## 一、filebeat是什么
### 1.1、filebeat和beats的關系
首先filebeat是Beats中的一員。
Beats在是一個輕量級日志采集器,其實Beats家族有6個成員,早期的ELK架構中使用Logstash收集、解析日志,但是Logstash對內存、cpu、io等資源消耗比較高。相比Logstash,Beats所占系統的CPU和內存幾乎可以忽略不計。
目前Beats包含六種工具:
* Packetbeat:網絡數據(收集網絡流量數據)
* Metricbeat:指標(收集系統、進程和文件系統級別的CPU和內存使用情況等數據)
* Filebeat:日志文件(收集文件數據)
* Winlogbeat:windows事件日志(收集Windows事件日志數據)
* Auditbeat:審計數據(收集審計日志)
* Heartbeat:運行時間監控(收集系統運行時的數據)
### 1.2、filebeat是什么
Filebeat是用于轉發和集中日志數據的輕量級傳送工具。Filebeat監視您指定的日志文件或位置,收集日志事件,并將它們轉發到Elasticsearch或 Logstash進行索引。
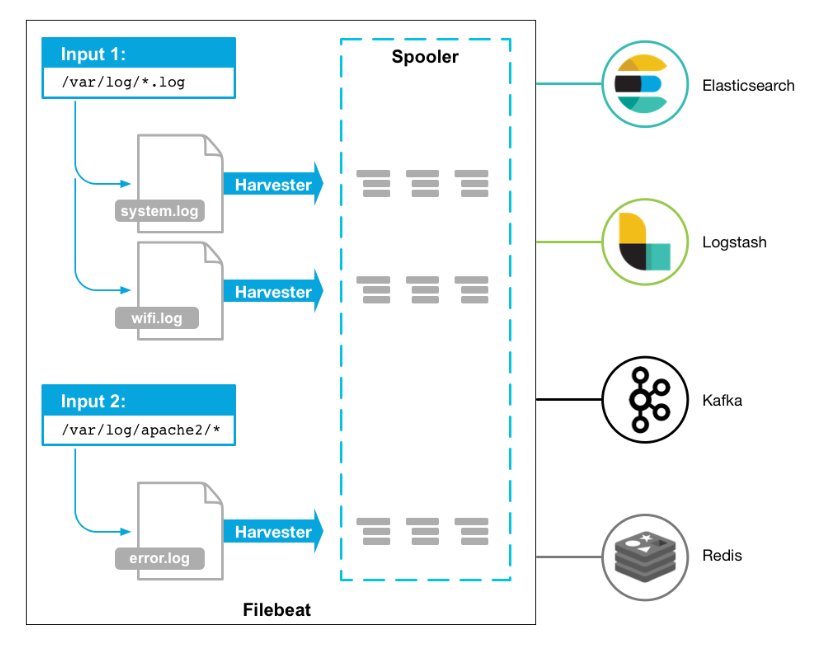
Filebeat的工作方式如下:啟動Filebeat時,它將啟動一個或多個輸入,這些輸入將在為日志數據指定的位置中查找。對于Filebeat所找到的每個日志,Filebeat都會啟動收集器。每個收集器都讀取單個日志以獲取新內容,并將新日志數據發送到libbeat,libbeat將聚集事件,并將聚集的數據發送到為Filebeat配置的輸出。
? ? ? ?工作的流程圖如下:
## 二、filebeat原理是什么
### 2.1、filebeat的構成
filebeat結構:由兩個組件構成,分別是inputs(輸入)和harvesters(收集器),這些組件一起工作來跟蹤文件并將事件數據發送到您指定的輸出,harvester負責讀取單個文件的內容。harvester逐行讀取每個文件,并將內容發送到輸出。為每個文件啟動一個harvester。harvester負責打開和關閉文件,這意味著文件描述符在harvester運行時保持打開狀態。如果在收集文件時刪除或重命名文件,Filebeat將繼續讀取該文件。這樣做的副作用是,磁盤上的空間一直保留到harvester關閉。默認情況下,Filebeat保持文件打開,直到達到close\_inactive
關閉harvester可以會產生的結果:
* 文件處理程序關閉,如果harvester仍在讀取文件時被刪除,則釋放底層資源。
* 只有在scan\_frequency結束之后,才會再次啟動文件的收集。
* 如果該文件在harvester關閉時被移動或刪除,該文件的收集將不會繼續
一個input負責管理harvesters和尋找所有來源讀取。如果input類型是log,則input將查找驅動器上與定義的路徑匹配的所有文件,并為每個文件啟動一個harvester。每個input在它自己的Go進程中運行,Filebeat當前支持多種輸入類型。每個輸入類型可以定義多次。日志輸入檢查每個文件,以查看是否需要啟動harvester、是否已經在運行harvester或是否可以忽略該文件
### 2.2、filebeat如何保存文件的狀態
Filebeat保留每個文件的狀態,并經常將狀態刷新到磁盤中的注冊表文件中。該狀態用于記住harvester讀取的最后一個偏移量,并確保發送所有日志行。如果無法訪問輸出(如Elasticsearch或Logstash),Filebeat將跟蹤最后發送的行,并在輸出再次可用時繼續讀取文件。當Filebeat運行時,每個輸入的狀態信息也保存在內存中。當Filebeat重新啟動時,來自注冊表文件的數據用于重建狀態,Filebeat在最后一個已知位置繼續每個harvester。對于每個輸入,Filebeat都會保留它找到的每個文件的狀態。由于文件可以重命名或移動,文件名和路徑不足以標識文件。對于每個文件,Filebeat存儲唯一的標識符,以檢測文件是否以前被捕獲。
### 2.3、filebeat何如保證至少一次數據消費
Filebeat保證事件將至少傳遞到配置的輸出一次,并且不會丟失數據。是因為它將每個事件的傳遞狀態存儲在注冊表文件中。在已定義的輸出被阻止且未確認所有事件的情況下,Filebeat將繼續嘗試發送事件,直到輸出確認已接收到事件為止。如果Filebeat在發送事件的過程中關閉,它不會等待輸出確認所有事件后再關閉。當Filebeat重新啟動時,將再次將Filebeat關閉前未確認的所有事件發送到輸出。這樣可以確保每個事件至少發送一次,但最終可能會有重復的事件發送到輸出。通過設置shutdown\_timeout選項,可以將Filebeat配置為在關機前等待特定時間
[回到頂部](https://www.cnblogs.com/zsql/p/13137833.html#_labelTop)
## 三、filebeat怎么玩
### 3.1、壓縮包方式安裝
本文采用壓縮包的方式安裝,linux版本,filebeat-7.7.0-linux-x86\_64.tar.gz
~~~
curl-L-Ohttps://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-7.7.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
tar -xzvf filebeat-7.7.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
~~~
配置示例文件:filebeat.reference.yml(包含所有未過時的配置項)
配置文件:filebeat.yml
### 3.2、基本命令
詳情見官網:[https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/current/command-line-options.html](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/current/command-line-options.html)
[](javascript:void(0); "復制代碼")
~~~
export #導出
run #執行(默認執行)
test #測試配置
keystore #秘鑰存儲
modules #模塊配置管理
setup #設置初始環境
~~~
[](javascript:void(0); "復制代碼")
例如:./filebeat test config? #用來測試配置文件是否正確
### 3.3、輸入輸出
支持的輸入組件:
Multilinemessages,Azureeventhub,CloudFoundry,Container,Docker,GooglePub/Sub,HTTPJSON,Kafka,Log,MQTT,NetFlow,Office365ManagementActivityAPI,Redis,s3,Stdin,Syslog,TCP,UDP(最常用的額就是log)
支持的輸出組件:
Elasticsearch,Logstash,Kafka,Redis,File,Console,ElasticCloud,Changetheoutputcodec(最常用的就是Elasticsearch,Logstash)
### 3.4、keystore的使用
keystore主要是防止敏感信息被泄露,比如密碼等,像ES的密碼,這里可以生成一個key為ES\_PWD,值為es的password的一個對應關系,在使用es的密碼的時候就可以使用${ES\_PWD}使用
~~~
創建一個存儲密碼的keystore:filebeat keystore create
然后往其中添加鍵值對,例如:filebeatk eystore add ES_PWD
使用覆蓋原來鍵的值:filebeat key store add ES_PWD–force
刪除鍵值對:filebeat key store remove ES_PWD
查看已有的鍵值對:filebeat key store list
~~~
例如:后期就可以通過${ES\_PWD}使用其值,例如:
output.elasticsearch.password:"${ES\_PWD}"
### 3.5、filebeat.yml配置(log輸入類型為例)
詳情見官網:[https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/current/filebeat-input-log.html](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/current/filebeat-input-log.html)
[](javascript:void(0); "復制代碼")
~~~
type: log #input類型為log
enable: true #表示是該log類型配置生效
paths: #指定要監控的日志,目前按照Go語言的glob函數處理。沒有對配置目錄做遞歸處理,比如配置的如果是:
- /var/log/* /*.log #則只會去/var/log目錄的所有子目錄中尋找以".log"結尾的文件,而不會尋找/var/log目錄下以".log"結尾的文件。
recursive_glob.enabled: #啟用全局遞歸模式,例如/foo/**包括/foo, /foo/*, /foo/*/*
encoding:#指定被監控的文件的編碼類型,使用plain和utf-8都是可以處理中文日志的
exclude_lines: ['^DBG'] #不包含匹配正則的行
include_lines: ['^ERR', '^WARN'] #包含匹配正則的行
harvester_buffer_size: 16384 #每個harvester在獲取文件時使用的緩沖區的字節大小
max_bytes: 10485760 #單個日志消息可以擁有的最大字節數。max_bytes之后的所有字節都被丟棄而不發送。默認值為10MB (10485760)
exclude_files: ['\.gz$'] #用于匹配希望Filebeat忽略的文件的正則表達式列表
ingore_older: 0 #默認為0,表示禁用,可以配置2h,2m等,注意ignore_older必須大于close_inactive的值.表示忽略超過設置值未更新的
文件或者文件從來沒有被harvester收集
close_* #close_ *配置選項用于在特定標準或時間之后關閉harvester。 關閉harvester意味著關閉文件處理程序。 如果在harvester關閉
后文件被更新,則在scan_frequency過后,文件將被重新拾取。 但是,如果在harvester關閉時移動或刪除文件,Filebeat將無法再次接收文件
,并且harvester未讀取的任何數據都將丟失。
close_inactive #啟動選項時,如果在制定時間沒有被讀取,將關閉文件句柄
讀取的最后一條日志定義為下一次讀取的起始點,而不是基于文件的修改時間
如果關閉的文件發生變化,一個新的harverster將在scan_frequency運行后被啟動
建議至少設置一個大于讀取日志頻率的值,配置多個prospector來實現針對不同更新速度的日志文件
