[TOC]
*****
# 1\. Matplotlib
[Matplotlib官網](https://matplotlib.org/)
matplotlib是PYTHON繪圖的基礎庫,是模仿matlab繪圖工具開發的一個開源庫。 PYTHON其它第三方繪圖庫都依賴與matplotlib。 本節課我們重點學習三種繪圖方式:
1. matplotlib繪制基礎圖形
2. pandas plot API
3. seaborn繪制統計圖形
我們可視化課程的重點是利用圖形去理解數據,而不是注重圖形的美觀。因此本課程講解的圖形都是基于數據統計分析的簡單圖形,類似于雷達圖這樣的復雜圖形不會在課程中講解。
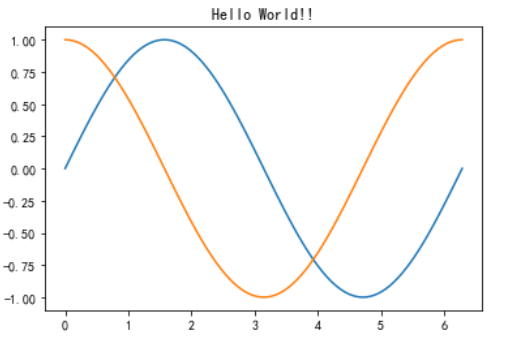
# 2\. Hello World
```
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] #用來正常顯示中文標簽
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False #用來正常顯示負號
#生成0到2pi的100個值,均等劃分,最后放到X的數組里
X = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi,100)# 均勻的劃分數據
#根據正弦函數生成100個值放在Y數組里
Y = np.sin(X)
Y1 = np.cos(X)
#在plt的空白畫布上添加標題
plt.title("Hello World!!")
#在畫布上描繪100個點
plt.plot(X,Y)
#在畫布上描繪100個點
plt.plot(X,Y1)
#顯示plt畫布
plt.show()
```
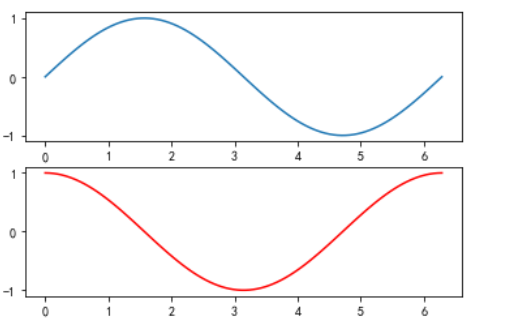
```
X = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi,100)
Y = np.sin(X)
#將畫布分成兩部分,分別繪制兩個圖,第一部分
plt.subplot(211) # 等價于 subplot(2,1,1)
plt.plot(X,Y)
#將畫布分成兩部分,分別繪制兩個圖,第二部分
plt.subplot(212)
#圖形顏色是紅色,Y值根據X數組值計算
plt.plot(X,np.cos(X),color = 'r')
```
*****
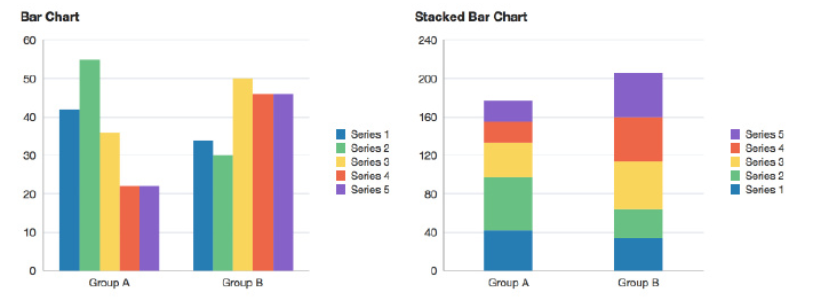
# 3\. BAR CHART 條形圖
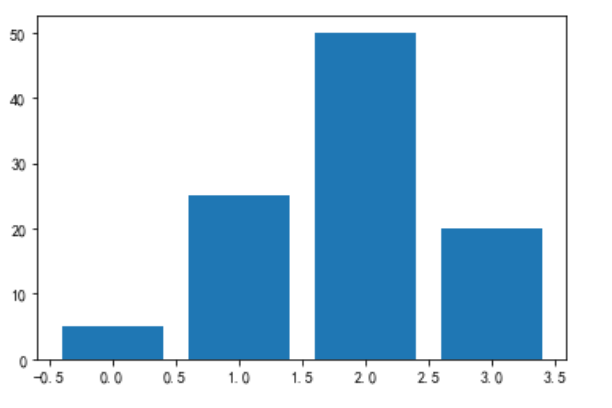
### 3.0.1. Verticle 垂直的
```
#列表
data = [5,25,50,20]
# 第一個參數列表是幾個條形的x坐標,data是幾個條形的y坐標
plt.bar(range(len(data)),data)
```
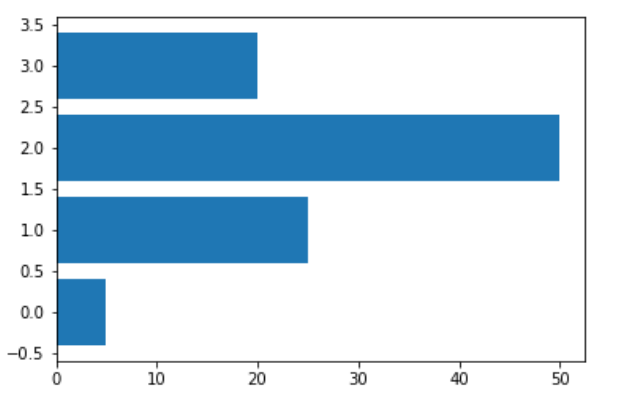
### 3.0.2. Horizontal 水平的
```
data = [5,25,50,20]
#barh()表示繪制水平的條形圖。第一個參數列表是幾個條形的y坐標,data是幾個條形的x坐標
plt.barh(range(len(data)),data)
```
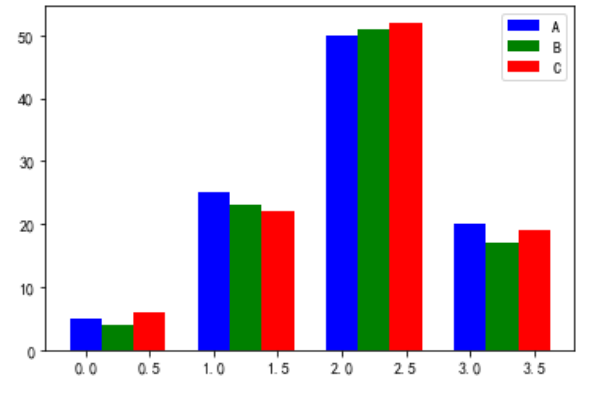
### 3.0.3. 多個bar
```
# 有三組分類變量的條形圖 data是它們的頻數列表
data = [[5,25,50,20],
[4,23,51,17],
[6,22,52,19]]
X = np.arange(4)
# label 標簽 標注
#寬度:width = 0.25 。 label = "A" 這個分類變量的名字是A
plt.bar(X + 0.00, data[0], color = 'b', width = 0.25,label = "A")
