[TOC]
# \*\* pygame.joystick\*\*
與游戲桿、游戲手柄、追蹤球進行交互的 pygame 模塊。
## **函數**
* pygame.joystick.init() — 初始化 joystick 模塊
* pygame.joystick.quit() — 卸載 joystick 模塊
* pygame.joystick.get\_init() — 如果 joystick 模塊已經初始化,返回 True
* pygame.joystick.get\_count() — 臨時設置某些組合鍵為被按下狀態
## **類**
* pygame.joystick.Joystick — 新建一個 Joystick 對象
joystick 模塊用來管理電腦上游戲桿類的設備。游戲桿類的設備包括追蹤球和游戲手柄。這個模塊允許使用多個按鈕和“帽鍵”。計算機可同時管理多個游戲桿類設備。
溫馨提示:以 PS4 次世代游戲手柄為例,本文出現的名稱含義如下。
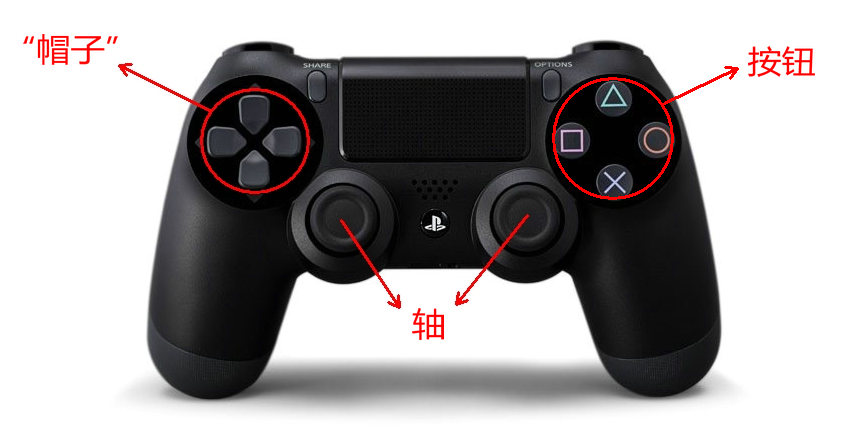
Joystick 類的每個實例代表一個插入電腦的游戲設備。如果一個游戲手柄上有多個游戲桿,在這個游戲設備上,一個 Joystick 對象可代表多個游戲桿。
用下面的代碼可快速初始化 joystick 模塊并且獲得 Joystick 實例的列表:
~~~
pygame.joystick.init()
joysticks = [pygame.joystick.Joystick(x) for x in range(pygame.joystick.get_count())]
~~~
以下事件類型由 joysticks 生成:
> JOYAXISMOTION JOYBALLMOTION JOYBUTTONDOWN JOYBUTTONUP JOYHATMOTION
由于事件隊列中的對象需要經常調用一些方法才能正常工作,所以 pygame.event.get,pygame.event.wait 或 pygame.event.pump 函數將會被經常用到。
## **函數詳解**
### **pygame.joystick.init()**
初始化 joystick 模塊。
init() -> None
這個函數被 pygame.init() 自動調用。
這個函數初始化 joystick 模塊,將會掃描系統上所有的游戲桿設備。這個模擬塊初始化后其他函數才能工作。
多次調用這個函數是沒問題的。
### **pygame.joystick.quit()**
卸載 joystick 模塊。
quit() -> None
卸載 joystick 模塊。
在你調用這個函數之后,任何游戲桿對象都不會再工作。
多次調用這個函數是沒問題的。
### **pygame.joystick.get\_init()**
如果 joystick 模塊已經初始化,返回 True。
get\_init() -> bool
測試 pygame.joystick.init() 是否已經被調用。
### **pygame.joystick.get\_count()**
返回游戲桿的數量。
get\_count() -> count
返回在系統上游戲桿設備的數量;如果沒有操縱桿設備,返回 0。
當你用 Joystick(id) 創建一個 joystick 對象,你輸入的數字(參數)必須小于這個數。
### **類 pygame.joystick.Joystick**
創建一個新的 Joystick 對象。
Joystick(id) -> Joystick
## **方法**
* pygame.joystick.Joystick.init() — 初始化
* pygame.joystick.Joystick.quit() — 卸載Joystick
* pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_init() — 檢查Joystick是否初始化
* pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_id() — 獲得Joystick ID
* pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_name() — 獲得 Joystick 系統名稱
* pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_numaxes() — 獲得 Joystick 操縱軸的數量
* pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_axis() — 獲得操縱軸的當前坐標
* pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_numballs() — 獲得 Joystick 上追蹤球的數量
* pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_ball() — 獲得追蹤球的相對位置
* pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_numbuttons() — 獲得 Joystick 上按鈕的數量
* pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_button() — 獲得當前按鈕狀態
* pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_numhats() — 獲得 Joystick 上帽鍵的數量
* pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_hat() — 獲得 的位置
創建一個新的 Joystick 來訪問物理設備。這個 id 的值必須在 0 到 pygame.joystick.get\_count() - 1 之間。
