## Java專題三:集合
[TOC]
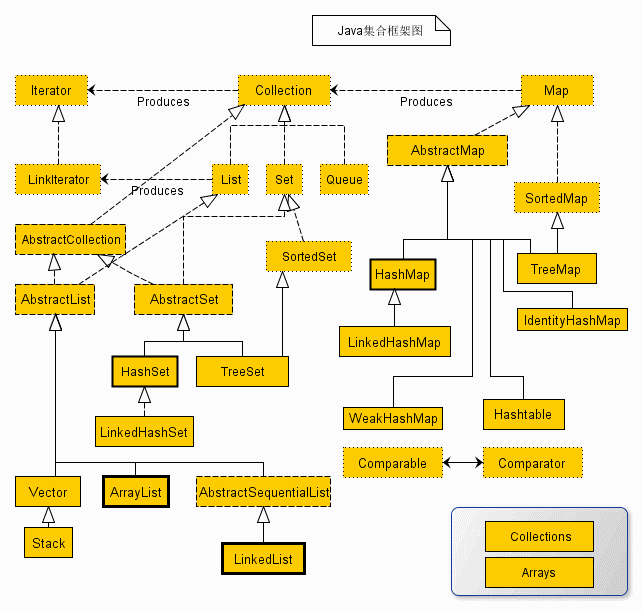
### 3.1. ArrayList
```java
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
private int size;
}
```
ArrayList 內部維護了一個Object類型的能**自動擴容的數組**,當ArrayList對象調用add方法添加元素時,會先將elementData數組所含元素個數+1(size+1)與elementData的容量(elementData.length)進行比較,如果超過了當前,則申請一個合適容量大小的Object數組,并將老的數組元素拷貝到新的elementData數組。
**插入元素**:
在長度為size的List指定位置index處插入元素,如果容量不夠,先擴容,然后使用System.arraycopy方法從index處開始拷貝size-1-index個元素至index+1處,并將待插入元素直接插入到index處。
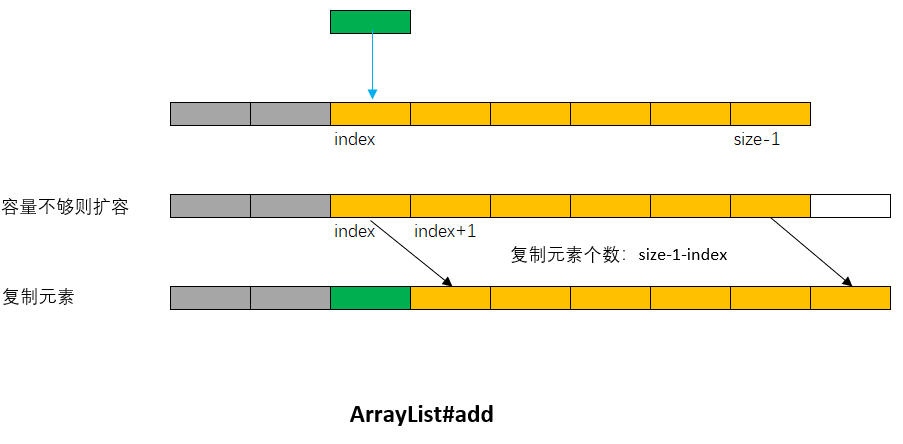
**刪除元素**:
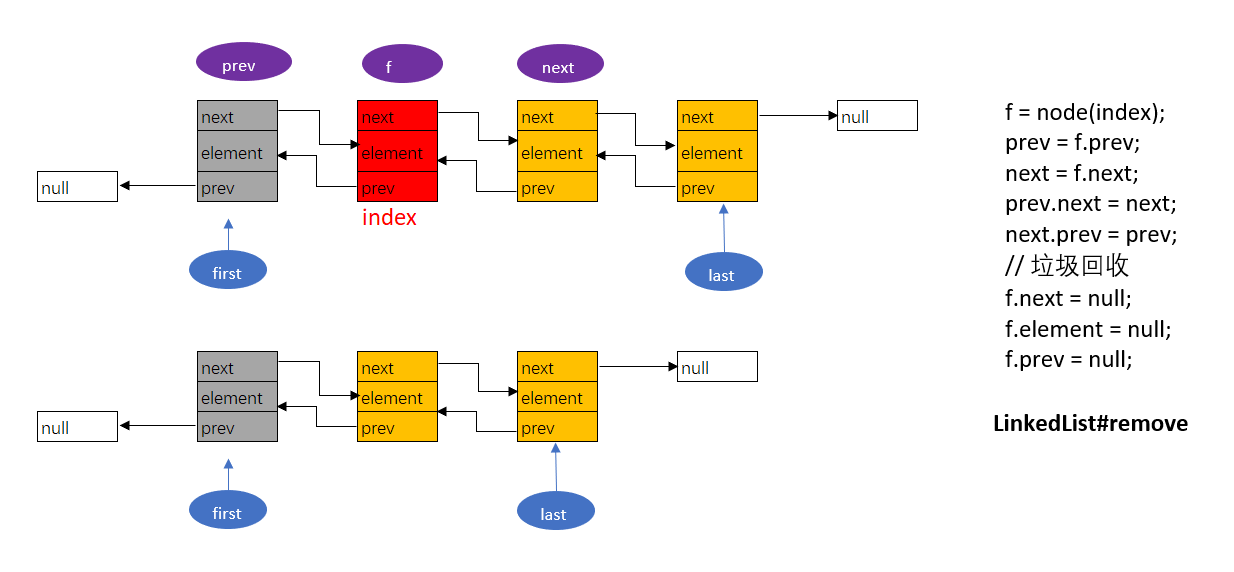
在長度為size的List指定位置index處刪除元素,使用System.arraycopy方法從index+1開始拷貝size-1-index個元素至index處,并將最后一個元素[size-1]置為空,給GC回收。
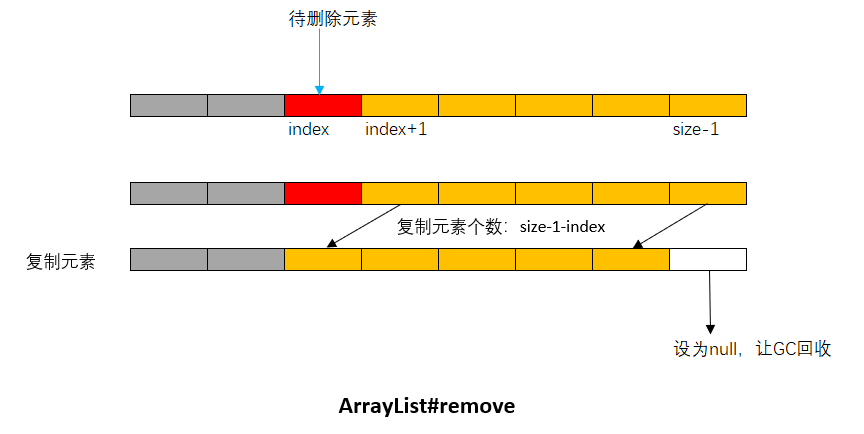
### 3.2. LinkedList
```java
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
transient int size = 0;
transient Node<E> first;
transient Node<E> last;
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
}
```
LinkedList是使用**雙向鏈表**數據結構來實現的,其中節點數據類型(與C語言之中的結構體類似)使用內部類實現。
### 3.3. HashMap
```java
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable {
transient Node<K,V>[] table;//哈希表
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
```
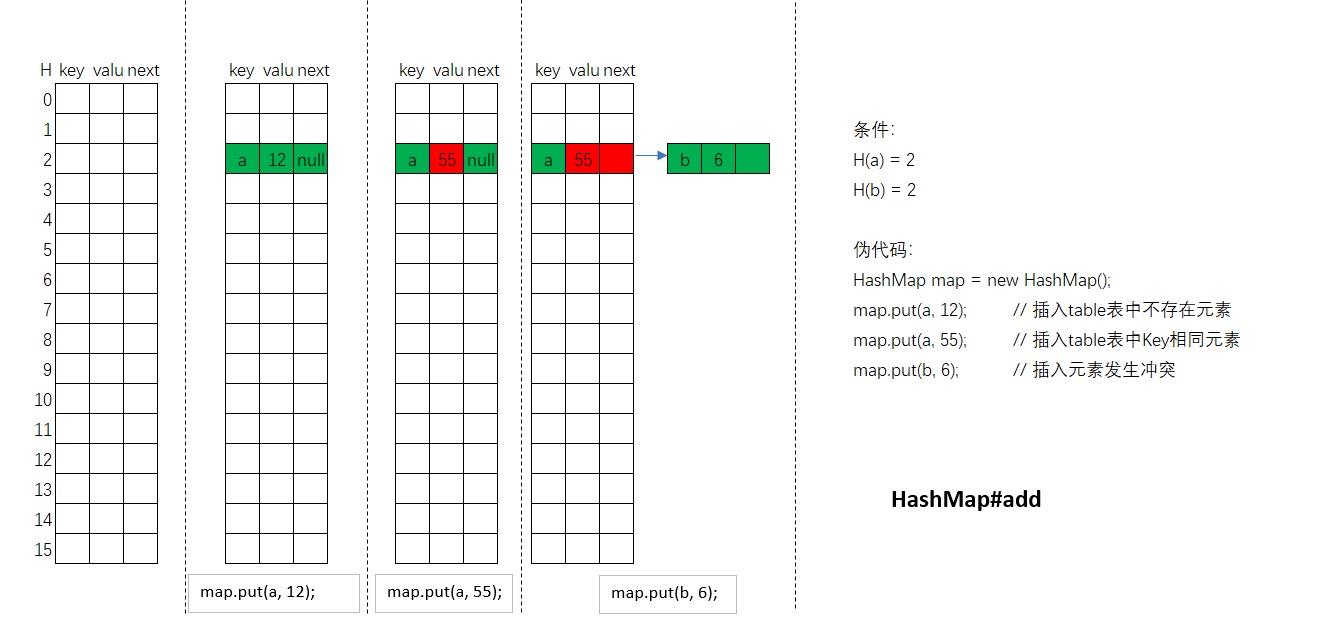
HashMap使用**哈希表**數據結構,其哈希函數為:H(key) = (n-1) & hash; 并使用鏈表數據結構處理沖突。
其中:
```java
n = table.length;
hash = hash(key);
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
```
說明:HashMap如果Key相等(equal方法返回true)則認為是同一元素,插入key相同的鍵值對,后面插入的value會覆蓋前面的value。
#### 3.3.1. 插入元素
1. 根據哈希函數計算判斷哈希表中該位置index是否已插入元素,如果沒有,則進入第2步,否則進入第3步
2. 直接給哈希表index位置賦值即可,如table[index] = newNode;插入結束。
3. 根據鍵key是否相等(equal方法)判斷是否是同一元素,如果是同一元素,則替換掉value,插入結束,否則進入第4步。