使用內部時間戳機制,來反映記錄日志的讀取,每次讀取到最后一行日志時開始倒計時使用2h 5m 來表示
close_rename #當選項啟動,如果文件被重命名和移動,filebeat關閉文件的處理讀取
close_removed #當選項啟動,文件被刪除時,filebeat關閉文件的處理讀取這個選項啟動后,必須啟動clean_removed
close_eof #適合只寫一次日志的文件,然后filebeat關閉文件的處理讀取
close_timeout #當選項啟動時,filebeat會給每個harvester設置預定義時間,不管這個文件是否被讀取,達到設定時間后,將被關閉
close_timeout 不能等于ignore_older,會導致文件更新時,不會被讀取如果output一直沒有輸出日志事件,這個timeout是不會被啟動的,
至少要要有一個事件發送,然后haverter將被關閉
設置0 表示不啟動
clean_inactived #從注冊表文件中刪除先前收獲的文件的狀態
設置必須大于ignore_older+scan_frequency,以確保在文件仍在收集時沒有刪除任何狀態
配置選項有助于減小注冊表文件的大小,特別是如果每天都生成大量的新文件
此配置選項也可用于防止在Linux上重用inode的Filebeat問題
clean_removed #啟動選項后,如果文件在磁盤上找不到,將從注冊表中清除filebeat
如果關閉close removed 必須關閉clean removed
scan_frequency #prospector檢查指定用于收獲的路徑中的新文件的頻率,默認10s
tail_files:#如果設置為true,Filebeat從文件尾開始監控文件新增內容,把新增的每一行文件作為一個事件依次發送,
而不是從文件開始處重新發送所有內容。
symlinks:#符號鏈接選項允許Filebeat除常規文件外,可以收集符號鏈接。收集符號鏈接時,即使報告了符號鏈接的路徑,
Filebeat也會打開并讀取原始文件。
backoff: #backoff選項指定Filebeat如何積極地抓取新文件進行更新。默認1s,backoff選項定義Filebeat在達到EOF之后
再次檢查文件之間等待的時間。
max_backoff: #在達到EOF之后再次檢查文件之前Filebeat等待的最長時間
backoff_factor: #指定backoff嘗試等待時間幾次,默認是2
harvester_limit:#harvester_limit選項限制一個prospector并行啟動的harvester數量,直接影響文件打開數
tags #列表中添加標簽,用過過濾,例如:tags: ["json"]
fields #可選字段,選擇額外的字段進行輸出可以是標量值,元組,字典等嵌套類型
默認在sub-dictionary位置
filebeat.inputs:
fields:
app_id: query_engine_12
fields_under_root #如果值為ture,那么fields存儲在輸出文檔的頂級位置
multiline.pattern #必須匹配的regexp模式
multiline.negate #定義上面的模式匹配條件的動作是 否定的,默認是false
假如模式匹配條件'^b',默認是false模式,表示講按照模式匹配進行匹配 將不是以b開頭的日志行進行合并
如果是true,表示將不以b開頭的日志行進行合并
multiline.match # 指定Filebeat如何將匹配行組合成事件,在之前或者之后,取決于上面所指定的negate
multiline.max_lines #可以組合成一個事件的最大行數,超過將丟棄,默認500
multiline.timeout #定義超時時間,如果開始一個新的事件在超時時間內沒有發現匹配,也將發送日志,默認是5s
max_procs #設置可以同時執行的最大CPU數。默認值為系統中可用的邏輯CPU的數量。
name #為該filebeat指定名字,默認為主機的hostname
~~~
[](javascript:void(0); "復制代碼")
### 3.6、實例一:logstash作為輸出
filebeat.yml配置
[](javascript:void(0); "復制代碼")
~~~
#=========================== Filebeat inputs =============================
filebeat.inputs:
# Each - is an input. Most options can be set at the input level, so
# you can use different inputs for various configurations.
# Below are the input specific configurations.
- type: log
# Change to true to enable this input configuration.
enabled: true
# Paths that should be crawled and fetched. Glob based paths.
paths: #配置多個日志路徑
- /var/logs/es_aaa_index_search_slowlog.log
- /var/logs/es_bbb_index_search_slowlog.log
- /var/logs/es_ccc_index_search_slowlog.log
- /var/logs/es_ddd_index_search_slowlog.log
