[TOC]
基于'com.squareup.okhttp3:okhttp:3.12.0'
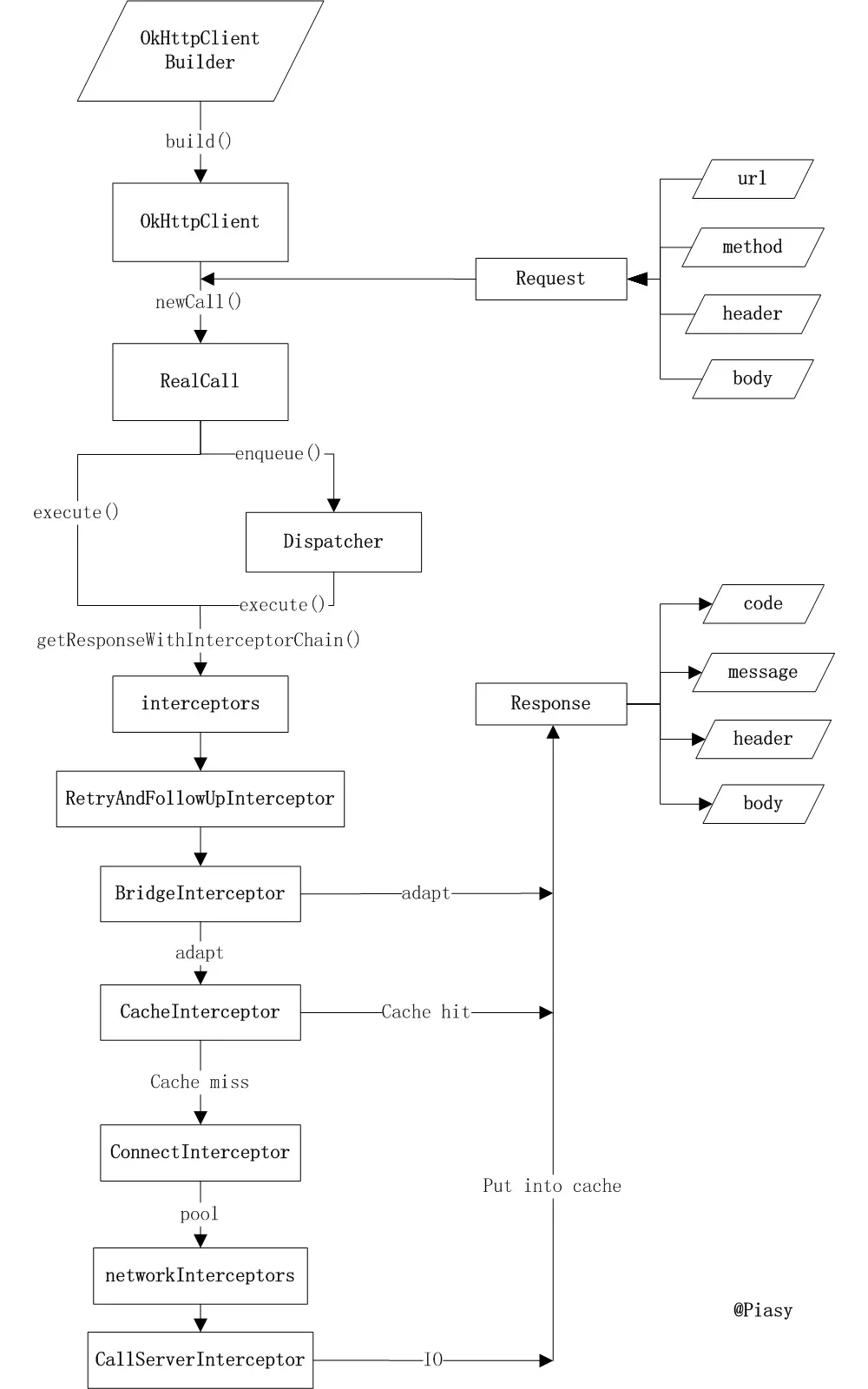
## 整體設計
## 線程池
### 個人理解
1. 如果請求是同步,請求直接加入請求同步隊列(runningAsyncCalls)中,然后那么就直接請求。
2. 如果請求是異步,判斷請求異步隊列(runningAsyncCalls)數量是否在64以內 以及 同一host的請求是是否在5以內。
3. 如果否,加入等待異步隊列(readyAsyncCalls)。
4. 如果是,則加入請求異步隊列(runningAsyncCalls),開始請求。
5. 請求結束后,調用finally里的方法。
6. 將自己移除請求異步隊列(runningAsyncCalls),并且在等待異步隊列(readyAsyncCalls)取出任務執行
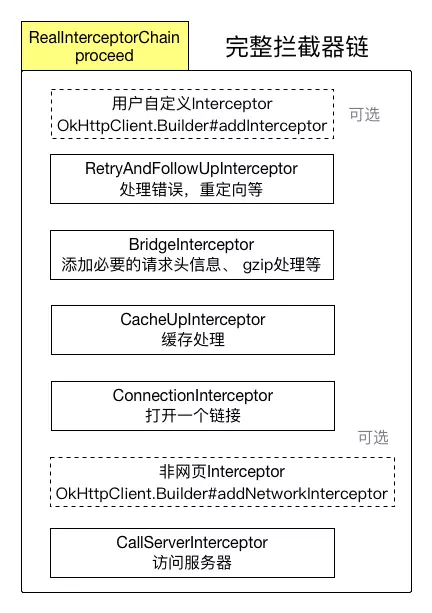
## 攔截器與責任鏈
~~~
RealCall
@Override
protected void execute() {
boolean signalledCallback = false;
try {
// 核心
Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
if (retryAndFollowUpInterceptor.isCanceled()) {
signalledCallback = true;
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, new IOException("Canceled"));
} else {
signalledCallback = true;
responseCallback.onResponse(RealCall.this, response);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
if (signalledCallback) {
// Do not signal the callback twice!
