# 捕獲線程運行期間的異常
上一篇文章我們學習了在我們使用application的時候在他出現問題或者人為終止的時候,我們怎么有機會捕獲異常或者人為的做一些操作,比如寫一些日志,或者發送一個RESTful或者關閉釋放一些資源,那么線程運行期間的異常該如何捕獲呢?我們知道線程的運行邏輯單元在run方法里,run方法的簽名是不允許拋出異常的,今天我們就來學習一下線程的Exception。
先來一段拋出異常的代碼:
```java
public class ThreadException {
private final static int A = 10;
private static final int B = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
/// 捕獲線程運行期間的異常
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1_000L);
int result = A / B;
System.out.println("result = " + result);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
t.start();
}
}
```
運行效果如下:
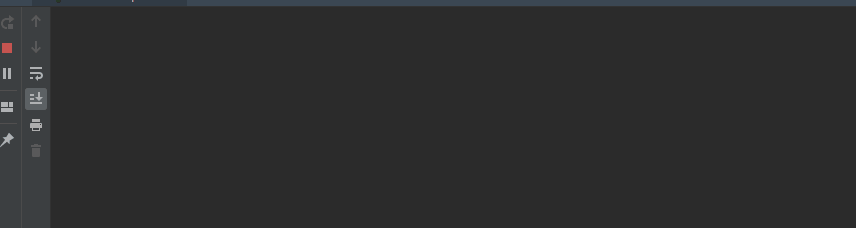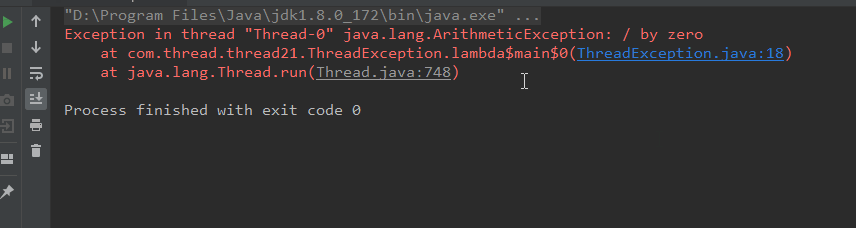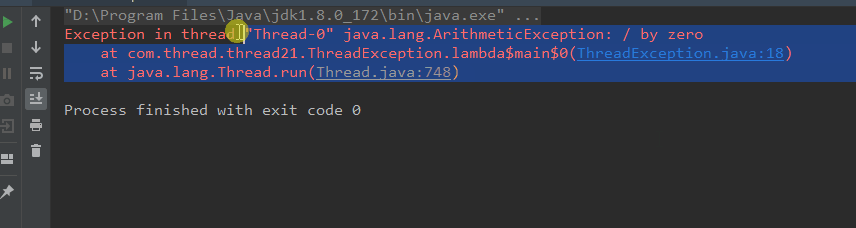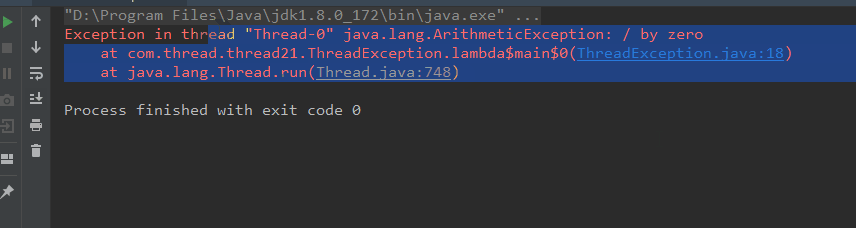
我們改造一下我們的代碼,Thread對象提供了`setUncaughtExceptionHandler`方法用來獲取線程中產生的異常。而且建議使用該方法為線程設置異常捕獲方法:
```java
t.setUncaughtExceptionHandler((thread, e) -> {
System.out.println(e);
System.out.println(thread.getName());
System.out.println(thread.getThreadGroup().getName());
System.out.println(thread.getThreadGroup().getParent().getName());
});
```
運行效果如下:
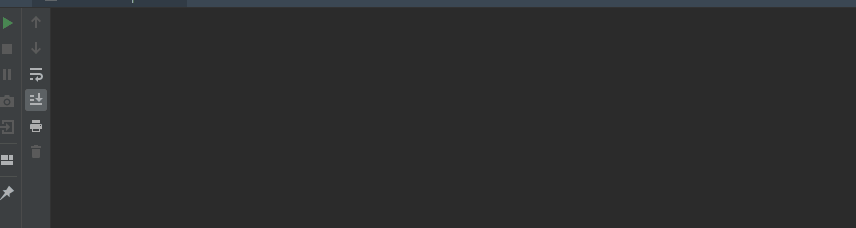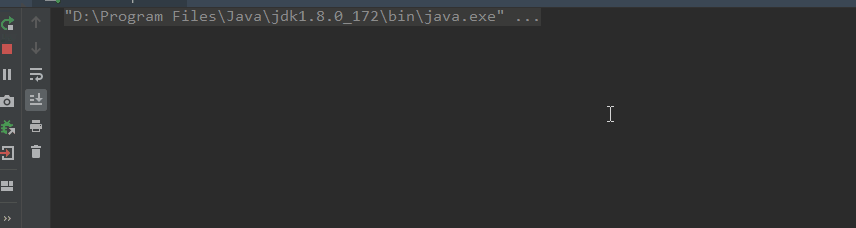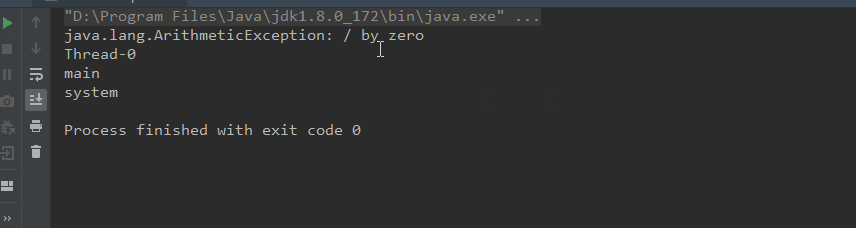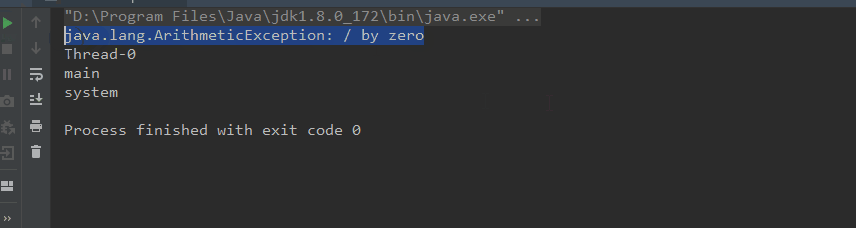
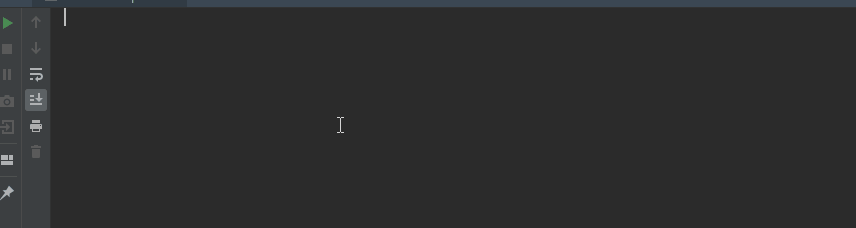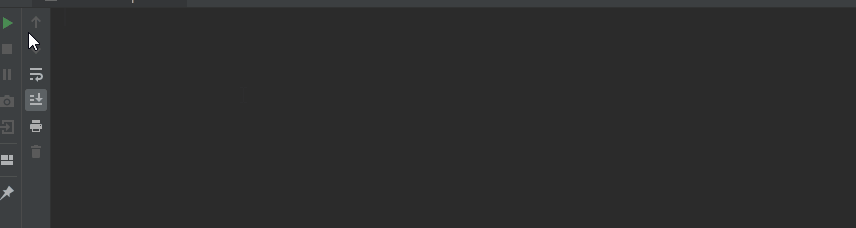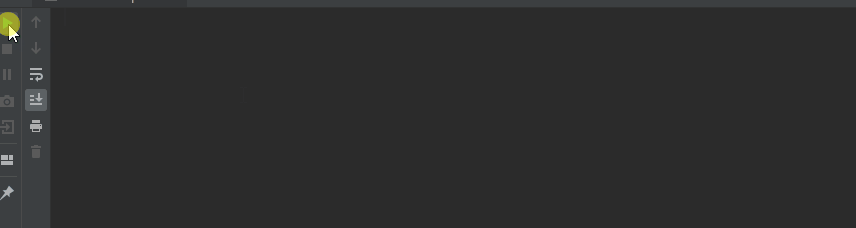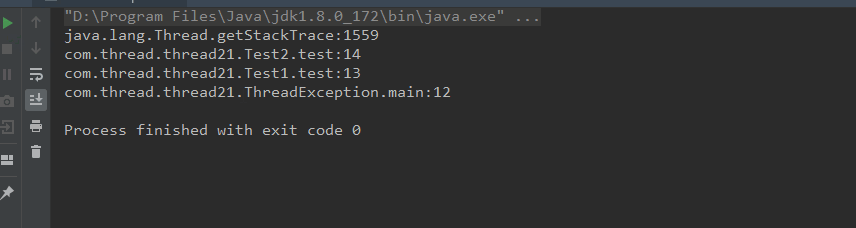
