[TOC]
## 常見API
```
//數據結構
Integer?
Character
//操作
contains
equlas
//棧
Stack? stack = new Stack
push?
peek(不出)?
pop
//隊列
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer
queue.peek(不出 )
queue.poll
// 比較
new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;
}
}
//遍歷
for(Map.Entry entry : valueCountMap.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue() > nums.length/2) {
return entry.getKey;
}
}
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(s.charAt(j));
```
## 位運行
本文解法基于此性質:二叉搜索樹的中序遍歷為?遞增序列?。位運算只有5種運算:與、或、異或、左移、右移。與、或、異或運算的規律可以用下表總結:|?與(&)?|?0?&?0?=?0?|?1?&?0?=?0?|?0?&?1?=?0?|?1?&?1?=?1?||?或(|)?|?0?|?0?=?0?|?1?|?0?=?1?|?0?|?1?=?1?|?1?|?1?=?1?||?異或(^)?|?0?^?0?=?0?|?1?^?0?=?1?|?0?^?1?=?1?|?1?^?1?=?0?|左移運算符m<<n表示把m左移n位。在左移n位的時候,最左邊的n位會被丟棄,同時在最右邊補上n個0。比如:00001010?<<?2?=?0010100010001010?<<?3?=?01010000
##二分算法
### 普通二分
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-search/solution/er-fen-cha-zhao-xiang-jie-by-labuladong/
這個場景是最簡單的,肯能也是大家最熟悉的,即搜索一個數,如果存在,返回其索引,否則返回 -1。
```
int binarySearch(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length - 1; // 注意
while(left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(nums[mid] == target)
return mid;
else if (nums[mid] < target)
left = mid + 1; // 注意
else if (nums[mid] > target)
right = mid - 1; // 注意
}
return -1;
}
```
1、為什么 while 循環的條件中是 <=,而不是 <?
答:因為初始化 right 的賦值是 nums.length - 1,即最后一個元素的索引,而不是 nums.length。
這二者可能出現在不同功能的二分查找中,區別是:前者相當于兩端都閉區間 [left, right],后者相當于左閉右開區間 [left, right),因為索引大小為 nums.length 是越界的。
我們這個算法中使用的是前者 [left, right] 兩端都閉的區間。這個區間其實就是每次進行搜索的區間。
什么時候應該停止搜索呢?當然,找到了目標值的時候可以終止:
if(nums[mid] == target)
return mid;
但如果沒找到,就需要 while 循環終止,然后返回 -1。那 while 循環什么時候應該終止?搜索區間為空的時候應該終止,意味著你沒得找了,就等于沒找到嘛。
while(left <= right) 的終止條件是 left == right + 1,寫成區間的形式就是 [right + 1, right],或者帶個具體的數字進去 [3, 2],可見這時候區間為空,因為沒有數字既大于等于 3 又小于等于 2 的吧。所以這時候 while 循環終止是正確的,直接返回 -1 即可。
while(left < right) 的終止條件是 left == right,寫成區間的形式就是 [left, right],或者帶個具體的數字進去 [2, 2],這時候區間非空,還有一個數 2,但此時 while 循環終止了。也就是說這區間 [2, 2] 被漏掉了,索引 2 沒有被搜索,如果這時候直接返回 -1 就是錯誤的。
當然,如果你非要用 while(left < right) 也可以,我們已經知道了出錯的原因,就打個補丁好了:
//...
while(left < right) {
// ...
}
return nums[left] == target ? left : -1;
2、為什么 left = mid + 1,right = mid - 1?我看有的代碼是 right = mid 或者 left = mid,沒有這些加加減減,到底怎么回事,怎么判斷?
答:這也是二分查找的一個難點,不過只要你能理解前面的內容,就能夠很容易判斷。
剛才明確了「搜索區間」這個概念,而且本算法的搜索區間是兩端都閉的,即 [left, right]。那么當我們發現索引 mid 不是要找的 target 時,下一步應該去搜索哪里呢?
當然是去搜索 [left, mid-1] 或者 [mid+1, right] 對不對?因為 mid 已經搜索過,應該從搜索區間中去除。
### 求邊界二分
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-first-and-last-position-of-element-in-sorted-array/solution/zhe-shi-er-fen-zui-zui-zui-jing-dian-de-xlvf3/
**求左邊界:向下取整,等號歸右,左加一
求右邊界:向上取整,等號歸左,右減一**
* 求左邊界
```
int left = 0, right = n-1;
while(left < right){//求左邊界(注意這里不要等號)
int mid = (left+right)>>1;//向下取整
if(nums[mid] >= target) right = mid;//等號歸右
else left = mid+1;//左加一
}
//此時right即為所求
```
* 求右邊界
```
int left = 0, right = n-1;
while(left<right){//求右邊界(注意這里不要等號)
int mid = (left + right +1)>>1;//向上取整
if(nums[mid] <= target) left = mid;//等號歸左
else right = mid-1;//右減一
}
//此時right即為所求
```
### 循環數組
[劍指 Offer 11. 旋轉數組的最小數字](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/xuan-zhuan-shu-zu-de-zui-xiao-shu-zi-lcof/)
## 單例模式
~~~
public class Singleton {
private volatile static Singleton singleton;
private Singleton (){}
public static Singleton getSingleton() {
if (singleton == null) {
synchronized (Singleton.class) {
if (singleton == null) {
singleton = new Singleton();
}
}
}
return singleton;
}
}
~~~
## 生產者消費者模型
生產者生產數據到緩沖區中,消費者從緩沖區中取數據。
如果緩沖區已經滿了,則生產者線程阻塞;
如果緩沖區為空,那么消費者線程阻塞。
~~~
public interface ITaskQueue{
public void add();
public int remove();
}
public class Consumer extends Thread{
