# 一致性哈希負載均衡算法的探討
### 前言
一致性哈希算法在很多領域有應用,例如分布式緩存領域的 MemCache,Redis,負載均衡領域的 Nginx,各類 RPC 框架。不同領域場景不同,需要顧及的因素也有所差異,本文主要討論在**負載均衡**中一致性哈希算法的設計。
在介紹一致性哈希算法之前,我將會介紹一些哈希算法,討論它們的區別和使用場景。也會給出一致性哈希算法的 Java 通用實現,可以直接引用,文末會給出 github 地址。
> 友情提示:閱讀本文前,最好對一致性哈希算法有所了解,例如你最好聽過一致性哈希環這個概念,我會在基本概念上縮短篇幅。
### [](https://www.cnkirito.moe/consistent-hash-lb/#%E4%B8%80%E8%87%B4%E6%80%A7%E5%93%88%E5%B8%8C%E8%B4%9F%E8%BD%BD%E5%9D%87%E8%A1%A1%E4%BB%8B%E7%BB%8D "一致性哈希負載均衡介紹")一致性哈希負載均衡介紹
負載均衡這個概念可以抽象為:從 n 個候選服務器中選擇一個進行通信的過程。負載均衡算法有多種多樣的實現方式:隨機、輪詢、最小負載優先等,其中也包括了今天的主角:一致性哈希負載均衡。一致性哈希負載均衡需要保證的是“相同的請求盡可能落到同一個服務器上”,注意這短短的一句描述,卻包含了相當大的信息量。“相同的請求” — 什么是相同的請求?一般在使用一致性哈希負載均衡時,需要指定一個 key 用于 hash 計算,可能是:
1. 請求方 IP
2. 請求服務名稱,參數列表構成的串
3. 用戶 ID
“盡可能” —為什么不是一定?因為服務器可能發生上下線,所以少數服務器的變化不應該影響大多數的請求。這也呼應了算法名稱中的“一致性”。
同時,一個優秀的負載均衡算法還有一個隱性要求:流量盡可能均勻分布。
綜上所述,我們可以概括出一致性哈希負載均衡算法的設計思路。
* 盡可能保證每個服務器節點均勻的分攤流量
* 盡可能保證服務器節點的上下線不影響流量的變更
### [](https://www.cnkirito.moe/consistent-hash-lb/#%E5%93%88%E5%B8%8C%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95%E4%BB%8B%E7%BB%8D "哈希算法介紹")哈希算法介紹
哈希算法是一致性哈希算法中重要的一個組成部分,你可以借助 Java 中的`int hashCode()`去理解它。 說到哈希算法,你想到了什么?Jdk 中的 hashCode、SHA-1、MD5,除了這些耳熟能詳的哈希算法,還存在很多其他實現,詳見[HASH 算法一覽](https://www.oschina.net/translate/state-of-hash-functions)。可以將他們分成三代:
* 第一代:SHA-1(1993),MD5(1992),CRC(1975),Lookup3(2006)
* 第二代:MurmurHash(2008)
* 第三代:CityHash, SpookyHash(2011)
這些都可以認為是廣義上的哈希算法,你可以在[wiki 百科](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_hash_functions)中查看所有的哈希算法。當然還有一些哈希算法如:Ketama,專門為一致性哈希算法而設計。
既然有這么多哈希算法,那必然會有人問:當我們在討論哈希算法時,我們再考慮哪些東西?我大概總結下有以下四點:
1. 實現復雜程度
2. 分布均勻程度
3. 哈希碰撞概率
4. 性能
先聊聊性能,是不是性能越高就越好呢?你如果有看過我曾經的文章[《該如何設計你的 PasswordEncoder?》](https://www.cnkirito.moe/spring-security-6/),應該能了解到,在設計加密器這個場景下,慢 hash 算法反而有優勢;而在負載均衡這個場景下,安全性不是需要考慮的因素,所以性能自然是越高越好。
優秀的算法通常比較復雜,但不足以構成評價標準,有點黑貓白貓論,所以 2,3 兩點:分布均勻程度,哈希碰撞概率成了主要考慮的因素。
我挑選了幾個值得介紹的哈希算法,重點介紹下。
1. MurmurHash 算法:高運算性能,低碰撞率,由 Austin Appleby 創建于 2008 年,現已應用到 Hadoop、libstdc++、nginx、libmemcached 等開源系統。2011 年 Appleby 被 Google 雇傭,隨后 Google 推出其變種的 CityHash 算法。官方只提供了 C 語言的實現版本。
