# C - `continue`語句
> 原文: [https://beginnersbook.com/2014/01/c-continue-statement/](https://beginnersbook.com/2014/01/c-continue-statement/)
**`continue`語句**用于[循環](https://beginnersbook.com/2014/01/c-loops-examples/)。當在循環內遇到 `continue`語句時,控制流跳轉到循環的開頭以進行下一次迭代,跳過當前迭代循環體內語句的執行。
## C - `continue`語句
語法:
```c
continue;
```
### `continue`語句的流程圖
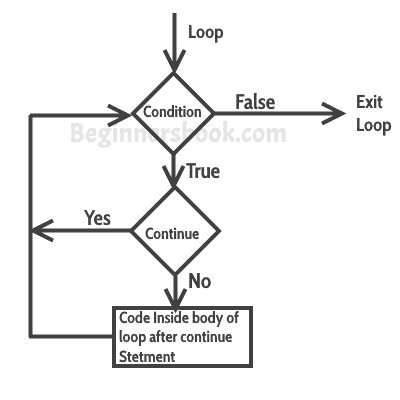
### 示例:`for`循環中的`continue`語句
```c
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for (int j=0; j<=8; j++)
{
if (j==4)
{
/* The continue statement is encountered when
* the value of j is equal to 4.
*/
continue;
}
/* This print statement would not execute for the
* loop iteration where j ==4 because in that case
* this statement would be skipped.
*/
printf("%d ", j);
}
return 0;
}
```
輸出:
```c
0 1 2 3 5 6 7 8
```
輸出中缺少值 4,為什么?當變量`j`的值為 4 時,程序遇到一個`continue`語句,它使控制流跳轉到`for`循環的開頭以進行下一次迭代,跳過當前迭代的語句(這就是`printf`在`j`等于 4 時沒有執行的原因)。
### 示例:在`while`循環中使用`continue`
在這個例子中,我們在`while`循環中使用`continue`。當使用`while`或`do-while`循環時,需要在`continue`上方放置一個遞增或遞減語句,以便在下一次迭代時更改計數器值。例如,如果我們不在`if`的正文中放置語句,那么`counter`的值將無限期地保持為 7。
```c
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int counter=10;
while (counter >=0)
{
if (counter==7)
{
counter--;
continue;
}
printf("%d ?", counter);
counter--;
}
return 0;
}
```
輸出:
```c
10 9 8 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
```
當計數器值為 7 時,將跳過`print`語句。
### `do-While`循環的`continue`的另一個例子
```c
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int j=0;
do
{
if (j==7)
{
j++;
continue;
}
printf("%d ", j);
j++;
}while(j<10);
return 0;
}
```
輸出:
```c
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9
```
- BeginnersBook C 語言教程
- 首先學習 C 基礎知識
- 如何安裝 Turbo C++:編譯并運行 C 程序
- C 程序結構 - 第一個 C 程序
- C 關鍵詞 - 保留字
- C 中的決策控制語句
- C 編程中的if語句
- C - if..else,嵌套if..else 和 else..if語句
- C 編程的switch-case語句
- C 中的循環
- C 編程中for的循環
- C 編程中的while循環
- C 編程的do-while循環
- C - 循環控制語句
- C 編程中的break語句
- C - continue語句
- C - goto語句
- C 中的數組教程
- C 編程中的數組
- C 編程中的二維(2D)數組
- C 編程中的指針和數組
- 在 C 編程中將數組傳遞給函數
- C - 字符串
- C - 字符串和字符串函數
- C 中的函數
- C 編程中的函數
- C 編程中的按值函數調用
- C 編程中的按引用函數調用
- 結構體
- C 編程中的結構
- C 編程中的指針
- C 編程中的指針
