[TOC]
>[success] # state 與 getter
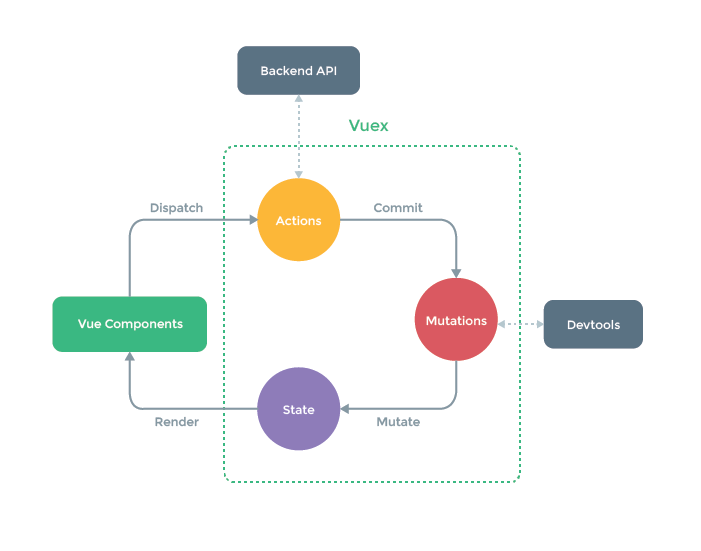
上圖就是 **Vuex** 狀態管理的 **流程** ,在 **Vue Components(組件)** 里可以觸發一個 **Actions(Actions里可以做異步接口請求)** , **請求完成** 后觸發一個 **Mutations** ,通過 **Mutations** 修改 **State** 的狀態值,**State** 修改之后會觸發 **vue組件視圖的渲染** 。
>[success] ## state
**state** 是 **vuex** 用來存放 **變量** 用的 **對象** ,為了提前做好準備,首先要將它**引入** :
1. 首先在 **store文件夾** 中 創建一個 **state.js**
**store/state.js**
~~~
const state = {
// 變量寫這里
}
export default state
~~~
2. 在 **store/index.js** 中引入 **state.js** ,首先想使用 **Vuex** , **Vuex** 作為 **Vue** 的 **插件** 肯定要先 **引入Vue** ,然后再 **引入Vuex** ,然后引入我們 **初始化項目** 時候寫好的 **mutations** 、 **actions** 、 **user** 以及剛剛寫的 **state** 這幾個 **js文件** ,然后引入 **Vue** 后通過 **Vue.use(Vuex)** 把 **Vuex** 加載進來,然后用 **new Vuex.Store()** 來 **創建實例** 。
**store/index.js**
~~~
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import state from './state' // state.js文件可以不寫.js結尾,這樣寫也會自動找到state.js文件
import mutations from './mutations'
import actions from './actions'
import user from './module/user' // 引入模塊文件
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state, // ES6對象簡寫的形式,state: state 等同與 state
mutations,
actions,
modules: { // 模塊引用
user
}
})
~~~
3. 在 **main.js** 中把 **stroe文件夾** 中 **index.js** 里寫好的 **Vuex實例** 引入并且 **掛載** 在 **根組件** 的 **實例**上
**main.js**
~~~
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
import './plugins/element.js'
import Bus from './lib/bus' // 引入Bus
Vue.config.productionTip = false
Vue.prototype.$bus = Bus // 掛載Bus到Vue原型鏈(全局掛載Bus)
new Vue({
router,
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
~~~
>[success] ### 使用方法
1. **訪問根狀態的state**
可以把 **state** 看做成 **Vue** 中的 **data** ,在里面定義一個 **變量**
**store/state.js**
~~~
const state = {
appName: 'admin'
}
export default state
~~~
**state** 中定義的 **變量** 可以在 **各個組件** 中使用,如下:
**store.vue**
~~~
<template>
<div>
<p>{{ appName }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
computed:{
appName(){
return this.$store.state.appName
}
}
}
</script>
~~~
在使用的組件中通過 **computed(計算屬性)** 來把 **state** 中的內容顯示在頁面上。
2. **訪問模塊中的state**
在 **模塊** 中定義的 **state** 變量 **userName**
**store/module/user.js**
~~~
const state = {
userName: '小明'
}
const mutations = {
//
}
const actions = {
//
}
export default {
state,
mutations,
actions
}
~~~
在組件中這樣使用
**store.vue**
~~~
<template>
<div>
<p>{{ userName }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
computed:{
userName(){
return this.$store.state.user.userName // this.$store.state.模塊名.模塊中的變量名
}
}
}
</script>
~~~
3. **mapState函數訪問state**
除了上面的 **2** 種方法還可以使用 **Vuex** 提供的 **mapState工具函數** 來訪問 **state**
*****
3.1 **使用 mapState 訪問 根狀態state**
**store.vue**
~~~
<template>
<div>
<p>{{ appName }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 結構賦值寫法
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
// 相當于這么寫
// import vuex from 'vuex'
