```
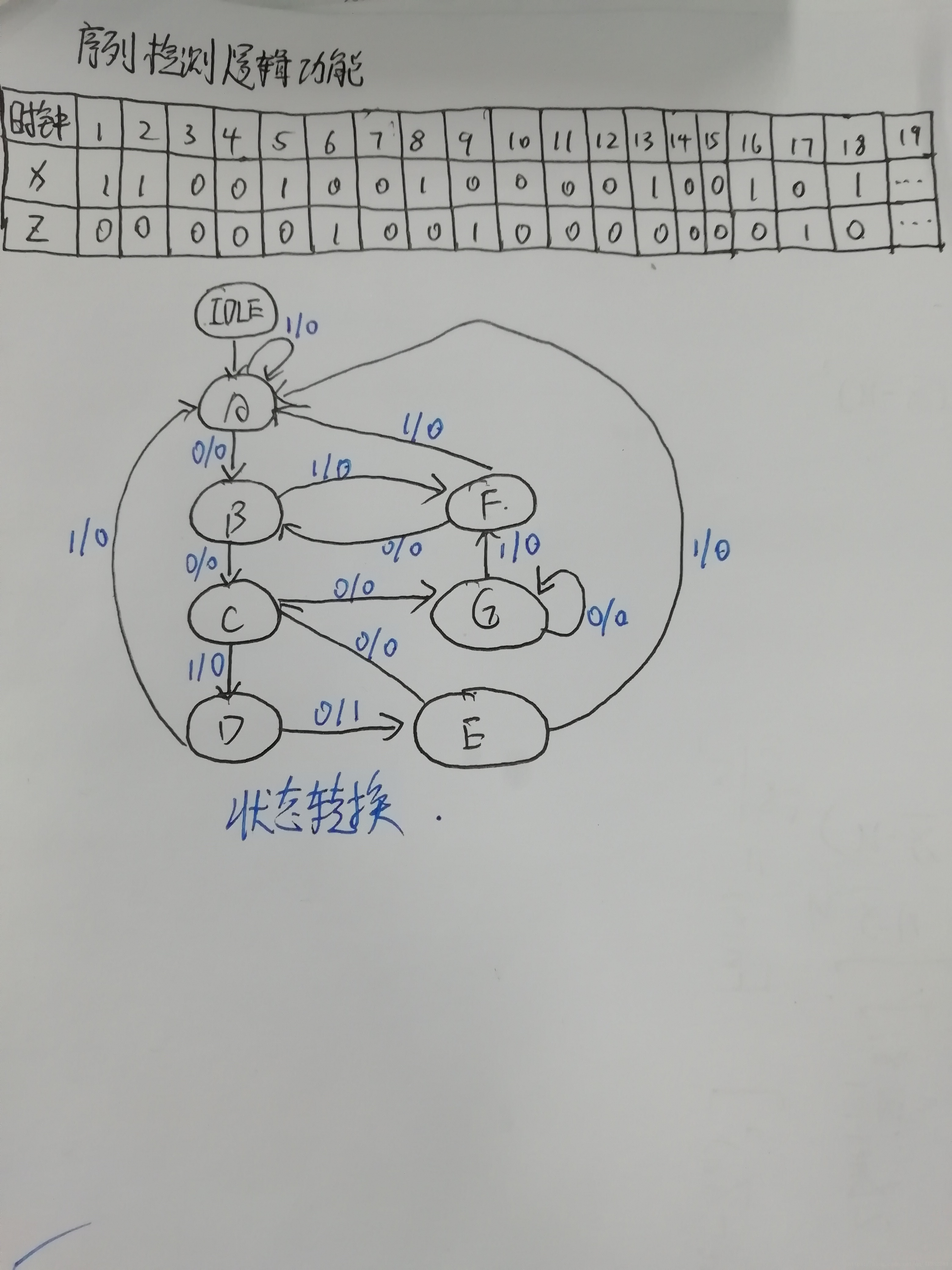
module cy4( clk,rst_b,In,Y);
input clk,rst_b,In;
output Y;
reg[2:0]current_state,next_state;
wire Y;
parameter IDLE = 3'd0,//每個十進制數代表不同的狀態
A = 3'd1,
B = 3'd2,
C = 3'd3,
D = 3'd4,
E = 3'd5,//輸出為1的狀態
F = 3'd6,
G = 3'd7;
assign Y = (next_state == D && In == 0)?1:0;
//狀態為D時又收到了0,表明10010收到應有輸出Y為高
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_b)
if(!rst_b) current_state <= IDLE;
else current_state <= next_state;
always @(In,current_state)
case(current_state)
IDLE: if(In == 1) next_state <= A;
else next_state <= IDLE;
A: if(In == 0) next_state <= B;
else next_state <= A;
B: if(In == 0) next_state <= C;
else next_state <= F;
C: if(In == 1) next_state <= D;
else next_state <= G;
D: if(In == 0) next_state <= E;
else next_state <= A;
E: if(In == 0) next_state <= C;
else next_state <= A;
F: if(In == 0) next_state <= B;
else next_state <= A;
G: if(In == 0) next_state <= G;
else next_state <= F;
default:next_state <= IDLE;
