# Java `Map`接口
> 原文: [https://www.programiz.com/java-programming/map](https://www.programiz.com/java-programming/map)
#### 在本教程中,我們將學習 Java `Map`接口及其方法。
Java 集合框架的`Map`接口提供了映射數據結構的功能。
它實現了`Collection`接口。
* * *
## 映射的工作原理
在 Java 中,`Map`的元素存儲在**鍵/值**對中。 **鍵**是與各個**值**相關聯的唯一值。
映射不能包含重復的鍵。 并且,每個鍵都與一個值相關聯。
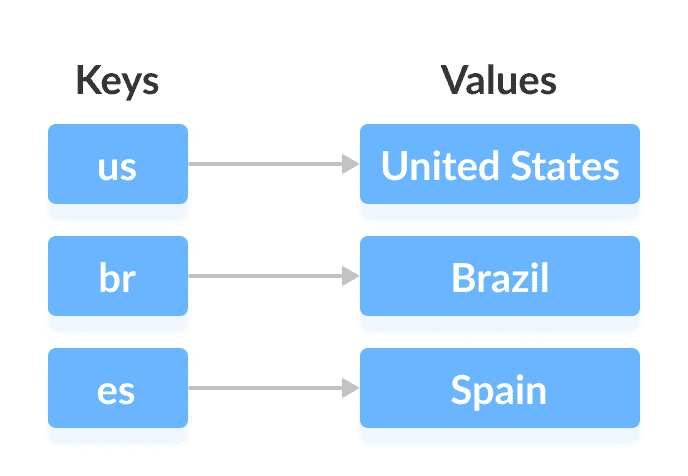
我們可以使用與它們關聯的鍵來訪問和修改值。
在上圖中,我們具有以下值:`Amarica`,`Brazil`和`Spain`。 并且我們有相應的鍵:`us`,`br`和`es`。
現在,我們可以使用它們的對應鍵訪問這些值。
**注意**: `Map`接口維護 3 個不同的集合:
* 鍵集
* 值集
* 鍵/值關聯(映射)集。
因此,我們可以分別訪問鍵,值和關聯。
* * *
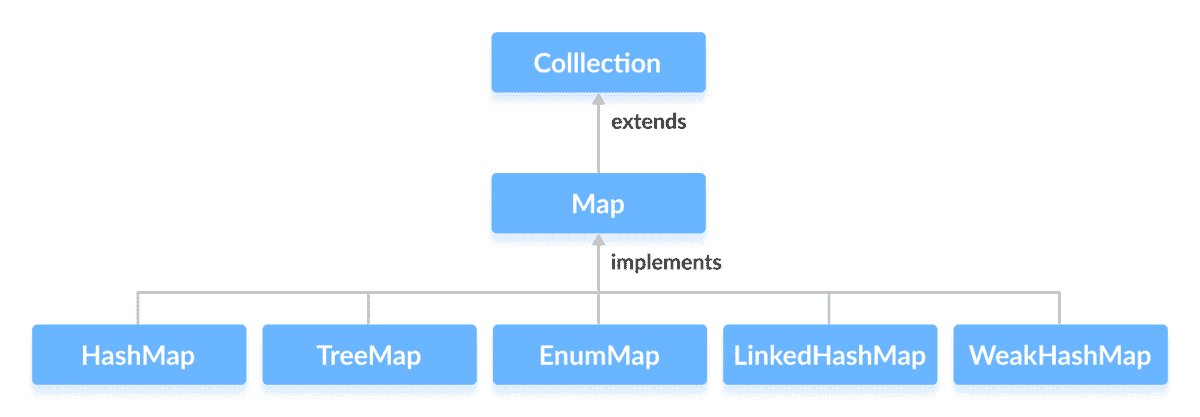
## 實現`Map`的類
由于`Map`是一個接口,因此我們無法從中創建對象。
為了使用`Map`接口的功能,我們可以使用以下類:
* [`HashMap`](/java-programming/hashmap "Java HashMap class")
* [`EnumMap`](/java-programming/enummap "Java EnumMap Class")
* [`LinkedHashMap`](/java-programming/linkedhashmap "Java LinkedHashMap class")
* [`WeakHashMap`](/java-programming/weakhashmap "Java WeakhashMap class")
* [`TreeMap`](/java-programming/treemap "Java TreeMap class")
這些類在集合框架中定義,并實現`Map`接口。
* * *
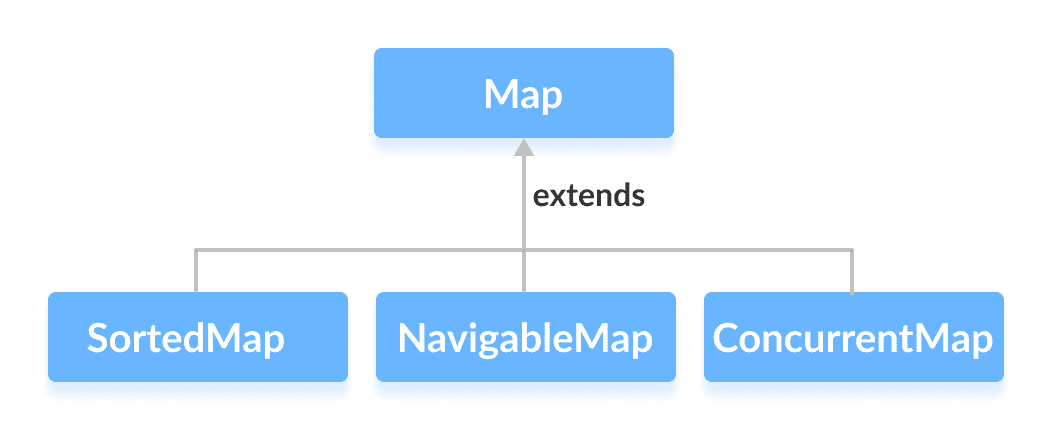
## 擴展`Map`的接口
`Map`接口還通過以下子接口擴展:
* [`SortedMap`](/java-programming/sortedmap "Java SortedMap Interface")
* [`NavigableMap`](/java-programming/navigablemap "Java NavigableMap Interface")
* [`ConcurrentMap`](/java-programming/concurrentmap "Java ConcurrentMap Interface")
* * *
## 如何使用映射?
在 Java 中,必須導入`java.util.Map`包才能使用`Map`。 導入包后,將按照以下方法創建映射。
```java
// Map implementation using HashMap
Map<Key, Value> numbers = new HashMap<>();
```
在上面的代碼中,我們創建了一個名為`number`的`Map`。 我們已經使用`HashMap`類來實現`Map`接口。
這里,