# 第二組條形圖緊挨著第一組,x坐標右移一個第一變量的寬度
plt.bar(X + 0.25, data[1], color = 'g', width = 0.25,label = "B")
# 第三組條形圖緊挨著第二組
plt.bar(X + 0.50, data[2], color = 'r', width = 0.25,label = "C")
# legend 圖例 圖示 調用legend()才會顯示分類變量標注
plt.legend()
```
*****
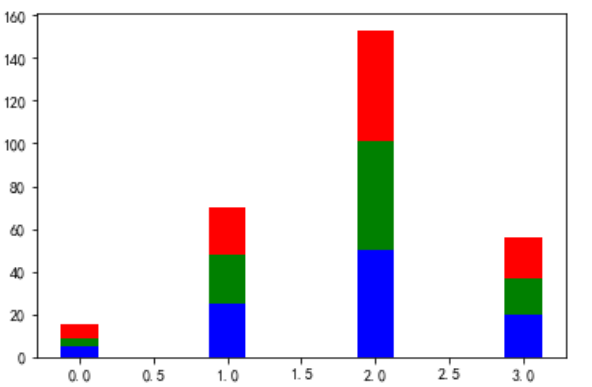
### 3.0.4. Stacked 堆
```
data = [[5,25,50,20],
[4,23,51,17],
[6,22,52,19]]
X = np.arange(4)
#三組分類變量的x坐標都相同,因為要堆疊起來
plt.bar(X, data[0], color = 'b', width = 0.25)
# bottom = data[0] 第二組條形的底部是在第一組條形的高度
plt.bar(X, data[1], color = 'g', width = 0.25,bottom = data[0])
# 第三組條形的底部是(第一組條形的高度+第二組條形的高度)
# 兩個列表的元素不能一一對應相加,先用np.array()把列表變為數組,數組可以元素上對應相加
plt.bar(X, data[2], color = 'r', width = 0.25,bottom = np.array(data[0]) + np.array(data[1]))
plt.show()
```
*****
# SCATTER POINTS 散點圖
散點圖用來衡量兩個連續變量之間的相關性
```
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
N = 50
#生成50個[0,1)之間的值
x = np.random.rand(N)
y = np.random.rand(N)
plt.scatter(x, y)
```
*****
```
N = 50
x = np.random.rand(N)
y = np.random.rand(N)
#生成的數值序列表示顏色
colors = np.random.randn(N)
#生成表示點面積大小的數值序列
area = np.pi * (15 * np.random.rand(N))**2 # 調整大小
# alpha是透明度
plt.scatter(x, y, c=colors, alpha=0.5, s = area)
```
*****
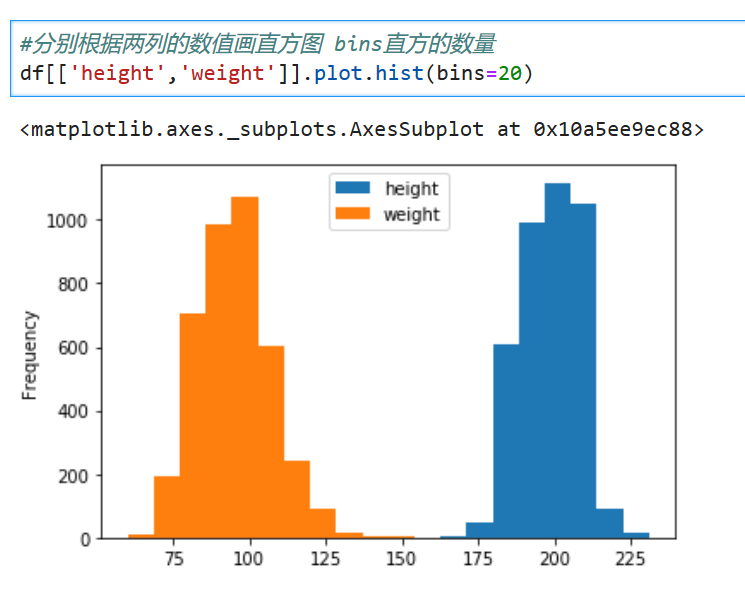
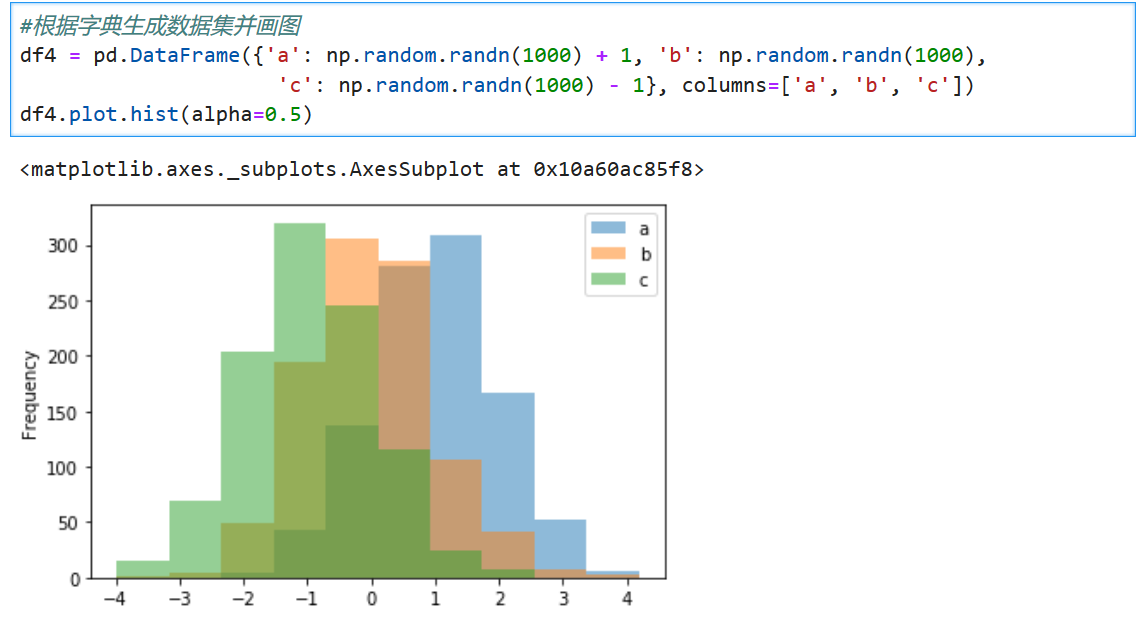
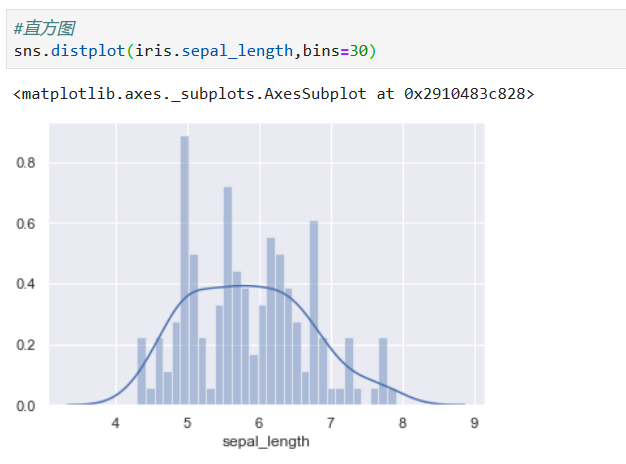
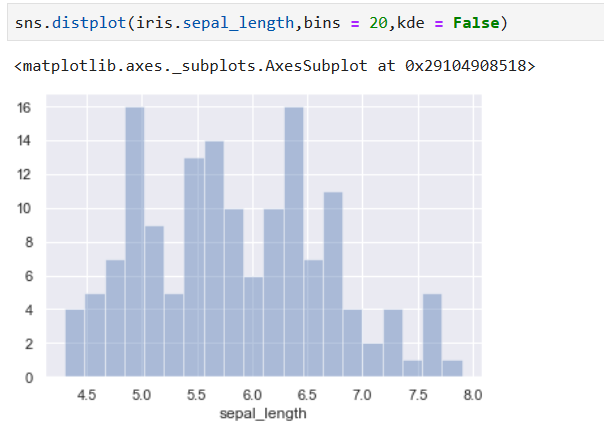
# Histogram
**解釋:直方圖是用來衡量連續變量的概率分布的。在構建直方圖之前,我們需要先定義好bin(值的范圍),也就是說我們需要先把連續值劃分成不同等份,然后計算每一份里面數據的數量。**
*****
```
a = np.random.rand(100)
#bins將數據值劃為20份
plt.hist(a,bins= 20)
#設置直方的高度在0到15之間
plt.ylim(0,15)
```
*****
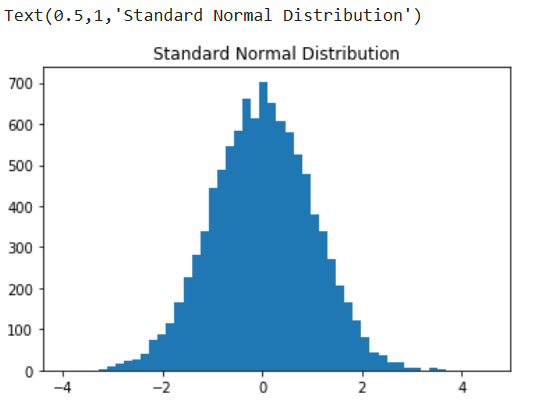
```
a = np.random.randn(10000)
plt.hist(a,bins=50)
plt.title("Standard Normal Distribution")
```
