[TOC]
# 說明
上一篇,
我們分析了中間件的執行過程,但對于中間件最里面一層還未展開分析,接下來三節將對其展開分析。`runWithRequest`方法:
```
protected function runWithRequest(Request $request)
{
.
.
.
return $this->app->middleware->pipeline()
->send($request)
->then(function ($request) {
return $this->dispatchToRoute($request);
});
}
```
未展開分析的是 `$this->dispatchToRoute($request)` 這一行代碼,接下來分析這一行。
在配置文件中關閉路由解析,即在`config/app.php`中將`
with_route`設置為`false`。以下分析假設訪問的URL為`www.tp6.com/demo/hello`,并創建好了`Demo`控制器和`hello`操作——其代碼如下:
```
<?php
namespace app\controller;
use app\BaseController;
class Demo extends BaseController
{
public function hello($name = 'ThinkPHP6')
{
return 'hello,' . $name;
}
}
```
# Url解析
`dispatchToRoute`方法:
```
protected function dispatchToRoute($request)
{
$withRoute = $this->app->config->get('app.with_route', true) ? function () {
$this->loadRoutes();
} : null;
return $this->app->route->dispatch($request, $withRoute);
}
```
主要邏輯都在`dispatch`方法:
```
public function dispatch(Request $request, $withRoute = null)
{
$this->request = $request;
$this->host = $this->request->host(true);
//加載路由配置、緩存等
$this->init();
if ($withRoute) {
//加載路由
$withRoute();
$dispatch = $this->check();
} else {
//如果沒有開啟路由,將執行這里的語句
//$this->path()得到PATHINFO,比如/demo/hello
$dispatch = $this->url($this->path());
}
// $dispatch是think\route\dispatch\Url的實例,該類繼承了Controller類
// 且該類中沒有init方法,所以這里執行的是其父類的init方法
$dispatch->init($this->app);
return $this->app->middleware->pipeline('route')
->send($request)
->then(function () use ($dispatch) {
return $dispatch->run();
});
}
```
因為前面設置關閉了路由解析,所以這里執行到`else`的語句:`$dispatch = $this->url($this->path());`,解析Url。Url方法如下:
```
public function url(string $url): UrlDispatch
{
// 第三個參數為PATHINFO
return new UrlDispatch($this->request, $this->group, $url);
}
```
該方法新建并返回一個`think\route\dispatch\Url`類的實例。我們來看看這個實例化都做了些什么。`think\route\dispatch\Url`類的構造函數:
```
public function __construct(Request $request, Rule $rule, $dispatch, array $param = [], int $code = null)
{
$this->request = $request;
$this->rule = $rule;
// 解析默認的URL規則
$dispatch = $this->parseUrl($dispatch);
parent::__construct($request, $rule, $dispatch, $this->param, $code);
}
```
最主要的邏輯是在`parseUrl`方法:
```
protected function parseUrl(string $url): array
{
// 獲取URL分隔符
$depr = $this->rule->config('pathinfo_depr');
// $this->rule->getRouter() 獲取路由對象
// 獲取路由綁定
$bind = $this->rule->getRouter()->getDomainBind();
if ($bind && preg_match('/^[a-z]/is', $bind)) {
$bind = str_replace('/', $depr, $bind);
// 如果有模塊/控制器綁定
$url = $bind . ('.' != substr($bind, -1) ? $depr : '') . ltrim($url, $depr);
}
// $path為[控制器,操作]這樣組成的數組,如["demo", "hello"]
$path = $this->rule->parseUrlPath($url);
if (empty($path)) {
return [null, null];
}
// 解析控制器
// 獲取控制器名
$controller = !empty($path) ? array_shift($path) : null;
// 檢查控制器是否合法
// 正則匹配:開頭是字母,后面是0個到多個字母、下劃線或者點
if ($controller && !preg_match('/^[A-Za-z][\w|\.]*$/', $controller)) {
throw new HttpException(404, 'controller not exists:' . $controller);
}
// 解析操作
$action = !empty($path) ? array_shift($path) : null;
$var = [];
// 解析額外參數
if ($path) {
// 正則匹配:一個至多個字母,下劃線,中間是‘|’,結尾是非‘|’的任意字符,比如 hello|123
preg_replace_callback('/(\w+)\|([^\|]+)/', function ($match) use (&$var) {
$var[$match[1]] = strip_tags($match[2]);
}, implode('|', $path));
}
$panDomain = $this->request->panDomain();
if ($panDomain && $key = array_search('*', $var)) {
// 泛域名賦值
$var[$key] = $panDomain;
}
// 設置當前請求的參數
$this->param = $var;
// 封裝路由
$route = [$controller, $action];
// 如果路由被定義過
if ($this->hasDefinedRoute($route)) {
throw new HttpException(404, 'invalid request:' . str_replace('|', $depr, $url));
}
return $route;
}
```
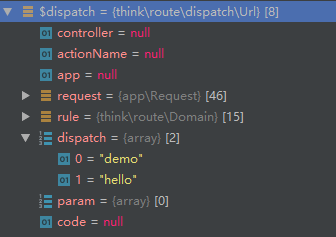
整個過程有點繁瑣,分析見注釋,該方法最后返回一個控制器和操作組成的數組,大概類似這樣:`[$controller, $action]`。
最終,`dispatch`方法的`$dispatch = $this->url($this->path());`語句得到一個`think\route\dispatch\Url`類的實例。該實例大概長這樣: