## Lifecycle
~~~java
public interface Lifecycle {
void start();
void stop();
boolean isRunning();
}
~~~
LifeCycle定義Spring容器對象的生命周期,任何spring管理對象都可以實現該接口。
當ApplicationContext本身接收啟動和停止信號(例如在運行時停止/重啟場景)時,spring容器將在容器上下文中找出所有實現了LifeCycle及其子類接口的類,并一一調用它們實現的類。spring是通過委托給生命周期處理器LifecycleProcessor來實現這一點的。
#### Lifecycly的不足
常規的Lifecycle接口只是在容器上下文**顯式**的調用start()/stop()方法時,才會去回調Lifecycle的實現類的start stop方法邏輯。并不意味著在上下文刷新時自動啟動。
~~~java
public class HelloLifeCycle implements Lifecycle {
private volatile boolean running = false;
public HelloLifeCycle() {
System.out.println("構造方法!!!");
}
@Override
public void start() {
System.out.println("lifycycle start");
running = true;
}
@Override
public void stop() {
System.out.println("lifycycle stop");
running = false;
}
@Override
public boolean isRunning() {
return running;
}
}
~~~
~~~java
@SpringBootApplication
public class EurekaClientApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaClientApplication.class, args);
}
}
~~~
結果是,控制臺沒有任何輸出,容器并沒有調用生命周期的回調方法。
當我們將啟動容器的類,顯式的加上start和stop方法后:
~~~java
@SpringBootApplication
public class EurekaClientApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext = SpringApplication.run(EurekaClientApplication.class, args);
applicationContext.start();
applicationContext.stop();
}
}
~~~
這時我們看控制臺,spring容器回調了生命周期的方法
~~~java
2020-12-27 22:40:18.312 INFO 12152 --- [ main] o.s.web.context.ContextLoader : Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in 1664 ms
構造方法!!!
2020-12-27 22:40:18.691 INFO 12152 --- [ main] o.s.s.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor : Initializing ExecutorService 'applicationTaskExecutor'
lifycycle start
2020-12-27 22:40:19.107 INFO 12152 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8086 (http) with context path ''
2020-12-27 22:40:19.112 INFO 12152 --- [ main] c.e.e.EurekaClientApplication : Started EurekaClientApplication in 3.44 seconds (JVM running for 4.891)
lifycycle stop
~~~
## LifecycleProcessor
LifecycleProcessor 負責管理ApplicationContext生命周期。是ApplicationContext很重要的一環,需要他的地方實在太多了。
LifecycleProcessor的onRefresh與onClose是比較重要的方法,onRefresh作用是容器啟動成功,onClose是只應用要關閉的時候。
請注意,LifecycleProcessor本身就是LifeCycle接口的擴展。它還添加了另外兩個方法來響應spring容器上下文的刷新(onRefresh)和關閉(close)。
~~~java
public interface LifecycleProcessor extends Lifecycle {
void onRefresh();
void onClose();
}
~~~
## DefaultLifecycleProcessor
DefaultLifecycleProcessor 是默認LifecycleProcessor實現,主要是負責所有的LifecycleProcessor實現執行,DefaultLifecycleProcessor是LifecycleProcessor的代理對象。
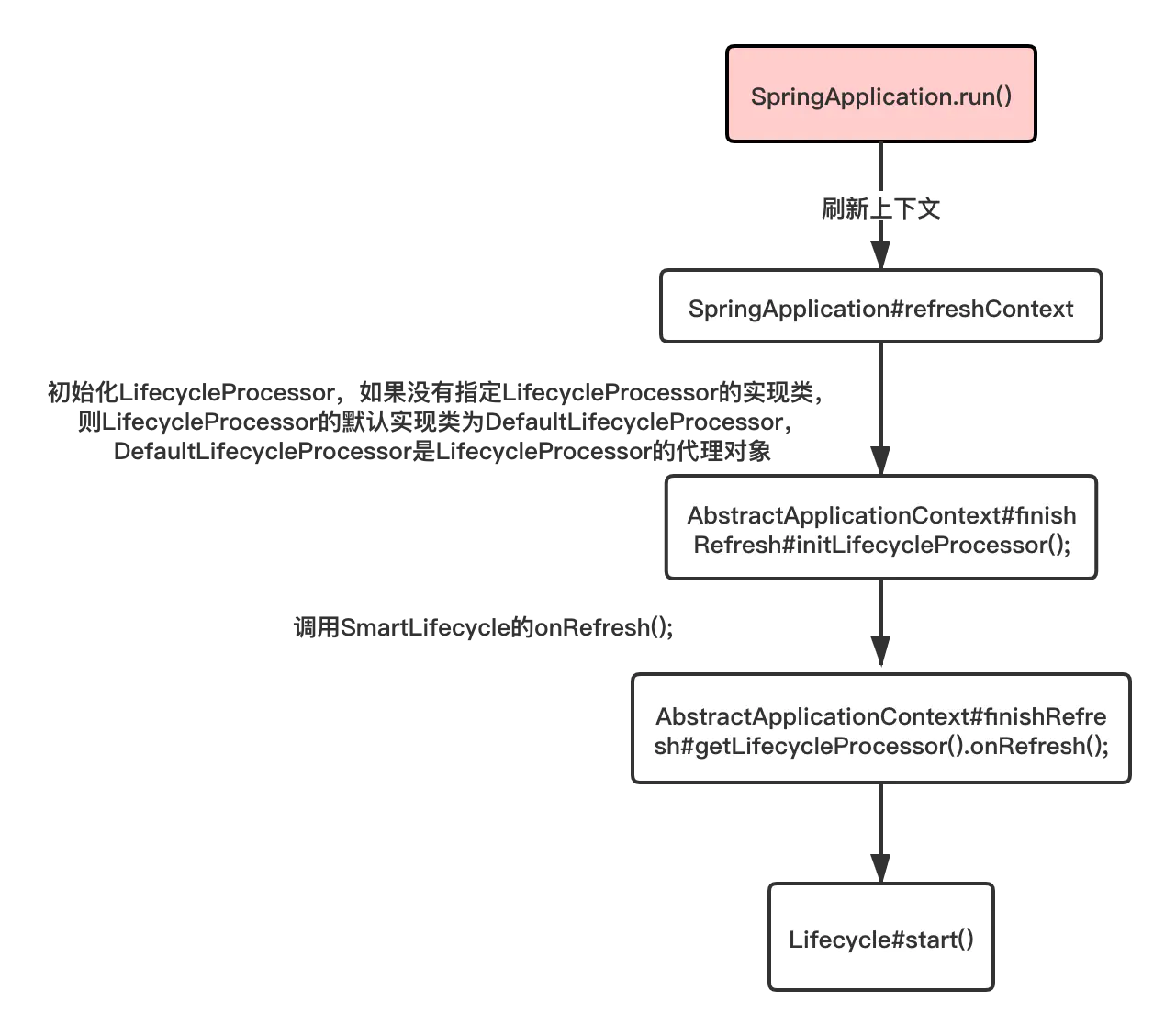
### 初始化LifecycleProcessor
AbstractApplicationContext#initLifecycleProcessor()
~~~java
/**
* 初始化LifecycleProcessor,如果上下文中沒有LifecycleProcessor的實現類,
* 就使用DefaultLifecycleProcessor作為LifecycleProcessor默認實現
* Initialize the LifecycleProcessor.
* Uses DefaultLifecycleProcessor if none defined in the context.
* @see org.springframework.context.support.DefaultLifecycleProcessor
*/
protected void initLifecycleProcessor() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
this.lifecycleProcessor =
beanFactory.getBean(LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME, LifecycleProcessor.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using LifecycleProcessor [" + this.lifecycleProcessor + "]");