*****
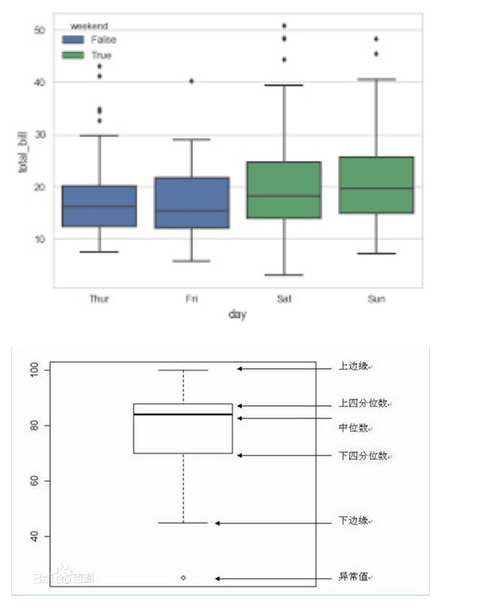
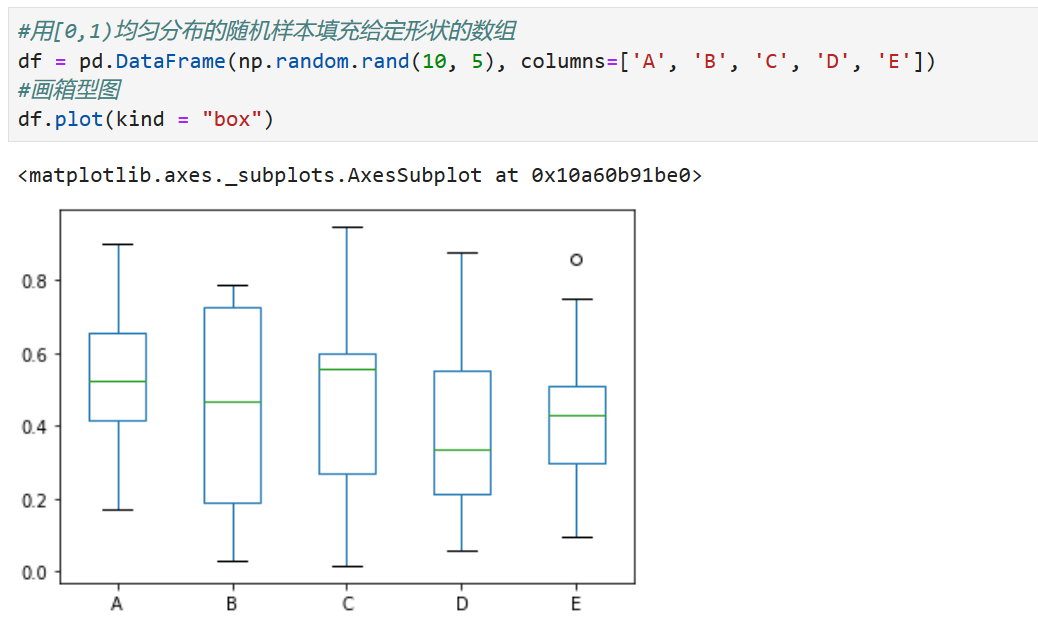
# BOXPLOTS 箱型圖
boxlot用于表達連續特征的百分位數分布。統計學上經常被用于檢測單變量的異常值,或者用于檢查離散特征和連續特征的關系
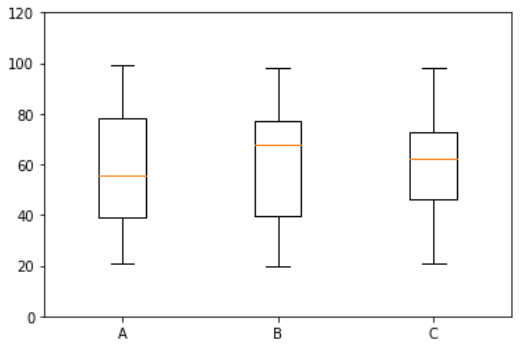
```
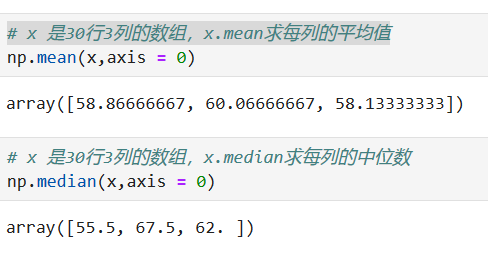
#生成20到100的整數,并且是30行3列的數組
x = np.random.randint(20,100,size = (30,3))
#根據三列數據會繪制出三個箱型圖
plt.boxplot(x)
#y軸取值是0到120
plt.ylim(0,120)
# x軸上標記是1,2,3。標記的標簽是A,B,c,如圖
plt.xticks([1,2,3],['A','B','C'])
#plt.hlines是畫一條橫線,y值是第一個參數,從xmin畫到xmanx
plt.hlines(y = np.mean(x,axis = 0)[1] ,xmin =0,xmax=3)
```
*****
*****
# COLORS/TEXTS/annotate

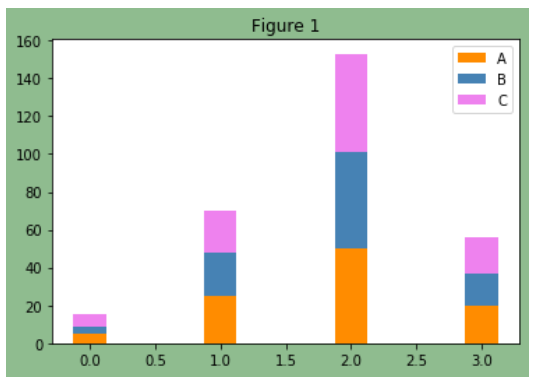
```
#設置畫布背景顏色為darkseagreen
fig, ax = plt.subplots(facecolor='darkseagreen')
data = [[5,25,50,20],
[4,23,51,17],
[6,22,52,19]]
#返回給定值內的均勻間隔值
X = np.arange(4)
plt.bar(X, data[0], color = 'darkorange', width = 0.25,label = 'A',bottom= 0)
plt.bar(X, data[1], color = 'steelblue', width = 0.25,bottom = data[0],label = 'B')
plt.bar(X, data[2], color = 'violet', width = 0.25,bottom = np.array(data[0]) + np.array(data[1]),label = 'C')
#設置圖像title
ax.set_title("Figure 1")
#顯示條形圖標注
plt.legend()
```
*****
**zip方法**

*****
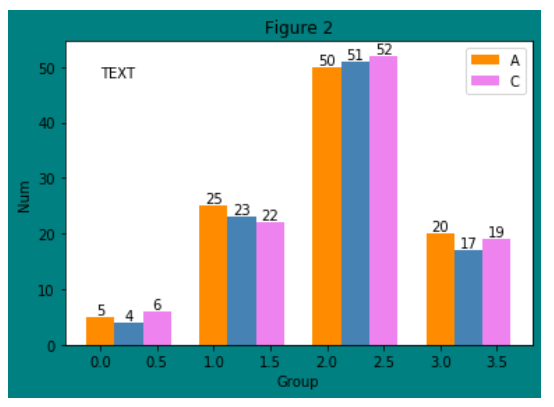
增加文字
~~~python
plt.text(x, y, s, fontdict=None, withdash=False, **kwargs)
~~~
```
fig, ax = plt.subplots(facecolor='teal')
data = [[5,25,50,20],
[4,23,51,17],
[6,22,52,19]]
X = np.arange(4)
plt.bar(X+0.00, data[0], color = 'darkorange', width = 0.25,label = 'A')
plt.bar(X+0.25, data[1], color = 'steelblue', width = 0.25)
plt.bar(X+0.50, data[2], color = 'violet', width = 0.25,label = 'C')
ax.set_title("Figure 2")
plt.legend()
# 添加文字描述
W = [0.00,0.25,0.50]
for i in range(3):
for a,b in zip(X+W[i],data[i]):
plt.text(a,b,"%.0f"% b,ha="center",va= "bottom")