Platform.get().log(INFO, "Callback failure for " + toLoggableString(), e);
} else {
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, e);
}
} finally {
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}
@Override
Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException {
// Build a full stack of interceptors.
List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors());
interceptors.add(retryAndFollowUpInterceptor);
interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar()));
interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache()));
interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client));
if (!forWebSocket) {
interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors());
}
interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket));
Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(
interceptors, null, null, null, 0, originalRequest);
return chain.proceed(originalRequest);
}
RealInterceptorChain
public Response proceed(Request request, StreamAllocation streamAllocation, HttpCodec httpCodec,
Connection connection) throws IOException {
.....
// 核心
RealInterceptorChain next = new RealInterceptorChain(
interceptors, streamAllocation, httpCodec, connection, index + 1, request);
Interceptor interceptor = interceptors.get(index);
Response response = interceptor.intercept(next);
.....
return response;
}
****Interceptor 真實攔截器
@Override
public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
.....
chain.proceed(originalRequest);//下一個攔截器
..
~~~
## RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor 重定向
當返回了3\*\*的狀態碼,說明需要進行重定向,此攔截器就會自從重定向后重新請求。最多請求20次。
~~~
public final class RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor implements Interceptor {
//最大重定向次數:
private static final int MAX_FOLLOW_UPS = 20;
@Override
public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
Request request = chain.request();
// 三個參數分別對應:(1)全局的連接池,(2)連接線路Address, (3)堆棧對象
streamAllocation = new StreamAllocation(
client.connectionPool(), createAddress(request.url()), callStackTrace);
int followUpCount = 0;
Response priorResponse = null;
while (true) {
if (canceled) {
streamAllocation.release();
throw new IOException("Canceled");
}
Response response = null;
boolean releaseConnection = true;
// 執行下一個攔截器,即BridgeInterceptor
response = ((RealInterceptorChain) chain).proceed(request, streamAllocation, null, null);
releaseConnection = false;
...
//核心 檢查是否符合要求
Request followUp = followUpRequest(response);
if (followUp == null) {
if (!forWebSocket) {
streamAllocation.release();
}
// 返回結果
return response;
}
//不符合,關閉響應流
closeQuietly(response.body());
// 是否超過最大限制
if (++followUpCount > MAX_FOLLOW_UPS) {
streamAllocation.release();
throw new ProtocolException("Too many follow-up requests: " + followUpCount);
}
if (followUp.body() instanceof UnrepeatableRequestBody) {
streamAllocation.release();
throw new HttpRetryException("Cannot retry streamed HTTP body", response.code());
}
if (!sameConnection(response, followUp.url())) {
streamAllocation.release();
streamAllocation = new StreamAllocation(
client.connectionPool(), createAddress(followUp.url()), callStackTrace);
} else if (streamAllocation.codec() != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Closing the body of " + response
+ " didn't close its backing stream. Bad interceptor?");
}
request = followUp;
priorResponse = response;
~~~
## BridgeInterceptor 添加請求頭
BridgeInterceptor比較簡單
**發送請求**
* header包括*Content-Type*、*Content-Length*、*Transfer-Encoding*、*Host*、*Connection*、*Accept-Encoding*、*User-Agent*。
* 如果需要gzip壓縮則進行gzip壓縮
* 加載*Cookie*
**響應**
* 首先保存*Cookie*
* 如果服務器返回的響應content是以gzip壓縮過的,則會先進行解壓縮,移除響應中的header Content-Encoding和Content-Length,構造新的響應返回。
* 否則直接返回response
~~~
public final class BridgeInterceptor implements Interceptor {
private final CookieJar cookieJar;
public BridgeInterceptor(CookieJar cookieJar) {
this.cookieJar = cookieJar;
}
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
Request userRequest = chain.request();
Request.Builder requestBuilder = userRequest.newBuilder();
RequestBody body = userRequest.body();
if (body != null) {
MediaType contentType = body.contentType();
if (contentType != null) {
requestBuilder.header("Content-Type", contentType.toString());
}
long contentLength = body.contentLength();
if (contentLength != -1) {
requestBuilder.header("Content-Length", Long.toString(contentLength));
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Transfer-Encoding");
} else {
requestBuilder.header("Transfer-Encoding", "chunked");
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Content-Length");
}
}
if (userRequest.header("Host") == null) {
requestBuilder.header("Host", hostHeader(userRequest.url(), false));
}
if (userRequest.header("Connection") == null) {
requestBuilder.header("Connection", "Keep-Alive");
}
// If we add an "Accept-Encoding: gzip" header field we're responsible for also decompressing
// the transfer stream.