#- c:\programdata\elasticsearch\logs\*
# Exclude lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It drops the lines that are
# matching any regular expression from the list.
#exclude_lines: ['^DBG']
# Include lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It exports the lines that are
# matching any regular expression from the list.
#include_lines: ['^ERR', '^WARN']
# Exclude files. A list of regular expressions to match. Filebeat drops the files that
# are matching any regular expression from the list. By default, no files are dropped.
#exclude_files: ['.gz$']
# Optional additional fields. These fields can be freely picked
# to add additional information to the crawled log files for filtering
#fields:
# level: debug
# review: 1
### Multiline options
# Multiline can be used for log messages spanning multiple lines. This is common
# for Java Stack Traces or C-Line Continuation
# The regexp Pattern that has to be matched. The example pattern matches all lines starting with [
#multiline.pattern: ^\[
# Defines if the pattern set under pattern should be negated or not. Default is false.
#multiline.negate: false
# Match can be set to "after" or "before". It is used to define if lines should be append to a pattern
# that was (not) matched before or after or as long as a pattern is not matched based on negate.
# Note: After is the equivalent to previous and before is the equivalent to to next in Logstash
#multiline.match: after
#================================ Outputs =====================================
#----------------------------- Logstash output --------------------------------
output.logstash:
# The Logstash hosts #配多個logstash使用負載均衡機制
hosts: ["192.168.110.130:5044","192.168.110.131:5044","192.168.110.132:5044","192.168.110.133:5044"]
loadbalance: true #使用了負載均衡
# Optional SSL. By default is off.
# List of root certificates for HTTPS server verifications
#ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/root/ca.pem"]
# Certificate for SSL client authentication
#ssl.certificate: "/etc/pki/client/cert.pem"
# Client Certificate Key
#ssl.key: "/etc/pki/client/cert.key"
~~~
[](javascript:void(0); "復制代碼")
./filebeat -e? ?#啟動filebeat
logstash的配置
[](javascript:void(0); "復制代碼")
~~~
input {
beats {
port => 5044
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://192.168.110.130:9200"] #這里可以配置多個
index => "query-%{yyyyMMdd}"
}
}
~~~
[](javascript:void(0); "復制代碼")
### 3.7、實例二:elasticsearch作為輸出
filebeat.yml的配置:
[](javascript:void(0); "復制代碼")
