[TOC]
## RecycleBin機制
```
/**
* The RecycleBin facilitates reuse of views across layouts. The RecycleBin
* has two levels of storage: ActiveViews and ScrapViews. ActiveViews are
* those views which were onscreen at the start of a layout. By
* construction, they are displaying current information. At the end of
* layout, all views in ActiveViews are demoted to ScrapViews. ScrapViews
* are old views that could potentially be used by the adapter to avoid
* allocating views unnecessarily.
*
* @see android.widget.AbsListView#setRecyclerListener(android.widget.AbsListView.RecyclerListener)
* @see android.widget.AbsListView.RecyclerListener
*/
class RecycleBin {
private RecyclerListener mRecyclerListener;
/**
* The position of the first view stored in mActiveViews.
*/
private int mFirstActivePosition;
/**
* Views that were on screen at the start of layout. This array is
* populated at the start of layout, and at the end of layout all view
* in mActiveViews are moved to mScrapViews. Views in mActiveViews
* represent a contiguous range of Views, with position of the first
* view store in mFirstActivePosition.
*/
private View[] mActiveViews = new View[0];
/**
* Unsorted views that can be used by the adapter as a convert view.
*/
private ArrayList<View>[] mScrapViews;
private int mViewTypeCount;
private ArrayList<View> mCurrentScrap;
/**
* Fill ActiveViews with all of the children of the AbsListView.
*
* @param childCount
* The minimum number of views mActiveViews should hold
* @param firstActivePosition
* The position of the first view that will be stored in
* mActiveViews
*/
void fillActiveViews(int childCount, int firstActivePosition) {
if (mActiveViews.length < childCount) {
mActiveViews = new View[childCount];
}
mFirstActivePosition = firstActivePosition;
final View[] activeViews = mActiveViews;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
AbsListView.LayoutParams lp = (AbsListView.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// Don't put header or footer views into the scrap heap
if (lp != null && lp.viewType != ITEM_VIEW_TYPE_HEADER_OR_FOOTER) {
// Note: We do place AdapterView.ITEM_VIEW_TYPE_IGNORE in
// active views.
// However, we will NOT place them into scrap views.
activeViews[i] = child;
}
}
}
/**
* Get the view corresponding to the specified position. The view will
* be removed from mActiveViews if it is found.
*
* @param position
* The position to look up in mActiveViews
* @return The view if it is found, null otherwise
*/
View getActiveView(int position) {
int index = position - mFirstActivePosition;
final View[] activeViews = mActiveViews;
if (index >= 0 && index < activeViews.length) {
final View match = activeViews[index];
activeViews[index] = null;
return match;
}
return null;
}
/**
* Put a view into the ScapViews list. These views are unordered.
*
* @param scrap
* The view to add
*/
void addScrapView(View scrap) {
AbsListView.LayoutParams lp = (AbsListView.LayoutParams) scrap.getLayoutParams();
if (lp == null) {
return;
}
// Don't put header or footer views or views that should be ignored
// into the scrap heap
int viewType = lp.viewType;
if (!shouldRecycleViewType(viewType)) {
if (viewType != ITEM_VIEW_TYPE_HEADER_OR_FOOTER) {
removeDetachedView(scrap, false);
}
return;
}
if (mViewTypeCount == 1) {
dispatchFinishTemporaryDetach(scrap);
mCurrentScrap.add(scrap);
} else {
dispatchFinishTemporaryDetach(scrap);
mScrapViews[viewType].add(scrap);
}
if (mRecyclerListener != null) {
mRecyclerListener.onMovedToScrapHeap(scrap);
}
}
/**
* @return A view from the ScrapViews collection. These are unordered.