boolean transparentGzip = false;
if (userRequest.header("Accept-Encoding") == null && userRequest.header("Range") == null) {
transparentGzip = true;
requestBuilder.header("Accept-Encoding", "gzip");
}
List<Cookie> cookies = cookieJar.loadForRequest(userRequest.url());
if (!cookies.isEmpty()) {
requestBuilder.header("Cookie", cookieHeader(cookies));
}
if (userRequest.header("User-Agent") == null) {
requestBuilder.header("User-Agent", Version.userAgent());
}
Response networkResponse = chain.proceed(requestBuilder.build());
HttpHeaders.receiveHeaders(cookieJar, userRequest.url(), networkResponse.headers());
Response.Builder responseBuilder = networkResponse.newBuilder()
.request(userRequest);
if (transparentGzip
&& "gzip".equalsIgnoreCase(networkResponse.header("Content-Encoding"))
&& HttpHeaders.hasBody(networkResponse)) {
GzipSource responseBody = new GzipSource(networkResponse.body().source());
Headers strippedHeaders = networkResponse.headers().newBuilder()
.removeAll("Content-Encoding")
.removeAll("Content-Length")
.build();
responseBuilder.headers(strippedHeaders);
String contentType = networkResponse.header("Content-Type");
responseBuilder.body(new RealResponseBody(contentType, -1L, Okio.buffer(responseBody)));
}
return responseBuilder.build();
}
/** Returns a 'Cookie' HTTP request header with all cookies, like {@code a=b; c=d}. */
private String cookieHeader(List<Cookie> cookies) {
StringBuilder cookieHeader = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0, size = cookies.size(); i < size; i++) {
if (i > 0) {
cookieHeader.append("; ");
}
Cookie cookie = cookies.get(i);
cookieHeader.append(cookie.name()).append('=').append(cookie.value());
}
return cookieHeader.toS
~~~
## CacheInterceptor 緩存處理
### 注意事項
1. 目前只支持GET,其他請求方式需要自己實現。
2. 需要服務器配合,通過head設置相關頭來控制緩存
3. 創建OkHttpClient時候需要配置Cache
### 流程
1. 如果配置了緩存,則從緩存中取出(可能為null)
2. 獲取緩存的策略.
3. 監測緩存
4. 如果禁止使用網絡(比如飛行模式),且緩存無效,直接返回
5. 如果緩存有效,使用網絡,不使用網絡
6. 如果緩存無效,執行下一個攔截器
7. 本地有緩存、根據條件判斷是使用緩存還是使用網絡的response
8. 把response緩存到本地
### CacheStrategy類詳解
緩存策略類,根據輸出的networkRequest和cacheResponse的值是否為null給出不同的策略,如下:
networkRequestcacheResponseresult 結果nullnullonly-if-cached (表明不進行網絡請求,且緩存不存在或者過期,一定會返回503錯誤)nullnon-null不進行網絡請求,直接返回緩存,不請求網絡non-nullnull需要進行網絡請求,而且緩存不存在或者過去,直接訪問網絡non-nullnon-nullHeader中包含ETag/Last-Modified標簽,需要在滿足條件下請求,還是需要訪問網絡
~~~
public Factory(long nowMillis, Request request, Response cacheResponse) {
this.nowMillis = nowMillis;
this.request = request;
this.cacheResponse = cacheResponse;
if (cacheResponse != null) {
this.sentRequestMillis = cacheResponse.sentRequestAtMillis();
this.receivedResponseMillis = cacheResponse.receivedResponseAtMillis();
Headers headers = cacheResponse.headers();
//獲取cacheReposne中的header中值
for (int i = 0, size = headers.size(); i < size; i++) {
String fieldName = headers.name(i);
String value = headers.value(i);
if ("Date".equalsIgnoreCase(fieldName)) {
servedDate = HttpDate.parse(value);
servedDateString = value;
} else if ("Expires".equalsIgnoreCase(fieldName)) {
expires = HttpDate.parse(value);
} else if ("Last-Modified".equalsIgnoreCase(fieldName)) {
lastModified = HttpDate.parse(value);
lastModifiedString = value;
} else if ("ETag".equalsIgnoreCase(fieldName)) {
etag = value;
} else if ("Age".equalsIgnoreCase(fieldName)) {
ageSeconds = HttpHeaders.parseSeconds(value, -1);
}
}
}
}
/**
* Returns a strategy to satisfy {@code request} using the a cached response {@code response}.
