## [126\. 單詞接龍 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/word-ladder-ii/)
>Hard
#### 思路
基于Hard必死原則,沒有什么思路。罷了,閱讀大佬文檔獲取思路。
* 只有一個字母不同的單詞,路組成相鄰的節點
* 相鄰的節點運動,就是每一步都變換一個字母
* beginWord 作為起點,endWord 作為終點
* 將beginWord 也加入到words中,作為無向圖的一部分
* 假如endWord 不在途中最終無解
* 題目轉換為從beginWord走到endWord的最短路徑
如圖:
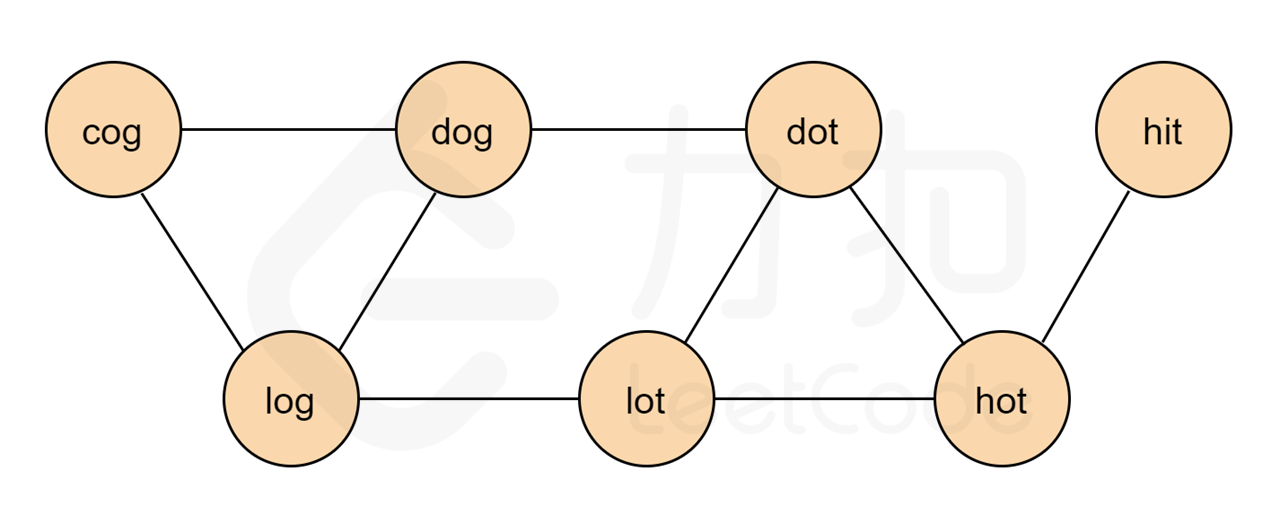
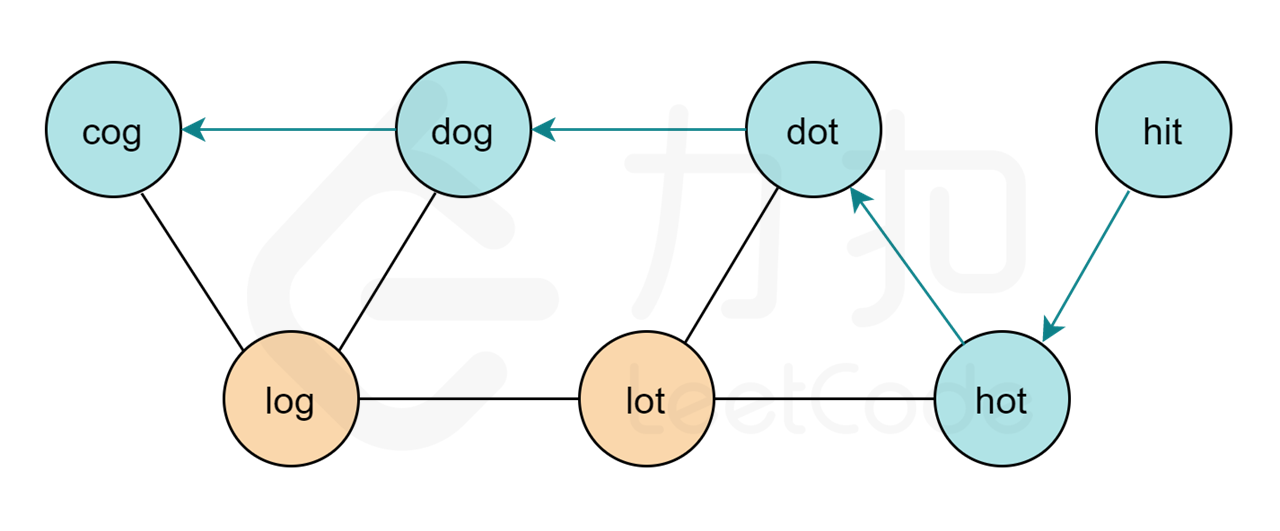
**待解決的問題**:
1. 解決重復問題,`hit→hot→hit`避免產生這種情況,形成環不符合題意
2. 如何構造圖,即如何找到一個單詞的相鄰節點
3. 如何記錄路徑,也就是說BFS結束之后,如何將對應的路徑保存下來
> 問題1:使用一個`visited`數組來記錄已經訪問過的節點,在訪問過程中,已經訪問過的,不進行訪問
> 問題2:遍歷word的單詞進行比較,不同字母數量超過1即為不相鄰
> 問題3:我們可以在做BFS的過程中,不單單將當前節點推到隊列中,也將父節點信息一起推到隊列當中
**題目難點** 本題的難點在于怎么合理的構造圖,兩兩建圖復雜度太高,這邊使用一個騷操作:使用通配符建表。相同通配符下的節點,都互相有邊。(操作實在太騷,大佬腦洞真大)
嘗試著寫一下代碼,TLE
#### 代碼 (TLE)
python3
```
class Solution:
def findLadders(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> List[List[str]]:
if endWord not in wordList:
return []
s = collections.defaultdict(list)
for w in wordList:
for i in range(len(w)):
s[w[:i] + '*' + w[i+1:]].append(w)
result = []
queue = []
queue.append([beginWord])
while len(queue) > 0:
cur_queue_size = len(queue)
found = False
for cur in range(cur_queue_size):
visited = set()
path = queue[0]
word = path[-1]
del queue[0]
for p in path:
visited.add(p)
for i in range(len(word)):
for c in s[word[:i] + '*' + word[i+1:]]:
if c not in visited:
