[TOC]
參考鏈接:[https://github.com/CyC2018/CS-Notes/blob/master/notes/%E5%89%91%E6%8C%87%20Offer%20%E9%A2%98%E8%A7%A3%20-%203~9.md](https://github.com/CyC2018/CS-Notes/blob/master/notes/%E5%89%91%E6%8C%87%20Offer%20%E9%A2%98%E8%A7%A3%20-%203~9.md)
## 1.字符串的排列
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/fe6b651b66ae47d7acce78ffdd9a96c7?tpId=13&tqId=11180&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
題目描述:輸入一個字符串,按字典序打印出該字符串中字符的所有排列。例如輸入字符串 abc,則打印出由字符 a, b, c 所能排列出來的所有字符串 abc, acb, bac, bca, cab 和 cba。
解題思路:
```js
function swap(arr, index1, index2) {
let tmp = arr[index1]
arr[index1] = arr[index2]
arr[index2] = tmp
}
// 去重的全排列就是從第一個數字起每個數分別與它后面非重復出現的數字交換。
// 用編程的話描述就是第 i 個數與第 j 個數交換時,要求 [i,j) 中沒有與第 j 個數相等的數
function isSwap (arr, nBegin, nEnd) {
for (let i = nBegin; i < nEnd; i++) {
if (arr[i] === arr[nEnd]) {
return false
}
}
return true
}
/**
*
* @param {*} arr 數組
* @param {*} cur 當前待交換的數的下標
* @param {*} n 末尾下標
*/
const res = []
function myPermutation(arr, cur, n) {
if (cur === n-1) {
res.push(arr.join(''))
} else {
for (let i = cur; i < n; i++) {
if (isSwap(arr, cur, i)) { // isSwap() 去重
swap(arr, cur, i)
myPermutation(arr, cur + 1, n)
swap(arr, cur, i)
}
}
}
}
function Permutation(str)
{
const chars = str.split('')
chars.sort() // 先轉換成數組升序排列
myPermutation(chars, 0, chars.length)
return res
}
console.log(Permutation('abc')) // [ 'abc', 'acb', 'bac', 'bca', 'cba', 'cab' ]
// 本地測試 ok,不知道為啥牛客輸出不對
```
## 2.二維數組中的查找
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/abc3fe2ce8e146608e868a70efebf62e?tpId=13&tqId=11154&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
題目描述:給定一個二維數組,其每一行從左到右遞增排序,從上到下也是遞增排序。給定一個數,判斷這個數是否在該二維數組中。
```js
Consider the following matrix:
[
[1, 4, 7, 11, 15],
[2, 5, 8, 12, 19],
[3, 6, 9, 16, 22],
[10, 13, 14, 17, 24],
[18, 21, 23, 26, 30]
]
Given target = 5, return true.
Given target = 20, return false.
```
解題思路:
要求時間復雜度 O(M + N),空間復雜度 O(1)。其中 M 為行數,N 為 列數。
該二維數組中的一個數,小于它的數一定在其左邊,大于它的數一定在其下邊。因此,從右上角開始查找,就可以根據 target 和當前元素的大小關系來縮小查找區間,當前元素的查找區間為左下角的所有元素。
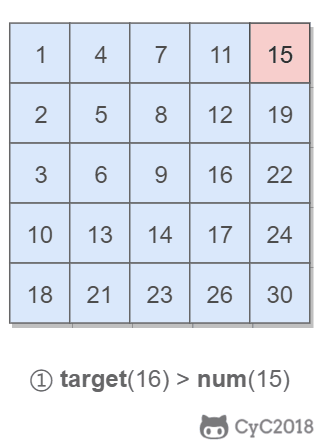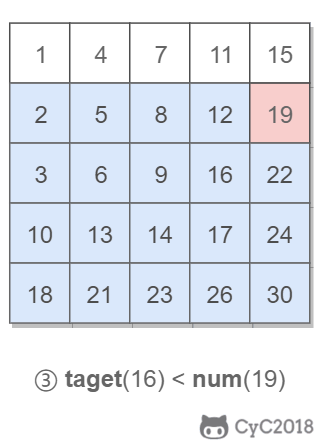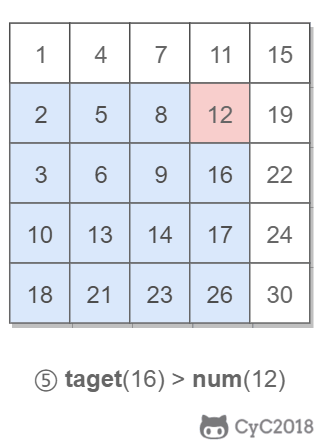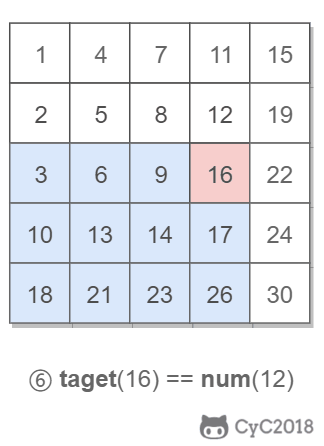
## 3.重建二叉樹
題目描述:根據二叉樹的前序遍歷和中序遍歷的結果,重建出該二叉樹。假設輸入的前序遍歷和中序遍歷的結果中都不含重復的數字。

解題思路:
前序遍歷的第一個值為根節點的值,使用這個值將中序遍歷結果分成兩部分,左部分為樹的左子樹中序遍歷結果,右部分為樹的右子樹中序遍歷的結果。

```js
function TreeNode(x) {
this.val = x;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
function reConstructBinaryTree(pre, vin)
{
/*
前序遍歷的第一個值為根節點的值,使用這個值將中序遍歷結果分成兩部分,
左部分為樹的左子樹中序遍歷結果,右部分為樹的右子樹中序遍歷的結果。
*/
if (pre.length === 0 || vin.length === 0) {
return null
}
let indexOfRoot = vin.indexOf(pre[0])
const vinLeft = vin.slice(0, indexOfRoot)
const vinRight = vin.slice(indexOfRoot + 1)
let root = new TreeNode(pre[0])
root.left = reConstructBinaryTree(pre.slice(1, indexOfRoot + 1), vinLeft) // 注意 pre 也要 slice
root.right = reConstructBinaryTree(pre.slice(indexOfRoot + 1), vinRight)
return root
}
```
## 4.二叉樹的下一個結點
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/9023a0c988684a53960365b889ceaf5e?tpId=13&tqId=11210&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
