
下面是視頻(優酷的清晰度有限):還是建議大家去B站觀看:[B站觀看地址](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1sE411P7C1/)。如果您覺得我做的工作對您有幫助,請去B站點贊、關注、轉發、收藏,您的支持是我不竭的創作動力!
```[youku]
XNDU5OTE4OTA5Mg
```
## 一、回顧Stream管道流map的基礎用法
最簡單的需求:將集合中的每一個字符串,全部轉換成大寫!
~~~
List<String> alpha = Arrays.asList("Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe", "Lemur");
//不使用Stream管道流
List<String> alphaUpper = new ArrayList<>();
for (String s : alpha) {
alphaUpper.add(s.toUpperCase());
}
System.out.println(alphaUpper); //[MONKEY, LION, GIRAFFE, LEMUR]
// 使用Stream管道流
List<String> collect = alpha.stream().map(String::toUpperCase).collect(Collectors.toList());
//上面使用了方法引用,和下面的lambda表達式語法效果是一樣的
//List<String> collect = alpha.stream().map(s -> s.toUpperCase()).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect); //[MONKEY, LION, GIRAFFE, LEMUR]
~~~
所以**map函數的作用就是針對管道流中的每一個數據元素進行轉換操作**。
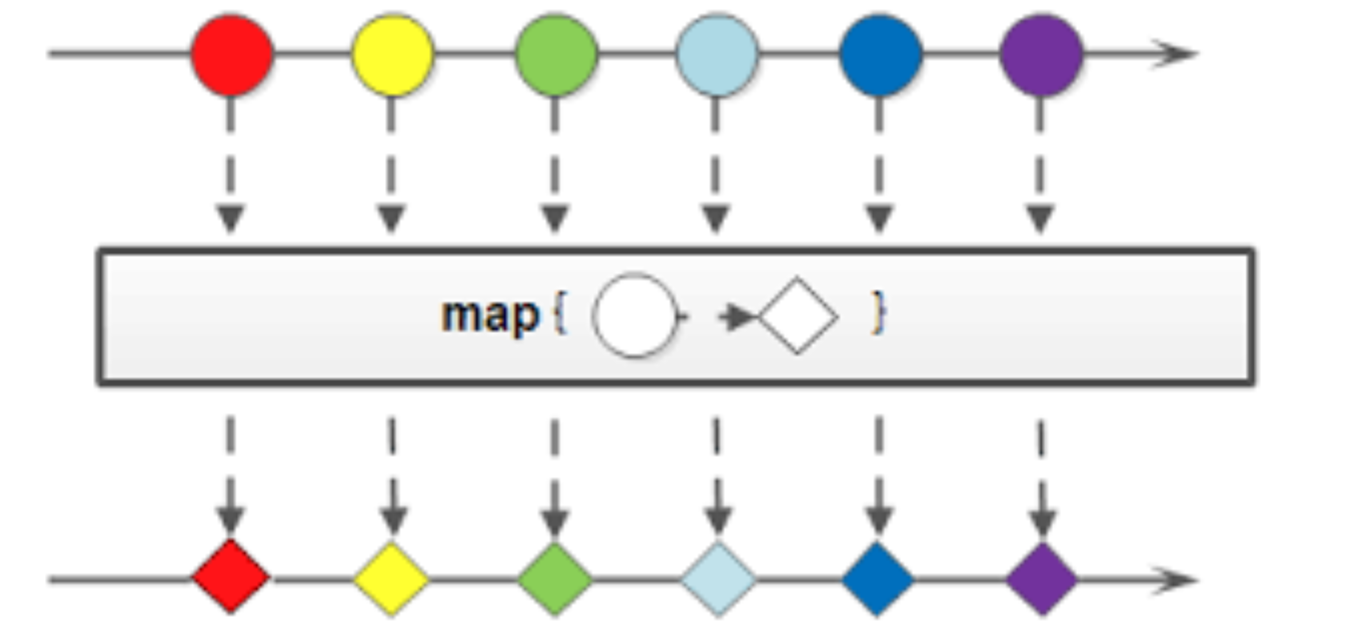
## 二、處理非字符串類型集合元素
map()函數不僅可以處理數據,還可以轉換數據的類型。如下:
~~~
List<Integer> lengths = alpha.stream()
.map(String::length)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(lengths); //[6, 4, 7, 5]
~~~
~~~
Stream.of("Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe", "Lemur")
.mapToInt(String::length)
.forEach(System.out::println);
~~~
輸出如下:
~~~
6
4
7
5
~~~
除了mapToInt。還有maoToLong,mapToDouble等等用法
## 三、再復雜一點:處理對象數據格式轉換
還是使用上一節中的Employee類,創建10個對象。需求如下:
* 將每一個Employee的年齡增加一歲
* 將性別中的“M”換成“male”,F換成Female。
~~~
public static void main(String[] args){
Employee e1 = new Employee(1,23,"M","Rick","Beethovan");
Employee e2 = new Employee(2,13,"F","Martina","Hengis");
Employee e3 = new Employee(3,43,"M","Ricky","Martin");
Employee e4 = new Employee(4,26,"M","Jon","Lowman");
Employee e5 = new Employee(5,19,"F","Cristine","Maria");
Employee e6 = new Employee(6,15,"M","David","Feezor");
Employee e7 = new Employee(7,68,"F","Melissa","Roy");
Employee e8 = new Employee(8,79,"M","Alex","Gussin");
Employee e9 = new Employee(9,15,"F","Neetu","Singh");
Employee e10 = new Employee(10,45,"M","Naveen","Jain");
List<Employee> employees = Arrays.asList(e1, e2, e3, e4, e5, e6, e7, e8, e9, e10);
/*List<Employee> maped = employees.stream()
.map(e -> {
e.setAge(e.getAge() + 1);
e.setGender(e.getGender().equals("M")?"male":"female");
return e;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());*/
List<Employee> maped = employees.stream()
.peek(e -> {
e.setAge(e.getAge() + 1);
e.setGender(e.getGender().equals("M")?"male":"female");
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(maped);
}
~~~
由于map的參數e就是返回值,所以可以用peek函數。peek函數是一種特殊的map函數,當函數沒有返回值或者參數就是返回值的時候可以使用peek函數。
## 四、flatMap
map可以對管道流中的數據進行轉換操作,但是如果管道中還有管道該如何處理?即:如何處理二維數組及二維集合類。實現一個簡單的需求:將“hello”,“world”兩個字符串組成的集合,元素的每一個字母打印出來。如果不用Stream我們怎么寫?寫2層for循環,第一層遍歷字符串,并且將字符串拆分成char數組,第二層for循環遍歷char數組。
~~~
List<String> words = Arrays.asList("hello", "word");
words.stream()
.map(w -> Arrays.stream(w.split(""))) //[[h,e,l,l,o],[w,o,r,l,d]]
.forEach(System.out::println);
~~~
輸出打印結果:
~~~
java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@3551a94
java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@531be3c5
~~~
* 用map方法是做不到的,這個需求用map方法無法實現。map只能針對一維數組進行操作,數組里面還有數組,管道里面還有管道,它是處理不了每一個元素的。
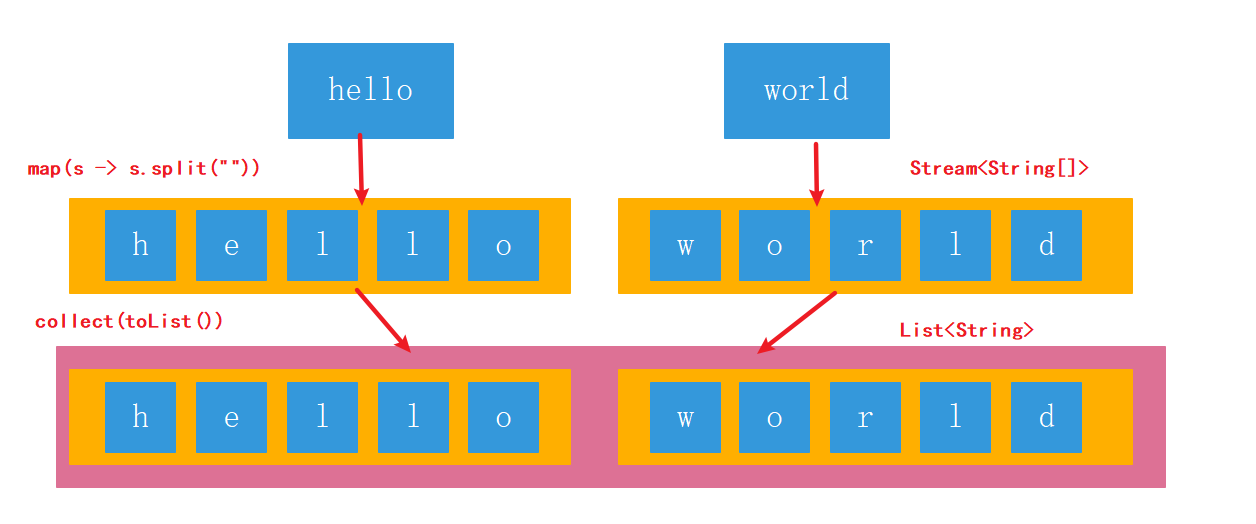
* flatMap可以理解為將若干個子管道中的數據全都,平面展開到父管道中進行處理。
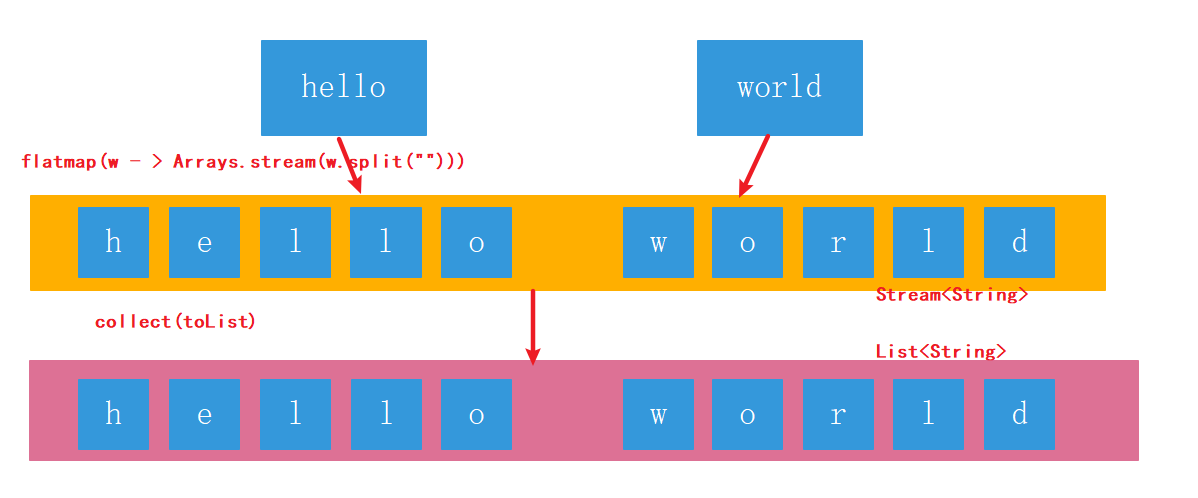
~~~
words.stream()
.flatMap(w -> Arrays.stream(w.split(""))) // [h,e,l,l,o,w,o,r,l,d]
.forEach(System.out::println);
~~~
輸出打印結果:
~~~
h
e
l
l
o
w
o
r
d
~~~
- 前言
- 1.lambda表達式會用了么
- 2.初識Stream-API
- 3.Stream的filter與謂語邏輯
- 4.Stream管道流的map操作
- 5.Stream的狀態與并行操作
- 6.Stream性能差?不要人云亦云
- 7.像使用SQL一樣排序集合
- 8.函數式接口Comparator
- 9.Stream查找與匹配元素
- 10.Stream集合元素歸約
- 11.StreamAPI終端操作
- 12.java8如何排序Map
- Stream流逐行文件處理
- java8-forEach(持續發布中)
- 筆者其它作品推薦
- vue深入淺出系列
- 手摸手教你學Spring Boot2.0
- Spring Security-JWT-OAuth2一本通
- 實戰前后端分離RBAC權限管理系統
- 實戰SpringCloud微服務從青銅到王者