4. 產生了沖突,使用鏈表尾插法將新元素插入。
#### 3.3.2. 刪除元素
1. 根據哈希函數計算判斷哈希表中該位置index判斷是否為null,如果不是null,則進入第2步,否則直接返回null,刪除結束。
2. 遍歷表中index位置的鏈表,查找與刪除元素Key相同的元素,找到的話進入第3步,否則返回null,刪除結束。
3. 根據鏈表的刪除元素方法刪除元素,刪除結束。
#### 3.3.3. 擴容
- `initialCapacity`: 初始容量,默認值為16(`DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY`),也可以通過構造方法`HashMap(int initialCapacity)`指定`initialCapacity`的值
- `MAXIMUM_CAPACITY`: 最大容量,HashMap的容量是動態增長的,但不是無限增長的
- `loadFactor`: 裝填因子,默認值為0.75f(`DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR`),也可以通過構造方法`HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)`指定`loadFactor`的值,表示在哈希表中能填充的最佳百分比,超過了該百分比發生沖突的可能性就比較大
- `size`: 初始容量,HashMap中已經插入的key-value對的數量
- `threshold`: 臨界值,當`size`大于這個臨界值,HashMap就得重新擴容
~~~
public class HashMap {
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4;
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
transient int size;
int threshold;
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}
}
~~~
### 3.4. HashSet
```java
public class HashSet<E>
extends AbstractSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;
// Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
}
```
HashSet內部維護了一個HashMap對象,通過HashMap的Key相同為同一元素原則確保HashSet添加元素不重復。
### 3.5. Hashtable
是線程安全的,不推薦使用
```java
public class Hashtable<K,V>
extends Dictionary<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
private transient Entry<?,?>[] table;
private transient int count;
private int threshold;
private float loadFactor;// 裝填因子
}
```
#### 3.5.1. 哈希與沖突方法
Hashtable使用**哈希表**數據結構,其構造哈希表的哈希函數(除留余數法)為:
```java
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
```
處理沖突方法,與HashMap一樣,采用鏈地址法,但是在表頭插入:
```java