- C - 指向指針的指針(雙重指針)
- C - 函數指針
- 將指針傳遞給 C 中的函數
- 文件 I/O
- 在 C 編程中進行文件 I/O
- 運算符優先級表
- C 編程語言中的運算符優先級和關聯性
- C 示例
- 帶輸出的 C 編程示例
- C 庫函數教程
- C strcat()函數
- C strncat()函數
- C strchr()函數
- C strcmp()函數
- C strncmp()函數
- C strcoll()函數
- C strcpy()函數
- C strncpy()函數
- C strrchr()函數
- C strspn()函數
- C strstr()函數
- C strcspn()函數
- C strlen()函數
- BeginnersBook C 語言示例
- 簡單的 C 程序
- C 語言中的 Hello World 程序
- C 程序:檢查給定的整數是正還是負
- C 程序:使用遞歸函數反轉給定的數字
- C 程序:查找最大的三個數字
- C 程序:顯示 Fibonacci 序列
- C 程序:使用遞歸查找數字的階乘
- C 程序:查找給定范圍內的素數
- C 程序:檢查阿姆斯特朗數
- C 程序:檢查數字是否為回文數
- C 程序:查找給定范圍內的回文數
- C 程序:檢查數字是偶數還是奇數
- C 程序:查找字符的 ASCII 值
- C 程序:查找int,float,double和char的大小
- C 程序:檢查字母是元音還是輔音
- CC 程序:檢查閏年
- C 程序:查找前 n 個自然數的和
- 字符串程序
- C 程序:將大寫字符串轉換為小寫字符串
- C 程序:將小寫字符串轉換為大寫字符串
- C 程序:按字母順序對字符串集進行排序
- C 程序:在不使用函數strlen()的情況下查找字符串的長度
- C 程序:在不使用strcat的情況下連接兩個字符串
- C 程序:使用遞歸來反轉字符串
- 數組程序
- C 程序:按升序排列數字
- C 程序:查找數組的最大元素
- C 程序:使用指針,遞歸和函數來查找數組元素的總和
- C 程序:查找數組中的元素數
- 排序程序
- C 冒泡排序程序
- C 中的插入排序程序
- C 中的選擇排序程序
- C 中的快速排序程序
- C 指針程序
- C 程序:使用指針查找最大的三個數字
- C 程序:使用指針計算字符串中的元音和輔音
- C 程序:使用指針打印字符串
- C 程序:使用指針交換兩個數字
- C 程序:創建,初始化和訪問指針變量
- 計算程序
- C 程序:計算并打印 nPr 的值
- C 程序:計算并打印 nCr 的值
- C 程序:兩個浮點數相乘
- C 程序:查找商和余數
- C 程序查找兩個數字的平均值
- 數字系統轉換程序
- C 程序:將二進制數轉換為十進制數
- C 程序:將十進制數轉換為二進制數
- C 程序:將十進制數轉換為八進制數
- C 程序:將八進制數轉換為十進制數
- C 程序:將二進制數轉換為八進制數
- C 程序:將八進制數轉換為二進制數
- 查找幾何圖形區域的程序
- C 程序:計算圓的面積和周長
- C 程序:計算等邊三角形的面積
- BeginnersBook C++ 教程
- 基礎
- Hello World - 第一個 C++ 程序
- C++ 中的變量
- C++ 中的數據類型
- C++ 中的運算符
- 控制語句
- C++ 中的if語句
- C++ 中的switch-case語句
- C++ 中的for循環
- C++ 中的while循環
- C++ 中的do-while循環
- C++ 中的continue語句
- C++ 中的break語句
- C++ 中的goto語句
- 函數
- C++ 中的函數
- C++ 函數中的默認參數
- C++ 遞歸
- 數組
- C++ 中的數組
- C++ 中的多維數組
- 在 C++ 中將數組傳遞給函數
- C++ 中的字符串
- 指針
- C++ 中的指針
- C++ this指針
- OOP
- C++ 中的 OOP 概念
- C++ 中的構造函數
- C++ 中的析構函數
- C++ 中的結構
- C++ 中的結構和函數
- C++ 中的枚舉
- C++ 中的繼承
- C++ 中的多態
- C++ 中的函數重載
- C++ 函數覆蓋
- C++ 中的虛函數:運行時多態
- C++ 封裝
- C++ 中的抽象
- C++ 中的接口:抽象類
- 從 C++ 中的函數傳遞和返回對象
- C++ 中的友元類和友元函數
- BeginnersBook 數據庫教程
- DBMS 簡介
- 數據庫應用 - DBMS
- DBMS 優于文件系統的優點
- DBMS 架構
- DBMS - 三層架構
- DBMS 中的數據視圖
- DBMS 中的數據抽象
- DBMS 中的實例和模式
- DBMS 中的數據模型
- 實體關系圖 - DBMS 中的 ER 圖
- DBMS 泛化
- DBMS 特化
- DBMS 聚合
- DBMS 中的關系模型
- RDBMS 概念
- DBMS 中的分層模型
- DBMS 語言
- DBMS 關系代數
- DBMS 關系演算
- DBMS 中的鍵
- DBMS 中的主鍵
- DBMS 中的超鍵
- DBMS 中的候選鍵
- DBMS 中的替代鍵
- DBMS 中的復合鍵
- DBMS 中的外鍵
- DBMS 中的約束
- DBMS 中的域約束
- DBMS 中的映射約束
- DBMS 中的基數
- DBMS 中的函數依賴
- DBMS 中的平凡函數依賴
- DBMS 中的非平凡函數依賴
- DBMS 中的多值依賴
- DBMS 中的傳遞依賴
- DBMS 中的范式:數據庫中的 1NF,2NF,3NF 和 BCNF
- DBMS 中的事務管理
- DBMS 中的 ACID 屬性
- DBMS 事務狀態
- DBMS 調度和調度類型
- DBMS 可串行化
- DBMS 沖突可串行化
- DBMS 查看可串行化
- DBMS 中的死鎖
- DBMS 中的并發控制
- BeginnersBook Java 教程
- Java 基礎知識教程
- Java 編程簡介
- Java 虛擬機(JVM),JDK 差異,JRE 和 JVM - 核心 Java
- 如何編譯和運行您的第一個 Java 程序
- Java 中的變量
- Java 中的數據類型
- Java 中的運算符
- Java 中的if和if-else語句
- Java 中的switch-case語句
- Java 中的for循環
- Java 中的while循環
- Java 中的 do-while 循環示例
- Java continue語句
- Java 中的break語句
- Java OOP 教程
- Java 中的構造函數 - 一個完整的研究
- Java - 靜態類,塊,方法和變量
- Java 編程中的繼承
- Java 中的繼承類型:單一,多重,多級和混合
- OOP 概念 - 什么是 java 中的聚合?
- OOP 概念 - java 中的關聯是什么?
- java 中的super關鍵字
- Java 中的方法重載
- java 中的方法覆蓋
- java 中方法重載和覆蓋之間的區別
- Java 中的多態
- java 的多態類型 - 運行時和編譯時多態
- java 中的靜態和動態綁定
- Java 中的抽象類
- Java 中的抽象方法
- java 中的接口
- Java 中抽象類和接口的區別
- Java 中的封裝
- java 中的包以及如何使用它們
- Java 訪問修飾符 - 公共、私有、受保護和默認
- Java 中的垃圾收集
- Java 中的final關鍵字 - final變量,方法和類
- Java 異常處理教程
- java 中的異常處理
- Java 中的try-catch - 異常處理
- Java finally塊 - 異常處理
- 如何在 java 中拋出異常
- java 中的用戶定義的異常
- Java 異常處理
- Java 注解,枚舉和正則表達式教程
- Java 枚舉教程
- Java 注解教程
- Java 正則表達式教程
- 其它核心 Java 教程
- Java - String類及其方法
- java 多線程
- Java 序列化
- Java AWT 初學者教程
- 適合初學者的 Java Swing 教程
- Java 自動裝箱和拆箱
- Java 中的包裝類
- Java 8 教程
- Java Lambda 表達式教程
- Java 8 中的方法引用
- Java 函數式接口
- Java 8 流教程
- Java 8 流過濾器
- Java 8 接口更改 - 默認方法和靜態方法
- Java 8 forEach方法
- Java 8 - Stream Collectors類
- Java 8 StringJoiner
- Java 8 Optional類
- Java 8 - 數組并行排序
- Java 9 特性
- Java 9 JShell(Java Shell) - REPL
- Java 9 - 創建不可變List的工廠方法
- Java 9 - 創建不可變Set的工廠方法
- Java 9 - 用于創建不可變Map的工廠方法
- Java 9 - 接口中的私有方法
- Java 9 - try-with-resource改進
- Java 9 - 匿名內部類和菱形運算符
- Java 9 - @SafeVarargs注解
- Java 9 - 流 API 改進
- 在 15 分鐘內學習 Java 9 模塊
- BeginnersBook Java 集合教程
- Java 集合 - List
- ArrayList
- ArrayList基礎知識
- java 中的ArrayList - 集合框架
- 如何初始化ArrayList
- 如何在 Java 中遍歷ArrayList
- 如何在 Java 中查找ArrayList的長度
- ArrayList排序
- 如何在 Java 中對ArrayList進行排序
- 如何在 Java 中按降序對ArrayList進行排序
- Java ArrayList對象排序(Comparable和Comparator)
- ArrayList添加/刪除
- Java ArrayList add()方法
- Java ArrayList add(int index, E element)
- Java ArrayList addAll(Collection c)方法
- 如何在 Java 中將所有List元素復制并添加到ArrayList
- Java ArrayList addAll(int index, Collection c)方法
- Java ArrayList remove(int index)方法
- Java ArrayList remove(Object obj)方法
- 在ArrayList中獲取/搜索
- 如何獲取ArrayList的子列表
- JavaArrayList lastIndexOf(Object Obj)方法
- Java ArrayList get()方法
- Java ArrayList indexOf()方法
- Java ArrayList contains()方法
- 關于ArrayList的其他教程
- 如何在 Java 中比較兩個ArrayList
- 如何在 java 中同步ArrayList
- 如何交換ArrayList中的兩個元素
- 如何在 Java 中覆蓋ArrayList的toString方法
- 如何在 java 中序列化ArrayList
- 如何在 java 中連接/組合兩個ArrayList
- 如何將ArrayList克隆到另一個ArrayList
- 如何在 Java 中清空ArrayList
- Java ArrayList isEmpty()方法
- Java ArrayList trimToSize()方法
- Java ArrayList set()方法示例
- Java ArrayList ensureCapacity()方法
- ArrayList轉換
- 如何在 java 中將ArrayList轉換為字符串數組
- 如何在 java 中將數組轉換為ArrayList
- 差異
- java 中ArrayList和Vector之間的區別
- Java 中ArrayList和HashMap的區別
- Java 中ArrayList和LinkedList的區別
- 鏈表
- LinkedList基礎知識
- Java 中的LinkedList
- 如何在 Java 中遍歷LinkedList
- LinkedList添加/刪除
- 使用add(E e)方法向LinkedList添加元素
- Java - 在LinkedList的特定索引處添加元素
- Java - 在LinkedList的開頭和結尾添加元素
- 在 Java 中將LinkedList添加到LinkedList的前面
- Java - 從LinkedList刪除第一個和最后一個元素
- Java - 從LinkedList的特定索引刪除元素
- Java - 從LinkedList刪除特定元素
- Java - 從LinkedList刪除所有元素
- 將List的所有元素附加到LinkedList
- 在鏈表中獲取/搜索
- Java - 從LinkedList獲取第一個和最后一個元素
- Java - 從LinkedList的特定索引獲取元素
- Java - 在LinkedList中搜索元素
- Java - 從LinkedList獲取子列表
- LinkedList Iterator / ListIterator
- Java - LinkedList Iterator
- Java - LinkedList ListIterator
- 以反向順序迭代LinkedList
- LinkedList上的其他教程
- Java - 替換LinkedList中的元素
- Java - 檢查LinkedList中是否存在特定元素
- 在 Java 中克隆一個通用的LinkedList
- Java - 獲取LinkedList中元素的最后一次出現的索引
- LinkedList push()和pop()方法
- Java - LinkedList poll(),pollFirst()和pollLast()方法
- Java - LinkedList peek(),peekFirst()和peekLast()方法
- 轉換
- Java - 將LinkedList轉換為ArrayList
- 如何使用 Java 中的toArray()將LinkedList轉換為數組
- Vector
- Vector基礎知識
- Java 中的Vector