*/
public CacheStrategy get() {
CacheStrategy candidate = getCandidate();
if (candidate.networkRequest != null && request.cacheControl().onlyIfCached()) {
// We're forbidden from using the network and the cache is insufficient.
return new CacheStrategy(null, null);
}
return candidate;
}
/**
* Returns a strategy to satisfy {@code request} using the a cached response {@code response}.
*/
public CacheStrategy get() {
//獲取當前的緩存策略
CacheStrategy candidate = getCandidate();
//如果是網絡請求不為null并且請求里面的cacheControl是只用緩存
if (candidate.networkRequest != null && request.cacheControl().onlyIfCached()) {
// We're forbidden from using the network and the cache is insufficient.
//使用只用緩存的策略
return new CacheStrategy(null, null);
}
return candidate;
}
/** Returns a strategy to use assuming the request can use the network. */
private CacheStrategy getCandidate() {
// No cached response.
//如果沒有緩存響應,返回一個沒有響應的策略
if (cacheResponse == null) {
return new CacheStrategy(request, null);
}
//如果是https,丟失了握手,返回一個沒有響應的策略
// Drop the cached response if it's missing a required handshake.
if (request.isHttps() && cacheResponse.handshake() == null) {
return new CacheStrategy(request, null);
}
// 響應不能被緩存
// If this response shouldn't have been stored, it should never be used
// as a response source. This check should be redundant as long as the
// persistence store is well-behaved and the rules are constant.
if (!isCacheable(cacheResponse, request)) {
return new CacheStrategy(request, null);
}
//獲取請求頭里面的CacheControl
CacheControl requestCaching = request.cacheControl();
//如果請求里面設置了不緩存,則不緩存
if (requestCaching.noCache() || hasConditions(request)) {
return new CacheStrategy(request, null);
}
//獲取響應的年齡
long ageMillis = cacheResponseAge();
//獲取上次響應刷新的時間
long freshMillis = computeFreshnessLifetime();
//如果請求里面有最大持久時間要求,則兩者選擇最短時間的要求
if (requestCaching.maxAgeSeconds() != -1) {
freshMillis = Math.min(freshMillis, SECONDS.toMillis(requestCaching.maxAgeSeconds()));
}
long minFreshMillis = 0;
//如果請求里面有最小刷新時間的限制
if (requestCaching.minFreshSeconds() != -1) {
//用請求中的最小更新時間來更新最小時間限制
minFreshMillis = SECONDS.toMillis(requestCaching.minFreshSeconds());
}
//最大驗證時間
long maxStaleMillis = 0;
//響應緩存控制器
CacheControl responseCaching = cacheResponse.cacheControl();
//如果響應(服務器)那邊不是必須驗證并且存在最大驗證秒數
if (!responseCaching.mustRevalidate() && requestCaching.maxStaleSeconds() != -1) {
//更新最大驗證時間
maxStaleMillis = SECONDS.toMillis(requestCaching.maxStaleSeconds());
}
//響應支持緩存
//持續時間+最短刷新時間<上次刷新時間+最大驗證時間 則可以緩存
//現在時間(now)-已經過去的時間(sent)+可以存活的時間<最大存活時間(max-age)
if (!responseCaching.noCache() && ageMillis + minFreshMillis < freshMillis + maxStaleMillis) {
Response.Builder builder = cacheResponse.newBuilder();
if (ageMillis + minFreshMillis >= freshMillis) {
builder.addHeader("Warning", "110 HttpURLConnection \"Response is stale\"");
}
long oneDayMillis = 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000L;
if (ageMillis > oneDayMillis && isFreshnessLifetimeHeuristic()) {
builder.addHeader("Warning", "113 HttpURLConnection \"Heuristic expiration\"");
}
//緩存響應
return new CacheStrategy(null, builder.build());
}
//如果想緩存request,必須要滿足一定的條件
// Find a condition to add to the request. If the condition is satisfied, the response body
// will not be transmitted.
String conditionName;
String conditionValue;
if (etag != null) {
conditionName = "If-None-Match";
conditionValue = etag;
} else if (lastModified != null) {
conditionName = "If-Modified-Since";
conditionValue = lastModifiedString;
} else if (servedDate != null) {
conditionName = "If-Modified-Since";
conditionValue = servedDateString;
} else {
//沒有條件則返回一個定期的request
return new CacheStrategy(request, null); // No condition! Make a regular request.