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>) tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
```
#### 3.5.2. Hashtable為什么key和value都不能為null
```
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
}
```
首先判斷了value是否為空,為空則拋出NullPointerException,
然后執行key.hashCode()方法時,如果key為null,不能在空指針上調用方法,也會拋出異常,
因此Hashtable中key和value都不能為null
### 3.6. TreeMap
```java
public class TreeMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;//用于接收用戶自定義的比較器
private transient Entry<K,V> root;//紅黑樹的根節點
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> left;
Entry<K,V> right;
Entry<K,V> parent;
boolean color = BLACK;
Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.parent = parent;
}
}
```
TreeMap內部使用**紅黑樹**數據結構,其中每個節點類型定義為內部類Entry類型,與TreeSet一樣能夠對插入的元素進行自動排序,元素規范與TreeSet一樣。
**什么是紅黑樹?**
首先紅黑樹是**二叉查找樹**,它們當中每一個節點的比較值都必須大于或等于在它的左子樹中的所有節點,并且小于或等于在它的右子樹中的所有節點。
**紅黑樹特點**:
1.根節點與葉節點都是黑色節點,其中葉節點為NULL節點。
2.每個紅色節點的兩個子節點都是黑色節點。
3.從根節點到所有葉子節點上的黑色節點數量是相同的。
### 3.7. EnumSet
> 添加枚舉類元素的專用集合類
#### 3.7.1. 與其他集合類區別:
- `EnumSet`內部實現不使用常見的`數據結構`,比如數組(`ArrayList`),鏈表(`LinkedList`),哈系表(`HashMap、Hashtable、HashSet`),紅黑樹(`TreeMap、TreeSet`)而是使用`位運算`完成集合的基本操作
- `EnumSet`是抽象類,只能通過`靜態工廠方法`構造EnumSet對象,具體如下:
`EnumSet<E> noneOf(Class<E> elementType)`:構造一個空的集合
`EnumSet<E> allOf(Class<E> elementType)`:構造一個包含枚舉類中所有枚舉項的集合
`EnumSet<E> of(E e)`:構造包含1個元素的集合
`EnumSet<E> of(E e1, E e2)`:構造包含2個元素的集合
`EnumSet<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3)`:構造包含3個元素的集合
`EnumSet<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4)`:構造包含4個元素的集合
`EnumSet<E> of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4, E e5)`:構造包含5個元素的集合