if c == endWord:
found = True
result.append(path + [c])
queue.append(path + [c])
if found:
break
if not len(result):
return []
return result
```
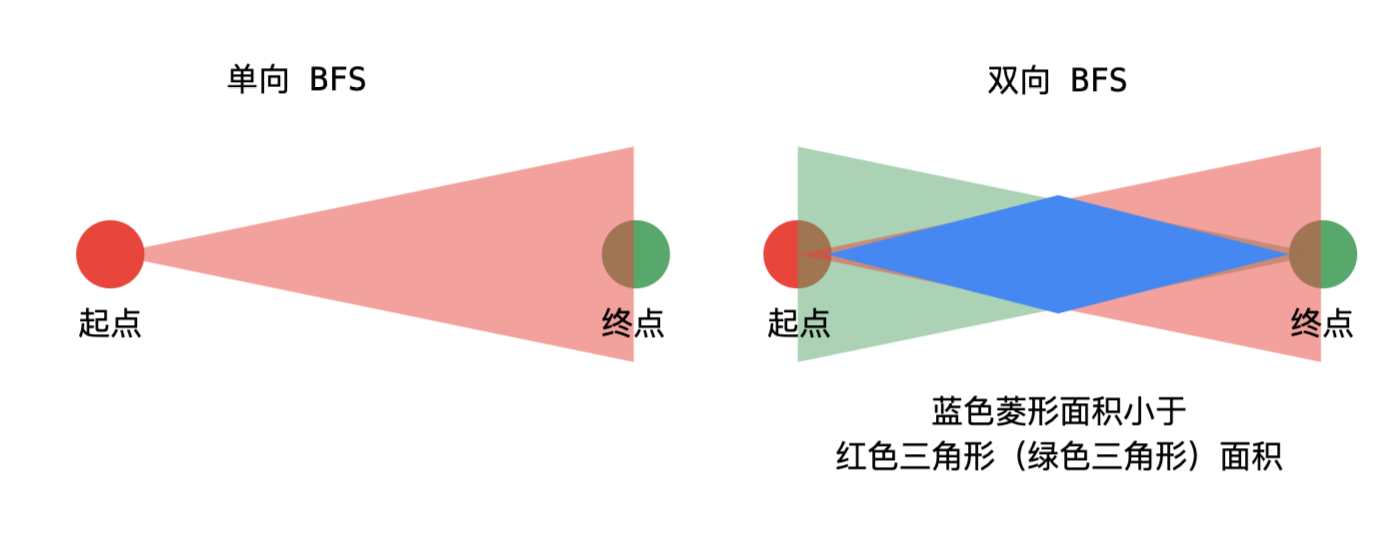
**改進代碼** 再次拜讀大佬解法,獲取新思路:使用雙向廣度優先進行優化(可怕)
* 我們使用BFS遍歷一個樹時,深度越深,同級的元素越多。
* 對于本題,已經確定了兩端,可以使用雙向BFS進行優化
如下圖:(圖片來自leetcode大神 [liweiwei](https://leetcode-cn.com/u/liweiwei1419/))
拖著被虐的疲憊不堪的心靈和身體,嘗試優化一下代碼,AC!
被虐的夠嗆,代碼參考了[Mcdull](https://leetcode-cn.com/u/mcdull0921/)大神的解題
#### 代碼
python3
```
class Solution:
def findLadders(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> List[List[str]]:
if endWord not in wordList:
return []
def makeMap(words):
s = collections.defaultdict(list)
for w in words:
for i in range(len(w)):
s[w[:i] + '*' + w[i+1:]].append(w)
return s
visited = set()
s = makeMap(wordList)
def neighborWords(word):
words = []
for i in range(len(word)):
for c in s[word[:i] + '*' + word[i+1:]]:
if c not in visited:
words.append(c)
return words
path = collections.defaultdict(set)
headqueue = set([beginWord]) # 頭部開始的隊列
tailqueue = set([endWord]) # 尾部開始的隊列
forward = True
while headqueue and tailqueue:
if len(headqueue) > len(tailqueue):
headqueue,tailqueue = tailqueue,headqueue
forward = not forward
temp = set()
for word in headqueue:
visited.add(word)
for word in headqueue:
for w in neighborWords(word):
temp.add(w)
if forward:
path[w].add(word)
