## RBAC Support in Kubernetes
Kubernetes 中的 RBAC 支持
> PS:在Kubernetes1.6版本中新增角色訪問控制機制(Role-Based Access,RBAC)讓集群管理員可以針對特定使用者或服務賬號的角色,進行更精確的資源訪問控制。在RBAC中,權限與角色相關聯,用戶通過成為適當角色的成員而得到這些角色的權限。這就極大地簡化了權限的管理。在一個組織中,角色是為了完成各種工作而創造,用戶則依據它的責任和資格來被指派相應的角色,用戶可以很容易地從一個角色被指派到另一個角色。
>
## RBAC vs ABAC
鑒權的作用是,決定一個用戶是否有權使用 Kubernetes API 做某些事情。它除了會影響 kubectl 等組件之外,還會對一些運行在集群內部并對集群進行操作的軟件產生作用,例如使用了 Kubernetes 插件的 Jenkins,或者是利用 Kubernetes API 進行軟件部署的 Helm。ABAC 和 RBAC 都能夠對訪問策略進行配置。
ABAC(Attribute Based Access Control)本來是不錯的概念,但是在 Kubernetes 中的實現比較難于管理和理解(怪我咯),而且需要對 Master 所在節點的 SSH 和文件系統權限,而且要使得對授權的變更成功生效,還需要重新啟動 API Server。
而 RBAC 的授權策略可以利用 kubectl 或者 Kubernetes API 直接進行配置。RBAC 可以授權給用戶,讓用戶有權進行授權管理,這樣就可以無需接觸節點,直接進行授權管理。RBAC 在 Kubernetes 中被映射為 API 資源和操作。
因為 Kubernetes 社區的投入和偏好,相對于 ABAC 而言,RBAC 是更好的選擇。
## 基礎概念
需要理解 RBAC 一些基礎的概念和思路,RBAC 是讓用戶能夠訪問 Kubernetes API 資源的授權方式。
在 RBAC 中定義了兩個對象,用于描述在用戶和資源之間的連接權限。
## Role and ClusterRole
在 RBAC API 中,Role 表示一組規則權限,權限只會增加(累加權限),不存在一個資源一開始就有很多權限而通過 RBAC 對其進行減少的操作;Role 可以定義在一個 namespace 中,如果想要跨 namespace 則可以創建 ClusterRole。
### 角色
角色是一系列的權限的集合,例如一個角色可以包含讀取 Pod 的權限和列出 Pod 的權限, ClusterRole 跟 Role 類似,但是可以在集群中到處使用.
**Role 只能用于授予對單個命名空間中的資源訪問權限**, 以下是一個對默認命名空間中 Pods 具有訪問權限的樣例:
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
namespace: default
name: pod-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # "" indicates the core API group
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
ClusterRole 具有與 Role 相同的權限角色控制能力,不同的是 ClusterRole 是集群級別的,ClusterRole 可以用于:
- 集群級別的資源控制(例如 node 訪問權限)
- 非資源型 endpoints(例如 /healthz 訪問)
- 所有命名空間資源控制(例如 pods)
以下是 ClusterRole 授權某個特定命名空間或全部命名空間(取決于綁定方式)訪問 secrets 的樣例
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
# "namespace" omitted since ClusterRoles are not namespaced
name: secret-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["secrets"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
### RoleBinding and ClusterRoleBinding
RoloBinding 可以將角色中定義的權限授予用戶或用戶組,RoleBinding 包含一組權限列表(subjects),**權限列表中包含有不同形式的待授予權限資源類型(users, groups, or service accounts)**;RoloBinding 同樣包含對被 Bind 的 Role 引用;RoleBinding 適用于某個命名空間內授權,而 ClusterRoleBinding 適用于集群范圍內的授權。
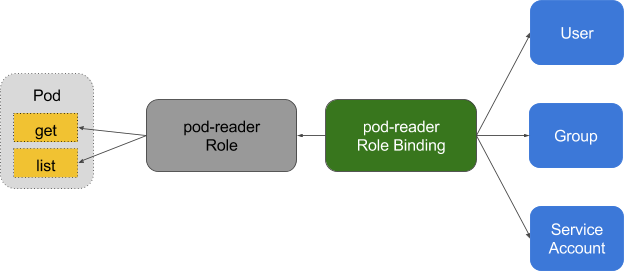
RoleBinding 可以在同一命名空間中引用對應的 Role,以下 RoleBinding 樣例將 default 命名空間的 pod-reader Role 授予 jane 用戶,此后 jane 用戶在 default 命名空間中將具有 pod-reader 的權限
# This role binding allows "jane" to read pods in the "default" namespace.
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: read-pods
namespace: default
subjects:
- kind: User
name: jane
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: pod-reader
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
**RoleBinding 同樣可以引用 ClusterRole 來對當前 namespace 內用戶、用戶組或 ServiceAccount 進行授權,這種操作允許集群管理員在整個集群內定義一些通用的 ClusterRole,然后在不同的 namespace 中使用 RoleBinding 來引用**
例如,以下 RoleBinding 引用了一個 ClusterRole,這個 ClusterRole 具有整個集群內對 secrets 的訪問權限;但是其授權用戶 dave 只能訪問 development 空間中的 secrets(因為 RoleBinding 定義在 development 命名空間)
# This role binding allows "dave" to read secrets in the "development" namespace.
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: read-secrets
namespace: development # This only grants permissions within the "development" namespace.
