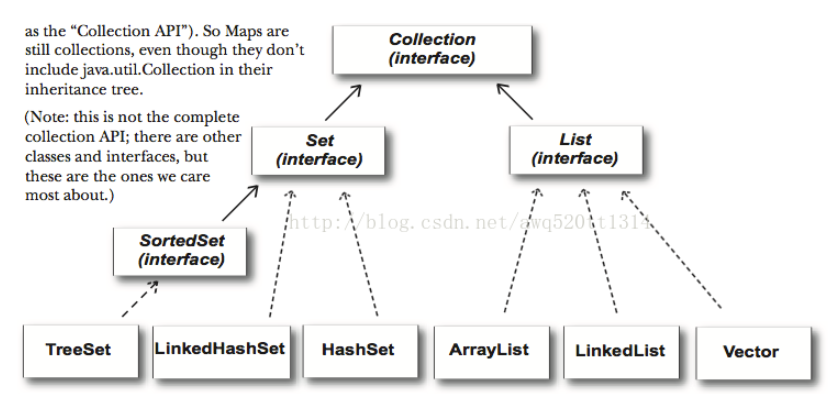
List(interface):List可以通過index知道元素的位置,它是<b>有序的</b>,并且允許元素<b>重復</b>
Set(interface):<b>無序的,不允許元素重復</b>
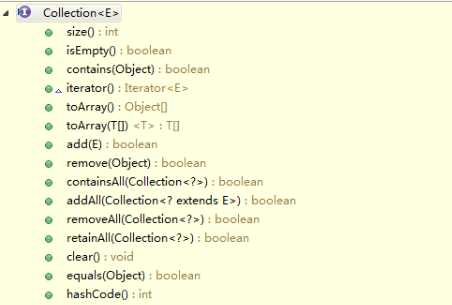
## collection的方法
# 二、List
有三個比較常用的繼承List接口的類,分別是ArrayList、LinkedList和Vector
List接口:有序的,此接口可以對列表中元素的插入位置精確控制,允許多個null值,元素可重復
ArrayList:ArrayList是個動態數組,擅長隨機訪問,非同步的
LinkedList:LinkedList是個雙向鏈表,不能隨機訪問,非同步
Vector:Vctor是同步 的,其他同ArrayList類似,是線程安全的動態數組。
## 2-1.ArrayList
ArrayList就是一個<b>動態數組</b>,按照添加對象的順序存儲對象,<b>隨機訪問</b>速度極快。缺點是不適合于在線性表中間需要頻繁進行插入和刪除操作。因為每次插入和刪除都需要移動數組中的元素。
~~~
//E是泛型,代表一種類型,讓ArrayList里存的是同一種類型的數據
List<E> list = new ArrayList<>();
~~~
### ArrayList常用API
set(int index,E element)

remove(int index)

indexOf(Object o)