題目描述:給定一個二叉樹和其中的一個結點,請找出中序遍歷順序的下一個結點并且返回。注意,樹中的結點不僅包含左右子結點,同時包含指向父結點的指針。
```java
public class TreeLinkNode {
int val;
TreeLinkNode left = null;
TreeLinkNode right = null;
TreeLinkNode next = null;
TreeLinkNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
```
解題思路:
① 如果一個節點的右子樹不為空,那么該節點的下一個節點是右子樹的最左節點;

② 否則,向上找第一個左鏈接指向的樹包含該節點的祖先節點。

```js
function GetNext(pNode)
{
// 1.如果一個節點的右子樹不為空,那么該節點的下一個節點是右子樹的最左節點
// 2.否則,向上找第一個左鏈接指向的樹包含該節點的祖先節點。
if (pNode.right !== null) {
let node = pNode.right
while (node.left !== null) {
node = node.left
}
return node
} else {
while (pNode.next !== null) {
let pFather = pNode.next
if (pFather.left === pNode) {
return pFather
}
pNode = pNode.next
}
}
return null
}
```
也可以先找到根節點,再順著中序遍歷的順序得到該節點的下一個節點。
## 5.用兩個棧實現隊列
題目描述:用兩個棧來實現一個隊列,完成隊列的 Push 和 Pop 操作。
解題思路:
in 棧用來處理入棧(push)操作,out 棧用來處理出棧(pop)操作。一個元素進入 in 棧之后,出棧的順序被反轉。當元素要出棧時,需要先進入 out 棧,此時元素出棧順序再一次被反轉,因此出棧順序就和最開始入棧順序是相同的,先進入的元素先退出,這就是隊列的順序。

## 6.旋轉數組的最小數字
題目描述:把一個數組最開始的若干個元素搬到數組的末尾,我們稱之為數組的旋轉。輸入一個非遞減排序的數組的一個旋轉,輸出旋轉數組的最小元素。

解題思路:
將旋轉數組對半分可以得到一個包含最小元素的新旋轉數組,以及一個非遞減排序的數組。新的旋轉數組的數組元素是原數組的一半,從而將問題規模減少了一半,這種折半性質的算法的時間復雜度為 O(logN)(為了方便,這里將 log2N 寫為 logN)。

此時問題的關鍵在于確定對半分得到的兩個數組哪一個是旋轉數組,哪一個是非遞減數組。我們很容易知道非遞減數組的第一個元素一定小于等于最后一個元素。
通過修改二分查找算法進行求解(l 代表 low,m 代表 mid,h 代表 high):
* 當 nums\[m\] <= nums\[h\] 時,表示 \[m, h\] 區間內的數組是非遞減數組,\[l, m\] 區間內的數組是旋轉數組,此時令 h = m;
* 否則 \[m + 1, h\] 區間內的數組是旋轉數組,令 l = m + 1。
如果數組元素允許重復,會出現一個特殊的情況:nums\[l\] == nums\[m\] == nums\[h\],此時無法確定解在哪個區間,需要切換到順序查找。例如對于數組 {1,1,1,0,1},l、m 和 h 指向的數都為 1,此時無法知道最小數字 0 在哪個區間。
~~~
public int minNumberInRotateArray(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0)
return 0;
int l = 0, h = nums.length - 1;
while (l < h) {
int m = l + (h - l) / 2;
if (nums[l] == nums[m] && nums[m] == nums[h])
return minNumber(nums, l, h);
else if (nums[m] <= nums[h])
h = m;
else
l = m + 1;
}
return nums[l];
}
private int minNumber(int[] nums, int l, int h) {
for (int i = l; i < h; i++)
if (nums[i] > nums[i + 1])
return nums[i + 1];
return nums[l];
}
~~~
## 7.矩陣中的路徑
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/c61c6999eecb4b8f88a98f66b273a3cc?tpId=13&tqId=11218&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
**題目描述:**
判斷在一個矩陣中是否存在一條包含某字符串所有字符的路徑。路徑可以從矩陣中的任意一個格子開始,每一步可以在矩陣中向上下左右移動一個格子。如果一條路徑經過了矩陣中的某一個格子,則該路徑不能再進入該格子。
例如下面的矩陣包含了一條 bfce 路徑。

**解題思路:**
使用回溯法(backtracking)進行求解,它是一種暴力搜索方法,通過搜索所有可能的結果來求解問題。回溯法在一次搜索結束時需要進行回溯(回退),將這一次搜索過程中設置的狀態進行清除,從而開始一次新的搜索過程。例如下圖示例中,從 f 開始,下一步有 4 種搜索可能,如果先搜索 b,需要將 b 標記為已經使用,防止重復使用。在這一次搜索結束之后,需要將 b 的已經使用狀態清除,并搜索 c。

~~~
private final static int[][] next = {{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}};
private int rows;
private int cols;
public boolean hasPath(char[] array, int rows, int cols, char[] str) {
if (rows == 0 || cols == 0) return false;
this.rows = rows;
this.cols = cols;
boolean[][] marked = new boolean[rows][cols];
char[][] matrix = buildMatrix(array);
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