* `key` - 用于關聯映射中每個元素(值)的唯一標識符
* `value` - 映射中與按鍵相關聯的元素
* * *
## 映射方法
`Map`接口包含`Collection`接口的所有方法。 這是因為`Collection`是`Map`的超級接口。
除了`Collection`接口中可用的方法外,`Map`接口還包括以下方法:
* **`put(K, V)`** - 將鍵`K`和值`V`的關聯插入到映射中。 如果鍵已經存在,則新值將替換舊值。
* **`putAll()`** - 將指定映射中的所有條目插入此映射。
* **`putIfAbsent(K, V)`** - 如果鍵`K`尚未與值`V`關聯,則插入關聯。
* **`get(K)`** - 返回與指定鍵`K`關聯的值。 如果找不到鍵,則返回`null`。
* **`getOrDefault(K, defaultValue)`** - 返回與指定鍵`K`關聯的值。 如果未找到鍵,則返回`defaultValue`。
* **`containsKey(K)`** - 檢查映射中是否存在指定的鍵`K`。
* **`containsValue(V)`** - 檢查指定值`V`是否存在于映射中。
* **`replace(K, V)`** - 用新的指定值`V`替換鍵`K`的值。
* **`replace(K, oldValue, newValue)`** - 僅當鍵`K`時,才將鍵`K`的值替換為新值`newValue`與值`oldValue`關聯。
* **`remove(K)`** - 從鍵`K`表示的映射中刪除條目。
* **`remove(K, V)`** - 從映射中刪除具有與值`V`關聯的鍵`K`的條目。
* **`keySet()`** - 返回映射中存在的所有鍵的集合。
* **`values()`** - 返回映射中存在的所有值的集合。
* **`entrySet()`** - 返回映射中存在的所有鍵/值映射的集合。
* * *
## `Map`接口的實現
**1.`HashMap`實現類**
```java
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a map using the HashMap
Map<String, Integer> numbers = new HashMap<>();
// Insert elements to the map
numbers.put("One", 1);
numbers.put("Two", 2);
System.out.println("Map: " + numbers);
// Access keys of the map
System.out.println("Keys: " + numbers.keySet());
// Access values of the map
System.out.println("Values: " + numbers.values());
// Access entries of the map
System.out.println("Entries: " + numbers.entrySet());
// Remove Elements from the map
int value = numbers.remove("Two");
System.out.println("Removed Value: " + value);
}
}
```
**輸出**
```java
Map: {One=1, Two=2}
Keys: [One, Two]
Values: [1, 2]