plt.xlabel("Group")
plt.ylabel("Num")
plt.text(0.0,48,"TEXT")
```
*****
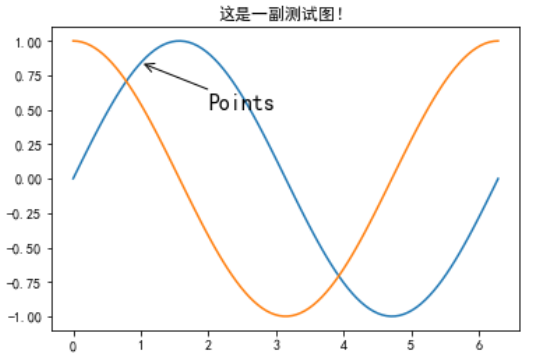
在數據可視化的過程中,圖片中的文字經常被用來注釋圖中的一些特征。使用annotate()方法可以很方便地添加此類注釋。在使用annotate時,要考慮兩個點的坐標:被注釋的地方xy(x, y)和插入文本的地方xytext(x, y)
```
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] #用來正常顯示中文標簽
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False #用來正常顯示負號
X = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi,100)# 均勻的劃分數據
Y = np.sin(X)
Y1 = np.cos(X)
plt.plot(X,Y)
plt.plot(X,Y1)
plt.annotate('Points',
#要注釋的地方
xy=(1, np.sin(1)),
# 文本的地方
xytext=(2, 0.5), fontsize=16,
#注釋的地方和文本產生聯系的符號
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->"))
plt.title("這是一副測試圖!")
```
*****
# Subplots
~~~python
matplotlib.pyplot.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=1, sharex=False, sharey=False, squeeze=True, subplot_kw=None, gridspec_kw=None, **fig_kw)
~~~
使用 **subplot** 繪制多個圖形
~~~python
subplot(nrows, ncols, index, **kwargs)
~~~
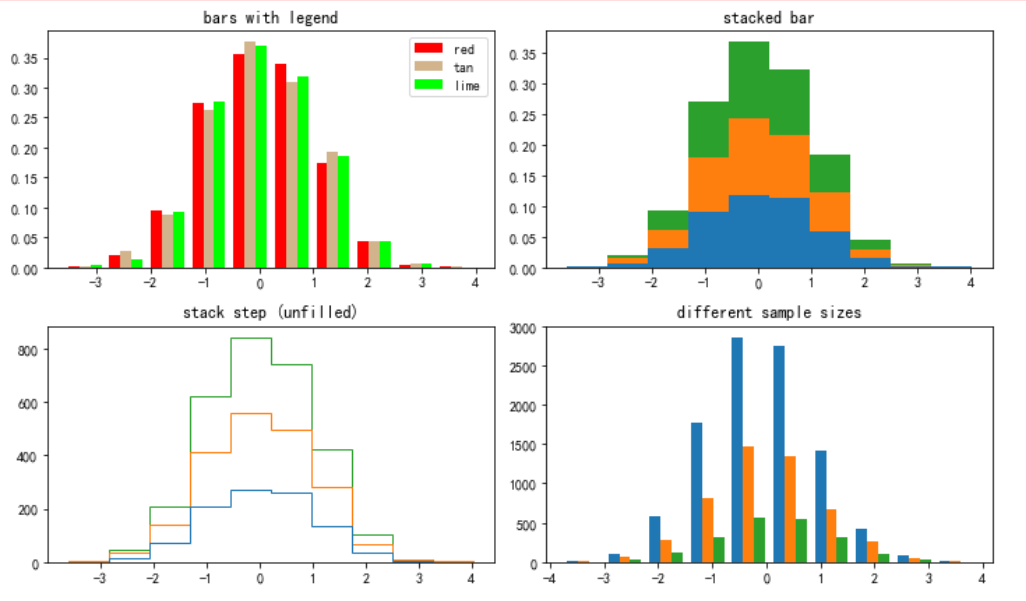
```
#在jupyter lab里調整圖片大小
%pylab inline
pylab.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (10, 6) # 調整圖片大小
np.random.seed(19680801)
#直方圖圖形份數
n_bins = 10
# 數據為1000行*3列
x = np.random.randn(1000, 3)
#將畫布橫的分成兩部分,縱軸分為兩部分,共分為4部分。放在數組中
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2,facecolor='white')
#將數組一維化,并將四個部分按索引順序儲存在變量中
ax0, ax1, ax2, ax3 = axes.flatten()
colors = ['red', 'tan', 'lime']
ax0.hist(x, n_bins, normed=1, histtype='bar', color=colors, label=colors)
ax0.legend(prop={'size': 10})
ax0.set_title('bars with legend')
ax1.hist(x, n_bins, normed=1, histtype='bar', stacked=True)
ax1.set_title('stacked bar')
ax2.hist(x, n_bins, histtype='step', stacked=True, fill=False)
ax2.set_title('stack step (unfilled)')