subjects:
- kind: User
name: dave
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: secret-reader
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
最后,使用 ClusterRoleBinding 可以對整個集群中的所有命名空間資源權限進行授權;以下 ClusterRoleBinding 樣例展示了授權 manager 組內所有用戶在全部命名空間中對 secrets 進行訪問
# This cluster role binding allows anyone in the "manager" group to read secrets in any namespace.
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: read-secrets-global
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: manager
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: secret-reader
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
## Referring to Resources
Kubernetes 集群內一些資源一般以其名稱字符串來表示,這些字符串一般會在 API 的 URL 地址中出現;同時某些資源也會包含子資源,例如 logs 資源就屬于 pods 的子資源,API 中 URL 樣例如下
GET /api/v1/namespaces/{namespace}/pods/{name}/log
**如果要在 RBAC 授權模型中控制這些子資源的訪問權限,可以通過 / 分隔符來實現**,以下是一個定義 pods 資資源 logs 訪問權限的 Role 定義樣例
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
namespace: default
name: pod-and-pod-logs-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods", "pods/log"]
verbs: ["get", "list"]
具體的資源引用可以通過 resourceNames 來定義,當指定 get、delete、update、patch 四個動詞時,可以控制對其目標資源的相應動作;以下為限制一個 subject 對名稱為 my-configmap 的 configmap 只能具有 get 和 update 權限的樣例
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
namespace: default
name: configmap-updater
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmap"]
resourceNames: ["my-configmap"]
verbs: ["update", "get"]
**值得注意的是,當設定了 resourceNames 后,verbs 動詞不能指定為 list、watch、create 和 deletecollection;因為這個具體的資源名稱不在上面四個動詞限定的請求 URL 地址中匹配到,最終會因為 URL 地址不匹配導致 Role 無法創建成功**
## Referring to Subjects
RoleBinding 和 ClusterRoleBinding 可以將 Role 綁定到 Subjects;Subjects 可以是 groups、users 或者 service accounts。
Subjects 中 Users 使用字符串表示,它可以是一個普通的名字字符串,如 “alice”;也可以是 email 格式的郵箱地址,如 “bob@example.com”;甚至是一組字符串形式的數字 ID。Users 的格式必須滿足集群管理員配置的驗證模塊,RBAC 授權系統中沒有對其做任何格式限定;但是 Users 的前綴 system: 是系統保留的,集群管理員應該確保普通用戶不會使用這個前綴格式
Kubernetes 的 Group 信息目前由 Authenticator 模塊提供,Groups 書寫格式與 Users 相同,都為一個字符串,并且沒有特定的格式要求;同樣 system: 前綴為系統保留
具有 system:serviceaccount: 前綴的用戶名和 system:serviceaccounts: 前綴的組為 Service Accounts
### Role Binding Examples
以下示例僅展示 RoleBinding 的 subjects 部分
指定一個名字為 alice@example.com 的用戶
subjects:
- kind: User
name: "alice@example.com"
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
指定一個名字為 frontend-admins 的組
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: "frontend-admins"
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
指定 kube-system namespace 中默認的 Service Account
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: default
namespace: kube-system
指定在 qa namespace 中全部的 Service Account
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:serviceaccounts:qa
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
指定全部 namspace 中的全部 Service Account
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:serviceaccounts
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
指定全部的 authenticated 用戶(1.5+)
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:authenticated
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
指定全部的 unauthenticated 用戶(1.5+)
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:unauthenticated
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
指定全部用戶
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:authenticated
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
- kind: Group
name: system:unauthenticated
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
- 第一章 kubernetes 功能介紹
- 第二章 在CentOS上部署kubernetes1.7.6集群
- 第三章 創建TLS證書和秘鑰
- 第四章 安裝kubectl命令行工具
- 第五章 創建kubeconfig 文件
- 第六章 etcd 集群部署
- 第七章 部署k8s-master-v1.7.6節點
- 第八章 部署k8s-v1.7.6 node 節點
- 第九章 kubectl 操作示例
- 第十章 在kubernetes 部署第一個應用
- 第十一章 kubernetes之pod 調度
- 第十二章 K8S服務組件之kube-dns&Dashboard
- 第十三章 Kubernetes中的角色訪問控制機制(RBAC)支持
- 第十四章 部署nginx ingress
- 第十五章 使用Prometheus監控Kubernetes集群和應用
- 第十六章 使用helm 應用部署工具
- 第十七章 kubernetes 從1.7 到1.8升級記錄
- 第十八章 在kubernetes 使用ceph
- 第十九章 基于 Jenkins 的 CI/CD(一)
- 第二十章 基于jenkins的CI/CD(二)
- 第二十一章 基于prometheus自定指標HPA彈性伸縮
