## 圖的表達方式及創建
### 二維數組表示法
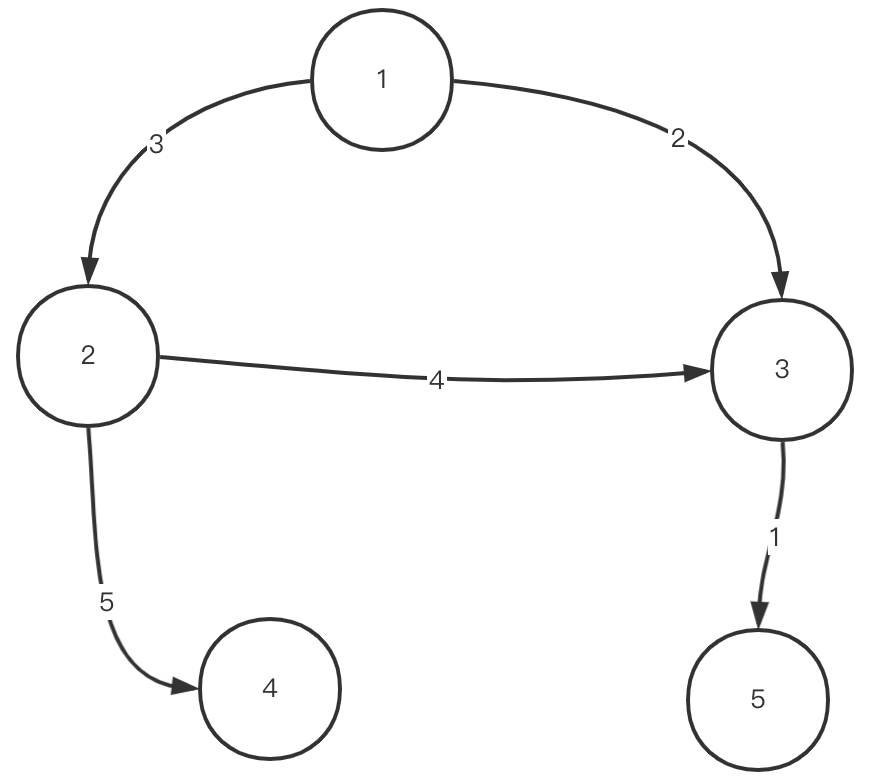
~~~
int[][] data = {
{1,2,3}, // 頂點1到頂點2有一條權值為3的邊
{2,3,4},// 頂點2到頂點3有一條權值為4的邊
{1,3,2},
{2,4,5},
{3,5,1}
};
~~~
### 按數據創建無向圖
~~~
Graph graph = Graph.createGraphUnDirect(data);
~~~
~~~
/**
* 從數組場景創建無向圖
* @param data eg,{{1,3,2},{2,3,3}}
* 表示 從頂點1到頂點3有權值為2的邊;頂點3到頂點1權值為2的邊
* 從頂點2到頂點3有權值為3的邊;頂點3到頂點2權值為3的邊
* @return
*/
public static Graph createGraphUnDirect(int[][] data){
Graph graph = new Graph();
for(int i=0;i<data.length;i++){
String from = data[i][0] + "";
String to = data[i][1] + "";
Integer weight = data[i][2];
// 將from頂點和to頂點加入到圖里
if(!graph.vertexs.containsKey(from)){
graph.vertexs.put(from,new Vertex(from));
}
if(!graph.vertexs.containsKey(to)){
graph.vertexs.put(to,new Vertex(to));
}
// 從圖里獲取from和to頂點
Vertex fromVertex = graph.vertexs.get(from);
Vertex toVertex = graph.vertexs.get(to);
// 創建從from頂點到to頂點的邊
Edge edge = new Edge(weight,fromVertex,toVertex);
// 創建反向的邊
Edge reverseEdge = new Edge(weight,toVertex,fromVertex);
// from和to頂點的入度和出度都+1
fromVertex.out++;
fromVertex.in++;
toVertex.out++;
toVertex.in++;
// 將to頂點加入到from頂點里的點集nexts里
fromVertex.nexts.add(toVertex);
// 將from頂點加入到to頂點里的點集nexts里
toVertex.nexts.add(fromVertex);
// 將邊加入到from頂點的邊集里
fromVertex.edges.add(edge);
// 將反向邊加入到to頂點的邊集里
toVertex.edges.add(reverseEdge);
// 將邊加入到圖里
graph.edges.add(edge);
// 將反向邊加入到圖里
graph.edges.add(reverseEdge);
}
return graph;
}
~~~
### 按數組創建有向圖
~~~
Graph graph = Graph.createGraph(data);
~~~
~~~
/**
* 從數組場景創建有向圖
* @param data eg,{{1,3,2},{2,3,3}}
* 表示 從頂點1到頂點3有權值為2的邊;
* 從頂點2到頂點3有權值為3的邊
* @return
*/
public static Graph createGraph(int[][] data){
Graph graph = new Graph();
for(int i=0;i<data.length;i++){
String from = data[i][0] + "";
String to = data[i][1] + "";
Integer weight = data[i][2];
// 將from頂點和to頂點加入到圖里
if(!graph.vertexs.containsKey(from)){
graph.vertexs.put(from,new Vertex(from));
}