if (backtracking(matrix, str, marked, 0, i, j))
return true;
return false;
}
private boolean backtracking(char[][] matrix, char[] str,
boolean[][] marked, int pathLen, int r, int c) {
if (pathLen == str.length) return true;
if (r < 0 || r >= rows || c < 0 || c >= cols
|| matrix[r][c] != str[pathLen] || marked[r][c]) {
return false;
}
marked[r][c] = true;
for (int[] n : next)
if (backtracking(matrix, str, marked, pathLen + 1, r + n[0], c + n[1]))
return true;
marked[r][c] = false;
return false;
}
private char[][] buildMatrix(char[] array) {
char[][] matrix = new char[rows][cols];
for (int r = 0, idx = 0; r < rows; r++)
for (int c = 0; c < cols; c++)
matrix[r][c] = array[idx++];
return matrix;
}
~~~
## 8.機器人的運動范圍
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/6e5207314b5241fb83f2329e89fdecc8?tpId=13&tqId=11219&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
**題目描述:**
地上有一個 m 行和 n 列的方格。一個機器人從坐標 (0, 0) 的格子開始移動,每一次只能向左右上下四個方向移動一格,但是不能進入行坐標和列坐標的數位之和大于 k 的格子。
例如,當 k 為 18 時,機器人能夠進入方格 (35,37),因為 3+5+3+7=18。但是,它不能進入方格 (35,38),因為 3+5+3+8=19。請問該機器人能夠達到多少個格子?
**解題思路:**
使用深度優先搜索(Depth First Search,DFS)方法進行求解。回溯是深度優先搜索的一種特例,它在一次搜索過程中需要設置一些本次搜索過程的局部狀態,并在本次搜索結束之后清除狀態。而普通的深度優先搜索并不需要使用這些局部狀態,雖然還是有可能設置一些全局狀態。
~~~
private static final int[][] next = {{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}};
private int cnt = 0;
private int rows;
private int cols;
private int threshold;
private int[][] digitSum;
public int movingCount(int threshold, int rows, int cols) {
this.rows = rows;
this.cols = cols;
this.threshold = threshold;
initDigitSum();
boolean[][] marked = new boolean[rows][cols];
dfs(marked, 0, 0);
return cnt;
}
private void dfs(boolean[][] marked, int r, int c) {
if (r < 0 || r >= rows || c < 0 || c >= cols || marked[r][c])
return;
marked[r][c] = true;
if (this.digitSum[r][c] > this.threshold)
return;
cnt++;
for (int[] n : next)
dfs(marked, r + n[0], c + n[1]);
}
private void initDigitSum() {
int[] digitSumOne = new int[Math.max(rows, cols)];
for (int i = 0; i < digitSumOne.length; i++) {
int n = i;
while (n > 0) {
digitSumOne[i] += n % 10;
n /= 10;
}
}
this.digitSum = new int[rows][cols];
for (int i = 0; i < this.rows; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < this.cols; j++)
this.digitSum[i][j] = digitSumOne[i] + digitSumOne[j];
}
~~~
## 9.剪繩子
[Leetcode](https://leetcode.com/problems/integer-break/description/)
**題目描述:**
把一根繩子剪成多段,并且使得每段的長度乘積最大
~~~
n = 2
return 1 (2 = 1 + 1)
n = 10
return 36 (10 = 3 + 3 + 4)
~~~
**解題思路:**
1、貪心
盡可能多剪長度為 3 的繩子,并且不允許有長度為 1 的繩子出現。如果出現了,就從已經切好長度為 3 的繩子中拿出一段與長度為 1 的繩子重新組合,把它們切成兩段長度為 2 的繩子。
證明:當 n >= 5 時,3(n - 3) - n = 2n - 9 > 0,且 2(n - 2) - n = n - 4 > 0。因此在 n >= 5 的情況下,將繩子剪成一段為 2 或者 3,得到的乘積會更大。又因為 3(n - 3) - 2(n - 2) = n - 5 >= 0,所以剪成一段長度為 3 比長度為 2 得到的乘積更大。
~~~java
public int integerBreak(int n) {
if (n < 2)
return 0;
if (n == 2)
return 1;
if (n == 3)
return 2;
int timesOf3 = n / 3;
if (n - timesOf3 * 3 == 1)
timesOf3--;
int timesOf2 = (n - timesOf3 * 3) / 2;
return (int) (Math.pow(3, timesOf3)) * (int) (Math.pow(2, timesOf2));
}
~~~
2、動態規劃???