你需要初始化 Joystick 來調用大多數 Joystick 函數。這是獨立于 joystick 模塊的初始化。當多個 Joystick 對象在同一個物理設備上創建時(它們擁有相同的 ID 值),這些 Joystick 對象的狀態和數值將會共享。
Joystick 對象允許你獲得 Joystick 設備上控制器類型的信息。一旦這個設備從 Pygame 事件隊列初始化,它將會開始對其輸入接收事件。
你可以在未初始化 Joystick 對象時,調用 Joystick.get\_name() 和 Joystick.get\_id() 方法。
## **方法詳解**
### **pygame.joystick.Joystick.init()**
初始化 Joystick。
init() -> None
Joystick 必須被初始化來獲得大多數有關控制的信息。
當 Joystick 初始化之后,Pygame 事件隊列將獲取 Joystick 的輸入。
多次調用這個方法是安全的。
### **pygame.joystick.Joystick.quit()**
卸載 Joystick。
quit() -> None
這將卸載 Joystick。
卸載之后,Pygame 事件隊列將不再接收設備傳來的事件。
多次調用這個方法是沒問題的。
### **pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_init()**
檢查 Joystick 是否已經初始化。
get\_init() -> bool
當這個 Joystick 對象已經調用 init() 函數初始化時,將返回 True。
### **pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_id()**
獲得 Joystick 的 ID。
get\_id() -> int
返回代表這個設備的整型 ID 值。
這和傳遞到 Joystick() 構造函數的值是一樣的。
即便沒有初始化 Joystick,調用這個方法也是安全的。
### **pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_name()**
獲得 Joystick 系統的名稱。
get\_name() -> string
返回這個 Joystick 設備的系統名稱。
系統分配給 Joystick 的名稱是不確定的,但可以確保是唯一的名稱來代表這個設備。
即便沒有初始化 Joystick,調用這個方法也是安全的。
### **pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_numaxes()**
獲得 Joystick 操縱軸的數量。
get\_numaxes() -> int
返回在 Joystick 上操縱軸的數量。
一般有兩個操縱軸用來表示坐標(rudders 和 throttles 被視為附加操縱軸)。
pygame.JOYAXISMOTION 的值是從 -1. 0到 1.0。0.0 表示軸在中間。
游戲手柄通常只用 -1,0,1 三個值,并且沒有其他中間值。
舊的模擬操縱軸并不是總用完整 -1 到 1 的范圍,而是在 0 左右的值。
模擬操縱軸經常受到一些干擾的影響,這將會導致一些小而快速的移動事件。
### **pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_axis()**
獲得操縱軸的當前坐標。
get\_axis(axis\_number) -> float
獲得操縱軸的當前坐標,其值是從 -1.0 到 1.0,0 在中間。
你可能需要考慮一些額外的盈余來處理抖動,偏移值是在 0 的上下游動。
軸的數量必須是從 0 到 get\_numaxes() - 1 的數字。
### **pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_numballs()**
獲得 Joystick 上追蹤球的數量。
get\_numballs() -> int
得到 Joystick 上追蹤球的數量。
這些設備和鼠標相似,但是它沒有絕對的坐標,它只有相對移動數值。
當球轉動的時候,會發送 pygame.JOYBALLMOTION 事件,這將會報告球移動的距離。
### **pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_ball()**
獲得追蹤球的相對位置。
get\_ball(ball\_number) -> x, y
返回 Joystick 追蹤球的相對移動位置。
數值是自上次調用 get\_ball 后的相對移動數值,以 x, y 表示。
追蹤球的數量必須是從 0 到 get\_numballs() - 1 的數字。
### **pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_numbuttons()**
獲得 Joystick 上按鈕的數量。
get\_numbuttons() -> int
返回 Joystick 上按鈕的數量。
這些按鈕有一個布爾狀態(開或關)。
當按鈕被按下或抬起的時候,會產生 pygame.JOYBUTTONDOWN 和 pygame.JOYBUTTONUP 事件。
### **pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_button()**
獲得當前按鈕的狀態。
get\_button(button) -> bool
返回當前按鈕狀態。
### **pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_numhats()**
獲得 Joystick 上帽鍵的數量。
get\_numhats() -> int
返回 Joystick 上帽鍵的數量。帽鍵就像 Joystick 上的微型數碼操縱桿。每個帽鍵有兩個軸作為輸入。
當帽鍵改變坐標的時候,會產生 pygame.JOYHATMOTION 事件。事件的位置屬性包含一對數值,這些值可以是 -1,0 或1 。(0, 0) 表示帽鍵在中間。
