## 1.1 注解的定義
* 日常開發中新建Java類,我們使用class、interface比較多,而注解和它們一樣,也是一種類的類型,它是用的修飾符為 @interface
### 1.1 注解類的寫法
* 我們新建一個注解MyTestAnnotation
~~~
public @interface MyTestAnnotation {
}
~~~
* 接著我們就可以在類或者方法上作用我們剛剛新建的注解
~~~
@MyTestAnnotation
public class test {
@MyTestAnnotation
public static void main(String[] args){
}
}
~~~
* 以上我們只是了解了注解的寫法,但是我們定義的注解中還沒寫任何代碼,現在這個注解毫無意義,要如何使注解工作呢?接下來我們接著了解元注解。
## 2. 元注解
* **元注解顧名思義我們可以理解為注解的注解**,它是作用在注解中,方便我們使用注解實現想要的功能。元注解分別有@Retention、 @Target、 @Document、 @Inherited和@Repeatable(JDK1.8加入)五種。
### 2.1 @Retention
> Retention英文意思有保留、保持的意思,它表示注解存在階段是保留在源碼(編譯期),字節碼(類加載)或者運行期(JVM中運行)。在@Retention注解中使用枚舉RetentionPolicy來表示注解保留時期
* @Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE),注解僅存在于源碼中,在class字節碼文件中不包含
* @Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS), 默認的保留策略,注解會在class字節碼文件中存在,但運行時無法獲得
* @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME), 注解會在class字節碼文件中存在,在運行時可以通過反射獲取到
* 如果我們是自定義注解,則通過前面分析,我們自定義注解如果只存著源碼中或者字節碼文件中就無法發揮作用,而在運行期間能獲取到注解才能實現我們目的,所以自定義注解中肯定是使用 **@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)**
~~~
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyTestAnnotation {
}
~~~
### 2.2 @Target 注解使用對象
> Target的英文意思是目標,這也很容易理解,使用@Target元注解表示我們的注解作用的范圍就比較具體了,可以是類,方法,方法參數變量等,同樣也是通過枚舉類ElementType表達作用類型
* @Target(ElementType.TYPE) 作用接口、類、枚舉、注解
* @Target(ElementType.FIELD) 作用屬性字段、枚舉的常量
* @Target(ElementType.METHOD) 作用方法
* @Target(ElementType.PARAMETER) 作用方法參數
* @Target(ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR) 作用構造函數
* @Target(ElementType.LOCAL\_VARIABLE)作用局部變量
* @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION\_TYPE)作用于注解(@Retention注解中就使用該屬性)
* @Target(ElementType.PACKAGE) 作用于包
* @Target(ElementType.TYPE\_PARAMETER) 作用于類型泛型,即泛型方法、泛型類、泛型接口 (jdk1.8加入)
* @Target(ElementType.TYPE\_USE) 類型使用.可以用于標注任意類型除了 class (jdk1.8加入)
* 一般比較常用的是ElementType.TYPE類型
~~~
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface MyTestAnnotation {
}
~~~
### 2.3 @Documented
* Document的英文意思是文檔。它的作用是能夠將注解中的元素包含到 Javadoc 中去。
### 2.4 @Inherited
Inherited的英文意思是繼承,但是這個繼承和我們平時理解的繼承大同小異,**一個被@Inherited注解了的注解**修飾了一個父類,如果他的子類沒有被其他注解修飾,則它的子類也繼承了父類的注解。
* 下面我們來看個@Inherited注解例子
~~~
/**自定義注解*/
@Documented
@Inherited
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface MyTestAnnotation {
}
/**父類標注自定義注解*/
@MyTestAnnotation
public class Father {
}
/**子類*/
public class Son extends Father {
}
/**測試子類獲取父類自定義注解*/
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args){
//獲取Son的class對象
Class<Son> sonClass = Son.class;
// 獲取Son類上的注解MyTestAnnotation可以執行成功
MyTestAnnotation annotation = sonClass.getAnnotation(MyTestAnnotation.class);
}
}
~~~
### 2.5 @Repeatable
* Repeatable的英文意思是可重復的。顧名思義說明被這個元注解修飾的**注解可以同時作用一個對象多次**,但是每次作用注解又可以代表不同的含義。
> 在生活中一個人往往是具有多種身份,如果我把每種身份當成一種注解該如何使用???