~~~
public int integerBreak(int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++)
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], Math.max(j * (i - j), dp[j] * (i - j)));
return dp[n];
}
~~~
## 10.二進制中 1 的個數
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/8ee967e43c2c4ec193b040ea7fbb10b8?tpId=13&tqId=11164&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
**題目描述:**
輸入一個整數,輸出該數二進制表示中 1 的個數。
`n&(n-1)`
該位運算去除 n 的位級表示中最低的那一位。
~~~
n : 10110100
n-1 : 10110011
n&(n-1) : 10110000
~~~
~~~
public int NumberOf1(int n) {
int cnt = 0;
while (n != 0) {
cnt++;
n &= (n - 1);
}
return cnt;
}
~~~
## 11.數值的整數次方
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/1a834e5e3e1a4b7ba251417554e07c00?tpId=13&tqId=11165&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
**題目描述:**
給定一個 double 類型的浮點數 base 和 int 類型的整數 exponent,求 base 的 exponent 次方。
**解題思路:**
快速冪算法
```js
function Power(base, exponent)
{
// write code here
if (exponent === 0) return 1
let p = Math.abs(exponent)
let res = 1 // 記錄乘積
while (p) {
if (p & 1) { // 當前最后1位為1
res *= base
}
base *= base
p = p >> 1
}
return exponent > 0 ? res : (1 / res) // 指數為負
}
module.exports = {
Power : Power
};
```
## 12.刪除鏈表中的重復結點
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/fc533c45b73a41b0b44ccba763f866ef?tpId=13&tqId=11209&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
**題目描述:**

**解題思路:**
```js
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead) {
if (pHead == null || pHead.next == null)
return pHead;
ListNode next = pHead.next;
if (pHead.val == next.val) {
while (next != null && pHead.val == next.val)
next = next.next;
return deleteDuplication(next);
} else {
pHead.next = deleteDuplication(pHead.next);
return pHead;
}
}
```
## 13.鏈表中環的入口
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/253d2c59ec3e4bc68da16833f79a38e4?tpId=13&tqId=11208&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
**題目描述:**
一個鏈表中包含環,請找出該鏈表的環的入口結點。要求不能使用額外的空間。
**解題思路:**
使用雙指針,一個指針 fast 每次移動兩個節點,一個指針 slow 每次移動一個節點。因為存在環,所以兩個指針必定相遇在環中的某個節點上。假設相遇點在下圖的 z1 位置,此時 fast 移動的節點數為 x+2y+z,slow 為 x+y,由于 fast 速度比 slow 快一倍,因此 x+2y+z=2(x+y),得到 x=z。
在相遇點,slow 要到環的入口點還需要移動 z 個節點,如果讓 fast 重新從頭開始移動,并且速度變為每次移動一個節點,那么它到環入口點還需要移動 x 個節點。在上面已經推導出 x=z,因此 fast 和 slow 將在環入口點相遇。

~~~
public ListNode EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode pHead) {
if (pHead == null || pHead.next == null)
return null;
ListNode slow = pHead, fast = pHead;
do {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
} while (slow != fast);
fast = pHead;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
~~~
## 14.反轉鏈表
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/75e878df47f24fdc9dc3e400ec6058ca?tpId=13&tqId=11168&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
遞歸:
~~~
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = null;
ListNode newHead = ReverseList(next);
next.next = head;
return newHead;
}
~~~
迭代:
```js
function ReverseList(pHead)
{
// write code here
if (pHead === null) return null
let prev = null, curr = pHead, next
while (curr !== null) {
next = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next
}
return prev
}
```
## 15.合并兩個排序的鏈表
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d8b6b4358f774294a89de2a6ac4d9337?tpId=13&tqId=11169&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
**題目描述:**

**解題思路:**
遞歸:
```js
function Merge(pHead1, pHead2)
{
if (pHead1 === null) {
return pHead2
}
if (pHead2 === null) {
return pHead1
}
if (pHead1.val <= pHead2.val) {
pHead1.next = Merge(pHead1.next, pHead2)
return pHead1
} else {
pHead2.next = Merge(pHead1, pHead2.next)
return pHead2
}
}
```
迭代:
```js
function ListNode(x){
this.val = x;
this.next = null;
}
function Merge(pHead1, pHead2)
{
let head = new ListNode(-1) // 頭插
let curr = head
while (pHead1 !== null && pHead2 !== null) {
if (pHead1.val <= pHead2.val) {
curr.next = pHead1
pHead1 = pHead1.next
} else {
curr.next = pHead2
pHead2 = pHead2.next
}