`EnumSet<E> of(E first, E... rest)`:構造包含多個元素的集合(使用可變參數)
`EnumSet<E> copyOf(EnumSet<E> s)`:構造包含參數中所有元素的集合
`EnumSet<E> copyOf(Collection<E> c)`:構造包含參數中所有元素的集合
#### 3.7.2.EnumSet作為集合類基本操作方法實現原理(位運算):
**說明**:
- 從EnumSet的`noneOf`可以看出,當枚舉類中的枚舉項`少于64`時,返回的是`RegularEnumSet類`(`EnumSet的實現類`)對象,大于64,返回的是JumboEnumSet類對象,為了方便分析,后面同一使用RegularEnumSet類解釋原理
```
// EnumSet#noneOf
public static <E extends Enum<E>> EnumSet<E> noneOf(Class<E> elementType) {
Enum<?>[] universe = getUniverse(elementType);
if (universe == null)
throw new ClassCastException(elementType + " not an enum");
if (universe.length <= 64)
return new RegularEnumSet<>(elementType, universe);
else
return new JumboEnumSet<>(elementType, universe);
}
```
- 測試用的枚舉類
```
enum Color{
RED("RED"),
BLUE("BLUE"),
YELLOW("YELLOW"),
BLACK("BLACK");
String name;
Color(String name){
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return this.name;
}
}
```
#### 3.7.3. add方法</h6>
public boolean add(E e) {
typeCheck(e);
long oldElements = elements;
elements |= (1L << ((Enum<?>)e).ordinal());
return elements != oldElements;
}
`ordinal()`為每個枚舉項的序號,從`0開始`,按聲明順序排列,如`[RED,BLUE,YELLOW,BLACK]`對應`[0,1,2,3]`;`1L << ((Enum<?>)e).ordinal()`(為了方便,這里稱之為`枚舉值`)則表示`1*2^(e.ordinal())`,Color.RED的`ordianl()`為`0`,對應`枚舉值`為`1*2^0=1`,其實就是第`ordinal()+1`位(從右往左數,個位為第1位)為1其它位為0的十進制數,對應十進制數為`00000001`(這里假設是8bit,實際是long型32bit);
則每個枚舉項表示如下:
枚舉項|序號|`1L << ((Enum<?>)e).ordinal()`|枚舉值
:-:|:-:|:-:|:-:
Color.RED|0|`00000001`|1
Color.BLUE|1|`00000010`|2
Color.YELLOW|2|`00000100`|4
Color.BLACK|3|`00001000`|8
`elements |=`就是對添加的不同元素的枚舉值進行求和,`相同`元素`相或`時`保持不變`
#### 3.7.4. remove方法
public boolean remove(Object e) {
if (e == null)