}
Headers.Builder conditionalRequestHeaders = request.headers().newBuilder();
Internal.instance.addLenient(conditionalRequestHeaders, conditionName, conditionValue);
Request conditionalRequest = request.newBuilder()
.headers(conditionalRequestHeaders.build())
.build();
//返回有條件的緩存request策略
return new CacheStrategy(conditionalRequest, cacheResponse);
~~~
通過上面分析,我們可以發現,OKHTTP實現的緩存策略實質上就是大量的if/else判斷,這些其實都是和RFC標準文檔里面寫死的。
### CacheInterceptor 類詳解
~~~
@Override
public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
//如果存在緩存,則從緩存中取出,有可能為null
Response cacheCandidate = cache != null
? cache.get(chain.request())
: null;
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
//獲取緩存策略對象
CacheStrategy strategy = new CacheStrategy.Factory(now, chain.request(), cacheCandidate).get();
//策略中的請求
Request networkRequest = strategy.networkRequest;
//策略中的響應
Response cacheResponse = strategy.cacheResponse;
//緩存非空判斷,
if (cache != null) {
cache.trackResponse(strategy);
}
//緩存策略不為null并且緩存響應是null
if (cacheCandidate != null && cacheResponse == null) {
closeQuietly(cacheCandidate.body()); // The cache candidate wasn't applicable. Close it.
}
//禁止使用網絡(根據緩存策略),緩存又無效,直接返回
// If we're forbidden from using the network and the cache is insufficient, fail.
if (networkRequest == null && cacheResponse == null) {
return new Response.Builder()
.request(chain.request())
.protocol(Protocol.HTTP_1_1)
.code(504)
.message("Unsatisfiable Request (only-if-cached)")
.body(Util.EMPTY_RESPONSE)
.sentRequestAtMillis(-1L)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build();
}
//緩存有效,不使用網絡
// If we don't need the network, we're done.
if (networkRequest == null) {
return cacheResponse.newBuilder()
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.build();
}
//緩存無效,執行下一個攔截器
Response networkResponse = null;
try {
networkResponse = chain.proceed(networkRequest);
} finally {
// If we're crashing on I/O or otherwise, don't leak the cache body.
if (networkResponse == null && cacheCandidate != null) {
closeQuietly(cacheCandidate.body());
}
}
//本地有緩存,根據條件選擇使用哪個響應
// If we have a cache response too, then we're doing a conditional get.
if (cacheResponse != null) {
if (networkResponse.code() == HTTP_NOT_MODIFIED) {
Response response = cacheResponse.newBuilder()
.headers(combine(cacheResponse.headers(), networkResponse.headers()))
.sentRequestAtMillis(networkResponse.sentRequestAtMillis())
.receivedResponseAtMillis(networkResponse.receivedResponseAtMillis())
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.networkResponse(stripBody(networkResponse))
.build();
networkResponse.body().close();
// Update the cache after combining headers but before stripping the
// Content-Encoding header (as performed by initContentStream()).
cache.trackConditionalCacheHit();
cache.update(cacheResponse, response);
return response;
} else {
closeQuietly(cacheResponse.body());
}
}
//使用網絡響應
Response response = networkResponse.newBuilder()
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.networkResponse(stripBody(networkResponse))
.build();
if (cache != null) {
//緩存到本地
if (HttpHeaders.hasBody(response) && CacheStrategy.isCacheable(response, networkRequest)) {
// Offer this request to the cache.
CacheRequest cacheRequest = cache.put(response);
return cacheWritingResponse(cacheRequest, response);
}
if (HttpMethod.invalidatesCache(networkRequest.method())) {
try {
cache.remove(networkRequest);
} catch (IOException ignored) {
// The cache cannot be written.
}
}
}
return response;
~~~
## ConnectInterceptor 連接相關
### ConnectInterceptor 詳情
~~~
public final class ConnectInterceptor implements Interceptor {
public final OkHttpClient client;
public ConnectInterceptor(OkHttpClient client) {
this.client = client;
}
@Override
public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
RealInterceptorChain realChain = (RealInterceptorChain) chain;
Request request = realChain.request();
StreamAllocation streamAllocation = realChain.streamAllocation();
// We need the network to satisfy this request. Possibly for validating a conditional GET.
boolean doExtensiveHealthChecks = !request.method().equals("GET");
HttpCodec httpCodec = streamAllocation.newStream(client, chain, doExtensiveHealthChecks);
RealConnection connection = streamAllocation.connection();
return realChain.proceed(request, streamAllocation, httpCodec, connection);
~~~
### RealConnection 詳情
RealConnection是Connection的實現類,代表著鏈接socket的鏈路,如果擁有了一個RealConnection就代表了我們已經跟服務器有了一條通信鏈路,而且通過
RealConnection代表是連接socket鏈路,RealConnection對象意味著我們已經跟服務端有了一條通信鏈路了。很多朋友這時候會想到,有通信鏈路了,是不是與意味著在這個類實現的三次握手,你們猜對了,的確是在這個類里面實現的三次握手。在講握手的之前,看下它的屬性和構造函數,對他有個大概的了解。
~~~
private final ConnectionPool connectionPool;
private final Route route;
// The fields below are initialized by connect() and never reassigned.
//下面這些字段,通過connect()方法開始初始化,并且絕對不會再次賦值
/** The low-level TCP socket. */
private Socket rawSocket; //底層socket
/**
* The application layer socket. Either an {@link SSLSocket} layered over {@link #rawSocket}, or
* {@link #rawSocket} itself if this connection does not use SSL.