- 如何在 java 中獲取Vector的子列表
- 如何使用 Java 中的Collections.sort對Vector進行排序
- 使用索引在 Java 中搜索元素
- 將一個Vector的所有元素復制到另一個Vector
- Vector中的刪除/排序/替換
- 刪除Vector元素
- 如何在 java 中使用索引刪除Vector元素
- 從 Java 中的Vector中刪除所有元素
- 使用索引替換Vector元素
- 如何設置Vector大小
- Iterator/ListIterator/Enum
- Java 中的Vector Enumeration
- Java 中的Vector迭代器
- Java 中的Vector ListIterator
- 轉換
- Java - 將Vector轉換為List
- Java - 將Vector轉換為ArrayList
- 如何在 java 中將Vector轉換為字符串數組
- Java 集合 - Set
- HashSet
- Java 中的HashSet類
- 從HashSet中刪除所有元素
- 如何迭代Set/HashSet
- 將HashSet轉換為數組
- 如何將HashSet轉換為TreeSet
- 將HashSet轉換為List / ArrayList
- HashSet和HashMap之間的區別
- LinkedHashSet
- Java 中的LinkedHashSet類
- Java 中List和Set之間的區別
- TreeSet
- Java 中的TreeSet類
- HashSet和TreeSet之間的區別
- Java 集合 - Map
- HashMap
- HashMap基礎知識
- Java 中的HashMap
- 如何在 java 中循環HashMap
- 如何按鍵和值對 Java 中的HashMap進行排序
- Java - 獲取HashMap的大小
- Java - 從HashMap中刪除映射
- Java - 從HashMap中刪除所有映射
- 如何檢查HashMap是否為空?
- 在HashMap中獲取/搜索
- Java - 檢查HashMap中是否存在特定鍵
- Java - 檢查HashMap中是否存在特定值
- 序列化/同步
- 如何在 java 中序列化HashMap
- 如何在 Java 中同步HashMap
- 差異
- HashMap和Hashtable之間的區別
- HashSet和HashMap之間的區別
- 關于HashMap的其他教程
- Java - HashMap Iterator
- 何將一個hashmap內容復制到另一個hashmap
- HashMap - 從鍵中獲取值
- Java - 從HashMap獲取鍵集視圖
- 用 Java 克隆HashMap
- TreeMap
- Java 中的TreeMap
- TreeMap Iterator示例 - Java
- 如何在 java 中按值對TreeMap進行排序
- 如何在 Java 中以相反的順序迭代TreeMap
- 如何從TreeMap中獲取子映射 - Java
- LinkedHashMap
- Java 中的LinkedHashMap
- HashTable
- java 中的Hashtable
- Java 集合 - Iterator/ListIterator
- Java Iterator
- Java 中的ListIterator
- Comparable和Comparator接口
- Java 中的Comparable接口
- Java 中的Comparator接口
- 集合面試問題
- Java 集合面試問題和解答
- BeginnersBook Java 示例
- Java 基礎程序
- Java 程序:相加兩個數字
- Java 程序:檢查偶數或奇數
- Java 程序:相加兩個二進制數
- Java 程序:相加兩個復數
- Java 程序:乘以兩個數字
- Java 程序:檢查閏年
- Java 程序:使用Switch Case檢查元音或輔音
- Java 程序:計算復合利率
- Java 程序:計算簡單利率
- Java 程序:查找商和余數
- Java 字符串程序
- 如何在 Java 中將字符串轉換為char
- Java 程序:在String中查找重復的字符
- java 程序:使用Stack,Queue,for或while循環檢查回文串
- Java 程序:按字母順序排序字符串
- Java 程序:反轉String中的單詞
- Java 程序:對字符串執行冒泡排序
- Java 程序:查找字符串中字符的出現
- Java 程序:計算字符串中的元音和輔音
- Java 數組程序
- Java 程序:使用數組計算平均值
- Java 程序:匯總數組的元素
- Java 程序:反轉數組
- Java 程序:按升序排序數組
- 如何在 Java 中將char數組轉換為字符串?