return false;
Class<?> eClass = e.getClass();
if (eClass != elementType && eClass.getSuperclass() != elementType)
return false;
long oldElements = elements;
elements &= ~(1L << ((Enum<?>)e).ordinal());
return elements != oldElements;
}
按照之前的`枚舉值相加`的想法,remove就是從`總枚舉值`中減去`待刪除元素的枚舉值`,因為是`位運算`,沒有直接相減,使用位操作`elements &= ~(1L << ((Enum<?>)e).ordinal());`
完成相減操作
#### 3.7.5. contains方法</h6>
public boolean contains(Object e) {
if (e == null)
return false;
Class<?> eClass = e.getClass();
if (eClass != elementType && eClass.getSuperclass() != elementType)
return false;
return (elements & (1L << ((Enum<?>)e).ordinal())) != 0;
}
contains方法就更好理解,每個枚舉項的枚舉值的值都`不一樣`,且`相互之間`進行`相與`操作為`0`,使用`總枚舉值`與`要查詢的枚舉項的枚舉值`進行`相與`操作,如果為`0`,說明`不存在`該枚舉項,否則`存在`
- JavaCook
- Java專題零:類的繼承
- Java專題一:數據類型
- Java專題二:相等與比較
- Java專題三:集合
- Java專題四:異常
- Java專題五:遍歷與迭代
- Java專題六:運算符
- Java專題七:正則表達式
- Java專題八:泛型
- Java專題九:反射
- Java專題九(1):反射
- Java專題九(2):動態代理
- Java專題十:日期與時間
- Java專題十一:IO與NIO
- Java專題十一(1):IO
- Java專題十一(2):NIO
- Java專題十二:網絡
- Java專題十三:并發編程
- Java專題十三(1):線程與線程池
- Java專題十三(2):線程安全與同步
- Java專題十三(3):內存模型、volatile、ThreadLocal
- Java專題十四:JDBC
- Java專題十五:日志
- Java專題十六:定時任務
- Java專題十七:JavaMail
- Java專題十八:注解
- Java專題十九:淺拷貝與深拷貝
- Java專題二十:設計模式
- Java專題二十一:序列化與反序列化
- 附加專題一:MySQL
- MySQL專題零:簡介
- MySQL專題一:安裝與連接
- MySQL專題二:DDL與DML語法
- MySQL專題三:工作原理
- MySQL專題四:InnoDB存儲引擎
- MySQL專題五:sql優化
- MySQL專題六:數據類型
- 附加專題二:Mybatis
- Mybatis專題零:簡介
- Mybatis專題一:配置文件
- Mybatis專題二:映射文件
- Mybatis專題三:動態SQL
- Mybatis專題四:源碼解析
- 附加專題三:Web編程
- Web專題零:HTTP協議
- Web專題一:Servlet
- Web專題二:Cookie與Session
- 附加專題四:Redis
- Redis專題一:數據類型
- Redis專題二:事務
- Redis專題三:key的過期
- Redis專題四:消息隊列
- Redis專題五:持久化