# Make a multiple-histogram of data-sets with different length.
x_multi = [np.random.randn(n) for n in [10000, 5000, 2000]]
ax3.hist(x_multi, n_bins, histtype='bar')
ax3.set_title('different sample sizes')
fig.tight_layout() # Adjust subplot parameters to give specified padding.
plt.show()
```
*****
**兩部分圖共享X軸或Y軸**
```
# ShareX or ShareY
N_points = 100000
n_bins = 20
#產生一個標準正態分布
# Generate a normal distribution, center at x=0 and y=5
x = np.random.randn(N_points)
y = .4 * x + np.random.randn(100000) + 5
#將畫布豎著分為兩部分,共享y軸
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, sharey=True, tight_layout=True)
# We can set the number of bins with the `bins` kwarg
axs[0].hist(x, bins=n_bins)
axs[1].hist(y, bins=n_bins)
```
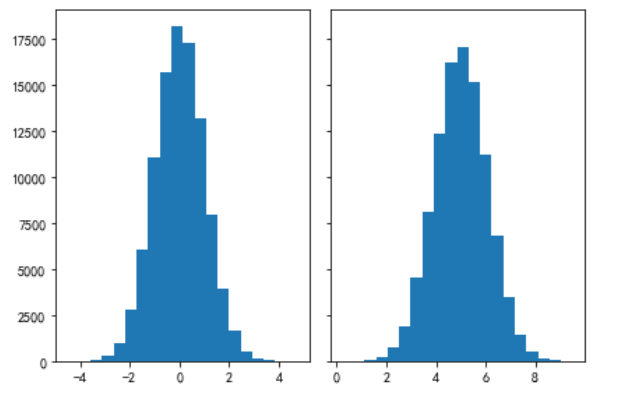
*****
# PANDAS API
利用pandas API畫圖
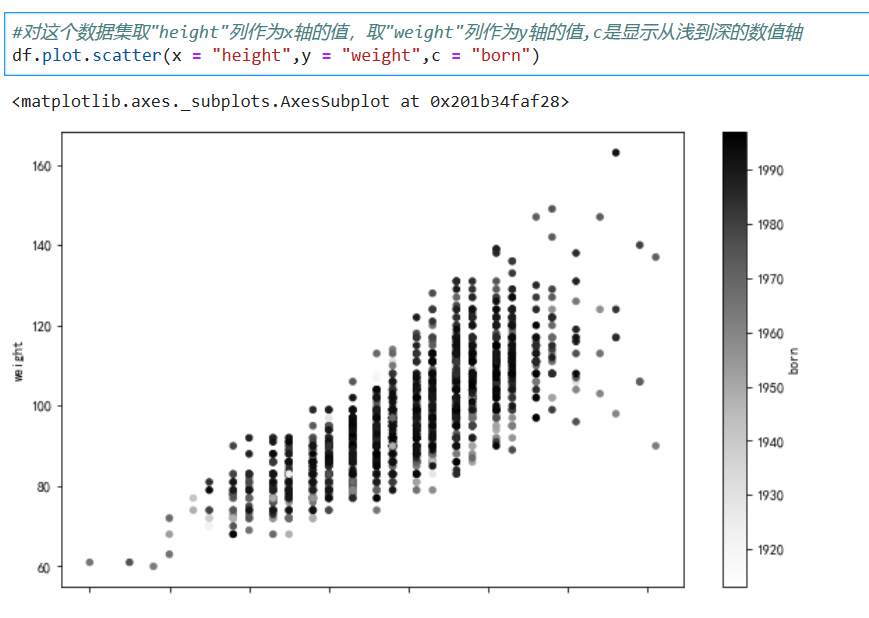
*****
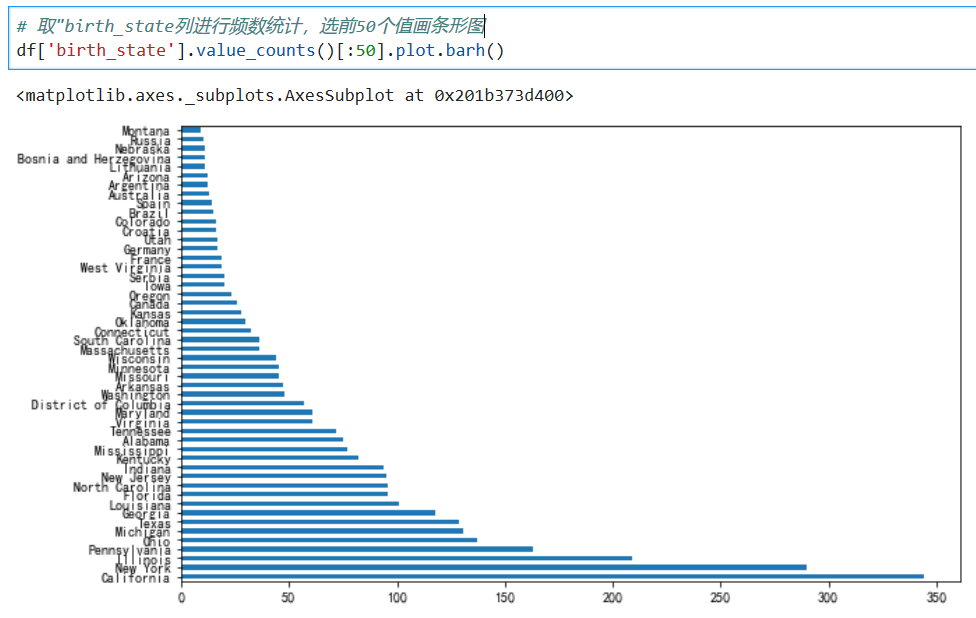
*****
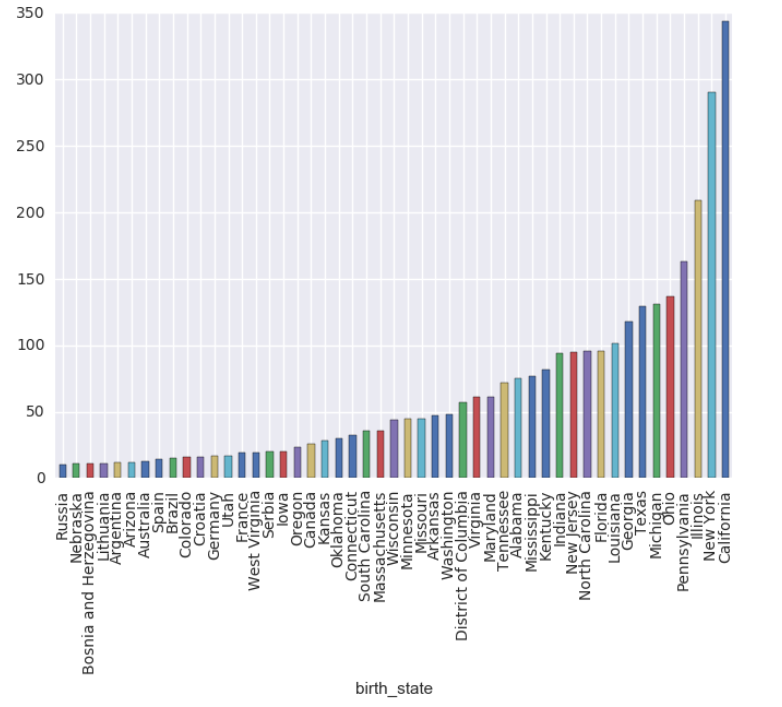
```
#按值分組
grouped = df.groupby("birth_state")
#每個分組行的數量
gs = grouped.size()
#大于10的組排序 并畫條形圖
gs[gs >=10].sort_values().plot.bar()
```
*****
*****
*****
*****
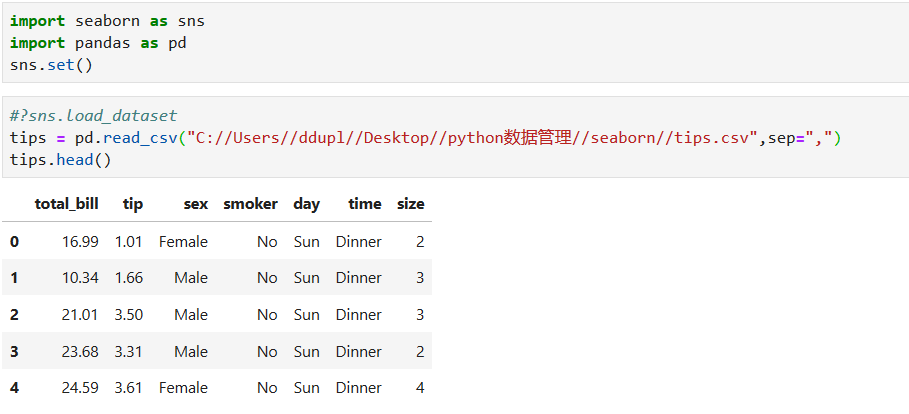
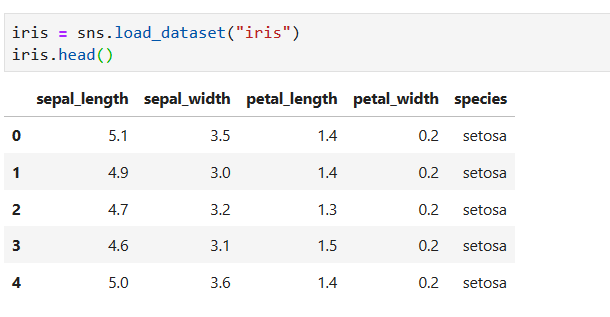
# Sseaborn: statistical data visualization
## Visualizing the distribution of a dataset
*****
*****
*****
*****
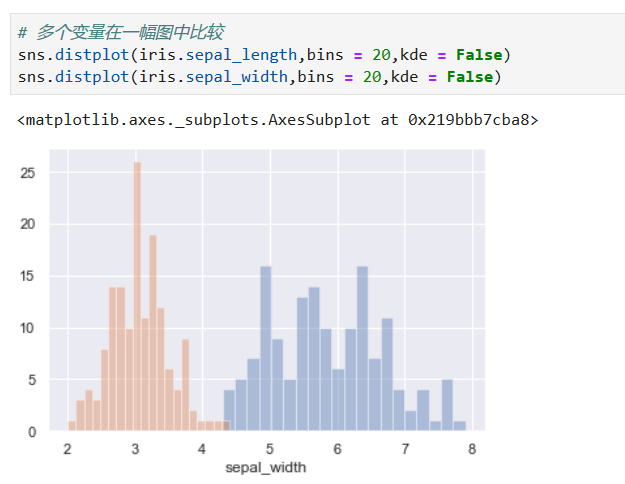