*/
private Socket socket; //應用層socket
//握手
private Handshake handshake;
//協議
private Protocol protocol;
// http2的鏈接
private Http2Connection http2Connection;
//通過source和sink,大家可以猜到是與服務器交互的輸入輸出流
private BufferedSource source;
private BufferedSink sink;
// The fields below track connection state and are guarded by connectionPool.
//下面這個字段是 屬于表示鏈接狀態的字段,并且有connectPool統一管理
/** If true, no new streams can be created on this connection. Once true this is always true. */
//如果noNewStreams被設為true,則noNewStreams一直為true,不會被改變,并且表示這個鏈接不會再創新的stream流
public boolean noNewStreams;
//成功的次數
public int successCount;
/**
* The maximum number of concurrent streams that can be carried by this connection. If {@code
* allocations.size() < allocationLimit} then new streams can be created on this connection.
*/
//此鏈接可以承載最大并發流的限制,如果不超過限制,可以隨意增加
public int allocationLimit =
~~~
#### connect()
~~~
public void connect( int connectTimeout, int readTimeout, int writeTimeout, boolean connectionRetryEnabled) {
if (protocol != null) throw new IllegalStateException("already connected");
// 線路的選擇
RouteException routeException = null;
List<ConnectionSpec> connectionSpecs = route.address().connectionSpecs();
ConnectionSpecSelector connectionSpecSelector = new ConnectionSpecSelector(connectionSpecs);
if (route.address().sslSocketFactory() == null) {
if (!connectionSpecs.contains(ConnectionSpec.CLEARTEXT)) {
throw new RouteException(new UnknownServiceException(
"CLEARTEXT communication not enabled for client"));
}
String host = route.address().url().host();
if (!Platform.get().isCleartextTrafficPermitted(host)) {
throw new RouteException(new UnknownServiceException(
"CLEARTEXT communication to " + host + " not permitted by network security policy"));
}
}
// 連接開始
while (true) {
try {
// 如果要求隧道模式,建立通道連接,通常不是這種
if (route.requiresTunnel()) {
connectTunnel(connectTimeout, readTimeout, writeTimeout);
} else {
// 一般都走這條邏輯了,實際上很簡單就是socket的連接
connectSocket(connectTimeout, readTimeout);
}
// https的建立
establishProtocol(connectionSpecSelector);
break;
} catch (IOException e) {
closeQuietly(socket);
closeQuietly(rawSocket);
socket = null;
rawSocket = null;
source = null;
sink = null;
handshake = null;
protocol = null;
http2Connection = null;
if (routeException == null) {
routeException = new RouteException(e);
} else {
routeException.addConnectException(e);
}
if (!connectionRetryEnabled || !connectionSpecSelector.connectionFailed(e)) {
throw routeException;
}
}
}
if (http2Connection != null) {
synchronized (connectionPool) {
allocationLimit = http2Connection.maxConcurrentStreams();
}
}
~~~
#### connectSocket()
~~~
/** Does all the work necessary to build a full HTTP or HTTPS connection on a raw socket. */
private void connectSocket(int connectTimeout, int readTimeout) throws IOException {
Proxy proxy = route.proxy();
Address address = route.address();
// 根據代理類型來選擇socket類型,是代理還是直連
rawSocket = proxy.type() == Proxy.Type.DIRECT || proxy.type() == Proxy.Type.HTTP
? address.socketFactory().createSocket()
: new Socket(proxy);
rawSocket.setSoTimeout(readTimeout);
try {
// 連接socket,之所以這樣寫是因為支持不同的平臺
//里面實際上是 socket.connect(address, connectTimeout);
Platform.get().connectSocket(rawSocket, route.socketAddress(), connectTimeout);
} catch (ConnectException e) {
ConnectException ce = new ConnectException("Failed to connect to " + route.socketAddress());
ce.initCause(e);
throw ce;
}
// 得到輸入/輸出流
source = Okio.buffer(Okio.source(rawSocket));
sink = Okio.buffer(Okio.sink(rawSocket));
}
~~~
### ConnectionPool 詳情
管理http和http/2的鏈接,以便減少網絡請求延遲。同一個address將共享同一個connection。該類實現了復用連接的目標。
~~~
/**
* Background threads are used to cleanup expired connections. There will be at most a single
* thread running per connection pool. The thread pool executor permits the pool itself to be
* garbage collected.
