## Java專題十一(1):IO
[TOC]
> IO是基于字節流和字符流操作的
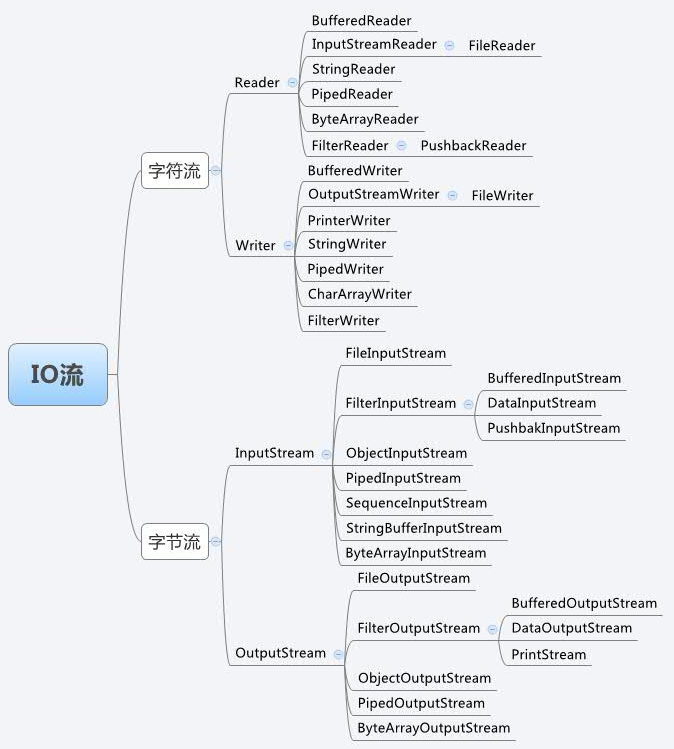
**IO基類**:
| | Reader |Writer |InputStream |OutputStream |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| 字符流 | ? | ? | | |
| 字節流 | | | ? | ? |
| 輸入流 | ? | | ? | |
| 輸出流 | | ? | | ? |
**各種資源IO類**:
| | Reader |Writer |InputStream |OutputStream |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| File | FileReader | FileWriter| FileInputStream | FileOutputStream |
| Buffer | BufferReader | BufferWriter | BufferedInputStream | BufferedOutputStream |
| Pipe | PipedReader | PipedWriter| PipedInputStream | PipedOutputStream |
| String | StringReader | StringWriter| | |
| ByteArray | ByteArrayReader | ByteArrayWriter| ByteArrayInputStream | ByteArrayOutputStream |
| CharArray | CharArrayReader | CharArrayWriter| | |
| Object | | |ObjectInputStream | ObjectOutputStream |
| Filter | FilterReader | FilterWriter| FilterInputStream | FilterOutputStream |
| Data | | | DataInputStream | DataOutputStream |
### 1.字節流轉換成字符(InputStreamReader)
```
public static String byte2Char(InputStream is, String charsetName)
throws IOException {
if (charsetName == null || !Charset.isSupported(charsetName)){
charsetName = DEFAULT_CHARSET;
}
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is, charsetName);
char[] cbuf = new char[DEFAULT_BYTE_SIZE];
StringBuilder sbf = new StringBuilder();
int readCount;
while((readCount = isr.read(cbuf)) > 0){
sbf.append(cbuf, 0, readCount);
}
return sbf.toString();
}
```
### 2.從文件中讀取字符(FileReader)
```
public static String readCharFromFile(String path) throws IOException {
File fi = new File(path);
if (fi.exists() && fi.isFile()){
FileReader fr = new FileReader(fi);
char[] cbuf = new char[DEFAULT_CHAR_SIZE];
int readCount;
StringBuilder sbf = new StringBuilder();
while((readCount = fr.read(cbuf)) > 0){
sbf.append(cbuf, 0, readCount);
}
return sbf.toString();
}
throw new FileNotFoundException();
}
```
### 3.字節流輸出到文件(FileOutputStream)
```
public static File writeByteToFile(InputStream is, String path, boolean append) throws IOException {
File fi = new File(path);
// create file first if not exists
if (!fi.exists()) {
fi.createNewFile();
append = false;
}
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(fi, append);
byte[] buf = new byte[DEFAULT_BYTE_SIZE];
int readCount;
while((readCount = is.read(buf)) > 0){
fos.write(buf, 0, readCount);
}
fos.close();
is.close();
return fi;
}
```
### 4.字符輸出到文件(FileWriter)
```
public static File writeCharToFile(String content, String path, boolean append) throws IOException {
File fi = new File(path);
// create file first if not exists
if (!fi.exists()) {
fi.createNewFile();
append = false;
}
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(fi, append);
fw.write(content, 0, content.length());
fw.close();
return fi;
}
```
字節流轉換成字符流,文件與字節,文件與字符轉換操作完整代碼見:
[IOTools](https://github.com/15045120/git-docs/blob/master/tools/IOTools.java)
- JavaCook
- Java專題零:類的繼承
- Java專題一:數據類型
- Java專題二:相等與比較
- Java專題三:集合
- Java專題四:異常
- Java專題五:遍歷與迭代
- Java專題六:運算符
- Java專題七:正則表達式
- Java專題八:泛型
- Java專題九:反射
- Java專題九(1):反射
- Java專題九(2):動態代理
- Java專題十:日期與時間
- Java專題十一:IO與NIO
- Java專題十一(1):IO
- Java專題十一(2):NIO
- Java專題十二:網絡
- Java專題十三:并發編程
- Java專題十三(1):線程與線程池
- Java專題十三(2):線程安全與同步
- Java專題十三(3):內存模型、volatile、ThreadLocal
- Java專題十四:JDBC
- Java專題十五:日志
- Java專題十六:定時任務
- Java專題十七:JavaMail
- Java專題十八:注解
- Java專題十九:淺拷貝與深拷貝
- Java專題二十:設計模式
- Java專題二十一:序列化與反序列化
- 附加專題一:MySQL
- MySQL專題零:簡介
- MySQL專題一:安裝與連接
- MySQL專題二:DDL與DML語法
- MySQL專題三:工作原理
- MySQL專題四:InnoDB存儲引擎
- MySQL專題五:sql優化
- MySQL專題六:數據類型
- 附加專題二:Mybatis
- Mybatis專題零:簡介
- Mybatis專題一:配置文件
- Mybatis專題二:映射文件
- Mybatis專題三:動態SQL
- Mybatis專題四:源碼解析
- 附加專題三:Web編程
- Web專題零:HTTP協議
- Web專題一:Servlet
- Web專題二:Cookie與Session
- 附加專題四:Redis
- Redis專題一:數據類型
- Redis專題二:事務
- Redis專題三:key的過期
- Redis專題四:消息隊列
- Redis專題五:持久化