### **pygame.joystick.Joystick.get\_hat()**
獲得 Joystick 上帽鍵的位置。
get\_hat(hat\_number) -> x, y
返回帽鍵的當前位置。
位置包含 x,y 兩個值。(0, 0) 表示在中間。-1 代表左/下,1 代表右/上。(x 對應左右, y 對應上下)。所以 (-1, 0) 代表左,(1, 0) 代表右,(0, 1) 代表上,(1, 1) 代表右上。
值只能取 -1, 0, 1 不允許其他值。
帽鍵的數量必須在 0 到 get\_numhats() - 1 之間。

示例代碼:
```
import pygame
# Define some colors
BLACK ? = ( ? 0, ? 0, ? 0)
WHITE ? = ( 255, 255, 255)
# This is a simple class that will help us print to the screen
# It has nothing to do with the joysticks, just outputting the
# information.
class TextPrint:
? def __init__(self):
? ? ? self.reset()
? ? ? self.font = pygame.font.Font(None, 20)
? def print(self, screen, textString):
? ? ? textBitmap = self.font.render(textString, True, BLACK)
? ? ? screen.blit(textBitmap, [self.x, self.y])
? ? ? self.y += self.line_height
? def reset(self):
? ? ? self.x = 10
? ? ? self.y = 10
? ? ? self.line_height = 15
? def indent(self):
? ? ? self.x += 10
? def unindent(self):
? ? ? self.x -= 10
pygame.init()
# Set the width and height of the screen [width,height]
size = [500, 700]
screen = pygame.display.set_mode(size)
pygame.display.set_caption("My Game")
#Loop until the user clicks the close button.
done = False
# Used to manage how fast the screen updates
clock = pygame.time.Clock()
# Initialize the joysticks
pygame.joystick.init()
# Get ready to print
textPrint = TextPrint()
# -------- Main Program Loop -----------
while done==False:
? # EVENT PROCESSING STEP
? for event in pygame.event.get(): # User did something
? ? ? if event.type == pygame.QUIT: # If user clicked close
? ? ? ? ? done=True # Flag that we are done so we exit this loop
? ? ? # Possible joystick actions: JOYAXISMOTION JOYBALLMOTION JOYBUTTONDOWN JOYBUTTONUP JOYHATMOTION
? ? ? if event.type == pygame.JOYBUTTONDOWN:
? ? ? ? ? print("Joystick button pressed.")
? ? ? if event.type == pygame.JOYBUTTONUP:
? ? ? ? ? print("Joystick button released.")
? # DRAWING STEP
? # First, clear the screen to white. Don't put other drawing commands
? # above this, or they will be erased with this command.
? screen.fill(WHITE)
? textPrint.reset()
? # Get count of joysticks
? joystick_count = pygame.joystick.get_count()
? textPrint.print(screen, "Number of joysticks: {}".format(joystick_count) )
? textPrint.indent()
? # For each joystick:
? for i in range(joystick_count):
? ? ? joystick = pygame.joystick.Joystick(i)
? ? ? joystick.init()
? ? ? textPrint.print(screen, "Joystick {}".format(i) )
? ? ? textPrint.indent()
? ? ? # Get the name from the OS for the controller/joystick
? ? ? name = joystick.get_name()
? ? ? textPrint.print(screen, "Joystick name: {}".format(name) )
? ? ? # Usually axis run in pairs, up/down for one, and left/right for
? ? ? # the other.