*/
//這是一個用于清楚過期鏈接的線程池,每個線程池最多只能運行一個線程,并且這個線程池允許被垃圾回收
private static final Executor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(0 /* corePoolSize */,
Integer.MAX_VALUE /* maximumPoolSize */, 60L /* keepAliveTime */, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(), Util.threadFactory("OkHttp ConnectionPool", true));
/** The maximum number of idle connections for each address. */
//每個address的最大空閑連接數。
private final int maxIdleConnections;
private final long keepAliveDurationNs;
//清理任務
private final Runnable cleanupRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
while (true) {
long waitNanos = cleanup(System.nanoTime());
if (waitNanos == -1) return;
if (waitNanos > 0) {
long waitMillis = waitNanos / 1000000L;
waitNanos -= (waitMillis * 1000000L);
synchronized (ConnectionPool.this) {
try {
ConnectionPool.this.wait(waitMillis, (int) waitNanos);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
}
}
}
}
};
//鏈接的雙向隊列
private final Deque<RealConnection> connections = new ArrayDeque<>();
//路由的數據庫
final RouteDatabase routeDatabase = new RouteDatabase();
//清理任務正在執行的標志
boolean cleanupRunning;
~~~
#### cleanup 方法
~~~
long cleanup(long now) {
int inUseConnectionCount = 0;
int idleConnectionCount = 0;
RealConnection longestIdleConnection = null;
long longestIdleDurationNs = Long.MIN_VALUE;
// Find either a connection to evict, or the time that the next eviction is due.
synchronized (this) {
for (Iterator<RealConnection> i = connections.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
RealConnection connection = i.next();
// If the connection is in use, keep searching.
if (pruneAndGetAllocationCount(connection, now) > 0) {
inUseConnectionCount++;
continue;
}
//統計空閑連接數量
idleConnectionCount++;
// If the connection is ready to be evicted, we're done.
long idleDurationNs = now - connection.idleAtNanos;
if (idleDurationNs > longestIdleDurationNs) {
//找出空閑時間最長的連接以及對應的空閑時間
longestIdleDurationNs = idleDurationNs;
longestIdleConnection = connection;
}
}
if (longestIdleDurationNs >= this.keepAliveDurationNs
|| idleConnectionCount > this.maxIdleConnections) {
// We've found a connection to evict. Remove it from the list, then close it below (outside
// of the synchronized block).
//在符合清理條件下,清理空閑時間最長的連接
connections.remove(longestIdleConnection);
} else if (idleConnectionCount > 0) {
// A connection will be ready to evict soon.
//不符合清理條件,則返回下次需要執行清理的等待時間,也就是此連接即將到期的時間
return keepAliveDurationNs - longestIdleDurationNs;
} else if (inUseConnectionCount > 0) {
// All connections are in use. It'll be at least the keep alive duration 'til we run again.
//沒有空閑的連接,則隔keepAliveDuration(分鐘)之后再次執行
return keepAliveDurationNs;
} else {
// No connections, idle or in use.
//清理結束
cleanupRunning = false;
return -1;
}
}
//關閉socket資源
closeQuietly(longestIdleConnection.socket());
// Cleanup again immediately.
//這里是在清理一個空閑時間最長的連接以后會執行到這里,需要立即再次執行清理
return 0;
~~~
### StreamAllocation 詳情
StreamAllocation根據"請求"尋找對應的"連接"、"流"。
## CallServerInterceptor 請求
### CallServerInterceptor
~~~
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
RealInterceptorChain realChain = (RealInterceptorChain) chain;
HttpCodec httpCodec = realChain.httpStream();
StreamAllocation streamAllocation = realChain.streamAllocation();
RealConnection connection = (RealConnection) realChain.connection();
Request request = realChain.request();
long sentRequestMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
//寫入請求頭
httpCodec.writeRequestHeaders(request);
Response.Builder responseBuilder = null;
if (HttpMethod.permitsRequestBody(request.method()) && request.body() != null) {
// If there's a "Expect: 100-continue" header on the request, wait for a "HTTP/1.1 100
// Continue" response before transmitting the request body. If we don't get that, return what
// we did get (such as a 4xx response) without ever transmitting the request body.
if ("100-continue".equalsIgnoreCase(request.header("Expect"))) {
httpCodec.flushRequest();
responseBuilder = httpCodec.readResponseHeaders(true);
}
//寫入請求體
if (responseBuilder == null) {
// Write the request body if the "Expect: 100-continue" expectation was met.
Sink requestBodyOut = httpCodec.createRequestBody(request, request.body().contentLength());
BufferedSink bufferedRequestBody = Okio.buffer(requestBodyOut);
request.body().writeTo(bufferedRequestBody);
bufferedRequestBody.close();
} else if (!connection.isMultiplexed()) {
// If the "Expect: 100-continue" expectation wasn't met, prevent the HTTP/1 connection from
// being reused. Otherwise we're still obligated to transmit the request body to leave the
// connection in a consistent state.
streamAllocation.noNewStreams();
}
}
httpCodec.finishRequest();
//讀取響應頭
if (responseBuilder == null) {
responseBuilder = httpCodec.readResponseHeaders(false);
}
Response response = responseBuilder
.request(request)
.handshake(streamAllocation.connection().handshake())
.sentRequestAtMillis(sentRequestMillis)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build();
//讀取響應體
int code = response.code();
if (forWebSocket && code == 101) {
// Connection is upgrading, but we need to ensure interceptors see a non-null response body.