1. 先聲明一個Persons類用來包含所有的身份
```
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Persons {
Person[] value();
}
```
Persons 注解是包含的意思,包含了Person注解數組
?
2. Person注解:
```
@Repeatable(Persons.class)
public @interface Person{
String role() default "";
}
```
**@Repeatable括號內的就相當于用來保存該注解內容的容器。**
?
3. 聲明一個Man類,給該類加上一些身份。
```
@Person(role="CEO")
@Person(role="husband")
@Person(role="father")
@Person(role="son")
public class Man {
String name="";
}
```
4. 在主方法中訪問該注解。
```
public static void main(String[] args) {
Annotation[] annotations = Man.class.getAnnotations();
System.out.println(annotations.length);
Persons p1=(Persons) annotations[0];
for(Person t:p1.value()){
System.out.println(t.role());
}
}
```
下面的代碼結果輸出相同,但是可以先判斷是否是相應的注解,比較嚴謹。?
```
if(Man.class.isAnnotationPresent(Persons.class)) {
Persons p2=Man.class.getAnnotation(Persons.class);
for(Person t:p2.value()){
System.out.println(t.role());
}
}
```
運行結果:?
```
1
CEO
husband
father
son
```
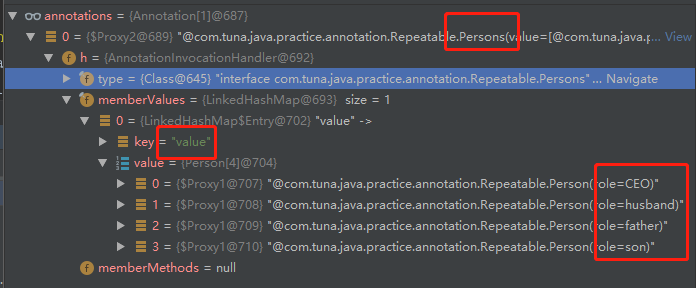
注意:雖然man類使用person修飾,但是他是被包裹在persons注解當中,所以程序運行要讀取persons外層注解
## 3. 注解的屬性
* 通過上一小節@Repeatable注解的例子,我們說到注解的屬性。注解的屬性其實和類中定義的變量有異曲同工之處,只是注解中的變量都是成員變量(屬性),并且注**解中是沒有方法的,只有成員變量**,變量名就是使用注解括號中對應的參數名,變量返回值注解括號中對應參數類型。相信這會你應該會對上面的例子有一個更深的認識。而@Repeatable注解中的變量則類型則是對應Annotation(接口)的泛型Class。
~~~
/**注解Repeatable源碼*/
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Repeatable {
/**
* Indicates the <em>containing annotation type</em> for the
* repeatable annotation type.
* @return the containing annotation type
*/
Class<? extends Annotation> value();
}
~~~
### 3.1 注解的本質
* 注解的本質就是一個Annotation接口
~~~
/**Annotation接口源碼*/
public interface Annotation {
boolean equals(Object obj);
int hashCode();
Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType();
}
~~~
* 通過以上源碼,我們知道注解本身就是Annotation接口的子接口,**也就是說注解中其實是可以有屬性和方法,但是接口中的屬性都是static final的,對于注解來說沒什么意義,而我們定義接口的方法就相當于注解的屬性,也就對應了前面說的為什么注解只有屬性成員變量,其實他就是接口的方法,這就是為什么成員變量會有括號**,不同于接口我們可以在注解的括號中給成員變量賦值。
### 3.2 注解屬性類型
注解屬性類型可以有以下列出的類型
1. 基本數據類型
2. String
3. 枚舉類型
4. 注解類型
5. Class類型
6. 以上類型的一維數組類型
### 3.3 注解成員變量賦值
* 如果注解又多個屬性,則可以在注解括號中用“,”號隔開分別給對應的屬性賦值,如下例子,注解在父類中賦值屬性
~~~
@Documented
@Inherited
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface MyTestAnnotation {
String name() default "mao";
int age() default 18;
}
@MyTestAnnotation(name = "father",age = 50)
public class Father {
}
~~~
### 3.4 獲取注解屬性
* 前面我們說了很多注解如何定義,放在哪,現在我們可以開始學習注解屬性的提取了,這才是使用注解的關鍵,獲取屬性的值才是使用注解的目的。
* 如果獲取注解屬性,當然是反射啦,主要有三個基本的方法
~~~
/**是否存在對應 Annotation 對象*/
public boolean isAnnotationPresent(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass) {
return GenericDeclaration.super.isAnnotationPresent(annotationClass);
}
/**獲取 Annotation 對象*/
public <A extends Annotation> A getAnnotation(Class<A> annotationClass) {
Objects.requireNonNull(annotationClass);
return (A) annotationData().annotations.get(annotationClass);
}
/**獲取所有 Annotation 對象數組*/
public Annotation[] getAnnotations() {
return AnnotationParser.toArray(annotationData().annotations);
}
~~~