curr = curr.next
}
if (pHead1 === null) {
curr.next = pHead2
}
if (pHead2 === null) {
curr.next = pHead1
}
return head.next
}
```
## 16.順時針打印矩陣
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/9b4c81a02cd34f76be2659fa0d54342a?tpId=13&tqId=11172&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
**題目描述:**
下圖的矩陣順時針打印結果為:1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 12, 16, 15, 14, 13, 9, 5, 6, 7, 11, 10

**解題思路:**
~~~
public ArrayList<Integer> printMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
ArrayList<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
int r1 = 0, r2 = matrix.length - 1, c1 = 0, c2 = matrix[0].length - 1;
while (r1 <= r2 && c1 <= c2) {
for (int i = c1; i <= c2; i++)
ret.add(matrix[r1][i]);
for (int i = r1 + 1; i <= r2; i++)
ret.add(matrix[i][c2]);
if (r1 != r2)
for (int i = c2 - 1; i >= c1; i--)
ret.add(matrix[r2][i]);
if (c1 != c2)
for (int i = r2 - 1; i > r1; i--)
ret.add(matrix[i][c1]);
r1++; r2--; c1++; c2--;
}
return ret;
}
~~~
## 17.樹的子結構
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/6e196c44c7004d15b1610b9afca8bd88?tpId=13&tqId=11170&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)

```js
function HasSubtree(pRoot1, pRoot2)
{
if (pRoot1 === null || pRoot2 === null) {
return false
}
return isSubtree(pRoot1, pRoot2) || HasSubtree(pRoot1.left, pRoot2) || HasSubtree(pRoot1.right, pRoot2)
}
function isSubtree (p1, p2) {
if (p2 === null) {
return true
}
if (p1 === null) {
return false
}
if (p1.val !== p2.val) {
return false
}
return isSubtree(p1.left, p2.left) && isSubtree(p1.right, p2.right)
}
```
## 18.對稱的二叉樹
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/ff05d44dfdb04e1d83bdbdab320efbcb?tpId=13&tqId=11211&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
```js
function isSymmetrical(pRoot)
{
if (pRoot === null) {
return true
}
return fn(pRoot.left, pRoot.right)
}
function fn (t1, t2) {
if (t1 === null && t2 === null) {
return true
}
if (t1 === null || t2 === null) {
return false
}
if (t1.val !== t2.val) {
return false
}
return fn(t1.left, t2.right) && fn(t1.right, t2.left)
}
```
## 19.棧的壓入、彈出序列
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d77d11405cc7470d82554cb392585106?tpId=13&tqId=11174&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
題目描述:
輸入兩個整數序列,第一個序列表示棧的壓入順序,請判斷第二個序列是否為該棧的彈出順序。假設壓入棧的所有數字均不相等。
例如序列 1,2,3,4,5 是某棧的壓入順序,序列 4,5,3,2,1 是該壓棧序列對應的一個彈出序列,但 4,3,5,1,2 就不可能是該壓棧序列的彈出序列。
解題思路:
```js
function IsPopOrder(pushV, popV)
{
let n = pushV.length
const stack = []
for (let pushIndex = 0, popIndex = 0; pushIndex < n; pushIndex++) {
stack.push(pushV[pushIndex])
// 按入棧序列壓入,當棧頂元素對應于出棧序列元素時彈出(用 popIndex 記錄),注意是用 while
while (popIndex < n && stack.length !== 0 && stack[stack.length - 1] === popV[popIndex]) {
stack.pop()
popIndex++
}
}
return stack.length === 0 ? true : false
}
```
## 20.把二叉樹打印成多行
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/445c44d982d04483b04a54f298796288?tpId=13&tqId=11213&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
```js
function Print(pRoot)
{
const Q = [], res = []
if (pRoot === null) return Q
Q.push(pRoot)
while (Q.length !== 0) {
let low = 0, high = Q.length // 這兩個變量確定了本層的結點數量
const line = []
while (low++ < high) {
let tmp = Q.shift()
line.push(tmp.val)
if (tmp.left !== null) {
Q.push(tmp.left)
}
if (tmp.right !== null) {
Q.push(tmp.right)
}
}
res.push(line)
}
return res
}
```
## 21.二叉搜索樹的后序遍歷序列
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/a861533d45854474ac791d90e447bafd?tpId=13&tqId=11176&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
輸入一個整數數組,判斷該數組是不是某二叉搜索樹的后序遍歷的結果。假設輸入的數組的任意兩個數字都互不相同。
```js
function VerifySquenceOfBST(sequence)
{
// BST特性:左子結點比根結點小,右子結點大于根結點
let size = sequence.length
if (size === 0) return false
let i = 0
while (--size) {
while (sequence[i++] < sequence[size]);
while (sequence[i++] > sequence[size]);
if (i < size) return false
i = 0
}
return true
}
```
