[TOC]
> last、first聚合函數可以返聚合之后指定列的最后一個或第一條記錄的值。
> 在如MongoDB的非關系型數據庫中,是支持這兩種聚合函數的。但是mysql、pgsql等這些關系型數據庫中并沒有直接提供last、first聚合函數,如果需要在這些關系型數據庫中實現與last、first函數一樣的效果,可以通過窗口函數或者其他方式實現。
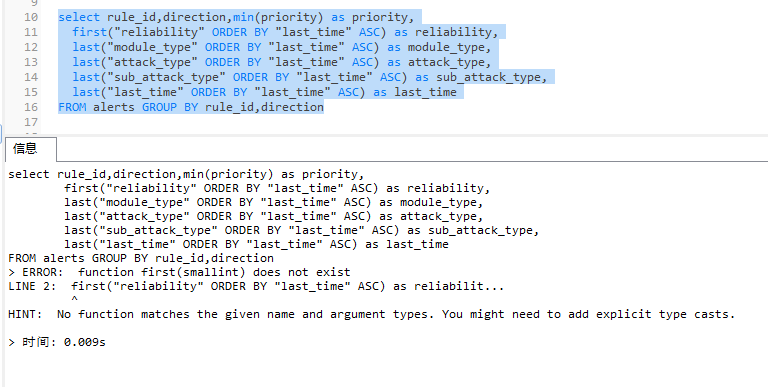
在mysql、pgsql中直接執行last、first聚合函數時會顯示報錯
首先,創建表結構如下,并隨機生成20條數據,其中last_time時間遞增。
```
postgres=# select id,rule_id,direction,priority,reliability,module_type,attack_type,sub_attack_type,last_time from alerts order by id
postgres-# \g
id | rule_id | direction | priority | reliability | module_type | attack_type | sub_attack_type | last_time
----+---------+-----------+----------+-------------+-------------+-------------+-----------------+------------
1 | 319 | 209 | 8 | 3 | 86 | 18 | 92 | 1614048983
2 | 319 | 209 | 9 | 6 | 54 | 72 | 79 | 1614048984
3 | 49 | 709 | 3 | 3 | 21 | 3 | 68 | 1614048985
4 | 144 | 508 | 3 | 5 | 37 | 11 | 89 | 1614048986
5 | 585 | 488 | 8 | 3 | 44 | 49 | 63 | 1614048987
6 | 675 | 396 | 5 | 5 | 32 | 27 | 36 | 1614048988
7 | 419 | 209 | 9 | 7 | 29 | 33 | 92 | 1614048989
8 | 903 | 877 | 3 | 6 | 35 | 79 | 81 | 1614048990
9 | 884 | 626 | 5 | 9 | 81 | 35 | 9 | 1614048991
10 | 916 | 574 | 9 | 9 | 71 | 54 | 43 | 1614048992
11 | 884 | 626 | 1 | 2 | 54 | 66 | 80 | 1614048993
12 | 35 | 332 | 8 | 2 | 57 | 24 | 57 | 1614048994
13 | 884 | 626 | 8 | 3 | 37 | 29 | 26 | 1614048995
14 | 825 | 294 | 4 | 8 | 54 | 5 | 42 | 1614048996
15 | 67 | 430 | 2 | 5 | 36 | 5 | 91 | 1614048997
16 | 409 | 134 | 4 | 4 | 78 | 65 | 51 | 1614048998
17 | 962 | 692 | 3 | 1 | 25 | 93 | 4 | 1614048999
18 | 765 | 807 | 4 | 6 | 78 | 83 | 77 | 1614049000
19 | 619 | 512 | 4 | 4 | 45 | 38 | 80 | 1614049001
20 | 619 | 512 | 8 | 1 | 60 | 75 | 45 | 1614049002
(20 rows)
```
需求:按照rule_id,direction字段聚合,priority字段取最小值,module_type、attack_type、sub_attack_type字段取聚合之后最后一條記錄的值,reliability字段取最早的一條記錄的值。
# <span style="font-size:15px">**第一種方式:通過pgsql的array_agg函數來實現** </span>
> pgsql 的ARRAY\_AGG函數可以將多個值合并到一個數組中,相當于MongoDB的addToSet,這里不做贅述。
> 利用array_agg函數,根據指定字段進行倒序或者升序排序之后,再取第一個值便可以實現。
```
// filter關鍵字為聚合指定字段時添加過濾,可加可不加,根據需求而定
SELECT "rule_id","direction",