endcase
endmodule
```
測試腳本代碼:
```
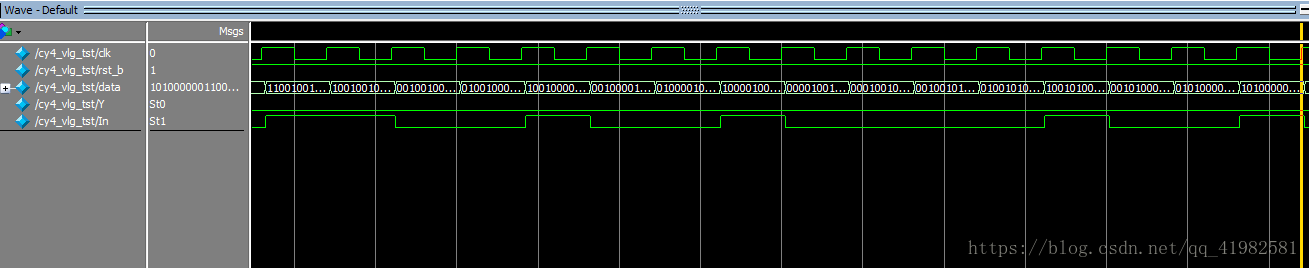
`timescale 1 ns/ 1 ps
`define halfperiod 20
module cy4_vlg_tst();
reg clk;
reg rst_b;
reg[23:0]data;
wire Y,In;
assign In = data[23];
cy4 i1 (
.In(In),
.Y(Y),
.clk(clk),
.rst_b(rst_b)
);
initial
begin
clk=0;
rst_b=1;
#2 rst_b=0;
#30 rst_b=1;//復位信號
data=20'b1100_1001_0000_1001_0100;//碼流數據
#(`halfperiod*1000)$stop;//運行500個時鐘周期后停止仿真
end
always #(`halfperiod)clk = ~clk;//時鐘信號
always @(posedge clk)
#2 data={data[22:0],data[23]};//移位輸出碼流
cy4 m(.In(In),.Y(Y),.clk(clk),.rst_b(rst_b));
//調用序列檢測器模塊
endmodule
```
- 空白目錄
- 流水線
- 流水線性能測評
- 計算機性能測評
- 流水線設計
- 購物車狀態機
- 序列檢測器
- 序列檢測10010
- 序列檢測10010帶圖
- 反相器
- 計數器
- 分頻電路
- 偶數分頻
- 奇數分頻
- 小數分頻
- 同步復位異步釋放all
- 對的-異步復位同步釋放原理
- 同步復位異步釋放
- 異步復位為什么要同步釋放 ?
- FPGA-異步復位同步釋放 通俗解釋
- 同步復位
- 狀態機
- 狀態機的分類
- 狀態機5個要素
- FIFO
- 異步fifo中同步為什么要用兩級觸發器
- 亞穩態
- 亞穩態的產生機理、消除辦法 (可以理解為什么打拍)
- 面向對象思想
- 為什么D觸發器有setup time和hold time的要求
- Tsu,Tco,Th,Tpd的概念
- verilog
- 自啟動
- 毛刺
- 馮諾依曼