Java 界中 Redis,Memcached,Cassandra,HBase,Lucene 都在使用它。
在 Java 的實現,Guava 的 Hashing 類里有,上面提到的 Jedis,Cassandra 里都有相關的 Util 類。
2. FNV 算法:全名為 Fowler-Noll-Vo 算法,是以三位發明人 Glenn Fowler,Landon Curt Noll,Phong Vo 的名字來命名的,最早在 1991 年提出。
特點和用途:FNV 能快速 hash 大量數據并保持較小的沖突率,它的高度分散使它適用于 hash 一些非常相近的字符串,比如 URL,hostname,文件名,text,IP 地址等。
3. Ketama 算法:將它稱之為哈希算法其實不太準確,稱之為一致性哈希算法可能更為合適,其他的哈希算法有通用的一致性哈希算法實現,只不過是替換了哈希方式而已,但 Ketama 是一整套的流程,我們將在后面介紹。
以上三者都是最合適的一致性哈希算法的強力爭奪者。
### [](https://www.cnkirito.moe/consistent-hash-lb/#%E4%B8%80%E8%87%B4%E6%80%A7%E5%93%88%E5%B8%8C%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95%E5%AE%9E%E7%8E%B0 "一致性哈希算法實現")一致性哈希算法實現
[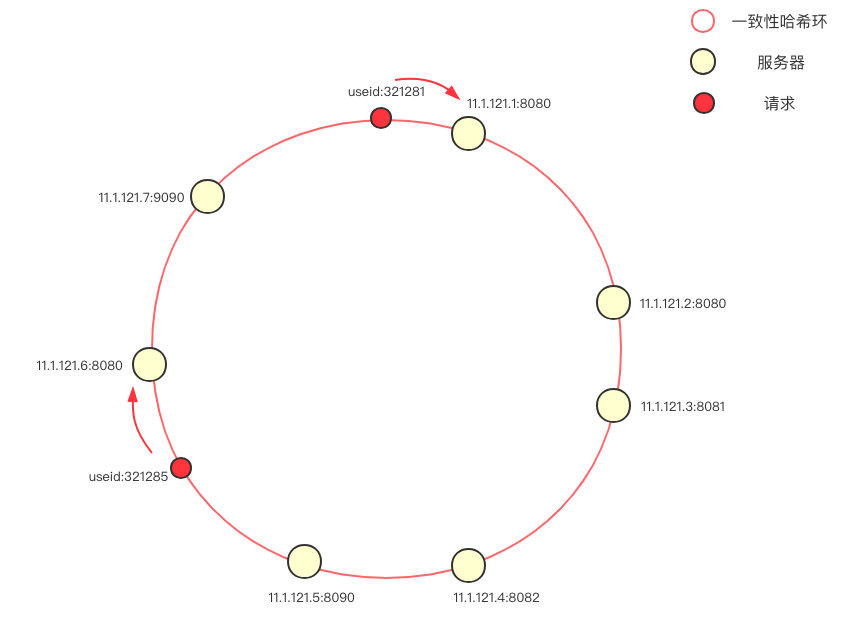](https://kirito.iocoder.cn/168f69205ef99590?w=861&h=635&f=png&s=59703 "一致性 hash")一致性 hash
一致性哈希的概念我不做贅述,簡單介紹下這個負載均衡中的一致性哈希環。首先將服務器(ip+ 端口號)進行哈希,映射成環上的一個節點,在請求到來時,根據指定的 hash key 同樣映射到環上,并順時針選取最近的一個服務器節點進行請求(在本圖中,使用的是 userId 作為 hash key)。
當環上的服務器較少時,即使哈希算法選擇得當,依舊會遇到大量請求落到同一個節點的問題,為避免這樣的問題,大多數一致性哈希算法的實現度引入了虛擬節點的概念。
[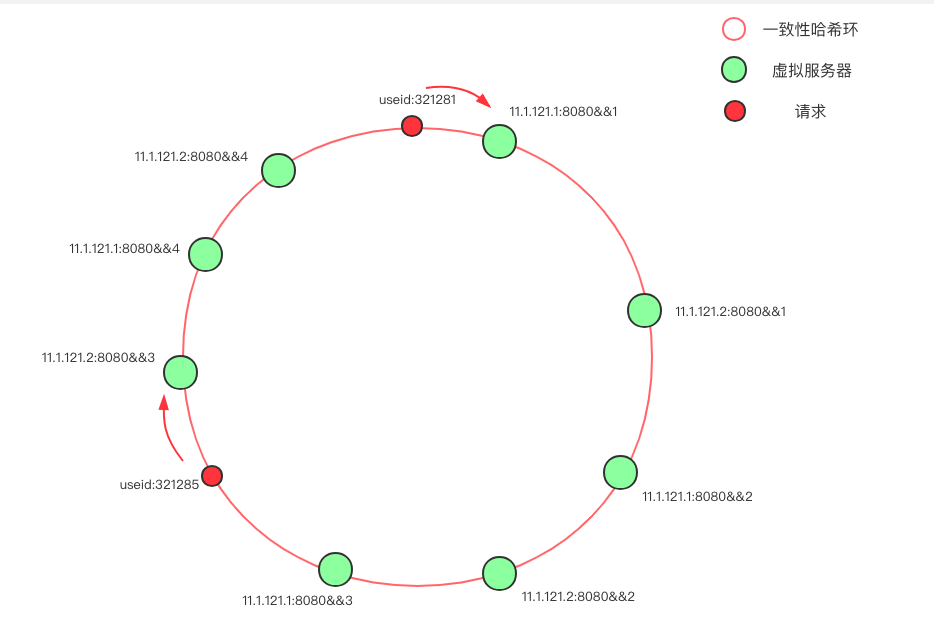](https://kirito.iocoder.cn/168f6921775875f4%3Fw=934&h=639&f=png&s=67921.png "一致性 hash 虛擬節點")一致性 hash 虛擬節點
在上圖中,只有兩臺物理服務器節點:11.1.121.1 和 11.1.121.2,我們通過添加后綴的方式,克隆出了另外三份節點,使得環上的節點分布的均勻。一般來說,物理節點越多,所需的虛擬節點就越少。
介紹完了一致性哈希換,我們便可以對負載均衡進行建模了:
```
public interface LoadBalancer {
Server select(List<Server> servers, Invocation invocation);
}
```
下面直接給出通用的算法實現:
```
public class ConsistentHashLoadBalancer implements LoadBalancer{
private HashStrategy hashStrategy = new JdkHashCodeStrategy();
private final static int VIRTUAL_NODE_SIZE = 10;
private final static String VIRTUAL_NODE_SUFFIX = "&&";
@Override
public Server select(List<Server> servers, Invocation invocation) {
int invocationHashCode = hashStrategy.getHashCode(invocation.getHashKey());
TreeMap<Integer, Server> ring = buildConsistentHashRing(servers);
Server server = locate(ring, invocationHashCode);
return server;
}
private Server locate(TreeMap<Integer, Server> ring, int invocationHashCode) {
// 向右找到第一個 key
Map.Entry<Integer, Server> locateEntry = ring.ceilingEntry(invocationHashCode);
if (locateEntry == null) {
// 想象成一個環,超過尾部則取第一個 key
locateEntry = ring.firstEntry();
}
return locateEntry.getValue();
}
private TreeMap<Integer, Server> buildConsistentHashRing(List<Server> servers) {
TreeMap<Integer, Server> virtualNodeRing = new TreeMap<>();
for (Server server : servers) {
for (int i = 0; i < VIRTUAL_NODE_SIZE; i++) {
// 新增虛擬節點的方式如果有影響,也可以抽象出一個由物理節點擴展虛擬節點的類
virtualNodeRing.put(hashStrategy.getHashCode(server.getUrl() + VIRTUAL_NODE_SUFFIX + i), server);
}
}
return virtualNodeRing;
}
}
```
對上述的程序做簡單的解讀:
Server 是對服務器的抽象,一般是 ip+port 的形式。
```
public class Server {
private String url;
}
Invocation 是對請求的抽象,包含一個用于 hash 的 key。
```
public class Invocation {
private String hashKey;
}
```
使用 TreeMap 作為一致性哈希環的數據結構,`ring.ceilingEntry`可以獲取環上最近的一個節點。在`buildConsistentHashRing`之中包含了構建一致性哈希環的過程,默認加入了 10 個虛擬節點。
計算方差,標準差的公式:
```
public class StatisticsUtil {
// 方差 s^2=[(x1-x)^2 +...(xn-x)^2]/n
public static double variance(Long[] x) {
int m = x.length;
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {// 求和
sum += x[i];
}
double dAve = sum / m;// 求平均值
double dVar = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {// 求方差
dVar += (x[i] - dAve)* (x[i] - dAve);
}
return dVar / m;
}
// 標準差σ=sqrt(s^2)
public static double standardDeviation(Long[] x) {
int m = x.length;
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {// 求和
sum += x[i];
}
double dAve = sum / m;// 求平均值
double dVar = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {// 求方差
dVar += (x[i] - dAve)* (x[i] - dAve);
}
return Math.sqrt(dVar / m);
}
}
```
其中,`HashStrategy`是下文中重點討論的一個內容,他是對 hash 算法的抽象,我們將會著重對比各種 hash 算法給測評結果帶來的差異性。
```blic interface HashStrategy {
int getHashCode(String origin);
}
```
### [](https://www.cnkirito.moe/consistent-hash-lb/#%E6%B5%8B%E8%AF%84%E7%A8%8B%E5%BA%8F "測評程序")測評程序
前面我們已經明確了一個優秀的一致性哈希算法的設計思路。這一節我們給出實際的量化指標:假設 m 次請求打到 n 個候選服務器上
* 統計每個服務節點收到的流量,計算方差、標準差。測量流量分布均勻情況,我們可以模擬 10000 個隨機請求,打到 100 個指定服務器,測試最后個節點的方差,標準差。
* 記錄 m 次請求落到的服務器節點,下線 20% 的服務器,重放流量,統計 m 次請求中落到跟原先相同服務器的概率。測量節點上下線的情況,我們可以模擬 10000 個隨機請求,打到 100 個指定服務器,之后下線 20 個服務器并重放流量,統計請求到相同服務器的比例。
```
public class LoadBalanceTest {
static String[] ips = {...}; // 100 臺隨機 ip
/**
* 測試分布的離散情況
*/
@Test
public void testDistribution() {
List<Server> servers = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ip : ips) {
servers.add(new Server(ip+":8080"));
}
LoadBalancer chloadBalance = new ConsistentHashLoadBalancer();
// 構造 10000 隨機請求
List<Invocation> invocations = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
invocations.add(new Invocation(UUID.randomUUID().toString()));
}
// 統計分布
AtomicLongMap<Server> atomicLongMap = AtomicLongMap.create();
for (Server server : servers) {
atomicLongMap.put(server, 0);
}
for (Invocation invocation : invocations) {
Server selectedServer = chloadBalance.select(servers, invocation);
atomicLongMap.getAndIncrement(selectedServer);
}
System.out.println(StatisticsUtil.variance(atomicLongMap.asMap().values().toArray(new Long[]{})));
System.out.println(StatisticsUtil.standardDeviation(atomicLongMap.asMap().values().toArray(new Long[]{})));
}
/**
* 測試節點新增刪除后的變化程度
*/
@Test
public void testNodeAddAndRemove() {
List<Server> servers = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ip : ips) {
servers.add(new Server(ip));
}
List<Server> serverChanged = servers.subList(0, 80);
ConsistentHashLoadBalancer chloadBalance = new ConsistentHashLoadBalancer();
// 構造 10000 隨機請求
List<Invocation> invocations = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
invocations.add(new Invocation(UUID.randomUUID().toString()));
}
int count = 0;
for (Invocation invocation : invocations) {
Server origin = chloadBalance.select(servers, invocation);
Server changed = chloadBalance.select(serverChanged, invocation);
if (origin.getUrl().equals(changed.getUrl())) count++;
}
System.out.println(count / 10000D);
}
```
### [](https://www.cnkirito.moe/consistent-hash-lb/#%E4%B8%8D%E5%90%8C%E5%93%88%E5%B8%8C%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95%E7%9A%84%E5%AE%9E%E7%8E%B0%E5%8F%8A%E6%B5%8B%E8%AF%84 "不同哈希算法的實現及測評")不同哈希算法的實現及測評
最簡單、經典的 hashCode 實現:
```
public class JdkHashCodeStrategy implements HashStrategy {
@Override
public int getHashCode(String origin) {
return origin.hashCode();
}
}
```
**FNV1\_32\_HASH 算法實現:**
```
public class FnvHashStrategy implements HashStrategy {
private static final long FNV_32_INIT = 2166136261L;
private static final int FNV_32_PRIME = 16777619;
@Override
public int getHashCode(String origin) {
final int p = FNV_32_PRIME;
int hash = (int) FNV_32_INIT;
for (int i = 0; i < origin.length(); i++)
hash = (hash ^ origin.charAt(i)) * p;
hash += hash << 13;
hash ^= hash >> 7;
hash += hash << 3;
hash ^= hash >> 17;
hash += hash << 5;
hash = Math.abs(hash);
return hash;
}
}
```
**CRC 算法:**
```
public class CRCHashStrategy implements HashStrategy {
private static final int LOOKUP_TABLE[] = {0x0000, 0x1021, 0x2042, 0x3063,
0x4084, 0x50A5, 0x60C6, 0x70E7, 0x8108, 0x9129, 0xA14A, 0xB16B,
0xC18C, 0xD1AD, 0xE1CE, 0xF1EF, 0x1231, 0x0210, 0x3273, 0x2252,
0x52B5, 0x4294, 0x72F7, 0x62D6, 0x9339, 0x8318, 0xB37B, 0xA35A,
0xD3BD, 0xC39C, 0xF3FF, 0xE3DE, 0x2462, 0x3443, 0x0420, 0x1401,
0x64E6, 0x74C7, 0x44A4, 0x5485, 0xA56A, 0xB54B, 0x8528, 0x9509,
0xE5EE, 0xF5CF, 0xC5AC, 0xD58D, 0x3653, 0x2672, 0x1611, 0x0630,
0x76D7, 0x66F6, 0x5695, 0x46B4, 0xB75B, 0xA77A, 0x9719, 0x8738,
0xF7DF, 0xE7FE, 0xD79D, 0xC7BC, 0x48C4, 0x58E5, 0x6886, 0x78A7,
0x0840, 0x1861, 0x2802, 0x3823, 0xC9CC, 0xD9ED, 0xE98E, 0xF9AF,
0x8948, 0x9969, 0xA90A, 0xB92B, 0x5AF5, 0x4AD4, 0x7AB7, 0x6A96,
0x1A71, 0x0A50, 0x3A33, 0x2A12, 0xDBFD, 0xCBDC, 0xFBBF, 0xEB9E,
0x9B79, 0x8B58, 0xBB3B, 0xAB1A, 0x6CA6, 0x7C87, 0x4CE4, 0x5CC5,
0x2C22, 0x3C03, 0x0C60, 0x1C41, 0xEDAE, 0xFD8F, 0xCDEC, 0xDDCD,
0xAD2A, 0xBD0B, 0x8D68, 0x9D49, 0x7E97, 0x6EB6, 0x5ED5, 0x4EF4,
0x3E13, 0x2E32, 0x1E51, 0x0E70, 0xFF9F, 0xEFBE, 0xDFDD, 0xCFFC,
0xBF1B, 0xAF3A, 0x9F59, 0x8F78, 0x9188, 0x81A9, 0xB1CA, 0xA1EB,
0xD10C, 0xC12D, 0xF14E, 0xE16F, 0x1080, 0x00A1, 0x30C2, 0x20E3,
0x5004, 0x4025, 0x7046, 0x6067, 0x83B9, 0x9398, 0xA3FB, 0xB3DA,
0xC33D, 0xD31C, 0xE37F, 0xF35E, 0x02B1, 0x1290, 0x22F3, 0x32D2,
0x4235, 0x5214, 0x6277, 0x7256, 0xB5EA, 0xA5CB, 0x95A8, 0x8589,
0xF56E, 0xE54F, 0xD52C, 0xC50D, 0x34E2, 0x24C3, 0x14A0, 0x0481,
0x7466, 0x6447, 0x5424, 0x4405, 0xA7DB, 0xB7FA, 0x8799, 0x97B8,
0xE75F, 0xF77E, 0xC71D, 0xD73C, 0x26D3, 0x36F2, 0x0691, 0x16B0,
0x6657, 0x7676, 0x4615, 0x5634, 0xD94C, 0xC96D, 0xF90E, 0xE92F,
0x99C8, 0x89E9, 0xB98A, 0xA9AB, 0x5844, 0x4865, 0x7806, 0x6827,
0x18C0, 0x08E1, 0x3882, 0x28A3, 0xCB7D, 0xDB5C, 0xEB3F, 0xFB1E,
0x8BF9, 0x9BD8, 0xABBB, 0xBB9A, 0x4A75, 0x5A54, 0x6A37, 0x7A16,
0x0AF1, 0x1AD0, 0x2AB3, 0x3A92, 0xFD2E, 0xED0F, 0xDD6C, 0xCD4D,
0xBDAA, 0xAD8B, 0x9DE8, 0x8DC9, 0x7C26, 0x6C07, 0x5C64, 0x4C45,
0x3CA2, 0x2C83, 0x1CE0, 0x0CC1, 0xEF1F, 0xFF3E, 0xCF5D, 0xDF7C,
0xAF9B, 0xBFBA, 0x8FD9, 0x9FF8, 0x6E17, 0x7E36, 0x4E55, 0x5E74,
0x2E93, 0x3EB2, 0x0ED1, 0x1EF0,};
/**
* Create a CRC16 checksum from the bytes. implementation is from
* mp911de/lettuce, modified with some more optimizations
*
* @param bytes
* @return CRC16 as integer value
*/
public static int getCRC16(byte[] bytes) {
int crc = 0x0000;
for (byte b : bytes) {
crc = ((crc << 8) ^ LOOKUP_TABLE[((crc >>> 8) ^ (b & 0xFF)) & 0xFF]);
}
return crc & 0xFFFF;
}
public static int getCRC16(String key) {
return getCRC16(key.getBytes(Charset.forName("UTF-8")));
}
@Override
public int getHashCode(String origin) {
// optimization with modulo operator with power of 2
// equivalent to getCRC16(key) % 16384
return getCRC16(origin) & (16384 - 1);
}
}
```
**Ketama 算法:**
```
public class KetamaHashStrategy implements HashStrategy {
private static MessageDigest md5Digest;
static {
try {
md5Digest = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("MD5 not supported", e);
}
}
@Override
public int getHashCode(String origin) {
byte[] bKey = computeMd5(origin);
long rv = ((long) (bKey[3] & 0xFF)<< 24)
| ((long) (bKey[2] & 0xFF)<< 16)
| ((long) (bKey[1] & 0xFF)<< 8)
| (bKey[0] & 0xFF);
return (int) (rv & 0xffffffffL);
}
/**
* Get the md5 of the given key.
*/
public static byte[] computeMd5(String k) {
MessageDigest md5;
try {
md5 = (MessageDigest) md5Digest.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("clone of MD5 not supported", e);
}
md5.update(k.getBytes());
return md5.digest();
}
}
```
**MurmurHash 算法:**
```
public class MurmurHashStrategy implements HashStrategy {
@Override
public int getHashCode(String origin) {
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.wrap(origin.getBytes());
int seed = 0x1234ABCD;
ByteOrder byteOrder = buf.order();
buf.order(ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN);
long m = 0xc6a4a7935bd1e995L;
int r = 47;
long h = seed ^ (buf.remaining() * m);
long k;
while (buf.remaining() >= 8) {
k = buf.getLong();
k *= m;
k ^= k >>> r;
k *= m;
h ^= k;
h *= m;
}
if (buf.remaining() > 0) {
ByteBuffer finish = ByteBuffer.allocate(8).order(
ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN);
// for big-endian version, do this first:
// finish.position(8-buf.remaining());
finish.put(buf).rewind();
h ^= finish.getLong();
h *= m;
}
h ^= h >>> r;
h *= m;
h ^= h >>> r;
buf.order(byteOrder);
return (int) (h & 0xffffffffL);
}
}
```
測評結果:
| | 方差 | 標準差 | 不變流量比例 |
| --- | --- | --- | --- |
| **JdkHashCodeStrategy** | 29574.08 | 171.97 | 0.6784 |
| **CRCHashStrategy** | 3013.02 | 54.89 | 0.7604 |
| **FnvHashStrategy** | 961.64 | 31.01 | 0.7892 |
| **KetamaHashStrategy** | 1254.64 | 35.42 | 0.7986 |
| **MurmurHashStrategy** | 815.72 | 28.56 | 0.7971 |
其中方差和標準差反映了均勻情況,越低越好,可以發現 MurmurHashStrategy,KetamaHashStrategy,FnvHashStrategy 都表現的不錯。
不變流量比例體現了服務器上下線對原有請求的影響程度,不變流量比例越高越高,可以發現 KetamaHashStrategy 和 MurmurHashStrategy 表現最為優秀。
我并沒有對小集群,小流量進行測試,樣本偏差性較大,僅從這個常見場景來看,MurmurHashStrategy 是一個不錯的選擇,多次測試后發現**FnvHashStrategy**,**KetamaHashStrategy**,**MurmurHashStrategy**差距不是很大。
至于性能測試,MurmurHash 也十分的高性能,我并沒有做測試(感興趣的同學可以對幾種 strategy 用 JMH 測評一下), 這里我貼一下 MurmurHash 官方的測評數據:
~~~
OneAtATime - 354.163715 mb/sec
FNV - 443.668038 mb/sec
SuperFastHash - 985.335173 mb/sec
lookup3 - 988.080652 mb/sec
MurmurHash 1.0 - 1363.293480 mb/sec
MurmurHash 2.0 - 2056.885653 mb/sec
~~~
> 擴大虛擬節點可以明顯降低方差和標準差,但虛擬節點的增加會加大內存占用量以及計算量
### [](https://www.cnkirito.moe/consistent-hash-lb/#Ketama-%E4%B8%80%E8%87%B4%E6%80%A7%E5%93%88%E5%B8%8C%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95%E5%AE%9E%E7%8E%B0 "Ketama 一致性哈希算法實現")Ketama 一致性哈希算法實現
Ketama 算法有其專門的配套實現方式
```
public class KetamaConsistentHashLoadBalancer implements LoadBalancer {
private static MessageDigest md5Digest;
static {
try {
md5Digest = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("MD5 not supported", e);
}
}
private final static int VIRTUAL_NODE_SIZE = 12;
private final static String VIRTUAL_NODE_SUFFIX = "-";
@Override
public Server select(List<Server> servers, Invocation invocation) {
long invocationHashCode = getHashCode(invocation.getHashKey());
TreeMap<Long, Server> ring = buildConsistentHashRing(servers);
Server server = locate(ring, invocationHashCode);