*/
View getScrapView(int position) {
ArrayList<View> scrapViews;
if (mViewTypeCount == 1) {
scrapViews = mCurrentScrap;
int size = scrapViews.size();
if (size > 0) {
return scrapViews.remove(size - 1);
} else {
return null;
}
} else {
int whichScrap = mAdapter.getItemViewType(position);
if (whichScrap >= 0 && whichScrap < mScrapViews.length) {
scrapViews = mScrapViews[whichScrap];
int size = scrapViews.size();
if (size > 0) {
return scrapViews.remove(size - 1);
}
}
}
return null;
}
public void setViewTypeCount(int viewTypeCount) {
if (viewTypeCount < 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can't have a viewTypeCount < 1");
}
// noinspection unchecked
ArrayList<View>[] scrapViews = new ArrayList[viewTypeCount];
for (int i = 0; i < viewTypeCount; i++) {
scrapViews[i] = new ArrayList<View>();
}
mViewTypeCount = viewTypeCount;
mCurrentScrap = scrapViews[0];
mScrapViews = scrapViews;
}
}
```
這里的RecycleBin代碼并不全,我只是把最主要的幾個方法提了出來。那么我們先來對這幾個方法進行簡單解讀,這對后面分析ListView的工作原理將會有很大的幫助。
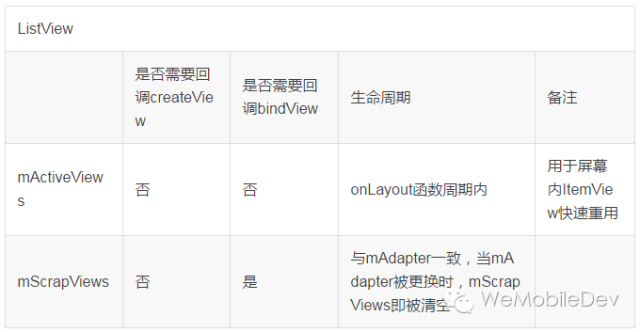
* fillActiveViews() 這個方法接收兩個參數,第一個參數表示要存儲的view的數量,第二個參數表示ListView中第一個可見元素的position值。RecycleBin當中使用mActiveViews這個數組來存儲View,調用這個方法后就會根據傳入的參數來將ListView中的指定元素存儲到mActiveViews數組當中。
* getActiveView() 這個方法和fillActiveViews()是對應的,用于從mActiveViews數組當中獲取數據。該方法接收一個position參數,表示元素在ListView當中的位置,方法內部會自動將position值轉換成mActiveViews數組對應的下標值。需要注意的是,mActiveViews當中所存儲的View,一旦被獲取了之后就會從mActiveViews當中移除,下次獲取同樣位置的View將會返回null,也就是說mActiveViews不能被重復利用。
* addScrapView() 用于將一個廢棄的View進行緩存,該方法接收一個View參數,當有某個View確定要廢棄掉的時候(比如滾動出了屏幕),就應該調用這個方法來對View進行緩存,RecycleBin當中使用mScrapViews和mCurrentScrap這兩個List來存儲廢棄View。
* getScrapView 用于從廢棄緩存中取出一個View,這些廢棄緩存中的View是沒有順序可言的,因此getScrapView()方法中的算法也非常簡單,就是直接從mCurrentScrap當中獲取尾部的一個scrap view進行返回。
* setViewTypeCount() 我們都知道Adapter當中可以重寫一個getViewTypeCount()來表示ListView中有幾種類型的數據項,而setViewTypeCount()方法的作用就是為每種類型的數據項都單獨啟用一個RecycleBin緩存機制。實際上,getViewTypeCount()方法通常情況下使用的并不是很多,所以我們只要知道RecycleBin當中有這樣一個功能就行了。
## 緩存機制
### 顯示
```
private View makeAndAddView(int position, int y, boolean flow, int childrenLeft,
boolean selected) {
View child;
if (!mDataChanged) {
// Try to use an exsiting view for this position
child = mRecycler.getActiveView(position);
if (child != null) {
// Found it -- we're using an existing child
// This just needs to be positioned
setupChild(child, position, y, flow, childrenLeft, selected, true);
return child;
}
}
// Make a new view for this position, or convert an unused view if possible