else:
path[word].add(w)
headqueue = temp
if headqueue & tailqueue: # 表示有相交
res = [[endWord]]
while res[0][0] != beginWord:
temp_res=[]
for curr in res:
for parent in path[curr[0]]:
temp_res.append([parent]+curr)
res = temp_res
return res
return []
```
- 目錄
- excel-sheet-column-number
- divide-two-integers
- house-robber
- fraction-to-recurring-decimal
- profile
- kids-with-the-greatest-number-of-candies
- qiu-12n-lcof
- new-21-game
- product-of-array-except-self
- minimum-depth-of-binary-tree
- univalued-binary-tree
- shun-shi-zhen-da-yin-ju-zhen-lcof
- permutations
- satisfiability-of-equality-equations
- word-ladder-ii
- ba-shu-zi-fan-yi-cheng-zi-fu-chuan-lcof
- palindrome-number
- network-delay-time
- daily-temperatures
- longest-common-prefix
- sum-of-mutated-array-closest-to-target
- 周賽專題
- make-two-arrays-equal-by-reversing-sub-arrays
- check-if-a-string-contains-all-binary-codes-of-size-k
- course-schedule-iv
- cherry-pickup-ii
- maximum-product-of-two-elements-in-an-array
- maximum-area-of-a-piece-of-cake-after-horizontal-and-vertical-cuts
- reorder-routes-to-make-all-paths-lead-to-the-city-zero
- probability-of-a-two-boxes-having-the-same-number-of-distinct-balls
- shuffle-the-array
- the-k-strongest-values-in-an-array
- design-browser-history
- paint-house-iii
- final-prices-with-a-special-discount-in-a-shop