*****
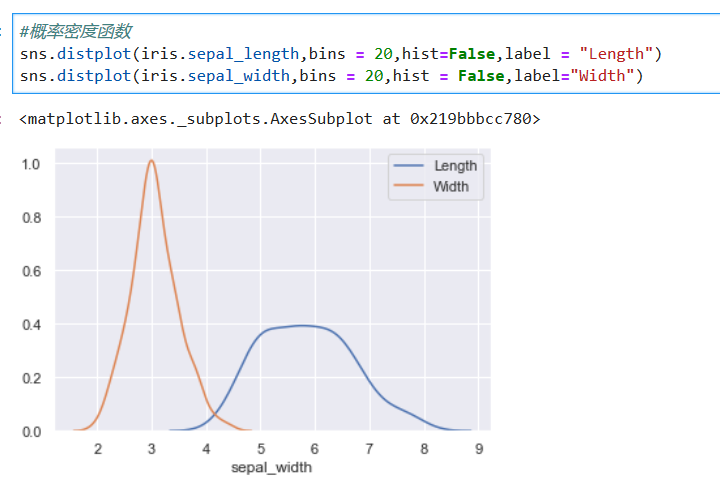
*****
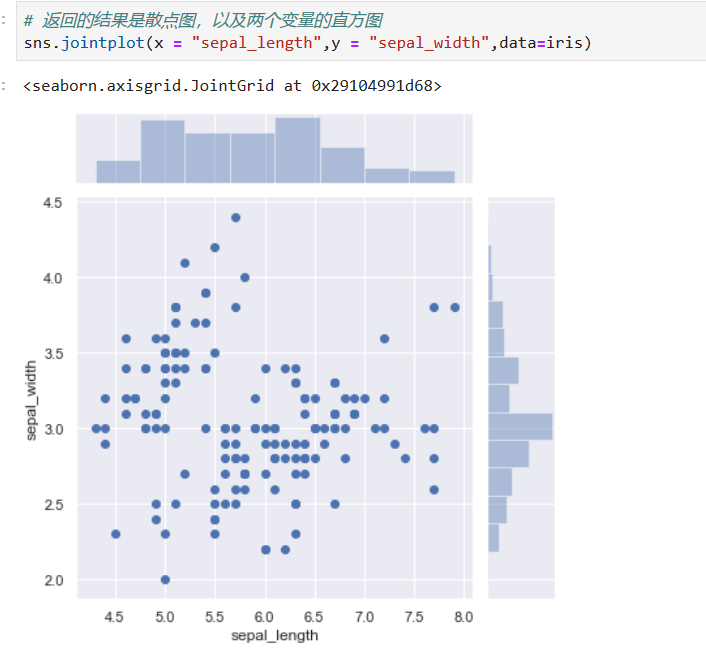
### Plotting bivariate distributions 繪制雙變量分布
*****
*****
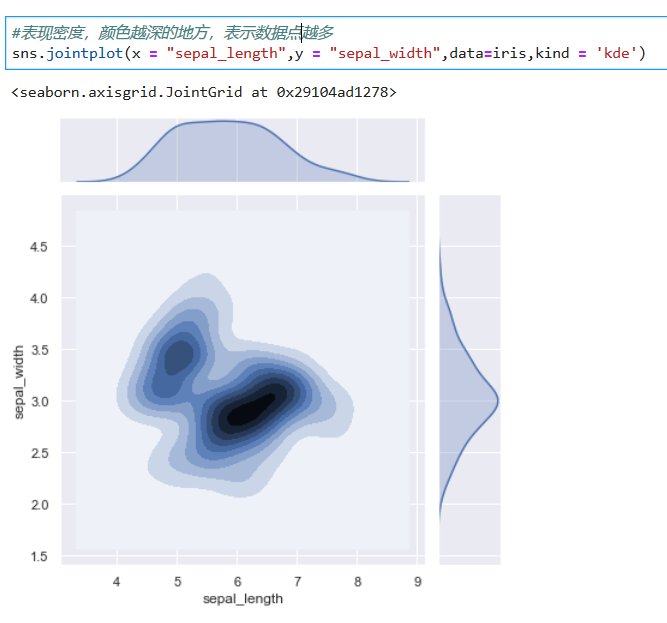
*****
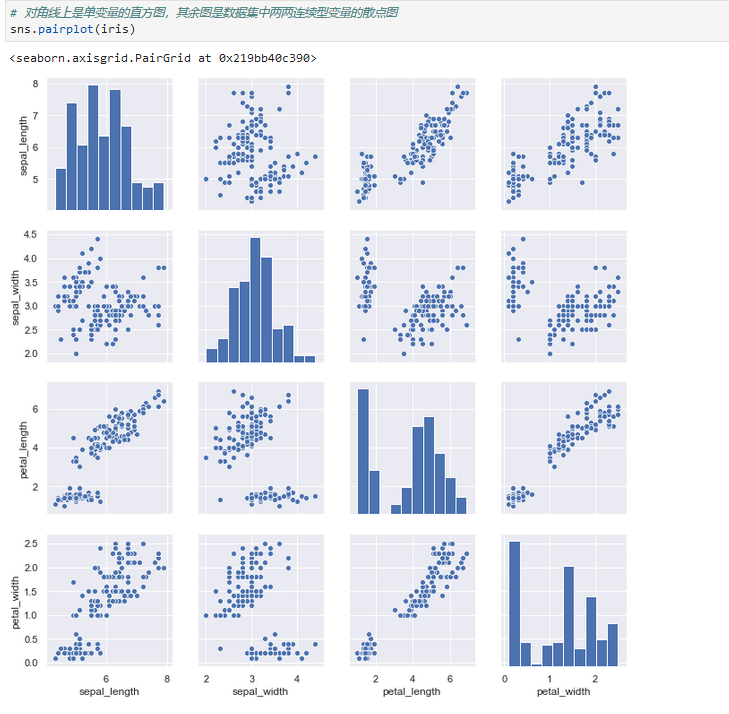
### Visualizing pairwise relationships in a dataset
可視化數據集中的成對關系
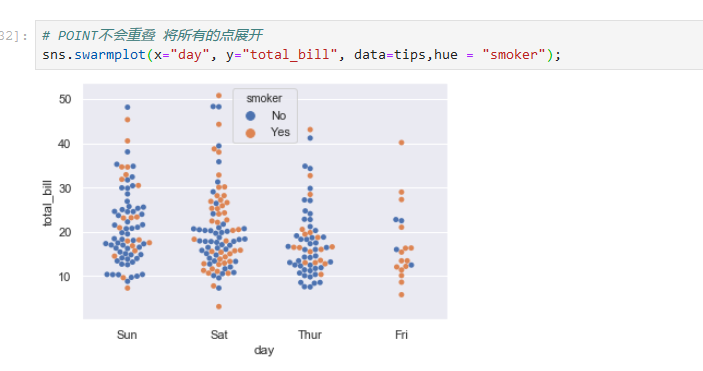
*****

*****
*****
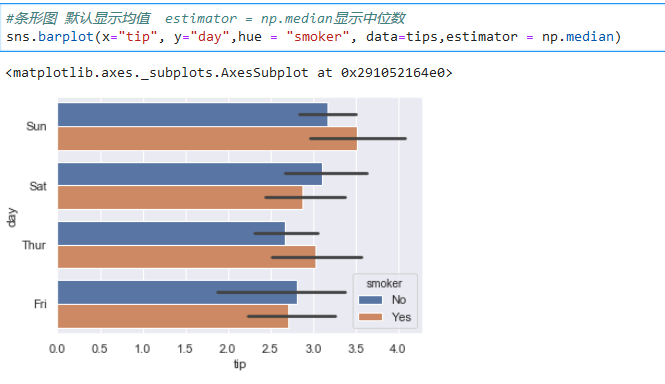
*****
## Visualizing linear relationships
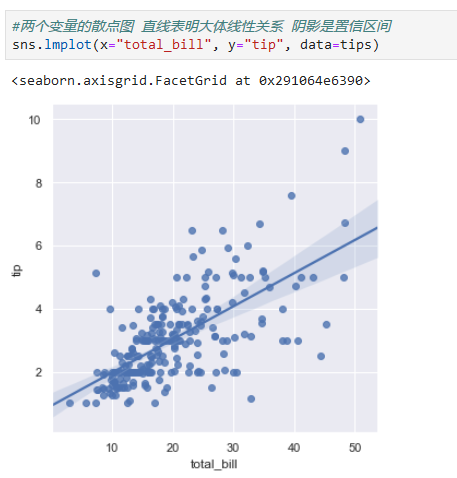
*****
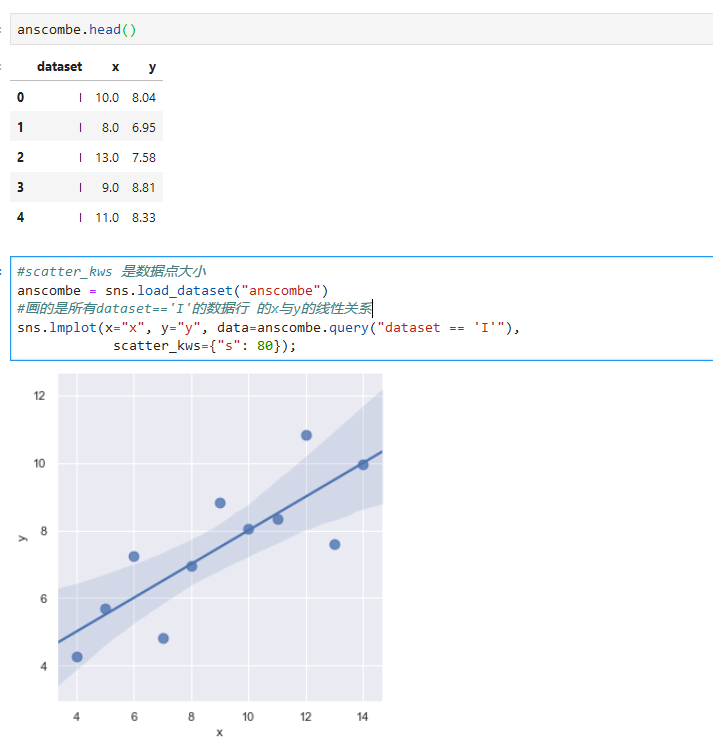
*****
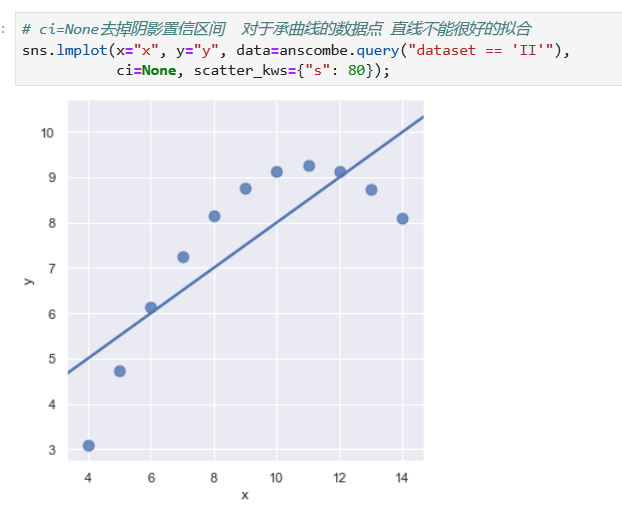