## 22.二叉樹中和為某一值的路徑
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/b736e784e3e34731af99065031301bca?tpId=13&tqId=11177&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
**題目描述:**
輸入一顆二叉樹和一個整數,打印出二叉樹中結點值的和為輸入整數的所有路徑。路徑定義為從樹的根結點開始往下一直到葉結點所經過的結點形成一條路徑。
下圖的二叉樹有兩條和為 22 的路徑:10, 5, 7 和 10, 12

**解題思路:**
```js
let res = []
let path = []
function FindPath(root, expectNumber)
{
if (root === null) { return [] }
backtracking(root, expectNumber)
return res
}
function backtracking (node, target) {
if (root === null) {
return
}
path.push(node.val)
if (node.val === target && node.left === null && node.right === null) {
res.push(path)
} else {
backtracking(node.left, target - node.val)
backtracking(node.right, target - node.val)
}
path.pop()
}
```
## 23.復雜鏈表的復制
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/f836b2c43afc4b35ad6adc41ec941dba?tpId=13&tqId=11178&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
題目描述:輸入一個復雜鏈表(每個節點中有節點值,以及兩個指針,一個指向下一個節點,另一個特殊指針指向任意一個節點),返回結果為復制后復雜鏈表的 head。
解題思路:
第一步,在每個節點的后面插入復制的節點。

第二步,對復制節點的 random 鏈接進行賦值。

第三步,拆分。

```js
function RandomListNode(x){
this.label = x;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
function Clone(pHead)
{
/*
1、復制每個節點,如:復制節點 A 得到 A1,將 A1 插入節點 A 后面
2、遍歷鏈表,A1->random = A->random->next;
3、將鏈表拆分成原鏈表和復制后的鏈表
*/
if (!pHead) return null
let currNode = pHead
// step1
while (currNode) {
let newNode = new RandomListNode(currNode.label)
newNode.next = currNode.next
currNode.next = newNode
currNode = newNode.next
}
// step2
currNode = pHead
while (currNode) {
let tempNode = currNode.next
if (currNode.random) {
tempNode.random = currNode.random.next
}
currNode = tempNode.next
}
// step3 拆分
let pCloneHead = pHead.next
let temp
currNode = pHead
while (currNode.next) {
temp = currNode.next
currNode.next = temp.next
currNode = temp
}
return pCloneHead
}
```
## 24.序列化二叉樹
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/cf7e25aa97c04cc1a68c8f040e71fb84?tpId=13&tqId=11214&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
請實現兩個函數,分別用來序列化和反序列化二叉樹。
```js
function TreeNode(x) {
this.val = x;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
const arr = []
function Serialize(pRoot)
{
if (pRoot === null) {
arr.push('#')
return
}
arr.push(pRoot.val)
Serialize(pRoot.left)
Serialize(pRoot.right)
}
function Deserialize(s)
{
if (arr.length < 1) {
return null
}
let root = null // '#' -> null
let temp = arr.shift()
if (typeof temp === 'number') {
root = new TreeNode(temp)
root.left = Deserialize('')
root.right = Deserialize('')
}
return root
}
```
## 25.最小的 K 個數
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/6a296eb82cf844ca8539b57c23e6e9bf?tpId=13&tqId=11182&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
解題思路:
1.快速選擇
* 復雜度:O(N) + O(1)
* 只有當允許修改數組元素時才可以使用
快速排序的 partition() 方法,會返回一個整數 j 使得 a\[l..j-1\] 小于等于 a\[j\],且 a\[j+1..h\] 大于等于 a\[j\],此時 a\[j\] 就是數組的第 j 大元素。可以利用這個特性找出數組的第 K 個元素,這種找第 K 個元素的算法稱為快速選擇算法。
```java
public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int[] nums, int k) {
ArrayList<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (k > nums.length || k <= 0)
return ret;
findKthSmallest(nums, k - 1);
/* findKthSmallest 會改變數組,使得前 k 個數都是最小的 k 個數 */
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
ret.add(nums[i]);
return ret;
}
public void findKthSmallest(int[] nums, int k) {
int l = 0, h = nums.length - 1;
while (l < h) {
int j = partition(nums, l, h);
if (j == k)
break;
if (j > k)
h = j - 1;
else
l = j + 1;
}
}
private int partition(int[] nums, int l, int h) {
int p = nums[l]; /* 切分元素 */
int i = l, j = h + 1;
while (true) {
while (i != h && nums[++i] < p) ;
while (j != l && nums[--j] > p) ;
if (i >= j)
break;
swap(nums, i, j);
}
swap(nums, l, j);
return j;
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int t = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = t;
}
```
2.大小為 K 的最小堆
* 復雜度:O(NlogK) + O(K)
* 特別適合處理海量數據
應該使用大頂堆來維護最小堆,而不能直接創建一個小頂堆并設置一個大小,企圖讓小頂堆中的元素都是最小元素。
維護一個大小為 K 的最小堆過程如下:在添加一個元素之后,如果大頂堆的大小大于 K,那么需要將大頂堆的堆頂元素去除。