* 下面結合前面的例子,我們來獲取一下注解屬性,在獲取之前我們自定義的注解必須使用元注解@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
~~~kotlin
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException {
/**
* 獲取類注解屬性
*/
Class<Father> fatherClass = Father.class;
boolean annotationPresent = fatherClass.isAnnotationPresent(MyTestAnnotation.class);
if(annotationPresent){
MyTestAnnotation annotation = fatherClass.getAnnotation(MyTestAnnotation.class);
System.out.println(annotation.name());
System.out.println(annotation.age());
}
/**
* 獲取方法注解屬性
*/
try {
Field age = fatherClass.getDeclaredField("age");
boolean annotationPresent1 = age.isAnnotationPresent(Age.class);
if(annotationPresent1){
Age annotation = age.getAnnotation(Age.class);
System.out.println(annotation.value());
}
Method play = PlayGame.class.getDeclaredMethod("play");
if (play!=null){
People annotation2 = play.getAnnotation(People.class);
Game[] value = annotation2.value();
for (Game game : value) {
System.out.println(game.value());
}
}
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
~~~
運行結果:
## 4. JDK 提供的注解
| 注解 | 作用 | 注意事項 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| @Override | 它是用來描述當前方法是一個重寫的方法,在編譯階段對方法進行檢查 | jdk1.5中它只能描述繼承中的重寫,jdk1.6中它可以描述接口實現的重寫,也能描述類的繼承的重寫 |
| @Deprecated | 它是用于描述當前方法是一個過時的方法 | 無 |
| @SuppressWarnings | 對程序中的警告去除。 | 無 |
## 5. 注解作用與應用
* 現在我們再次回頭看看開頭官方文檔的那句描述
> Java 注解用于為 Java 代碼提供元數據。作為元數據,注解不直接影響你的代碼執行,但也有一些類型的注解實際上可以用于這一目的。
* 經過我們前面的了解,注解其實是個很方便的東西,它存活的時間,作用的區域都可以由你方便設置,只是你用注解來干嘛的問題
### 5.1 使用注解進行參數配置
* 下面我們看一個銀行轉賬的例子,假設銀行有個轉賬業務,轉賬的限額可能會根據匯率的變化而變化,我們可以利用注解靈活配置轉賬的限額,而不用每次都去修改我們的業務代碼。
~~~kotlin
/**定義限額注解*/
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface BankTransferMoney {
double maxMoney() default 10000;
}
/**轉賬處理業務類*/
public class BankService {
/**
* @param money 轉賬金額
*/
@BankTransferMoney(maxMoney = 15000)
public static void TransferMoney(double money){
System.out.println(processAnnotationMoney(money));
}
private static String processAnnotationMoney(double money) {
try {
Method transferMoney = BankService.class.getDeclaredMethod("TransferMoney",double.class);
boolean annotationPresent = transferMoney.isAnnotationPresent(BankTransferMoney.class);
if(annotationPresent){
BankTransferMoney annotation = transferMoney.getAnnotation(BankTransferMoney.class);
double l = annotation.maxMoney();
if(money>l){
return "轉賬金額大于限額,轉賬失敗";
}else {
return"轉賬金額為:"+money+",轉賬成功";
}
}
} catch ( NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "轉賬處理失敗";
}
public static void main(String[] args){
TransferMoney(10000);
}
}
~~~
運行結果:

* 通過上面的例子,只要匯率變化,我們就改變注解的配置值就可以直接改變當前最大限額。
### 注解的作用
* 提供信息給編譯器: 編譯器可以利用注解來檢測出錯誤或者警告信息,打印出日志。
* 編譯階段時的處理: 軟件工具可以用來利用注解信息來自動生成代碼、文檔或者做其它相應的自動處理。
* 運行時處理: 某些注解可以在程序運行的時候接受代碼的提取,自動做相應的操作。
* 正如官方文檔的那句話所說,注解能夠提供元數據,轉賬例子中處理獲取注解值的過程是我們開發者直接寫的注解提取邏輯,**處理提取和處理 Annotation 的代碼統稱為 APT(Annotation Processing Tool)**。上面轉賬例子中的processAnnotationMoney方法就可以理解為APT工具類。
- 計算機網絡
- 基礎_01
- tcp/ip
- http轉https
- Let's Encrypt免費ssl證書(基于haproxy負載)
- what's the http?