child = obtainView(position, mIsScrap);
// This needs to be positioned and measured
setupChild(child, position, y, flow, childrenLeft, selected, mIsScrap[0]);
return child;
}
View obtainView(int position, boolean[] isScrap) {
isScrap[0] = false;
View scrapView;
scrapView = mRecycler.getScrapView(position);
View child;
if (scrapView != null) {
child = mAdapter.getView(position, scrapView, this);
if (child != scrapView) {
mRecycler.addScrapView(scrapView);
if (mCacheColorHint != 0) {
child.setDrawingCacheBackgroundColor(mCacheColorHint);
}
} else {
isScrap[0] = true;
dispatchFinishTemporaryDetach(child);
}
} else {
child = mAdapter.getView(position, null, this);
if (mCacheColorHint != 0) {
child.setDrawingCacheBackgroundColor(mCacheColorHint);
}
}
return child;
}
```
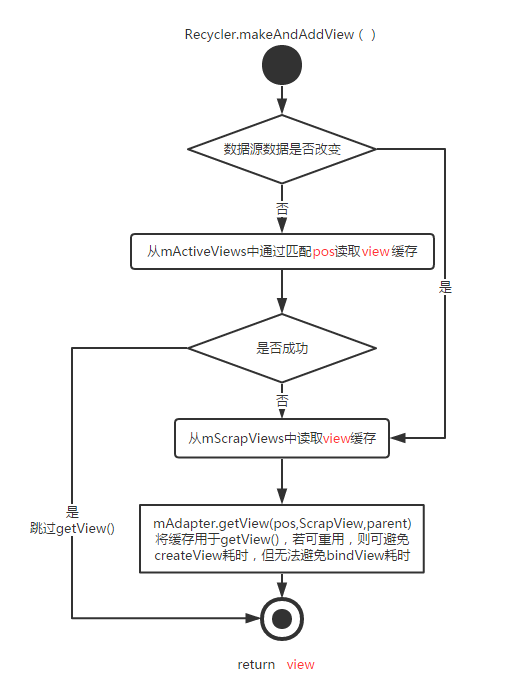
1. 從RecycleBin當中快速獲取一個active view
2. 從RecycleBin的getScrapView()方法來嘗試獲取一個廢棄緩存中的View
### 滑出屏幕
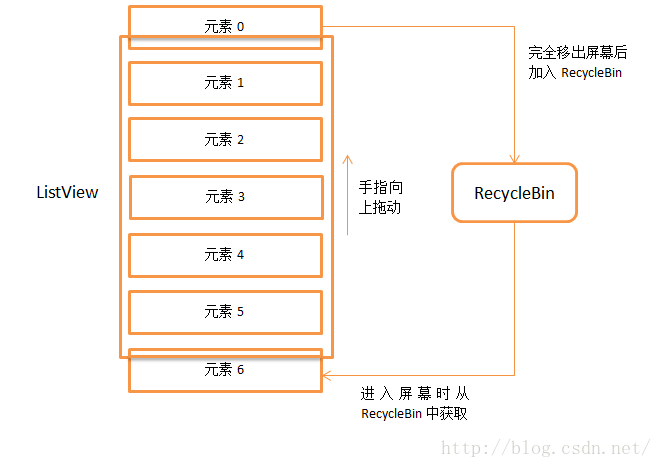
當ListView向下滑動的時候,就會進入一個for循環當中,從上往下依次獲取子View,第47行當中,如果該子View的bottom值已經小于top值了,就說明這個子View已經移出屏幕了,所以會調用RecycleBin的addScrapView()方法將這個View加入到廢棄緩存當中
## 參考資料
[Android ListView工作原理完全解析,帶你從源碼的角度徹底理解](https://blog.csdn.net/guolin_blog/article/details/44996879)
- Android
- 四大組件
- Activity
- Fragment
- Service
- 序列化
- Handler
- Hander介紹
- MessageQueue詳細
- 啟動流程
- 系統啟動流程
- 應用啟動流程
- Activity啟動流程
- View
- view繪制
- view事件傳遞
- choreographer
- LayoutInflater
- UI渲染概念
- Binder
- Binder原理
- Binder最大數據
- Binder小結
- Android組件
- ListView原理
- RecyclerView原理
- SharePreferences
- AsyncTask
- Sqlite
- SQLCipher加密
- 遷移與修復
- Sqlite內核
- Sqlite優化v2
- sqlite索引
- sqlite之wal
- sqlite之鎖機制
- 網絡
- 基礎
- TCP
- HTTP
- HTTP1.1
- HTTP2.0
- HTTPS
- HTTP3.0
- HTTP進化圖
- HTTP小結
- 實踐
- 網絡優化
- Json
- ProtoBuffer
- 斷點續傳
- 性能
- 卡頓
- 卡頓監控
- ANR
- ANR監控
- 內存
- 內存問題與優化
- 圖片內存優化
- 線下內存監控
- 線上內存監控
- 啟動優化
- 死鎖監控
- 崩潰監控
- 包體積優化
- UI渲染優化
- UI常規優化
- I/O監控
- 電量監控
- 第三方框架
- 網絡框架
- Volley
- Okhttp
- 網絡框架n問
- OkHttp原理N問
- 設計模式
- EventBus
- Rxjava
- 圖片
- ImageWoker
- Gilde的優化
- APT
- 依賴注入
- APT
- ARouter
- ButterKnife
- MMKV
- Jetpack
- 協程
- MVI
- Startup
- DataBinder
- 黑科技
- hook
- 運行期Java-hook技術
- 編譯期hook
- ASM
- Transform增量編譯
- 運行期Native-hook技術
- 熱修復
- 插件化
- AAB
- Shadow
- 虛擬機
- 其他
- UI自動化
- JavaParser
- Android Line
- 編譯
- 疑難雜癥
- Android11滑動異常
- 方案
- 工業化
- 模塊化
- 隱私合規
- 動態化
- 項目管理
- 業務啟動優化
- 業務架構設計
- 性能優化case
- 性能優化-排查思路
- 性能優化-現有方案
- 登錄
- 搜索
- C++
- NDK入門
- 跨平臺
- H5
- Flutter
- Flutter 性能優化
- 數據跨平臺