```java
public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int[] nums, int k) {
if (k > nums.length || k <= 0)
return new ArrayList<>();
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o2 - o1);
for (int num : nums) {
maxHeap.add(num);
if (maxHeap.size() > k)
maxHeap.poll();
}
return new ArrayList<>(maxHeap);
}
```
## 26.連續子數組的最大和
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/459bd355da1549fa8a49e350bf3df484?tpId=13&tqId=11183&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
題目描述:{6, -3, -2, 7, -15, 1, 2, 2},連續子數組的最大和為 8(從第 0 個開始,到第 3 個為止)。
```js
function FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(array)
{
const d = []
d[0] = array[0]
for (let i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
d[i] = Math.max(d[i - 1] + array[i], array[i])
}
return Math.max(...d)
}
```
## 27.把數組排成最小的數
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/8fecd3f8ba334add803bf2a06af1b993?tpId=13&tqId=11185&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
題目描述:輸入一個正整數數組,把數組里所有數字拼接起來排成一個數,打印能拼接出的所有數字中最小的一個。例如輸入數組 {3,32,321},則打印出這三個數字能排成的最小數字為 321323。
```js
function PrintMinNumber(numbers)
{
// write code here
numbers.sort(compare)
return numbers.join('')
}
/*
根據拼接后的字符串比較大小
ab < ba : a < b 如323 < 332 -> 32 < 3
ab > ba : a > b
ab = ba : a = b
*/
function compare(a, b) {
let ab = a + '' + b
let ba = b + '' + a
if (ab < ba) {
return -1 // 如果第一個參數應該在第二個參數之前,返回一個負數
} else if (ab > ba) {
return 1
} else {
return 0
}
}
```
## 28.丑數
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/6aa9e04fc3794f68acf8778237ba065b?tpId=13&tqId=11186&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
題目描述:把只包含因子 2、3 和 5 的數稱作丑數(Ugly Number)。例如 6、8 都是丑數,但 14 不是,因為它包含因子 7。習慣上我們把 1 當做是第一個丑數。求按從小到大的順序的第 N 個丑數。
```js
function GetUglyNumber_Solution(index)
{
if (index < 7) return index
let p2 = 0, p3 = 0, p5 = 0, newNum = 1 // 三個隊列的指針,newNum為從隊列頭選出來的最小數
const arr = []
arr.push(newNum)
while (arr.length < index) {
newNum = Math.min(arr[p2] * 2, arr[p3] * 3, arr[p5] * 5) // 選出三個隊列頭最小的數
// 這三個if有可能進入一個或者多個,進入多個是三個隊列頭最小的數有多個的情況
if (arr[p2] * 2 === newNum) p2++
if (arr[p3] * 3 === newNum) p3++
if (arr[p5] * 5 === newNum) p5++
arr.push(newNum)
}
return newNum
}
```
## 29.兩個鏈表的第一個公共結點
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/6ab1d9a29e88450685099d45c9e31e46?tpId=13&tqId=11189&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
題目描述:

解題思路:
設 A 的長度為 a + c,B 的長度為 b + c,其中 c 為尾部公共部分長度,可知 a + c + b = b + c + a。
當訪問鏈表 A 的指針訪問到鏈表尾部時,令它從鏈表 B 的頭部重新開始訪問鏈表 B;同樣地,當訪問鏈表 B 的指針訪問到鏈表尾部時,令它從鏈表 A 的頭部重新開始訪問鏈表 A。這樣就能控制訪問 A 和 B 兩個鏈表的指針能同時訪問到交點。
```js
function FindFirstCommonNode(pHead1, pHead2)
{
// 設 A 的長度為 a + c,B 的長度為 b + c,其中 c 為尾部公共部分長度,可知 a + c + b = b + c + a
// 當 A 指針走到尾部時讓其指向 B 頭部,當 B 指針走到尾部時讓其指向 A 頭部
let l1 = pHead1
let l2 = pHead2
while (l1 !== l2) {
l1 = l1 === null ? pHead2 : l1.next
l2 = l2 === null ? pHead1 : l2.next
}
return l1
}
```
## 30.和為 S 的兩個數字
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/390da4f7a00f44bea7c2f3d19491311b?tpId=13&tqId=11195&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
題目描述:輸入一個遞增排序的數組和一個數字 S,在數組中查找兩個數,使得他們的和正好是 S。如果有多對數字的和等于 S,輸出兩個數的乘積最小的。
解題思路:
使用雙指針,一個指針指向元素較小的值,一個指針指向元素較大的值。指向較小元素的指針從頭向尾遍歷,指向較大元素的指針從尾向頭遍歷。
* 如果兩個指針指向元素的和 sum == target,那么得到要求的結果;
* 如果 sum > target,移動較大的元素,使 sum 變小一些;
* 如果 sum < target,移動較小的元素,使 sum 變大一些。
```js
function FindNumbersWithSum(array, sum)
{
let low = 0, high = array.length - 1
let multi = 10000000, res = []
while (low < high) {
let add = array[low] + array[high]
if (add === sum) {
if (array[low] * array[high] < multi) {
res = [array[low], array[high]]
multi = array[low] * array[high]
}
low++
high--
} else if (add > sum) {
high--
} else {
low++
}
}
return res
}
```
## 31.和為 S 的連續正數序列
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/c451a3fd84b64cb19485dad758a55ebe?tpId=13&tqId=11194&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
題目描述:
輸出所有和為 S 的連續正數序列。