if(!graph.vertexs.containsKey(to)){
graph.vertexs.put(to,new Vertex(to));
}
// 從圖里獲取from和to頂點
Vertex fromVertex = graph.vertexs.get(from);
Vertex toVertex = graph.vertexs.get(to);
// 創建從from頂點到to頂點的邊
Edge edge = new Edge(weight,fromVertex,toVertex);
// from頂點的出度+1,to頂點的入度+1
fromVertex.out++;
toVertex.in++;
// 將to頂點加入到from頂點里的nexts里
fromVertex.nexts.add(toVertex);
// 將邊加入到from頂點的邊集里
fromVertex.edges.add(edge);
// 將邊加入到圖里
graph.edges.add(edge);
}
return graph;
}
~~~
### 字符箭頭數組表示法
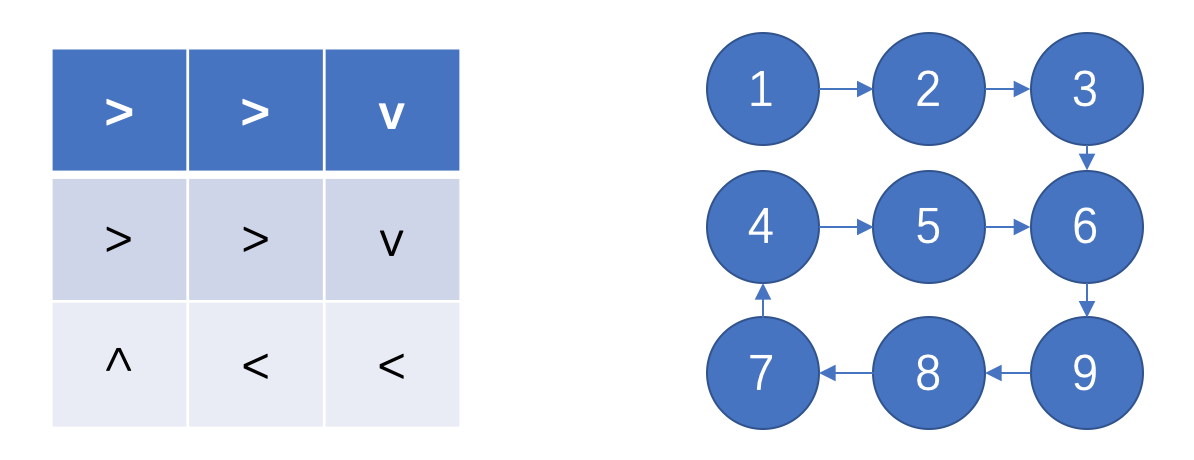
~~~
String[] arrows = {">>v",">>v","^<<"};
~~~
~~~
/**
* 從箭頭數組場景創建有向圖
* @param arrows eg, 自主編號
* {
* ">>v", 1,2,3
* "v^<", 4,5,6
* "<><" 7,8,9
* }
* 表示 從頂點1到頂點2有邊;頂點2到頂點3有邊;頂點3到頂點6有邊
* 頂點4到頂點7有邊;頂點5到頂點2有邊;頂點6到頂點5有邊
* 頂點8到頂點9有邊;頂點9到頂點8有邊
* @return
*/
public static Graph createGraphFromArrowString(String[] arrows){
Graph graph = new Graph();
int row = arrows.length;
int col = arrows[0].length();
// 設置上下左右的坐標規則
Map<Character,int[]> ruleMap = new HashMap<>();
ruleMap.put('^',new int[]{-1,0});
ruleMap.put('v',new int[]{1,0});
ruleMap.put('<',new int[]{0,-1});
ruleMap.put('>',new int[]{0,1});
for(int i=0;i<row;i++){
for(int j=0;j<col;j++){
String from = (i * col + j + 1) + "";
int[] rule = ruleMap.get(arrows[i].charAt(j));
int nextI = i + rule[0];
int nextJ = j + rule[1];
String to = (nextI * col + (nextJ + 1)) + "";
// 無權,默認為1
Integer weight = 1;
// 判斷to點的坐標在合法范圍內
if(nextI >=0 && nextI < row && nextJ >=0 && nextJ < col){
// 將from頂點和to頂點加入到圖里
if(!graph.vertexs.containsKey(from)){
graph.vertexs.put(from,new Vertex(from));
}
if(!graph.vertexs.containsKey(to)){
graph.vertexs.put(to,new Vertex(to));
}
// 從圖里獲取from和to頂點
Vertex fromVertex = graph.vertexs.get(from);
Vertex toVertex = graph.vertexs.get(to);
// 創建從from頂點到to頂點的邊
Edge edge = new Edge(weight,fromVertex,toVertex);
fromVertex.out++;
toVertex.in++;
// 將to頂點加入到from頂點里的點集nexts里
fromVertex.nexts.add(toVertex);