min("priority") as "priority",
(array_agg("reliability" ORDER BY "last_time" ASC) FILTER (WHERE attack_ip = '1.1.1.1'))[1] as "reliability",
(array_agg("module_type" ORDER BY "last_time" DESC) FILTER (WHERE attack_ip = '1.1.1.1'))[1] as "module_type",
(array_agg("attack_type" ORDER BY "last_time" DESC) FILTER (WHERE attack_ip = '1.1.1.1'))[1] as "attack_type",
(array_agg("sub_attack_type" ORDER BY "last_time" DESC) FILTER (WHERE attack_ip = '1.1.1.1'))[1] as "sub_attack_type",
(array_agg("last_time" ORDER BY "last_time" DESC) FILTER (WHERE attack_ip = '1.1.1.1'))[1] as "last_time"
FROM alerts where attack_ip = '1.1.1.1' GROUP BY "rule_id","direction"
```
# <span style="font-size:15px">**第二種方式:通過pgsql 的窗口函數+join方式來實現** </span>
> pgsql提供了first_value、last_value的窗口函數,可以在查詢時返回取分組內排序后,截止到當前行的第一個值或者最后一個值,詳見 [pgsql窗口函數解析](http://docs.linchunyu.top/2280090)
```
// 先使用first_value、last_value窗口函數,獲取指定列的第一個值或者最后一個值之后,再join關聯聚合
// 因為外層是聚合,所以必須有聚合函數才可以獲取到對應的字段。
// 此時字段已經取得第一個或者最后一個值,因為外層的select獲取該字段時,采用min、max都是一樣的。
SELECT b.rule_id,b.direction, min(priority) as priority,min(b.reliability) as reliability, min(b.module_type) as module_type,
min(b.attack_type) as attack_type,min(b.sub_attack_type) as sub_attack_type, min(b.last_time) as last_time
from alerts a INNER JOIN (
SELECT id,rule_id,direction,
FIRST_VALUE(reliability)over(partition by rule_id,direction order by last_time asc) as reliability,
FIRST_VALUE(module_type)over(partition by rule_id,direction order by last_time desc) as module_type,
FIRST_VALUE(attack_type)over(partition by rule_id,direction order by last_time desc) as attack_type,
FIRST_VALUE(sub_attack_type)over(partition by rule_id,direction order by last_time desc) as sub_attack_type,
FIRST_VALUE(last_time)over(partition by rule_id,direction order by last_time desc) as last_time
from alerts
) b on a.id = b.id GROUP BY b.rule_id,b.direction
```
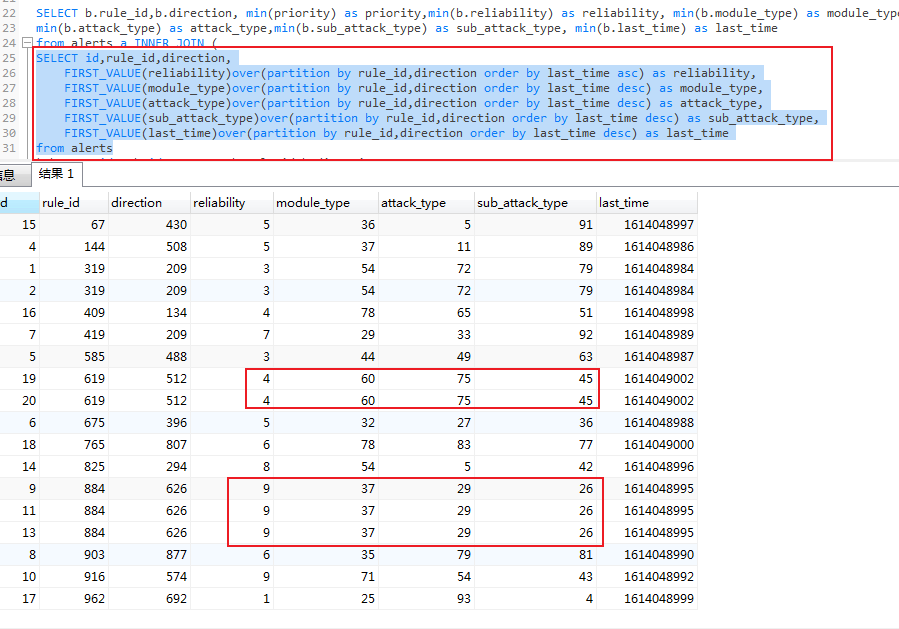
如圖,僅執行join內的select語句,使用窗口函數的字段值都是一樣的
# <span style="font-size:15px">**第三種方式:創建內置聚合函數(無外部依賴)** </span>
> 此方式為SQL語言實現,沒有外部依賴關系。