可以看到異常的詳細堆棧信息已經打印出來了,下面做個實驗來輸出一下,先建幾個類分別進行調用,如下:
```java
public class ThreadException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// stack trace
new Test1().test();
}
}
```
```java
public class Test1 {
private Test2 test2 = new Test2();
public void test() {
test2.test();
}
}
```
```java
public class Test2 {
public void test() {
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace();
Stream.of(stackTrace)
.filter(e -> !e.isNativeMethod())
.forEach(e ->
Optional.of(e.getClassName() + "." + e.getMethodName() + ":" + e.getLineNumber())
.ifPresent(System.out::println)
);
}
}
```
運行效果如下:
這個在后續使用中有補充再繼續補充,后面開始學習ThreadGroupApI的學習,然后實現一個線程池,java并發編程的基礎就碼一遍了。
- 微服務
- 服務器相關
- 操作系統
- 極客時間操作系統實戰筆記
- 01 程序的運行過程:從代碼到機器運行
- 02 幾行匯編幾行C:實現一個最簡單的內核
- 03 黑盒之中有什么:內核結構與設計
- Rust
- 入門:Rust開發一個簡單的web服務器
- Rust的引用和租借
- 函數與函數指針
- Rust中如何面向對象編程
- 構建單線程web服務器
- 在服務器中增加線程池提高吞吐
- Java
- 并發編程
- 并發基礎
- 1.創建并啟動線程
- 2.java線程生命周期以及start源碼剖析
- 3.采用多線程模擬銀行排隊叫號
- 4.Runnable接口存在的必要性
- 5.策略模式在Thread和Runnable中的應用分析
- 6.Daemon線程的創建以及使用場景分析
- 7.線程ID,優先級
- 8.Thread的join方法
- 9.Thread中斷Interrupt方法學習&采用優雅的方式結束線程生命周期
- 10.編寫ThreadService實現暴力結束線程
- 11.線程同步問題以及synchronized的引入
- 12.同步代碼塊以及同步方法之間的區別和關系
- 13.通過實驗分析This鎖和Class鎖的存在
- 14.多線程死鎖分析以及案例介紹
- 15.線程間通信快速入門,使用wait和notify進行線程間的數據通信