? ? ? axes = joystick.get_numaxes()
? ? ? textPrint.print(screen, "Number of axes: {}".format(axes) )
? ? ? textPrint.indent()
? ? ? for i in range( axes ):
? ? ? ? ? axis = joystick.get_axis( i )
? ? ? ? ? textPrint.print(screen, "Axis {} value: {:>6.3f}".format(i, axis) )
? ? ? textPrint.unindent()
? ? ? buttons = joystick.get_numbuttons()
? ? ? textPrint.print(screen, "Number of buttons: {}".format(buttons) )
? ? ? textPrint.indent()
? ? ? for i in range( buttons ):
? ? ? ? ? button = joystick.get_button( i )
? ? ? ? ? textPrint.print(screen, "Button {:>2} value: {}".format(i,button) )
? ? ? textPrint.unindent()
? ? ? # Hat switch. All or nothing for direction, not like joysticks.
? ? ? # Value comes back in an array.
? ? ? hats = joystick.get_numhats()
? ? ? textPrint.print(screen, "Number of hats: {}".format(hats) )
? ? ? textPrint.indent()
? ? ? for i in range( hats ):
? ? ? ? ? hat = joystick.get_hat( i )
? ? ? ? ? textPrint.print(screen, "Hat {} value: {}".format(i, str(hat)) )
? ? ? textPrint.unindent()
? ? ? textPrint.unindent()
? # ALL CODE TO DRAW SHOULD GO ABOVE THIS COMMENT
? # Go ahead and update the screen with what we've drawn.
? pygame.display.flip()
? # Limit to 20 frames per second
? clock.tick(20)
# Close the window and quit.
# If you forget this line, the program will 'hang'
# on exit if running from IDLE.
pygame.quit ()
```
- 一、Python基礎
- 1. 序言
- 1.1 Python簡介
- 1.2 安裝和使用IDE
- 1.3 語言特性和基礎概念
- 2. 基本數據類型
- 2.2 字符串型
- 2.2.2 ASCII簡介
- 2.2.4 字符串常用函數
- 3. 條件分支
- 3.3 閑聊條件判斷和運算符優先級
- 10.正則表達式
- 【降龍十八章】Python小技巧
- 18.1 學習網址
- 18.2 PIP切換源
- 18.3 使用whl來安裝
- 【工具優化】IDE優化技巧
- Anaconda
- Jupyter Notebook 的 Markdown 添加大綱
- Jupyter Notebook中圖片縮放和居左
- Anaconda設置環境變量
- Pycharm
- PyCharm新建文檔配置
- 設置字體和字號
- 設置主題和字體配色
- 保存和導入配置
- 設置對選擇內容自動添加引號
- 推薦安裝的插件
- Markdown
- 表格格式
- 二、Python進階
- copy和deepcopy
- 《零基礎入門學習 Python 》【小甲魚版】
- 001.和Python的第一次接觸+習題復習
- 002.用Python設計的第一個游戲 +習題復習
- Pygame詳解
- Pygame詳解:前言
- Pygame詳解(一):Color類
- Pygame詳解(二):display 模塊
- Pygame詳解(三):draw 模塊
- Pygame詳解(四):event 模塊
- Pygame詳解(五):font 模塊
- Pygame詳解(六):image 模塊
- Pygame詳解(七):key 模塊
- Pygame詳解(八):locals 模塊
- Pygame詳解(九):mixer 模塊
- Pygame詳解(十):mouse 模塊
- Pygame詳解(十一):Rect 對象
- Pygame詳解(十二):Surface 對象
- Pygame詳解(十三):time 模塊
- Pygame詳解(十四):music 模塊
- Pygame詳解(十五):pygame 模塊
- Pygame詳解(十六):cursors 模塊
- Pygame詳解(十七):joystick 模塊
- Pygame詳解(十八):mask 模塊
- Pygame詳解(二十一):BufferProxy 對象
- Pygame詳解(二十三):gfxdraw 模塊
- Pygame詳解(二十五):Overlay 對象
- Pygame詳解(二十八):sndarray 模塊
- Pygame詳解(三十一):camera 模塊
- Pygame詳解(三十二):cdrom 模塊
- Pygame詳解(三十六):version 模塊
- pygame rect相關知識
- Tkinter詳解
- Tkinter 組件詳解(一):Label
- Tkinter 組件詳解(二):Button