// 將邊加入到from頂點的邊集里
fromVertex.edges.add(edge);
// 將邊加入到圖里
graph.edges.add(edge);
}
}
}
return graph;
}
~~~
- Redis來回摩擦
- redis的數據結構SDS和DICT
- redis的持久化和事件模型
- Java
- 從何而來之Java IO
- 發布Jar包到公共Maven倉庫
- Java本地方法調用
- 面試突擊
- Linux
- Nginx
- SpringBoot
- Springboot集成Actuator和SpringbootAdminServer監控
- SpringCloud
- Spring Cloud初識
- Spring Cloud的5大核心組件
- Spring Cloud的注冊中心
- Spring Cloud注冊中心之Eureka
- Spring Cloud注冊中心之Consul
- Spring Cloud注冊中心之Nacos
- Spring Cloud的負載均衡之Ribbon
- Spring Cloud的服務調用之Feign
- Spring Cloud的熔斷器
- Spring Cloud熔斷器之Hystrix
- Spring Cloud的熔斷器監控
- Spring Cloud的網關
- Spring Cloud的網關之Zuul
- Spring Cloud的配置中心
- Spring Cloud配置中心之Config Server
- Spring Cloud Config配置刷新
- Spring Cloud的鏈路跟蹤
- Spring Cloud的鏈路監控之Sleuth
- Spring Cloud的鏈路監控之Zipkin
- Spring Cloud集成Admin Server
- Docker
- docker日常基本使用
- docker-machine的基本使用
- Kubernetes
- kubernetes初識
- kubeadm安裝k8s集群
- minikube安裝k8s集群
- k8s的命令行管理工具
- k8s的web管理工具
- k8s的相關發行版
- k3s初識及安裝
- rancher的安裝及使用
- RaspberryPi
- 運維
- 域名證書更新
- 騰訊云主機組建內網
- IDEA插件開發
- 第一個IDEA插件hello ide開發
- 千呼萬喚始出來的IDEA筆記插件mdNote
- 大剛學算法
- 待整理
- 一些概念和知識點
- 位運算
- 數據結構
- 字符串和數組
- LC242-有效的字母異位詞
- 鏈表
- LC25-K個一組翻轉鏈表
- LC83-刪除有序單鏈表重復的元素
- 棧
- LC20-有效的括號
- 隊列
- 雙端隊列
- 優先隊列
- 樹
- 二叉樹
- 二叉樹的遍歷
- 二叉樹的遞歸序
- 二叉樹的前序遍歷(遞歸)
- 二叉樹的前序遍歷(非遞歸)
- 二叉樹的中序遍歷(遞歸)
- 二叉樹的中序遍歷(非遞歸)
- 二叉樹的后序遍歷(遞歸)
- 二叉樹的后序遍歷(非遞歸)
- 二叉樹的廣度優先遍歷(BFS)
- 平衡二叉樹
- 二叉搜索樹
- 滿二叉樹
- 完全二叉樹
- 二叉樹的打印(二維數組)
- 樹的序列化和反序列化
- 前綴樹
- 堆
- Java系統堆優先隊列
- 集合數組實現堆
- 圖
- 圖的定義
- 圖的存儲方式
- 圖的Java數據結構(鄰接表)
- 圖的表達方式及對應場景創建
- 圖的遍歷
- 圖的拓撲排序
- 圖的最小生成樹之Prim算法
- 圖的最小生成樹之Kruskal算法
- 圖的最小單元路徑之Dijkstra算法
- 位圖
- Java實現位圖
- 并查集
- Java實現并查集
- 滑動窗口
- 單調棧
- 排序
- 冒泡排序BubbleSort
- 選擇排序SelectSort
- 插入排序InsertSort
- 插入排序InsertXSort
- 歸并排序MergeSort
- 快速排序QuickSort
- 快速排序優化版QuickFastSort
- 堆排序HeapSort
- 哈希Hash
- 哈希函數
- guava中的hash函數
- hutool中的hash函數
- 哈希表實現
- Java之HashMap的實現
- Java之HashSet的實現
- 一致性哈希算法
- 經典問題
- 荷蘭國旗問題
- KMP算法
- Manacher算法
- Go
