>[success] # 鏈表法
~~~
1.上個章節'散列函數'是通過ascii 碼的形式,這種形式會出現,雖然字符串不同,但是組成的
ascii碼是一樣的,這就出現了'散列沖突',解決其中一個方法就是使用鏈表的方法
2.如圖就是當有相同的ascii碼時候,存儲的不在是單單對象值,而是一個鏈表依次連接
~~~
* 如圖
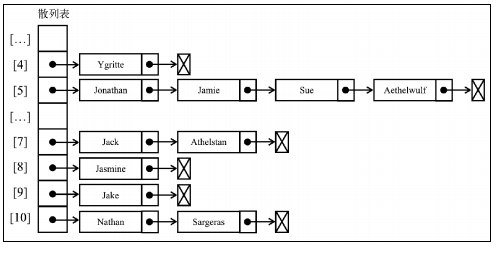
>[danger] ##### 代碼實現
~~~
class ValuePair {
constructor(key, value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
toString() {
return `[#${this.key}: ${this.value}]`;
}
}
function defaultToString(item) {
if (item === null) {
return 'NULL';
} if (item === undefined) {
return 'UNDEFINED';
} if (typeof item === 'string' || item instanceof String) {
return `${item}`;
}
return item.toString();
}
class HashTableSeparateChaining {
constructor(toStrFn = defaultToString) {
this.toStrFn = toStrFn;
this.table = {};
}
loseloseHashCode(key) {
if (typeof key === 'number') {
return key;
}
const tableKey = this.toStrFn(key);
let hash = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < tableKey.length; i++) {
hash += tableKey.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % 37;
}
hashCode(key) {
return this.loseloseHashCode(key);
}
put(key, value) {
if (key != null && value != null) {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
if (this.table[position] == null) {
this.table[position] = new LinkedList(); // 用鏈表來存
}
this.table[position].push(new ValuePair(key, value));
return true;
}
return false;
}
get(key) {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
const linkedList = this.table[position];
if (linkedList != null && !linkedList.isEmpty()) {
let current = linkedList.getHead();
while (current != null) {
if (current.element.key === key) {
return current.element.value;
}
current = current.next;
}
}
return undefined;
}
remove(key) {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
const linkedList = this.table[position];
if (linkedList != null && !linkedList.isEmpty()) {
let current = linkedList.getHead();
while (current != null) {
if (current.element.key === key) {
linkedList.remove(current.element);
if (linkedList.isEmpty()) {
delete this.table[position];
}
return true;
}
current = current.next;
}
}
return false;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
size() {
let count = 0;
Object.values(this.table).forEach(linkedList => {
count += linkedList.size();
});
return count;
}
clear() {
this.table = {};
}
getTable() {
return this.table;
}
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return '';
}
const keys = Object.keys(this.table);
let objString = `{${keys[0]} => ${this.table[keys[0]].toString()}}`;
for (let i = 1; i < keys.length; i++) {
objString = `${objString},{${keys[i]} => ${this.table[
keys[i]
].toString()}}`;
}
return objString;
}
}
~~~
- 接觸數據結構和算法
- 數據結構與算法 -- 大O復雜度表示法
- 數據結構與算法 -- 時間復雜度分析
- 最好、最壞、平均、均攤時間復雜度
- 基礎數據結構和算法
- 線性表和非線性表
- 結構 -- 數組
- JS -- 數組
- 結構 -- 棧
- JS -- 棧
- JS -- 棧有效圓括號
- JS -- 漢諾塔
- 結構 -- 隊列
- JS -- 隊列
- JS -- 雙端隊列
- JS -- 循環隊列
- 結構 -- 鏈表
- JS -- 鏈表
- JS -- 雙向鏈表
- JS -- 循環鏈表
- JS -- 有序鏈表
- 結構 -- JS 字典
- 結構 -- 散列表
- 結構 -- js 散列表
- 結構 -- js分離鏈表
- 結構 -- js開放尋址法
- 結構 -- 遞歸
- 結構 -- js遞歸經典問題
- 結構 -- 樹
- 結構 -- js 二搜索樹
- 結構 -- 紅黑樹
- 結構 -- 堆
- 結構 -- js 堆
- 結構 -- js 堆排序
- 結構 -- 排序
- js -- 冒泡排序
- js -- 選擇排序
- js -- 插入排序
- js -- 歸并排序
- js -- 快速排序
- js -- 計數排序
- js -- 桶排序
- js -- 基數排序
- 結構 -- 算法
- 搜索算法
- 二分搜索
- 內插搜索
- 隨機算法
- 簡單
- 第一題 兩數之和
- 第七題 反轉整數
- 第九題 回文數
- 第十三題 羅馬數字轉整數
- 常見一些需求
- 把原始 list 轉換成樹形結構