~~~
###################### Filebeat Configuration Example #########################
# This file is an example configuration file highlighting only the most common
# options. The filebeat.reference.yml file from the same directory contains all the
# supported options with more comments. You can use it as a reference.
#
# You can find the full configuration reference here:
# https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/index.html
# For more available modules and options, please see the filebeat.reference.yml sample
# configuration file.
#=========================== Filebeat inputs =============================
filebeat.inputs:
# Each - is an input. Most options can be set at the input level, so
# you can use different inputs for various configurations.
# Below are the input specific configurations.
- type: log
# Change to true to enable this input configuration.
enabled: true
# Paths that should be crawled and fetched. Glob based paths.
paths:
- /var/logs/es_aaa_index_search_slowlog.log
- /var/logs/es_bbb_index_search_slowlog.log
- /var/logs/es_ccc_index_search_slowlog.log
- /var/logs/es_dddd_index_search_slowlog.log
#- c:\programdata\elasticsearch\logs\*
# Exclude lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It drops the lines that are
# matching any regular expression from the list.
#exclude_lines: ['^DBG']
# Include lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It exports the lines that are
# matching any regular expression from the list.
#include_lines: ['^ERR', '^WARN']
# Exclude files. A list of regular expressions to match. Filebeat drops the files that
# are matching any regular expression from the list. By default, no files are dropped.
#exclude_files: ['.gz$']
# Optional additional fields. These fields can be freely picked
# to add additional information to the crawled log files for filtering
#fields:
# level: debug
# review: 1
### Multiline options
# Multiline can be used for log messages spanning multiple lines. This is common
# for Java Stack Traces or C-Line Continuation
# The regexp Pattern that has to be matched. The example pattern matches all lines starting with [
#multiline.pattern: ^\[
# Defines if the pattern set under pattern should be negated or not. Default is false.
#multiline.negate: false
# Match can be set to "after" or "before". It is used to define if lines should be append to a pattern
# that was (not) matched before or after or as long as a pattern is not matched based on negate.
# Note: After is the equivalent to previous and before is the equivalent to to next in Logstash
#multiline.match: after
#============================= Filebeat modules ===============================
filebeat.config.modules:
# Glob pattern for configuration loading
path: ${path.config}/modules.d/*.yml
# Set to true to enable config reloading
reload.enabled: false
# Period on which files under path should be checked for changes
#reload.period: 10s
#==================== Elasticsearch template setting ==========================
#================================ General =====================================
# The name of the shipper that publishes the network data. It can be used to group
# all the transactions sent by a single shipper in the web interface.
name: filebeat222
# The tags of the shipper are included in their own field with each
# transaction published.
#tags: ["service-X", "web-tier"]
# Optional fields that you can specify to add additional information to the
# output.
#fields:
# env: staging
#cloud.auth:
#================================ Outputs =====================================
#-------------------------- Elasticsearch output ------------------------------
output.elasticsearch:
# Array of hosts to connect to.
hosts: ["192.168.110.130:9200","92.168.110.131:9200"]
# Protocol - either `http` (default) or `https`.
#protocol: "https"
# Authentication credentials - either API key or username/password.
#api_key: "id:api_key"
username: "elastic"
password: "${ES_PWD}" #通過keystore設置密碼
~~~
[](javascript:void(0); "復制代碼")
./filebeat -e? ?#啟動filebeat
查看elasticsearch集群,有一個默認的索引名字filebeat-%{\[beat.version\]}-%{+yyyy.MM.dd}

### 3.8、filebeat模塊
官網:[https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/current/filebeat-modules.html](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/current/filebeat-modules.html)
這里我使用elasticsearch模式來解析es的慢日志查詢,操作步驟如下,其他的模塊操作也一樣:
前提: 安裝好Elasticsearch和kibana兩個軟件,然后使用filebeat
具體的操作官網有:[https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/current/filebeat-modules-quickstart.html](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/current/filebeat-modules-quickstart.html)
**第一步,配置filebeat.yml文件**
[](javascript:void(0); "復制代碼")