}
}
else {
DefaultLifecycleProcessor defaultProcessor = new DefaultLifecycleProcessor();
defaultProcessor.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
this.lifecycleProcessor = defaultProcessor;
beanFactory.registerSingleton(LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME, this.lifecycleProcessor);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No '" + LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using " +
"[" + this.lifecycleProcessor.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
~~~
**從beanFactory獲得LifecycleProcessor實現類**
~~~java
/**
* 獲取所有實現了 Lifecycle 和 SmartLifecycle 的類
* Retrieve all applicable Lifecycle beans: all singletons that have already been created,
* as well as all SmartLifecycle beans (even if they are marked as lazy-init).
* @return the Map of applicable beans, with bean names as keys and bean instances as values
*/
protected Map<String, Lifecycle> getLifecycleBeans() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
Map<String, Lifecycle> beans = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// 獲取所有實現了Lifecycle接口的類
String[] beanNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(Lifecycle.class, false, false);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
String beanNameToRegister = BeanFactoryUtils.transformedBeanName(beanName);
boolean isFactoryBean = beanFactory.isFactoryBean(beanNameToRegister);
String beanNameToCheck = (isFactoryBean ? BeanFactory.FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName : beanName);
if ((beanFactory.containsSingleton(beanNameToRegister) &&
(!isFactoryBean || matchesBeanType(Lifecycle.class, beanNameToCheck, beanFactory))) ||
matchesBeanType(SmartLifecycle.class, beanNameToCheck, beanFactory)) {
Object bean = beanFactory.getBean(beanNameToCheck);
if (bean != this && bean instanceof Lifecycle) {
beans.put(beanNameToRegister, (Lifecycle) bean);
}
}
}
return beans;
}
~~~
獲取到所有的SmartLifecycle實現類,且如果autoStartupOnly()方法返回true,則執行SmartLifecycle實現類的start()方法
~~~java
/**
* Start the specified bean as part of the given set of Lifecycle beans,
* making sure that any beans that it depends on are started first.
* @param lifecycleBeans a Map with bean name as key and Lifecycle instance as value
* @param beanName the name of the bean to start
*/
private void doStart(Map<String, ? extends Lifecycle> lifecycleBeans, String beanName, boolean autoStartupOnly) {
Lifecycle bean = lifecycleBeans.remove(beanName);
if (bean != null && bean != this) {
String[] dependenciesForBean = getBeanFactory().getDependenciesForBean(beanName);
for (String dependency : dependenciesForBean) {
doStart(lifecycleBeans, dependency, autoStartupOnly);
}
if (!bean.isRunning() &&
(!autoStartupOnly || !(bean instanceof SmartLifecycle) || ((SmartLifecycle) bean).isAutoStartup())) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Starting bean '" + beanName + "' of type [" + bean.getClass().getName() + "]");
}
try {
// 調用Lifecycle的start()方法
bean.start();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to start bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Successfully started bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
}
}
~~~
LifecycleProcessor生命周期大致流程圖如下: