
在這篇文章中,您將學習**如何使用Java對Map進行排序**。前幾日有位朋友面試遇到了這個問題,看似很簡單的問題,但是如果不仔細研究一下也是很容易讓人懵圈的面試題。所以我決定寫這樣一篇文章。在Java中,有多種方法可以對Map進行排序,但是我們將重點介紹Java 8 Stream,這是實現目標的一種非常優雅的方法。
## 一、什么是Java 8 Stream
使用Java 8 Streams,我們可以按鍵和按值對映射進行排序。下面是它的工作原理:
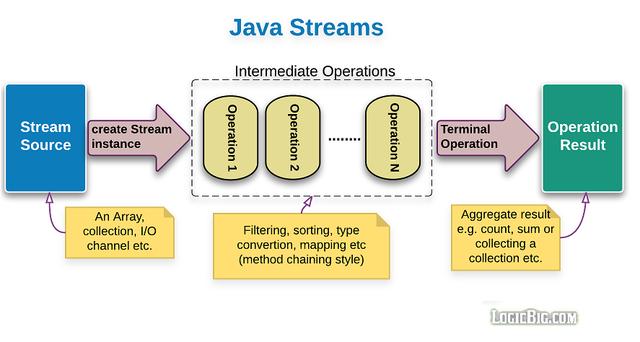
1. 將Map或List等集合類對象轉換為Stream對象
2. 使用Streams的`sorted()`方法對其進行排序
3. 最終將其返回為`LinkedHashMap`(可以保留排序順序)
`sorted()`方法以a`Comparator`作為參數,從而可以按任何類型的值對Map進行排序。如果對Comparator不熟悉,可以看本號前幾天的文章,有一篇文章專門介紹了使用Comparator對List進行排序。
## 二、學習一下HashMap的merge()函數
在學習Map排序之前,有必要講一下HashMap的merge()函數,該函數應用場景就是當Key重復的時候,如何處理Map的元素值。這個函數有三個參數:
* 參數一:向map里面put的鍵
* 參數二:向map里面put的值
* 參數三:如果鍵發生重復,如何處理值。可以是一個函數,也可以寫成lambda表達式。
```
String k = "key";
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>() {{
put(k, 1);
}};
map.merge(k, 2, (oldVal, newVal) -> oldVal + newVal);
```
看上面一段代碼,我們首先創建了一個HashMap,并往里面放入了一個鍵值為k:1的元素。當我們調用merge函數,往map里面放入k:2鍵值對的時候,k鍵發生重復,就執行后面的lambda表達式。表達式的含義是:返回舊值oldVal加上新值newVal(1+2),現在map里面只有一項元素那就是k:3。
> 其實lambda表達式很簡單:表示匿名函數,箭頭左側是參數,箭頭右側是函數體。函數的參數類型和返回值,由代碼上下文來確定。
## 三、按Map的鍵排序
下面一個例子使用Java 8 Stream按Map的鍵進行排序:
~~~java
// 創建一個Map,并填入數據
Map<String, Integer> codes = new HashMap<>();
codes.put("United States", 1);
codes.put("Germany", 49);
codes.put("France", 33);
codes.put("China", 86);
codes.put("Pakistan", 92);
// 按照Map的鍵進行排序
Map<String, Integer> sortedMap = codes.entrySet().stream()
.sorted(Map.Entry.comparingByKey())
.collect(
Collectors.toMap(
Map.Entry::getKey,
Map.Entry::getValue,
(oldVal, newVal) -> oldVal,
LinkedHashMap::new
)
);
// 將排序后的Map打印
sortedMap.entrySet().forEach(System.out::println);
~~~
看上文中第二段代碼:
* 首先使用entrySet().stream() 將Map類型轉換為Stream流類型。
* 然后使用sorted方法排序,排序的依據是Map.Entry.comparingByKey(),也就是按照Map的鍵排序
* 最后用collect方法將Stream流轉成LinkedHashMap。 其他參數都好說,重點看第三個參數,就是一個merge規則的lambda表達式,與merge方法的第三個參數的用法一致。由于本例中沒有重復的key,所以新值舊值隨便返回一個即可。
上面的程序將在控制臺上打印以下內容,鍵(國家/地區名稱)以自然字母順序排序:
~~~plaintext
China=86
France=33
Germany=49
Pakistan=92
United States=1
~~~
> **請注意**使用`LinkedHashMap`來存儲排序的結果以保持順序。默認情況下,`Collectors.toMap()`返回`HashMap`。`HashMap`不能保證元素的順序。
如果希望按照鍵進行逆向排序,加入下圖中紅色部分代碼即可。

## 四、按Map的值排序
當然,您也可以使用Stream API按其值對Map進行排序:
~~~java
Map<String, Integer> sortedMap2 = codes.entrySet().stream()
.sorted(Map.Entry.comparingByValue())
.collect(Collectors.toMap(
Map.Entry::getKey,
Map.Entry::getValue,
(oldVal, newVal) -> oldVal,
LinkedHashMap::new));
sortedMap2.entrySet().forEach(System.out::println);
~~~
這是顯示Map按值排序的輸出:
~~~plaintext
United States=1
France=33
Germany=49
China=86
Pakistan=92
~~~
## 五、使用TreeMap按鍵排序
大家可能都知道TreeMap內的元素是有順序的,所以利用TreeMap排序也是可取的一種方法。您需要做的就是創建一個`TreeMap`對象,并將數據從`HashMap`put到`TreeMap`中,非常簡單:
~~~java
// 將 `HashMap` 轉為 `TreeMap`
Map<String, Integer> sorted = new TreeMap<>(codes);
~~~
這是輸出:
~~~plaintext
China=86
France=33
Germany=49
Pakistan=92
United States=1
~~~
如上所示,鍵(國家/地區名稱)以自然字母順序排序。
## 最后:上文代碼
```
String k = "key";
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>() {{
put(k, 1);
}};
map.merge(k, 2, (oldVal, newVal) -> oldVal + newVal);
// 創建一個Map,并填入數據
Map<String, Integer> codes = new HashMap<>();
codes.put("United States", 1);
codes.put("Germany", 49);
codes.put("France", 33);
codes.put("China", 86);
codes.put("Pakistan", 92);
// 按照Map的鍵進行排序
Map<String, Integer> sortedMap = codes.entrySet().stream()
.sorted(Map.Entry.comparingByKey())
.collect(
Collectors.toMap(
Map.Entry::getKey,
Map.Entry::getValue,
(oldVal, newVal) -> oldVal,
LinkedHashMap::new
)
);
// 將排序后的Map打印
sortedMap.entrySet().forEach(System.out::println);
// sort the map by values
Map<String, Integer> sorted = codes.entrySet().stream()
.sorted(Map.Entry.comparingByValue())
.collect(Collectors.toMap(
Map.Entry::getKey,
Map.Entry::getValue,
(oldVal, newVal) -> oldVal,
LinkedHashMap::new));
sorted.entrySet().forEach(System.out::println);
```
- 前言
- 1.lambda表達式會用了么
- 2.初識Stream-API
- 3.Stream的filter與謂語邏輯
- 4.Stream管道流的map操作
- 5.Stream的狀態與并行操作
- 6.Stream性能差?不要人云亦云
- 7.像使用SQL一樣排序集合
- 8.函數式接口Comparator
- 9.Stream查找與匹配元素
- 10.Stream集合元素歸約
- 11.StreamAPI終端操作
- 12.java8如何排序Map
- Stream流逐行文件處理
- java8-forEach(持續發布中)
- 筆者其它作品推薦
- vue深入淺出系列
- 手摸手教你學Spring Boot2.0
- Spring Security-JWT-OAuth2一本通
- 實戰前后端分離RBAC權限管理系統
- 實戰SpringCloud微服務從青銅到王者