~~~
#============================== Kibana =====================================
# Starting with Beats version 6.0.0, the dashboards are loaded via the Kibana API.
# This requires a Kibana endpoint configuration.
setup.kibana:
# Kibana Host
# Scheme and port can be left out and will be set to the default (http and 5601)
# In case you specify and additional path, the scheme is required: http://localhost:5601/path
# IPv6 addresses should always be defined as: https://[2001:db8::1]:5601
host: "192.168.110.130:5601" #指定kibana
username: "elastic" #用戶
password: "${ES_PWD}" #密碼,這里使用了keystore,防止明文密碼
# Kibana Space ID
# ID of the Kibana Space into which the dashboards should be loaded. By default,
# the Default Space will be used.
#space.id:
#================================ Outputs =====================================
# Configure what output to use when sending the data collected by the beat.
#-------------------------- Elasticsearch output ------------------------------
output.elasticsearch:
# Array of hosts to connect to.
hosts: ["192.168.110.130:9200","192.168.110.131:9200"]
# Protocol - either `http` (default) or `https`.
#protocol: "https"
# Authentication credentials - either API key or username/password.
#api_key: "id:api_key"
username: "elastic" #es的用戶
password: "${ES_PWD}" # es的密碼
#這里不能指定index,因為我沒有配置模板,會自動生成一個名為filebeat-%{[beat.version]}-%{+yyyy.MM.dd}的索引
~~~
[](javascript:void(0); "復制代碼")
**第二步:配置elasticsearch的慢日志路徑**
1cd filebeat-7.7.0-linux-x86_64/modules.d
vim? elasticsearch.yml

**第三步:生效es模塊**
~~~
./filebeat modules elasticsearch
~~~
查看生效的模塊
~~~
./filebeat modules list
~~~

**第四步:初始化環境**
~~~
./filebeat setup -e
~~~
?
**?第五步:啟動filebeat**
~~~
./filebeat -e
~~~
查看elasticsearch集群,如下圖所示,把慢日志查詢的日志都自動解析出來了:

?到這里,elasticsearch這個module就實驗成功了
- springcloud
- springcloud的作用
- springboot服務提供者和消費者
- Eureka
- ribbon
- Feign
- feign在微服務中的使用
- feign充當http請求工具
- Hystrix 熔斷器
- Zuul 路由網關
- Spring Cloud Config 分布式配置中心
- config介紹與配置
- Spring Cloud Config 配置實戰
- Spring Cloud Bus
- gateway
- 概念講解
- 實例
- GateWay
- 統一日志追蹤
- 分布式鎖
- 1.redis
- springcloud Alibaba
- 1. Nacos
- 1.1 安裝
- 1.2 特性
- 1.3 實例
- 1. 整合nacos服務發現
- 2. 整合nacos配置功能
- 1.4 生產部署方案
- 環境隔離
- 原理講解
- 1. 服務發現
- 2. sentinel
- 3. Seata事務
- CAP理論
- 3.1 安裝
- 分布式協議
- 4.熔斷和降級
- springcloud與alibba
- oauth
- 1. abstract
- 2. oauth2 in micro-service
- 微服務框架付費
- SkyWalking
- 介紹與相關資料
- APM系統簡單對比(zipkin,pinpoint和skywalking)
- server安裝部署
- agent安裝
- 日志清理
- 統一日志中心
- docker安裝部署
- 安裝部署
- elasticsearch 7.x
- logstash 7.x
- kibana 7.x
- ES索引管理
- 定時清理數據
- index Lifecycle Management
- 沒數據排查思路
- ELK自身組件監控
- 多租戶方案
- 慢查詢sql
- 日志審計
- 開發
- 登錄認證
- 鏈路追蹤
- elk
- Filebeat
- Filebeat基礎
- Filebeat安裝部署
- 多行消息Multiline
- how Filebeat works
- Logstash
- 安裝
- rpm安裝
- docker安裝Logstash
- grok調試
- Grok語法調試
- Grok常用表達式
- 配置中常見判斷
- filter提取器
- elasticsearch
- 安裝
- rpm安裝
- docker安裝es
- 使用
- 概念
- 基礎
- 中文分詞
- 統計
- 排序
- 倒排與正排索引
- 自定義dynamic
- 練習
- nested object
- 父子關系模型
- 高亮
- 搜索提示
- kibana
- 安裝
- docker安裝
- rpm安裝
- 整合
- 收集日志
- 慢sql
- 日志審計s
- 云
- 分布式架構
- 分布式鎖
- Redis實現
- redisson
- 熔斷和降級