- Java 遞歸程序
- Java 程序:使用for,while和遞歸來反轉一個數字
- java 程序:使用遞歸檢查回文字符串
- Java 程序:使用遞歸來反轉字符串
- java 程序:使用遞歸查找給定數字的階乘
- Java 數字程序
- Java 程序:顯示前n個或前 100 個素數
- Java 程序:顯示 1 到 100 和 1 到n的素數
- Java 程序:將Integer分解為數字
- Java 程序:檢查素數
- Java 程序:檢查給定數字是否為完美平方
- Java 程序:不使用sqrt查找數字的平方根
- Java 程序:在給定范圍之間打印 Armstrong 數字
- Java 程序:查找自然數之和
- Java 程序:用于檢查數字是正還是負
- Java 程序:生成隨機數
- Java 程序:檢查 Armstrong 數
- Java 程序:查找兩個數字的 GCD
- Java 程序:找到三個數字中最大的一個
- Java 程序:使用按位 XOR 運算符交換兩個數字
- Java 程序:使用三元運算符查找最小的三個數字
- Java 程序:使用三元運算符查找三個數字中的最大數字
- Java 程序:打印備用素數
- Java 程序:打印 1 到n或 1 到 100 的偶數
- Java 程序:打印 1 到n或 1 到 100 的奇數
- Java 輸入/輸出程序
- Java 程序:從標準輸入讀取整數值
- Java 程序:獲取 IP 地址
- Java 程序:從用戶獲取輸入
- Java 程序:幾何計算
- Java 程序:計算矩形面積
- Java 程序:計算正方形的面積
- Java 程序:計算三角面積
- Java 程序:計算圓的面積和周長
- Java 排序/搜索程序
- Java 程序:升序和降序的冒泡排序
- Java 程序:線性搜索
- Java 程序:執行二分搜索
- Java 程序:選擇排序
- Java 轉換程序
- Java 程序:八進制到十進制的轉換
- Java 程序:十進制到八進制的轉換
- Java 程序:十六進制到十進制的轉換
- Java 程序:十進制到十六進制的轉換
- Java 程序:二進制到八進制的轉換
- Java 程序:String到boolean的轉換
- Java 程序:布爾值到String的轉換
- Java 程序:int到char的轉換
- Java 程序:char到int的轉換
- Java 程序:char到String的轉換
- Java 程序:long到int的轉換
- Java 程序:int到long的轉換
- Java 程序:十進制到二進制的轉換
- Java 程序:二進制到十進制的轉換
- Java 程序:查找字符的 ASCII 值
- Java 程序:String到int的轉換
- Java 程序:int到String的轉換
- Java 程序:String到double的轉換
- Java 程序:double到字符串的轉換
- Java 程序:字符串到long的轉換
- Java 程序:long到字符串的轉換
- 其他 Java 程序
- Java 程序:打印 Floyd 三角形
- Java 程序:打印 Pascal 三角形
- Java 程序:使用循環顯示 Fibonacci 序列
- Java 程序:使用For和While循環查找階乘
- Java 程序:使用Switch Case制作計算器
- Java 程序:計算和顯示學生成績
- Java 程序:使用方法重載執行算術運算
- Java 程序:使用方法重載查找幾何圖形的面積
- BeginnersBook Java IO 教程
- 如何在 Java 中創建文件
- 如何在 Java 中讀取文件 - BufferedInputStream
- 如何在 java 中使用FileOutputStream寫入文件
- 使用BufferedWriter,PrintWriter,FileWriter附加到 java 中的文件
- 如何在 Java 中刪除文件 - delete()方法
- 如何以 GZIP 格式壓縮文件
- 如何使用 Java 將文件復制到另一個文件
- 如何在 java 中獲取文件的最后修改日期
- 如何在 Java 中創建只讀文件
- 如何在 Java 中檢查文件是否隱藏
- BeginnersBook Java 字符串教程
- Java 字符串方法
- Java String charAt()方法
- Java Stringequals()和equalsIgnoreCase()方法
- Java String compareTo()方法
- Java String compareToIgnoreCase()方法