> 直接在數據庫執行以下語句即可,創建完之后可以直接使用last、first函數聚合,[WIKI](https://wiki.postgresql.org/wiki/First/last_(aggregate))
```
-- Create a function that always returns the first non-NULL item
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.first_agg ( anyelement, anyelement )
RETURNS anyelement AS $$
SELECT CASE WHEN $1 IS NULL THEN $2 ELSE $1 END;
$$ LANGUAGE SQL STABLE;
-- And then wrap an aggreagate around it
CREATE AGGREGATE public.first (
sfunc = public.first_agg,
basetype = anyelement,
stype = anyelement
);
-- Create a function that always returns the last non-NULL item
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.last_agg ( anyelement, anyelement )
RETURNS anyelement AS $$
SELECT $2;
$$ LANGUAGE SQL STABLE;
-- And then wrap an aggreagate around it
CREATE AGGREGATE public.last (
sfunc = public.last_agg,
basetype = anyelement,
stype = anyelement
);
```
```
// 此方式可以直接使用last、first聚合函數,對指定字段進行取第一條/最后一條的操作,同時支持根據指定字段進行排序
// 如reliability字段,實際上是聚合之后,根據last_time升序排序之后取第一條
select rule_id,direction,min(priority) as priority,
first("reliability" ORDER BY "last_time" ASC) as reliability,
last("module_type" ORDER BY "last_time" ASC) as module_type,
last("attack_type" ORDER BY "last_time" ASC) as attack_type,
last("sub_attack_type" ORDER BY "last_time" ASC) as sub_attack_type,
last("last_time" ORDER BY "last_time" ASC) as last_time
FROM alerts GROUP BY rule_id,direction
```
# <span style="font-size:15px">**第四種方式:引入外部聚合擴展(有外部依賴)** </span>
[外部last_first聚合擴展庫下載地址](https://debian.pkgs.org/sid/debian-main-amd64/postgresql-13-first-last-agg_0.1.4-4-gd63ea3b-3+b1_amd64.deb.html)
詳見 [pgsql安裝擴展](http://docs.linchunyu.top/2280100)
<br>
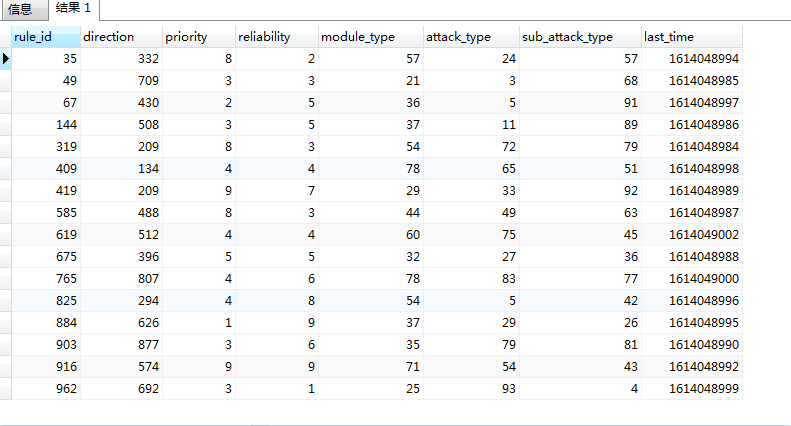
**結果分析:**
以上語句執行結果都是相同的,如下,可以對比建表時的數據。
如rule_id為884、direction為626的數據,取最第一個reliability的值,則是id為9的數據對應的reliability字段值。
- PHP
- PHP基礎
- PHP介紹
- 如何理解PHP是弱類型語言
- 超全局變量
- $_SERVER詳解
- 字符串處理函數
- 常用數組函數
- 文件處理函數
- 常用時間函數
- 日歷函數
- 常用url處理函數
- 易混淆函數區別(面試題常見)
- 時間戳
- PHP進階
- PSR規范
- RESTFUL規范
- 面向對象
- 三大基本特征和五大基本原則
- 訪問權限
- static關鍵字
- static關鍵字
- 靜態變量與普通變量
- 靜態方法與普通方法
- const關鍵字
- final關鍵字
- abstract關鍵字