- 16.多Product多Consumer之間的通訊導致出現程序假死的原因分析
- 17.使用notifyAll完善多線程下的生產者消費者模型
- 18.wait和sleep的本質區別
- 19.完善數據采集程序
- 20.如何實現一個自己的顯式鎖Lock
- 21.addShutdownHook給你的程序注入鉤子
- 22.如何捕獲線程運行期間的異常
- 23.ThreadGroup API介紹
- 24.線程池原理與自定義線程池一
- 25.給線程池增加拒絕策略以及停止方法
- 26.給線程池增加自動擴充,閑時自動回收線程的功能
- JVM
- C&C++
- GDB調試工具筆記
- C&C++基礎
- 一個例子理解C語言數據類型的本質
- 字節順序-大小端模式
- Php
- Php源碼閱讀筆記
- Swoole相關
- Swoole基礎
- php的五種運行模式
- FPM模式的生命周期
- OSI網絡七層圖片速查
- IP/TCP/UPD/HTTP
- swoole源代碼編譯安裝
- 安全相關
- MySql
- Mysql基礎
- 1.事務與鎖
- 2.事務隔離級別與IO的關系
- 3.mysql鎖機制與結構
- 4.mysql結構與sql執行
- 5.mysql物理文件
- 6.mysql性能問題
- Docker&K8s
- Docker安裝java8
- Redis
- 分布式部署相關
- Redis的主從復制
- Redis的哨兵
- redis-Cluster分區方案&應用場景
- redis-Cluster哈希虛擬槽&簡單搭建
- redis-Cluster redis-trib.rb 搭建&原理
- redis-Cluster集群的伸縮調優
- 源碼閱讀筆記
- Mq
- ELK
- ElasticSearch
- Logstash
- Kibana
- 一些好玩的東西
- 一次折騰了幾天的大華攝像頭調試經歷
- 搬磚實用代碼
- python讀取excel拼接sql
- mysql大批量插入數據四種方法
- composer好用的鏡像源
- ab
- 環境搭建與配置
- face_recognition本地調試筆記
- 虛擬機配置靜態ip
- Centos7 Init Shell
- 發布自己的Composer包
- git推送一直失敗怎么辦
- Beyond Compare過期解決辦法
- 我的Navicat for Mysql
- 小錯誤解決辦法
- CLoin報錯CreateProcess error=216
- mysql error You must reset your password using ALTER USER statement before executing this statement.
- VM無法連接到虛擬機
- Jetbrains相關
- IntelliJ IDEA 筆記
- CLoin的配置與使用
- PhpStormDocker環境下配置Xdebug
- PhpStorm advanced metadata
- PhpStorm PHP_CodeSniffer