例如和為 100 的連續序列有:
~~~
[9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16]
[18, 19, 20, 21, 22]。
~~~
解題思路:
```js
function FindContinuousSequence(sum)
{
const res = []
let pHigh = 2, pLow = 1 // 雙指針,總和小于 sum,high ++,否則 low++
while (pHigh > pLow) {
let currSum = (pHigh + pLow) * (pHigh - pLow + 1) / 2 // 等差數列
if (currSum < sum) pHigh++
else if (currSum === sum) {
let temp = []
for (let i = pLow; i <= pHigh; i++) {
temp.push(i)
}
res.push(temp)
pHigh++
} else {
pLow++
}
}
return res
}
```
## 32.不用加減乘除做加法
題目描述:寫一個函數,求兩個整數之和,要求不得使用 +、-、\*、/ 四則運算符號。
解題思路:
```js
function Add(num1, num2)
{
while (num2 !== 0) {
let temp = num1 ^ num2 // 不算進位部分
num2 = (num1 & num2) << 1 // 進位部分
num1 = temp
}
return num1
}
```
## 33.構建乘積數組
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/94a4d381a68b47b7a8bed86f2975db46?tpId=13&tqId=11204&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
題目描述:給定一個數組 A\[0, 1,..., n-1\],請構建一個數組 B\[0, 1,..., n-1\],其中 B 中的元素 B\[i\]=A\[0\]\*A\[1\]\*...\*A\[i-1\]\*A\[i+1\]\*...\*A\[n-1\]。要求不能使用除法。
**解題思路:**
B\[i\]的值可以看作下圖的矩陣中每行的乘積。
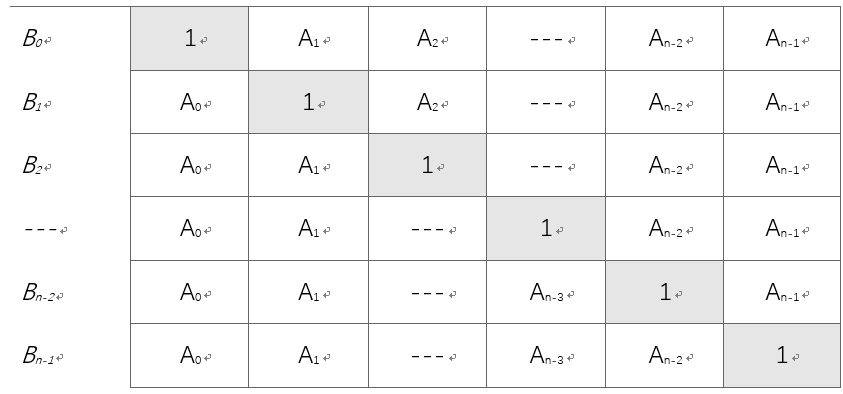
```js
function multiply(array)
{
let len = array.length
const B = []
B[0] = 1
// 計算下三角連乘
for (let i = 1; i < len; i++) {
B[i] = B[i-1] * array[i-1]
}
// 計算上三角
let temp = 1
for (let j = len - 2; j >= 0; j--) {
temp *= array[j+1]
B[j] *= temp
}
return B
}
```
## 34.樹中兩個節點的最低公共祖先
### 二叉查找樹
[Leetcode : 235. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree](https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/description/)
二叉查找樹中,兩個節點 p, q 的公共祖先 root 滿足 root.val >= p.val && root.val <= q.val。

```js
var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {
if (root === null) return null
if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
}
if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
}
return root // we allow a node to be a descendant of itself
};
```
### 普通二叉樹
[Leetcode : 236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree](https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/description/)
在左右子樹中查找是否存在 p 或者 q,如果 p 和 q 分別在兩個子樹中,那么就說明根節點就是最低公共祖先。

```js
var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {
if (root === null || root === p || root === q) return root
let left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
let right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
if (left !== null && right !== null) return root
return left !== null ? left : right
};
```
- 序言 & 更新日志
- H5
- Canvas
- 序言
- Part1-直線、矩形、多邊形
- Part2-曲線圖形
- Part3-線條操作
- Part4-文本操作
- Part5-圖像操作
- Part6-變形操作
- Part7-像素操作
- Part8-漸變與陰影
- Part9-路徑與狀態
- Part10-物理動畫
- Part11-邊界檢測
- Part12-碰撞檢測
- Part13-用戶交互
- Part14-高級動畫
- CSS
- SCSS
- codePen
- 速查表
- 面試題
- 《CSS Secrets》
- SVG
- 移動端適配
- 濾鏡(filter)的使用
- JS
- 基礎概念
- 作用域、作用域鏈、閉包
- this
- 原型與繼承
- 數組、字符串、Map、Set方法整理
- 垃圾回收機制
- DOM
- BOM
- 事件循環
- 嚴格模式
- 正則表達式
- ES6部分
- 設計模式
- AJAX
- 模塊化
- 讀冴羽博客筆記
- 第一部分總結-深入JS系列
- 第二部分總結-專題系列
- 第三部分總結-ES6系列
- 網絡請求中的數據類型
- 事件
- 表單
- 函數式編程
- Tips
- JS-Coding
- Framework
- Vue
- 書寫規范
- 基礎
- vue-router & vuex
- 深入淺出 Vue
- 響應式原理及其他
- new Vue 發生了什么
- 組件化
- 編譯流程
- Vue Router
- Vuex
- 前端路由的簡單實現
- React
- 基礎
- 書寫規范
- Redux & react-router
- immutable.js
- CSS 管理
- React 16新特性-Fiber 與 Hook
- 《深入淺出React和Redux》筆記
- 前半部分
- 后半部分
- react-transition-group
- Vue 與 React 的對比
- 工程化與架構
- Hybird
- React Native
- 新手上路
- 內置組件
- 常用插件
- 問題記錄
- Echarts
- 基礎
- Electron
- 序言
- 配置 Electron 開發環境 & 基礎概念
- React + TypeScript 仿 Antd
- TypeScript 基礎
- React + ts
- 樣式設計
- 組件測試
- 圖標解決方案
- Storybook 的使用
- Input 組件
- 在線 mock server
- 打包與發布
- Algorithm
- 排序算法及常見問題
- 劍指 offer
- 動態規劃
- DataStruct
- 概述
- 樹
- 鏈表
- Network
- Performance
- Webpack
- PWA
- Browser
- Safety
- 微信小程序
- mpvue 課程實戰記錄
- 服務器
- 操作系統基礎知識
- Linux
- Nginx
- redis
- node.js
- 基礎及原生模塊
- express框架
- node.js操作數據庫
- 《深入淺出 node.js》筆記
- 前半部分
- 后半部分
- 數據庫
- SQL
- 面試題收集
- 智力題
- 面試題精選1
- 面試題精選2
- 問答篇
- 2025面試題收集
- Other
- markdown 書寫
- Git
- LaTex 常用命令
- Bugs