ITaskQueue queue;
public Consumer(ITaskQueue queue){
this.queue = queue;
}
public void run(){
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep((long) (1000 * Math.random()));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
queue.remove();
}
}
}
public class Producer extends Thread{
ITaskQueue queue;
public Producer(ITaskQueue queue){
this.queue = queue;
}
public void run(){
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep((long) (1000 * Math.random()));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
queue.add();
}
}
~~~
### 使用synchronized wait notify
~~~
public void TaskQueue1 implements ITaskQueue{
//當前資源數量
private int num = 0;
//資源池中允許存放的資源數目
private int size = 10;
public synchronized void add(){
if(num >= size){
wait();
}else{
num ++;
notifyAll();
}
}
public synchronized void remove(){
if(num <= 0){
wait();
}else{
num --;
notifyAll();
}
}
}
~~~
### 使用BlockingQueue
~~~
public void TaskQueue2 implements ITaskQueue{
private ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>();
public void add(){
queue.put(1);
}
public void remove(){
queue.talke();
}
}
~~~
## 排序
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-an-array/
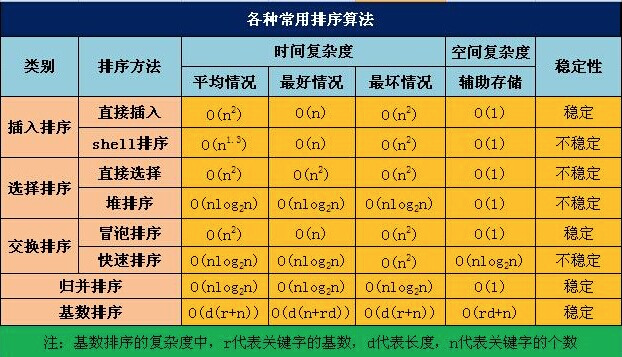
### 快排
1. 從數列中挑出一個元素,稱為 “基準”(pivot);
2. 重新排序數列,所有元素比基準值小的擺放在基準前面,所有元素比基準值大的擺在基準的后面(相同的數可以到任一邊)。在這個分區退出之后,該基準就處于數列的中間位置。這個稱為分區(partition)操作;
3. 遞歸地(recursive)把小于基準值元素的子數列和大于基準值元素的子數列排序。
```
public class QuickSort {
public static void quickSort(int[] arr,int low,int high){
int i,j,temp,t;
if(low>high){
return;
}
i=low;
j=high;
//temp就是基準位
temp = arr[low];
while (i<j) {
//先看右邊,依次往左遞減
while (temp<=arr[j]&&i<j) {
j--;
}
//再看左邊,依次往右遞增
while (temp>=arr[i]&&i<j) {
i++;
}
//如果滿足條件則交換
if (i<j) {
t = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[i];
arr[i] = t;
}
}
//最后將基準為與i和j相等位置的數字交換
arr[low] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
//遞歸調用左半數組
quickSort(arr, low, j-1);
//遞歸調用右半數組
quickSort(arr, j+1, high);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] arr = {10,7,2,4,7,62,3,4,2,1,8,9,19};
quickSort(arr, 0, arr.length-1);
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}
```
### 歸并
1. 把長度為n的輸入序列分成兩個長度為n/2的子序列;
2. 對這兩個子序列分別采用歸并排序;
3. 將兩個排序好的子序列合并成一個最終的排序序列。

### 大頂堆
## 二叉樹
[二叉樹的后序遍歷(遞歸與非遞歸實現)](https://blog.csdn.net/LK274857347/article/details/77678464)
### 深度優先的遍歷(棧)
#### 先序遍歷
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/
#### 中序遍歷
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/
#### 后序遍歷
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000016674584
好理解,雙堆棧法
1. 用一個棧實現`根->右->左`的遍歷
2. 用另一個棧將遍歷順序反過來,使之變成`左->右->根`
```
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new LinkedList<>();
if (root == null) return result;
Stack<TreeNode> toVisit = new Stack<>();
Stack<TreeNode> reversedStack = new Stack<>();
toVisit.push(root);
TreeNode cur;
while (!toVisit.isEmpty()) {
cur = toVisit.pop();
reversedStack.push(cur); // result.add(cur.val);
if (cur.left != null) toVisit.push(cur.left); // 左節點入棧
if (cur.right != null) toVisit.push(cur.right); // 右節點入棧
}
while (!reversedStack.isEmpty()) {
cur = reversedStack.pop();
result.add(cur.val);
}
return result;
}
}
```
#### 層次遍歷
### 廣度優先的遍歷(隊列)
- Java
- Object
- 內部類
- 異常
- 注解
- 反射
- 靜態代理與動態代理
- 泛型
- 繼承
- JVM
- ClassLoader
- String
- 數據結構
- Java集合類
- ArrayList
- LinkedList
- HashSet
- TreeSet
- HashMap
- TreeMap
- HashTable
- 并發集合類
- Collections
- CopyOnWriteArrayList
- ConcurrentHashMap
- Android集合類
- SparseArray
- ArrayMap
- 算法
- 排序
- 常用算法
- LeetCode
- 二叉樹遍歷
- 劍指
- 數據結構、算法和數據操作
- 高質量的代碼
- 解決問題的思路
- 優化時間和空間效率
- 面試中的各項能力
- 算法心得
- 并發
- Thread
- 鎖
- java內存模型
- CAS
- 原子類Atomic
- volatile
- synchronized
- Object.wait-notify
- Lock
- Lock之AQS
- Lock子類
- 鎖小結
- 堵塞隊列
- 生產者消費者模型
- 線程池