### ArrayList四個注意點
a.如果在初試化ArrayList的時候沒有指定初始長度的話,默認長度為10
~~~
/**
* Default initial capacity.
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
~~~
b.ArrayList在增加新元素的時候如果超過了原始的容量的話,ArrayList擴容ensureCapacity的方案為<b>“原始容量*1.5+1”</b>
~~~
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (minCapacity > oldCapacity) {
Object oldData[] = elementData;
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity * 3)/2 + 1;
if (newCapacity < minCapacity)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
}
~~~
c.ArrayList是線程不安全的,在多線程的情況下不要使用。多線程用Vector。
d.ArrayList實現遍歷的幾種方法。
~~~
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list=new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("Hello");
list.add("World");
list.add("HAHAHAHA");
//第一種遍歷方法使用foreach遍歷List
for (String str : list) { //也可以改寫for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++)這種形式
System.out.println(str);
}
//第二種遍歷,把鏈表變為數組相關的內容進行遍歷
String[] strArray=new String[list.size()];
list.toArray(strArray);
for(int i=0;i<strArray.length;i++) //這里也可以改寫為foreach(String str:strArray)這種形式
{
System.out.println(strArray[i]);
}
//第三種遍歷 使用迭代器進行相關遍歷
Iterator<String> ite=list.iterator();
while(ite.hasNext())
{
System.out.println(ite.next());
}
}
}
~~~
## 2-2.LinkedList
LinkedList是一個<b>雙向鏈表</b>,優點在于適合于在鏈表中間需要頻繁進行<b>插入和刪除</b>操作,缺點是隨機訪問速度較慢,查找每個元素都需要從頭開始一個個找。
遍歷LinkedList
~~~
List<String> list=new LinkedList<String>();
list.add("Hello");
list.add("World");
list.add("HAHAHAHA");
for(String str:list){
System.out.println(str);
}
~~~
## 2-3.Vector
vector和arraylist基本一致,區別在于vector中的絕大部分方法都使用了<b>synchronized</b>鎖,使得vector多線程的情況下是安全的。vector是允許設置默認的增長長度,vector的默認擴容方式為原來的2倍。
# 三、Set
set接口也是collection的一個常用子接口。set接口區別于list接口的特點在于:
set中的元素不能重復,并且是無序的,最多允許一個null值。
注意:雖然set中元素沒有順序,但是元素在set中的位置是由該元素的hashcode決定的,其具體位置其實是<b>固定的</b>。
## 1.HashSet
~~~
/**
* Constructs a new, empty set; the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance has
* default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
~~~
由hashset的部分源碼可知,hashset的底層就是<b>基于hashmap</b>來實現的。
hashset使用和理解中容易出現的誤區:
a.hashset中存儲元素的位置是固定的
hashset中存儲元素是<b>無序的</b>,由于hashset底層是基于hash算法實現的,使用了hashcode,所以hashset中相應的元素的位置是固定的
b.遍歷hashset的幾種方法
~~~
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add("hello");
set.add("world");
set.add("hello");
//1.使用foreach循環遍歷
for(String str:set){
System.out.println(str);
}
//2.使用迭代器遍歷
Iterator<String> iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
~~~
## 2.LinkedHashSet
~~~
public class LinkedHashSet<E>
extends HashSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2851667679971038690L;
/**
* Constructs a new, empty linked hash set with the specified initial
* capacity and load factor.
*/
~~~
由linkedhashset的源碼可知,linkedhashset不僅是set的子接口,還是上面<b>hashset的子類</b>。
通過查看底層源碼發現,其底層是基于linkedhashmap。
### linkedhashset和hashset異同點
1.**hashset和linkedhashset都出于速度原因使用了散列,故都沒排序,而linkedset使用了鏈表維護了元素的插入順序**
2.hashset是linkedhashset的父類
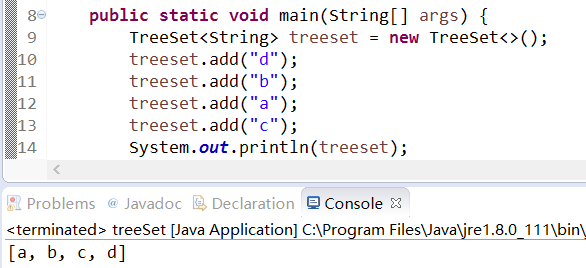
## 3.TreeSet
treeset是一種<b>排序二叉樹</b>。存入set集合中的值,會按照值的大小進行相關的排序操作,底層算法是<b>基于紅黑樹</b>來實現的。
### treeset和hashset的區別和聯系
1.hashset是通過hashmap實現的,treeset是通過treemap實現的,只是用了map的key值。
2.map的key和set都有一個共同的特性就是集合的唯一性。treemap更是多了一個排序的功能。
3. hashCode和equal()是HashMap用的, 因為無需排序所以只需要關注定位和唯一性即可.
?????????? a. hashCode是用來計算hash值的,hash值是用來確定hash表索引的.
?????????? b. hash表中的一個索引處存放的是一張鏈表, 所以還要通過equal方法循環比較鏈上的每一個對象
????????????? 才可以真正定位到鍵值對應的Entry.
???????????c. put時,如果hash表中沒定位到,就在鏈表前加一個Entry,如果定位到了,則更換Entry中的value,并返回舊value
4. 由于TreeMap需要排序,所以需要一個Comparator為鍵值進行大小比較.當然也是用Comparator定位的.
?????????? a. Comparator可以在創建TreeMap時指定
?????????? b. 如果創建時沒有確定,那么就會使用key.compareTo()方法,這就要求key必須實現Comparable接口.
?????????? c. TreeMap是使用Tree數據結構實現的,所以使用compare接口就可以完成定位了.