response = response.newBuilder()
.body(Util.EMPTY_RESPONSE)
.build();
} else {
response = response.newBuilder()
.body(httpCodec.openResponseBody(response))
.build();
}
if ("close".equalsIgnoreCase(response.request().header("Connection"))
|| "close".equalsIgnoreCase(response.header("Connection"))) {
streamAllocation.noNewStreams();
}
if ((code == 204 || code == 205) && response.body().contentLength() > 0) {
throw new ProtocolException(
"HTTP " + code + " had non-zero Content-Length: " + response.body().contentLength());
}
return response;
~~~
### HttpCodec
在okHttp中,HttpCodec是網絡讀寫的管理類,也可以理解為解碼器(注釋上就是這樣寫的),它有對應的兩個子類,Http1Codec和Http2Codec,分別對應HTTP/1.1以及HTTP/2.0協議
~~~
/** Encodes HTTP requests and decodes HTTP responses. */
public interface HttpCodec {
int DISCARD_STREAM_TIMEOUT_MILLIS = 100;
//寫入請求體
Sink createRequestBody(Request request, long contentLength);
//寫入請求頭
void writeRequestHeaders(Request request) throws IOException;
//相當于flush,把請求刷入底層socket
void flushRequest() throws IOException;
//相當于flush,把請求輸入底層socket并不在發出請求
void finishRequest() throws IOException;
//讀取響應頭
Response.Builder readResponseHeaders(boolean expectContinue) throws IOException;
//讀取響應體
ResponseBody openResponseBody(Response response) throws IOException;
//讀取響應體
void cancel
~~~
### Http1Codec
~~~
public final class Http1Codec implements HttpCodec {
final OkHttpClient client;
final StreamAllocation streamAllocation;
final BufferedSource source;
final BufferedSink sink;
int state = STATE_IDLE;
private long headerLimit = HEADER_LIMIT;
}
~~~
### Http2Codec
由于HTTP/2 里面支持一個"連接"可以發送多個請求,所以和HTTP/1.x有著本質的區別,所以Http1Codec里面有source和sink,而Http2Codec沒有,因為在HTTP/1.x里面一個連接對應一個請求。而HTTP2則不是,一個TCP連接上可以跑多個請求。所以OkHttp里面用一個Http2Connection代表一個連接。然后用Http2Stream代表一個請求的流。
## 參考資料
[OKHttp源碼解析](https://www.jianshu.com/p/82f74db14a18)
- Android
- 四大組件
- Activity
- Fragment
- Service
- 序列化
- Handler
- Hander介紹
- MessageQueue詳細
- 啟動流程
- 系統啟動流程
- 應用啟動流程
- Activity啟動流程
- View
- view繪制
- view事件傳遞
- choreographer
- LayoutInflater
- UI渲染概念
- Binder
- Binder原理
- Binder最大數據
- Binder小結
- Android組件
- ListView原理
- RecyclerView原理
- SharePreferences
- AsyncTask
- Sqlite
- SQLCipher加密
- 遷移與修復
- Sqlite內核
- Sqlite優化v2
- sqlite索引
- sqlite之wal
- sqlite之鎖機制
- 網絡
- 基礎
- TCP
- HTTP
- HTTP1.1
- HTTP2.0
- HTTPS
- HTTP3.0
- HTTP進化圖
- HTTP小結
- 實踐
- 網絡優化
- Json
- ProtoBuffer
- 斷點續傳
- 性能
- 卡頓
- 卡頓監控
- ANR
- ANR監控
- 內存
- 內存問題與優化
- 圖片內存優化
- 線下內存監控
- 線上內存監控
- 啟動優化
- 死鎖監控
- 崩潰監控
- 包體積優化
- UI渲染優化
- UI常規優化
- I/O監控
- 電量監控
- 第三方框架
- 網絡框架
- Volley
- Okhttp
- 網絡框架n問
- OkHttp原理N問
- 設計模式
- EventBus
- Rxjava
- 圖片
- ImageWoker
- Gilde的優化
- APT
- 依賴注入
- APT
- ARouter
- ButterKnife
- MMKV
- Jetpack
- 協程
- MVI
- Startup
- DataBinder
- 黑科技
- hook
- 運行期Java-hook技術
- 編譯期hook
- ASM
- Transform增量編譯
- 運行期Native-hook技術
- 熱修復
- 插件化
- AAB
- Shadow
- 虛擬機
- 其他
- UI自動化
- JavaParser
- Android Line
- 編譯
- 疑難雜癥
- Android11滑動異常
- 方案
- 工業化
- 模塊化
- 隱私合規
- 動態化
- 項目管理
- 業務啟動優化
- 業務架構設計
- 性能優化case
- 性能優化-排查思路
- 性能優化-現有方案
- 登錄
- 搜索
- C++
- NDK入門
- 跨平臺
- H5
- Flutter
- Flutter 性能優化
- 數據跨平臺