Entries: [One=1, Two=2]
Removed Value: 2
```
要了解有關`HashMap`的更多信息,請訪問 [Java HashMap](/java-programming/hashmap "Java HashMap Class") 。
* * *
**2.`TreeMap`實現類**
```java
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating Map using TreeMap
Map<String, Integer> values = new TreeMap<>();
// Insert elements to map
values.put("Second", 2);
values.put("First", 1);
System.out.println("Map using TreeMap: " + values);
// Replacing the values
values.replace("First", 11);
values.replace("Second", 22);
System.out.println("New Map: " + values);
// Remove elements from the map
int removedValue = values.remove("First");
System.out.println("Removed Value: " + removedValue);
}
}
```
**輸出**:
```java
Map using TreeMap: {First=1, Second=2}
New Map: {First=11, Second=22}
Removed Value: 11
```
要了解有關`TreeMap`的更多信息,請訪問 [Java TreeMap](/java-programming/treemap "Java TreeMap Class") 。
- Programiz C 語言教程
- C 簡介
- C 關鍵字和標識符
- C 變量,常量和字面值
- C 數據類型
- C 輸入輸出(I/O)
- C 編程運算符
- C 簡單示例
- C 流程控制
- C if...else語句
- C for循環
- C while和do...while循環
- C break和continue
- C switch語句
- C goto聲明
- C 控制流程示例
- C 函數
- C 函數
- C 用戶定義的函數
- C 編程中用戶定義函數的類型
- C 遞歸
- C 存儲類
- C 函數示例
- C 數組
- C 數組
- C 多維數組
- 將數組傳遞給 C 中的函數
- C 編程指針
- C 指針
- 數組和指針之間的關系
- C 按引用調用:使用指針
- C 動態內存分配
- C 數組和指針示例
- C 字符串
- C 編程字符串
- 使用庫函數進行 C 編程中的字符串操作
- C 編程中的字符串示例
- 結構與聯合
- 結構
- 結構和指針
- C 結構與函數
- C 聯合
- C 結構示例
- C 文件
- C 文件處理
- C 文件示例
- 其他主題
- 枚舉
- C 預處理器和宏
- C 標準庫函數
- C 示例
- C 程序:打印金字塔和圖案
- C 程序:檢查數字是否為質數
- C 程序:檢查數字是否為回文
- C 程序:HelloWorld
- C 程序:打印整數(由用戶輸入)
- C 程序:相加兩個整數
- C 程序:將兩個浮點數相乘
- C 程序:查找字符的 ASCII 值