*****
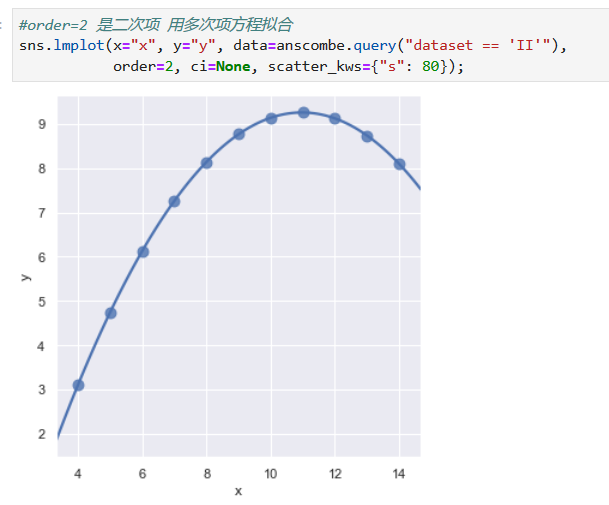
*****
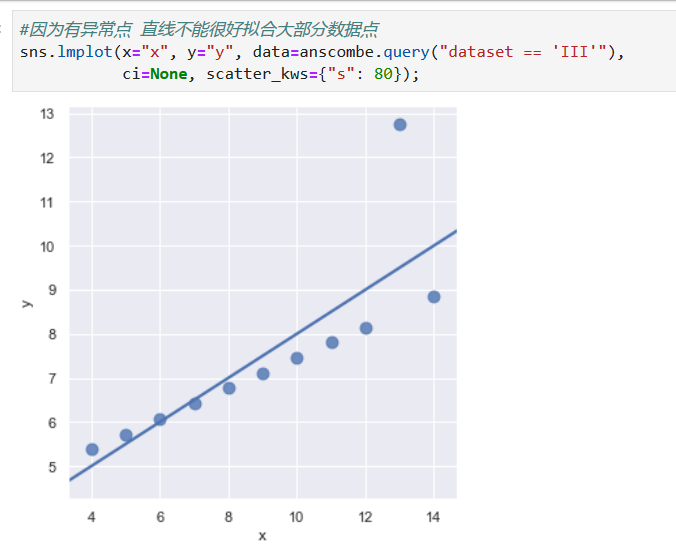
*****
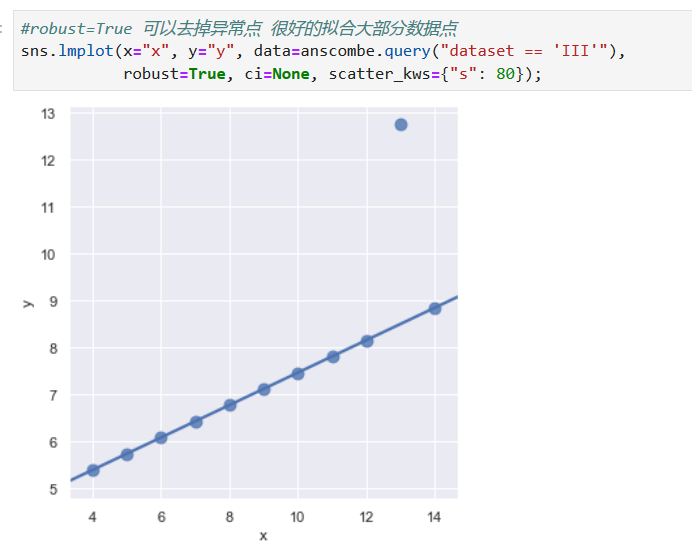
*****
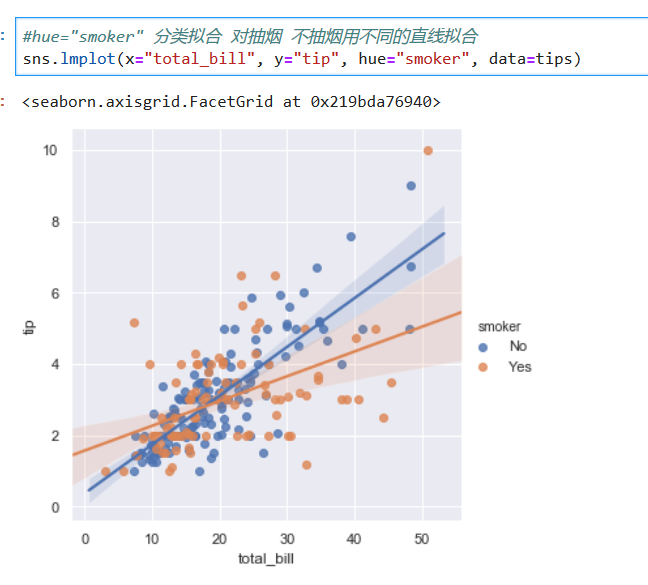
- 第五節 Pandas數據管理
- 1.1 文件讀取
- 1.2 DataFrame 與 Series
- 1.3 常用操作
- 1.4 Missing value
- 1.5 文本數據
- 1.6 分類數據
- 第六節 pandas數據分析
- 2.1 索引選取
- 2.2. 分組計算
- 2.3. 表聯結
- 2.4. 數據透視與重塑(pivot table and reshape)
- 2.5 官方小結圖片
- 第七節 NUMPY科學計算
- 第八節 python可視化
- 第九節 統計學
- 01 單變量
- 02 雙變量
- 03 數值方法
- 第十節 概率
- 01 概率
- 02 離散概率分布
- 03 連續概率分布
- 第一節 抽樣與抽樣分布
- 01抽樣
- 02 點估計
- 03 抽樣分布
- 04 抽樣分布的性質
- 第十三節 區間估計
- 01總體均值的區間估計:??已知
- 02總體均值的區間估計:??未知
- 03總體容量的確定
- 04 總體比率