// const mapState = vuex.mapState
export default {
computed:{
...mapState([
'appName'
])
// 上面的跟下面這個效果是一樣的
// appName(){
// return this.$store.state.appName
// }
}
}
</script>
~~~
**mapState** 方法會 **返回一個對象** ,使用 **擴展運算符扁平化的展開這個對象**,然而 **mapState** 也可以 **傳入一個對象的寫法**
**store.vue**
~~~
<template>
<div>
<p>{{ appName }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 結構賦值寫法
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
// 相當于這么寫
// import vuex from 'vuex'
// const mapState = vuex.mapState
export default {
computed:{
...mapState({
appName: state => state.appName // state是根狀態的state
})
}
}
</script>
~~~
3.2 **使用 mapState 訪問 module 中的 state**
**store.vue**
~~~
<template>
<div>
<p>{{ userName }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 結構賦值寫法
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
// 相當于這么寫
// import vuex from 'vuex'
// const mapState = vuex.mapState
export default {
computed:{
...mapState({
userName: state => state.user.userName // state.模塊名稱.模塊里的state變量名
})
}
}
</script>
~~~
3.3 **命名空間訪問 module 中的 state**
**命名空間** 的寫法需要在 **module(模塊)** 中添加一個 **namespaced:true** 表示開啟 **命名空間**,如果獲取的是 **根狀態的state** 就 **不需要在store/index.js** 添加 **namespaced:true** 。
**store/module/user.js**
~~~
const state = {
userName: '小明'
}
const mutations = {
//
}
const actions = {
//
}
export default {
namespaced: true,
state,
mutations,
actions
}
~~~
如果你設置了 **namespaced: true** 就可以在 **組件** 中使用 **Vuex** 的另外一個方法 **createNamespacedHelpers** 方法,這個方法可以傳入一個 **命名空間的模塊名**,這樣寫的話就不用給 **mapState** 寫第一個參數(**模塊名稱**)
**store.vue**
~~~
<template>
<div>
<p>{{ userName }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { createNamespacedHelpers } from 'vuex'
const { mapState } = createNamespacedHelpers('user') // 命名空間的參數是模塊名,這時mapState就包含了user模塊
export default {
computed:{
...mapState({
userName: state => state.userName // 這樣就可以不用state.user.userName這樣指向模塊名再指向變量了
})
}
}
</script>
~~~
或者也可以不用 **createNamespacedHelpers**, 用 **mapState** 直接寫,如下:
**store.vue**
~~~
<template>
<div>
<p>{{ userName }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed:{
...mapState('user', { // 第一個參數是模塊名
userName: state => state.userName // 這里依舊不用像state.user.userName這樣指向模塊名再指向變量
})
}
}
</script>
~~~
>[success] ## getter
1. **getter** 可以理解為組件里的 **計算屬性** ,下面的代碼中是 **計算屬性** 的使用方法:
**store.vue**
~~~
<template>
<div>
<input type="text" v-model="inputVal">
計算值:{{ inputValueLastLetter }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
name: 'demo',
data(){
return{
inputVal: ''
}
},
computed: {
inputValueLastLetter(){
return this.inputVal.substr(-1, 1) // 截取字符串的最后一位
}
}
}
</script>
~~~
2. **getter**是**vuex** 中的 **計算屬性** ,為了提前做好準備,首先創建一個 **getters.js** 文件
**store/getters.js**
~~~
const getters = {
// 這里寫Vuex的計算屬性
}
export default getters
~~~
3. 然后將 **getters.js** 引入到 **store/index.js** 中
**store/index.js**
~~~
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import state from './state' // state.js文件可以不寫.js結尾,這樣寫也會自動找到state.js文件
import getters from './getters'
import mutations from './mutations'
import actions from './actions'
import user from './module/user' // 引入模塊文件
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state, // ES6對象簡寫的形式,state: state 等同與 state
getters,
mutations,
actions,
modules: { // 模塊引用
user
}
})
~~~
>[success] ### 使用方法
1. **訪問根狀態的getter**
**store/state.js**
~~~
const state = {
appVersion: 1.0
}
export default state
~~~
**store/getters.js**
~~~
const getters = {
// state代表當前同級別(state.js)里的state
appNameWithVersion: (state) => {
return state.appVersion + 0.1
}
}
export default getters
~~~
上面 **計算屬性** 的 **第一個參數state** ,實際上就是 **store/state.js** 中的變量,然后在組件中 **使用getter**
**store.vue**
~~~
<template>
<div>
{{ appNameWithVersion }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
name: 'demo',
computed: {
appNameWithVersion(){
return this.$store.getters.appNameWithVersion
}
}
}
</script>
~~~
2. **訪問模塊中的getter** ,這里使用的是 **Vuex** 提供的工具方法 **mapGetters** 來獲取 **getter**
****
2.1 **mapGetters配合命名空間使用**
**store/module/user.js**
~~~
const state = {
userName: '小明'
}
const mutations = {
//
}
const actions = {
//
}
const getters = {
firstLetter: (state) => { // 定義getter
return state.userName.substr(0, 1)
}
}
export default {
namespaced: true,
getters,
state,
mutations,
actions
}
~~~
使用 **mapGetters** 配合 **命名空間** 獲取 **module(模塊)** 中的 **getter** 一定要設置 **namespaced: true** ,然后組件里這樣使用
**store.vue**
~~~
<template>
<div>
{{ firstLetter }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default{
name: 'demo',
computed: {
// 獲取根getter寫法
// ...mapGetters(['appNameWithVersion'])
// 獲取模塊getter寫法
...mapGetters('user',['firstLetter']) // ...mapGetters('模塊名',['getter名'])
}
}
</script>
~~~
或者可以使用 **mapGetters** 配合 **Vuex** 提供的 **createNamespacedHelpers** 方法一起使用來獲取 **模塊** 中的 **getter**
**store.vue**
~~~
<template>
<div>
{{ firstLetter }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { createNamespacedHelpers } from 'vuex'
const { mapGetters } = createNamespacedHelpers('user') // createNamespacedHelpers('模塊名稱')
export default{
name: 'demo',
computed: {
// 獲取模塊getter寫法
...mapGetters(['firstLetter']), // ...mapGetters(['getter名'])
}
}
</script>
~~~
2.2 **直接使用mapGetters獲取【模塊】以及【根狀態】 的 【getter】(不配合命名空間使用)**
上面的例子是配合 **命名空間** 使用 **mapGetters** ,以及在 **命名空間** 的情況下用 **mapGetters** 配合**createNamespacedHelpers** 一起使用看起來 **比較繁瑣** ,實際上 **mapGetters 不使用命名空間也是可以直接獲取到 根狀態 和 模塊 中的getter** 如下:
1. **根狀態下的 state 跟 getter**
**store/state.js**
~~~
const state = {
appVersion: 1.0
}
export default state
~~~
**store/getters.js**
~~~
const getters = {
// state代表當前同級別(state.js)里的state
appNameWithVersion: (state) => {