- Java String startsWith()方法
- Java String endsWith()方法
- Java String trim()和hashCode()方法
- Java String indexOf()方法
- Java String lastIndexOf()方法
- Java - String substring()方法
- Java String concat()方法
- Java String replace(),replaceFirst()和replaceAll()方法
- Java String contains()方法
- Java - String toLowerCase()和toUpperCase()方法
- Java String intern()方法
- Java String isEmpty()方法
- Java String join()方法
- Java 正則表達式教程
- Java String split()方法
- Java String format()方法
- Java - String toCharArray()方法
- Java - String copyValueOf()方法
- Java - String getChars()方法
- Java String valueOf()方法
- Java - String contentEquals()方法
- Java - String regionMatches()方法
- Java - String getBytes()方法
- Java String length()方法
- Java - String matches()方法
- 流行的 Java 字符串教程
- Java 程序:String到int的轉換
- Java 程序:int到String的轉換
- Java 程序:String到double的轉換
- Java 程序:double到字符串的轉換
- Java 程序:字符串到long的轉換
- Java 程序:long到字符串的轉換
- 如何在 Java 中將InputStream轉換為字符串
- String和StringBuffer之間的區別
- Java 程序:String到boolean的轉換
- Java 程序:布爾值到String的轉換
- 在 Java 中將String對象轉換為Boolean對象
- 如何在 Java 中僅刪除字符串的尾隨空格
- java - 使用空格和零左填充字符串
- java - 使用空格和零右填充字符串
- Java 程序:在String中查找重復的字符
- 如何在 Java 中將字符串轉換為字符
- 如何在 Java 中將char數組轉換為字符串?
- 在 Java 中將String轉換為日期
- 在 Java 中將Date轉換為String
- Java - ASCII 到String的轉換
- Java - float到String的轉換
- Java - StackTrace到String的轉換
- Java - Writer到String的轉換
- Java - String到ArrayList轉換
- Java 8 StringJoiner
- Java 程序:反轉String中的單詞
- Java 程序:使用遞歸來反轉字符串
- BeginnersBook JSP 教程
- 概述
- Java 服務器頁面簡介
- Java 服務器頁面(JSP)生命周期
- 指令
- JSP 指令 - page,include和TagLib
- JSP 中的Include指令
- JSP 帶參數的include指令
- Scriptlets
- JSP Scriptlets
- 動作標簽
- JSP 動作
- JSP include動作標簽
- JSP 帶參數的include動作
- JSP forward動作標簽
- jsp:useBean,jsp:setProperty和jsp:getProperty動作標簽
- 表達式
- JSP 表達式標簽
- 聲明
- JSP 聲明標簽 - JSP 教程
- JSP 隱式對象
- Jsp 隱式對象
- JSP 中的out隱式對象
- JSP 中的request隱式對象
- JSP 中的response隱式對象
- JSP 中的Session隱式對象
- JSP 中的application隱式對象
- JSP 中的exception隱式對象
- JSP 中的pageContext隱式對象
- JSP 中的config隱式對象
- JSP 中的表達式語言(EL)
- JSP 表達式語言(EL)
- 異常處理
- JSP 中的異常處理
- 自定義標簽