- self、$this、parent::關鍵字
- 接口(interface)
- trait關鍵字
- instanceof關鍵字
- 魔術方法
- 構造函數和析構函數
- 私有屬性的設置獲取
- __toString()方法
- __clone()方法
- __call()方法
- 類的自動加載
- 設計模式詳解
- 關于設計模式的一些建議
- 工廠模式
- 簡單工廠模式
- 工廠方法模式
- 抽象工廠模式
- 區別和適用范圍
- 策略模式
- 單例模式
- HTTP
- 定義
- 特點
- 工作過程
- request
- response
- HTTP狀態碼
- URL
- GET和POST的區別
- HTTPS
- session與cookie
- 排序算法
- 冒泡排序算法
- 二分查找算法
- 直接插入排序算法
- 希爾排序算法
- 選擇排序算法
- 快速排序算法
- 循環算法
- 遞歸與尾遞歸
- 迭代
- 日期相關的類
- DateTimeInterface接口
- DateTime類
- DateTimeImmutable類
- DateInterval類
- DateTimeZone類
- DatePeriod類
- format參數格式
- DateInterval的format格式化參數
- 預定義接口
- ArrayAccess(數組式訪問)接口
- Serializable (序列化)接口
- Traversable(遍歷)接口
- Closure類
- Iterator(迭代器)接口
- IteratorAggregate(聚合迭代器) 接口
- Generator (生成器)接口
- composer
- composer安裝與使用
- python
- python3執行tarfile解壓文件報錯:tarfile.ReadError:file could not be opened successfully
- golang
- 單元測試
- 單元測試框架
- Golang內置testing包
- GoConvey庫
- testify庫
- 打樁與mock
- GoMock框架
- Gomonkey框架
- HTTP Mock
- httpMock
- mux庫/httptest
- 數據庫
- MYSQL
- SQL語言的分類
- 事務(重點)
- 索引
- 存儲過程
- 觸發器
- 視圖
- 導入導出數據庫
- 優化mysql數據庫的方法
- MyISAM與InnoDB區別
- 外連接、內連接的區別
- 物理文件結構
- PostgreSQL
- 編譯安裝
- pgsql常用命令
- pgsql應用目錄(bin目錄)文件結構解析
- pg_ctl
- initdb
- psql
- clusterdb
- cluster命令
- createdb
- dropdb
- createuser
- dropuser
- pg_config
- pg_controldata
- pg_checksums
- pgbench
- pg_basebackup
- pg_dump
- pg_dumpall
- pg_isready
- pg_receivewal
- pg_recvlogical
- pg_resetwal
- pg_restore
- pg_rewind
- pg_test_fsync
- pg_test_timing
- pg_upgrade
- pg_verifybackup
- pg_archivecleanup
- pg_waldump
- postgres
- reindexdb
- vacuumdb
- ecpg
- pgsql數據目錄文件結構解析
- pgsql數據目錄文件結構解析
- postgresql.conf解析
- pgsql系統配置參數說明
- pgsql索引類型
- 四種索引類型解析
- 索引之ctid解析
- 索引相關操作
- pgsql函數解析
- pgsql系統函數解析
- pgsql窗口函數解析
- pgsql聚合函數解析
- pgsql系統表解析
- pg_stat_all_indexes
- pg_stat_all_tables
- pg_statio_all_indexes
- pg_statio_all_tables
- pg_stat_database
- pg_stat_statements
- pg_extension
- pg_available_extensions
- pg_available_extension_versions
- pgsql基本原理
- 進程和內存結構
- 存儲結構
- 數據文件的內部結構
- 垃圾回收機制VACUUM
- 事務日志WAL
- 并發控制
- 介紹
- 事務ID-txid
- 元組結構-Tuple Structure