return state.appVersion + 0.1
}
}
export default getters
~~~
2. **模塊下的 state 跟 getter**
**store/module/user.js**
~~~
const state = {
userName: '小明'
}
const mutations = {
//
}
const actions = {
//
}
const getters = {
firstLetter: (state) => { // 定義getter
return state.userName.substr(0, 1)
}
}
export default {
// namespaced: true, // 注意這里沒有開啟命名空間
getters,
state,
mutations,
actions
}
~~~
3. **在組件中使用 mapGetters 獲取 【根狀態】 、 【模塊中】的 getter**
**store.vue**
~~~
<template>
<div>
{{ firstLetter }}
{{ appNameWithVersion }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default{
name: 'demo',
computed: {
// 直接使用mapGetters獲取【模塊】、【根狀態】中的getter即可
...mapGetters(['firstLetter','appNameWithVersion']), // ...mapGetters(['getter名'])
}
}
</script>
~~~
- vue 26課
- Vue-cli3.0項目搭建
- Vue-ui 創建cli3.0項目
- Vue-ui 界面詳解
- 項目目錄詳解
- public文件夾
- favicon.ico
- index.html
- src文件夾
- api文件夾
- assets文件夾
- components文件夾
- config文件夾
- directive文件夾
- lib文件夾
- mock文件夾
- mock簡明文檔
- router文件夾
- store文件夾
- views文件夾
- App.vue
- main.js
- .browserslistrc
- .editorconfig
- .eslintrc.js
- .gitignore
- babel.config.js
- package-lock.json
- package.json
- postcss.config.js
- README.en.md
- README.md
- vue.config.js
- Vue Router
- 路由詳解(一)----基礎篇
- 路由詳解(二)----進階篇
- Vuex
- Bus
- Vuex-基礎-state&getter
- Vuex-基礎-mutation&action/module
- Vuex-進階
- Ajax請求
- 解決跨域問題
- 封裝axios
- Mock.js模擬Ajax響應
- 組件封裝
- 從數字漸變組件談第三方JS庫使用
- 從SplitPane組件談Vue中如何【操作】DOM
- 渲染函數和JSX快速掌握
- 遞歸組件的使用
- 登陸/登出以及JWT認證
- 響應式布局
- 可收縮多級菜單的實現
- vue雜項
- vue遞歸組件
- vue-cli3.0多環境打包配置
- Vue+Canvas實現圖片剪切
- vue3系統入門與項目實戰
- Vue語法初探
- 初學編寫 HelloWorld 和 Counter
- 編寫字符串反轉和內容隱藏功能
- 編寫TodoList功能了解循環與雙向綁定
- 組件概念初探,對 TodoList 進行組件代碼拆分
- Vue基礎語法
- Vue 中應用和組件的基礎概念
- 理解 Vue 中的生命周期函數
- 常用模版語法講解
- 數據,方法,計算屬性和偵聽器
- 樣式綁定語法
- 條件渲染
- 列表循環渲染
- 事件綁定
- 表單中雙向綁定指令的使用
- 探索組件的理念
- 組件的定義及復用性,局部組件和全局組件
- 組件間傳值及傳值校驗
- 單向數據流的理解
- Non-Props 屬性是什么
- 父子組件間如何通過事件進行通信
- 組件間雙向綁定高級內容
- 使用匿名插槽和具名插槽解決組件內容傳遞問題
- 作用域插槽
- 動態組件和異步組件
- 基礎語法知識點查缺補漏
- Vue 中的動畫
- 使用 Vue 實現基礎的 CSS 過渡與動畫效果
- 使用 transition 標簽實現單元素組件的過渡和動畫效果
- 組件和元素切換動畫的實現
- 列表動畫
- 狀態動畫
- Vue 中的高級語法
- Mixin 混入的基礎語法
- 開發實現 Vue 中的自定義指令
- Teleport 傳送門功能
- 更加底層的 render 函數
- 插件的定義和使用
- 數據校驗插件開發實例
- Composition API
- Setup 函數的使用
- ref,reactive 響應式引用的用法和原理
- toRef 以及 context 參數
- 使用 Composition API 開發TodoList
- computed方法生成計算屬性
- watch 和 watchEffect 的使用和差異性
- 生命周期函數的新寫法
- Provide,Inject,模版 Ref 的用法
- Vue 項目開發配套工具講解
- VueCLI 的使用和單文件組件
- 使用單文件組件編寫 TodoList
- Vue-Router 路由的理解和使用
- VueX 的語法詳解
- CompositionAPI 中如何使用 VueX
- 使用 axios 發送ajax 請求
- Vue3.0(正式版) + TS
- 你好 Typescript: 進入類型的世界
- 什么是 Typescript
- 為什么要學習 Typescript
- 安裝 Typescript
- 原始數據類型和 Any 類型
- 數組和元組
- Interface- 接口初探
- 函數
- 類型推論 聯合類型和 類型斷言
- class - 類 初次見面
- 類和接口 - 完美搭檔
- 枚舉(Enum)
- 泛型(Generics) 第一部分
- 泛型(Generics) 第二部分 - 約束泛型
- 泛型第三部分 - 泛型在類和接口中的使用
- 類型別名,字面量 和 交叉類型
- 聲明文件
- 內置類型
- 總結