return server;
}
private Server locate(TreeMap<Long, Server> ring, Long invocationHashCode) {
// 向右找到第一個 key
Map.Entry<Long, Server> locateEntry = ring.ceilingEntry(invocationHashCode);
if (locateEntry == null) {
// 想象成一個環,超過尾部則取第一個 key
locateEntry = ring.firstEntry();
}
return locateEntry.getValue();
}
private TreeMap<Long, Server> buildConsistentHashRing(List<Server> servers) {
TreeMap<Long, Server> virtualNodeRing = new TreeMap<>();
for (Server server : servers) {
for (int i = 0; i < VIRTUAL_NODE_SIZE / 4; i++) {
byte[] digest = computeMd5(server.getUrl() + VIRTUAL_NODE_SUFFIX + i);
for (int h = 0; h < 4; h++) {
Long k = ((long) (digest[3 + h * 4] & 0xFF)<< 24)
| ((long) (digest[2 + h * 4] & 0xFF)<< 16)
| ((long) (digest[1 + h * 4] & 0xFF)<< 8)
| (digest[h * 4] & 0xFF);
virtualNodeRing.put(k, server);
}
}
}
return virtualNodeRing;
}
private long getHashCode(String origin) {
byte[] bKey = computeMd5(origin);
long rv = ((long) (bKey[3] & 0xFF)<< 24)
| ((long) (bKey[2] & 0xFF)<< 16)
| ((long) (bKey[1] & 0xFF)<< 8)
| (bKey[0] & 0xFF);
return rv;
}
private static byte[] computeMd5(String k) {
MessageDigest md5;
try {
md5 = (MessageDigest) md5Digest.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("clone of MD5 not supported", e);
}
md5.update(k.getBytes());
return md5.digest();
}
}
```
稍微不同的地方便在于:Ketama 將四個節點標為一組進行了虛擬節點的設置。
| | 方差 | 標準差 | 不變流量比例 |
| --- | --- | --- | --- |
| **KetamaConsistentHashLoadBalancer** | 911.08 | 30.18 | 0.7936 |
實際結果并沒有太大的提升,可能和測試數據的樣本規模有關。
### [](https://www.cnkirito.moe/consistent-hash-lb/#%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93 "總結")總結
優秀的哈希算法和一致性哈希算法可以幫助我們在大多數場景下應用的高性能,高穩定性,但在實際使用一致性哈希負載均衡的場景中,最好針對實際的集群規模和請求哈希方式進行壓測,力保流量均勻打到所有的機器上,這才是王道。
不僅僅是分布式緩存,負載均衡等等有限的場景,一致性哈希算法、哈希算法,尤其是后者,是一個用處很廣泛的常見算法,了解它的經典實現是很有必要的,例如 MurmurHash,在 guava 中就有其 Java 實現,當需要高性能,分布均勻,碰撞概率小的哈希算法時,可以考慮使用它。
本文代碼的 github 地址:[https://github.com/lexburner/consistent-hash-algorithm](https://github.com/lexburner/consistent-hash-algorithm)
### [](https://www.cnkirito.moe/consistent-hash-lb/#%E6%89%A9%E5%B1%95%E9%98%85%E8%AF%BB "擴展閱讀")擴展閱讀
[深入理解 RPC 之集群篇](https://www.cnkirito.moe/rpc-cluster/)
[《該如何設計你的 PasswordEncoder?》](https://www.cnkirito.moe/spring-security-6/)
- 前言
- 服務器開發設計
- Reactor模式
- 一種心跳,兩種設計
- 聊聊 TCP 長連接和心跳那些事
- 學習TCP三次握手和四次揮手
- Linux基礎
- Linux的inode的理解
- 異步IO模型介紹
- 20個最常用的GCC編譯器參數
- epoll
- epoll精髓
- epoll原理詳解及epoll反應堆模型
- epoll的坑
- epoll的本質
- socket的SO_REUSEADDR參數全面分析
- 服務器網絡
- Protobuf
- Protobuf2 語法指南
- 一種自動反射消息類型的 Protobuf 網絡傳輸方案
- 微服務
- RPC框架
- 什么是RPC
- 如何科學的解釋RPC
- RPC 消息協議
- 實現一個極簡版的RPC
- 一個基于protobuf的極簡RPC
- 如何基于protobuf實現一個極簡版的RPC
- 開源RPC框架
- thrift
- grpc
- brpc
- Dubbo
- 服務注冊,發現,治理
- Redis
- Redis發布訂閱
- Redis分布式鎖
- 一致性哈希算法
- Redis常見問題
- Redis數據類型
- 緩存一致性
- LevelDB
- 高可用
- keepalived基本理解
- keepalived操做
- LVS 學習
- 性能優化
- Linux服務器程序性能優化方法
- SRS性能(CPU)、內存優化工具用法
- centos6的性能分析工具集合
- CentOS系統性能工具 sar 示例!
- Linux性能監控工具集sysstat
- gdb相關
- Linux 下如何產生core文件(core dump設置)