- 事務狀態記錄-Commit Log (clog)
- 事務快照-Transaction Snapshot
- 事務快照實例
- 事務隔離
- 事務隔離級別
- 讀已提交-Read committed
- 可重復讀-Repeatable read
- 可序列化-Serializable
- 讀未提交-Read uncommitted
- 鎖機制
- 擴展機制解析
- 擴展的定義
- 擴展的安裝方式
- 自定義創建擴展
- 擴展的管理
- 擴展使用實例
- 在pgsql中使用last、first聚合函數
- pgsql模糊查詢不走索引的解決方案
- pgsql的pg_trgm擴展解析與驗證
- 高可用
- LNMP
- LNMP環境搭建
- 一鍵安裝包
- 搭建方法
- 配置文件目錄
- 服務器管理系統
- 寶塔(Linux)
- 安裝與使用
- 開放API
- 自定義apache日志
- 一鍵安裝包LNMP1.5
- LNMP1.5:添加、刪除站點
- LNMP1.5:php多版本切換
- LNMP1.5 部署 thinkphp項目
- Operation not permitted解決方法
- Nginx
- Nginx的產生
- 正向代理和反向代理
- 負載均衡
- Linux常用命令
- 目錄與文件相關命令
- 目錄操作命令
- 文件編輯命令
- 文件查看命令
- 文件查找命令
- 文件權限命令
- 文件上傳下載命令
- 用戶和群組相關命令
- 用戶與用戶組的關系
- 用戶相關的系統配置文件
- 用戶相關命令
- 用戶組相關命令
- 壓縮與解壓相關命令
- .zip格式
- .tar.gz格式
- .gz格式
- .bz2格式
- 查看系統版本
- cpuinfo詳解
- meminfo詳解
- getconf獲取系統信息
- 磁盤空間相關命令
- 查看系統負載情況
- 系統環境變量
- 網絡相關命令
- ip命令詳解
- ip命令格式詳解
- ip address命令詳解
- ip link命令詳解
- ip rule命令詳解
- ip route命令詳解
- nslookup命令詳解
- traceroute命令詳解
- netstat命令詳解
- route命令詳解
- tcpdump命令詳解
- 系統進程相關命令
- ps命令詳解
- pstree命令詳解
- kill命令詳解
- 守護進程-supervisord
- 性能監控相關命令
- top命令詳解
- iostat命令詳解
- pidstat命令詳解
- iotop命令詳解
- mpstat命令詳解
- vmstat命令詳解
- ifstat命令詳解
- sar命令詳解
- iftop命令詳解
- 定時任務相關命令
- ssh登錄遠程主機
- ssh口令登錄
- ssh公鑰登錄
- ssh帶密碼登錄
- ssh端口映射
- ssh配置文件
- ssh安全設置
- 歷史紀錄
- history命令詳解
- linux開啟操作日志記錄
- 拓展
- git
- git初始化本地倉庫-https
- git初始化倉庫-ssh
- git-查看和設置config配置
- docker
- 概念
- docker原理
- docker鏡像原理
- docker Overlay2 文件系統原理
- docker日志原理
- docker日志驅動
- docker容器日志管理
- 原理論證
- 驗證容器的啟動是作為Docker Daemon的子進程
- 驗證syslog類型日志驅動
- 驗證journald類型日志驅動
- 驗證local類型日志驅動
- 修改容器的hostname
- 修改容器的hosts
- 驗證聯合掛載技術
- 驗證啟動多個容器對于磁盤的占用情況
- 驗證寫時復制原理
- 驗證docker內容尋址原理
- docker存儲目錄
- /var/lib/docker目錄
- image目錄
- overlay2目錄
- 數據卷
- 具名掛載和匿名掛載
- 數據卷容器
- Dockerfile詳解
- dockerfile指令詳解
- 實例:構造centos
- 實例:CMD和ENTRYPOINT的區別
- docker網絡詳解
- docker-compose
- 緩存
- redis
- redis的數據類型和應用場景
- redis持久化
- RDB持久化
- AOF持久化
- redis緩存穿透、緩存擊穿、緩存雪崩
- 常見網絡攻擊類型
- CSRF攻擊
- XSS攻擊
- SQL注入
- Cookie攻擊
- 歷史項目經驗
- 圖片上傳項目實例
- 原生php上傳方法實例
- base64圖片流
- tp5的上傳方法封裝實例
- 多級關系的遞歸查詢
- 數組轉樹結構
- thinkphp5.1+ajax實現導出Excel
- JS 刪除數組的某一項
- 判斷是否為索引數組
- ip操作