- JSP 自定義標簽
- 如何訪問自定義標簽的主體
- BeginnersBook JSTL 教程
- JSTL 核心標簽
- JSTL<c:out>核心標簽
- JSTL<c:set>核心標簽
- JSTL<c:delete>核心標簽
- JSTL<c:if>核心標簽
- JSTL<c:choose>,<c:when>,<c:otherwise>核心標簽
- JSTL<c:catch>核心標簽
- JSTL<c:import>核心標簽
- JSTL<c:forEach>和<c:forTokens>核心標簽
- JSTL<c:param>核心標簽
- JSTL<c:url>核心標簽
- JSTL<c:redirect>核心標簽
- JSTL 函數
- fn:contains() - JSTL 函數
- fn:containsIgnoreCase() - JSTL 函數
- fn:indexOf() - JSTL 函數
- fn:escapeXml() - JSTL 函數
- fn:join()和fn:split()JSTL 函數
- fn:length() - JSTL 函數
- fn:trim()和fn:startsWith()JSTL 函數
- fn:endsWith() - JSTL 函數
- fn:substring(),fn:substringAfter()和fn:substringBefore()函數
- fn:toUpperCase() - JSTL 函數
- fn:toLowerCase() - JSTL 函數
- fn:replace() - JSTL 函數
- BeginnersBook Kotlin 教程
- BeginnersBook MongoDB 教程
- NoSQL 數據庫簡介
- MongoDB 簡介
- 將關系數據庫映射到 MongoDB
- 如何為 Windows 安裝和配置 MongoDB
- 在 MongoDB 中創建數據庫
- 刪除 MongoDB 中的數據庫
- 在 MongoDB 中創建集合
- 刪除 MongoDB 中的集合
- MongoDB 插入文檔
- MongoDB 使用find()方法查詢文檔
- MongoDB - 更新集合中的文檔
- MongoDB 從集合中刪除文檔
- MongoDB 投影
- MongoDB - limit()和skip()方法
- MongoDB sort()方法
- MongoDB 索引教程
- BeginnersBook Perl 教程
- 在 Windows,Mac,Linux 和 Unix 上安裝 Perl
- 第一個 Perl 計劃
- Perl 語法
- Perl 中的數據類型
- Perl 變量
- my關鍵字 - Perl 中的本地和全局變量
- Perl 中的標量
- Perl 中的use strict和use warnings
- Perl - 列表和數組
- Perl 中的哈希
- Perl 運算符 - 完整指南
- Perl 中的條件語句
- Perl 中的if語句
- Perl 中的if-else語句
- perl 中的if-elsif-else語句
- Perl 中的unless語句
- Perl 中的unless-else語句
- Perl 中的unless-elsif語句
- Perl 中的Switch Case
- Perl 中的given-when-default語句
- Perl 中的循環和循環控制語句
- Perl 中的for循環
- Perl while循環
- Perl - do-while循環
- Perl - foreach循環
- Perl 中的until循環
- Perl 中的子程序
- Perl - 字符串
- Perl 字符串轉義序列
- BeginnersBook Servlet 教程
- 適用于初學者的 Servlet 教程
- Servlet API
- Servlet接口解釋
- GenericServlet類
- HttpServlet類
- 如何在 Eclipse IDE 中創建和運行 Servlet
- Servlet 生命周期
- Servlet 的工作原理
- 項目的web.xml文件中的welcome-file-list標簽
- 如何在web.xml文件中使用load-on-startup標簽
- ServletRequest接口
- Servlet 中的RequestDispatcher方法
- ServletConfig接口
- ServletContext接口
- ServletResponse接口
- Servlet 中的HttpSession
- Servlet 中的Cookie
- Servlet 面試問答