- 網關
- 網絡IO
- http
- 工具
- Git
- 初始本地倉庫并上傳
- git保存密碼
- Gitflow
- maven
- 1.生命周期命令
- 聚合與繼承
- 插件管理
- assembly
- 資源管理插件
- 依賴范圍
- 分環境打包
- dependencyManagement
- 版本分類
- 找不到主類
- 無法加載主類
- 私服
- svn
- gradle
- 手動引入第三方jar包
- 打包exe文件
- Windows
- java
- 設計模式
- 七大原則
- 1.開閉原則
- 2. 里式替換原則
- 3. 依賴倒置原則
- 4. 單一職責原則
- 單例模式
- 工廠模式
- 簡單工廠
- 工廠方法模式
- 抽象工廠模式
- 觀察者模式
- 適配器模式
- 建造者模式
- 代理模式
- 適配器模式
- 命令模式
- json
- jackson
- poi
- excel
- easy-poi
- 規則
- 模板
- 合并單元格
- word
- 讀取
- java基礎
- 類路徑與jar
- 訪問控制權限
- 類加載
- 注解
- 異常處理
- String不可變
- 跨域
- transient關鍵字
- 二進制編碼
- 泛型1
- 與或非
- final詳解
- Java -jar
- 正則
- 讀取jar
- map
- map計算
- hashcode計算原理
- 枚舉
- 序列化
- URLClassLoader
- 環境變量和系統變量
- java高級
- java8
- 1.Lambda表達式和函數式接口
- 2.接口的默認方法和靜態方法
- 3.方法引用
- 4.重復注解
- 5.類型推斷
- 6.拓寬注解的應用場景
- java7-自動關閉資源機制
- 泛型
- stream
- 時區的正確理解
- StringJoiner字符串拼接
- 注解
- @RequestParam和@RequestBody的區別
- 多線程
- 概念
- 線程實現方法
- 守護線程
- 線程阻塞
- 筆試題
- 類加載
- FutureTask和Future
- 線程池
- 同步與異步
- 高效簡潔的代碼
- IO
- ThreadLocal
- IO
- NIO
- 圖片操作
- KeyTool生成證書
- 壓縮圖片
- restful
- 分布式session
- app保持session
- ClassLoader.getResources 能搜索到的資源路徑
- java開發規范
- jvm
- 高并發
- netty
- 多線程與多路復用
- 異步與事件驅動
- 五種IO模型
- copy on write
- code style
- 布隆過濾器
- 筆試
- 數據庫
- mybatis
- mybatis與springboot整合配置
- pagehelper
- 分頁數據重復問題
- Java與數據庫之間映射
- 攔截器
- 攔截器應用
- jvm
- 堆內存測試
- 線程棧
- 直接內存
- 內存結構
- 內存模型
- 垃圾回收
- 調優
- 符號引用
- 運行參數
- 方法區
- 分帶回收理論
- 快捷開發
- idea插件
- 注釋模板
- git
- pull沖突
- push沖突
- Excel處理
- 圖片處理
- 合并單元格
- easypoi
- 模板處理
- 響應式編程
- reactor
- reactor基礎
- jingyan
- 規范
- 數據庫