- C 程序:商和余數
- C 程序:查找int,float,double和char的大小
- C 程序:long關鍵字演示
- C 程序:交換兩個數字
- C 程序:檢查數字是偶數還是奇數
- C 程序:檢查字符是元音還是輔音
- C 程序:查找三個數字中最大的數字
- C 程序:查找二次方程的根
- C 程序:檢查閏年
- C 程序:檢查數字是正數還是負數
- C 程序:檢查字符是否為字母
- C 程序:計算自然數之和
- C 程序:查找數字階乘
- C 程序:生成乘法表
- C 程序:顯示斐波那契數列
- C 程序:查找兩個數字的 GCD
- C 程序:查找兩個數字的 LCM
- C 程序:使用循環從 A 到 Z 顯示字符
- C 程序:計算整數中的位數
- C 程序:反轉數字
- C 程序:計算數字的冪
- C 程序:顯示兩個間隔之間的質數
- C 程序:檢查阿姆斯特朗數
- C 程序:在兩個間隔之間顯示阿姆斯特朗數
- C 程序:顯示數字因數
- C 程序:使用switch...case制作一個簡單的計算器
- C 程序:使用函數顯示區間內的質數
- C 程序:使用用戶定義的函數檢查質數或阿姆斯特朗數
- C 程序:檢查一個數字是否可以表示為兩個質數之和
- C 程序:使用遞歸查找自然數之和
- C 程序:使用遞歸查找數字的階乘
- C 程序:使用遞歸查找 GCD
- C 程序:將二進制數轉換為十進制,反之亦然
- C 程序:將八進制數轉換為十進制,反之亦然
- C 程序:將二進制數轉換為八進制,反之亦然
- C 程序:使用遞歸來反轉句子
- C 程序:使用遞歸計算冪
- C 程序:使用數組計算平均值
- C 程序:查找數組中的最大元素
- C 程序:計算標準差
- C 程序:使用多維數組相加兩個矩陣
- C 程序:使用多維數組將兩個矩陣相乘
- C 程序:查找矩陣的轉置
- C 程序:通過將矩陣傳遞給函數來將兩個矩陣相乘
- C 程序:使用指針訪問數組元素
- C 程序:使用按引用調用以循環順序交換數字
- C 程序:使用動態內存分配查找最大數字
- C 程序:查找字符串中字符的頻率
- C 程序:計算元音,輔音等的數量
- C 程序:刪除字符串中除字母之外的所有字符
- C 程序:查找字符串的長度
- C 程序:連接兩個字符串
- C 程序:不使用strcpy()復制字符串
- C 程序:按字典順序(字典順序)對元素進行排序
- C 程序:使用程序存儲學生信息
- C 程序:使用結構相加兩個距離(以英寸-英尺系統為單位)
- C 程序:通過將結構傳遞給函數來相加兩個復數
- C 程序:計算兩個時間段之間的差異
- C 程序:使用結構存儲學生信息
- C 程序:在結構中動態存儲數據
- C 程序:將句子寫入文件
- C 程序:從文件中讀取一行并顯示它
- C 程序:顯示自己的源代碼作為輸出
- Programiz C++ 教程
- C++ 簡介
- C++ 變量,文字和常量
- C++ 數據類型
- C++ 基本輸入/輸出
- C++ 類型轉換
- C++ 運算符
- C++ 注釋
- C++ 流控制
- C++ if,if...else和嵌套if...else
- C++ for循環
- C++ while和do...while循環
- C++ break語句
- C++ switch..case語句
- C++ goto語句
- C++ 函數
- C++ 函數
- C++ 中用戶定義函數的類型
- C++ 函數重載
- C++ 編程默認參數(參數)
- C++ 存儲類
- C++ 遞歸
- C++ 通過引用返回
- C++ 數組和字符串
- C++ 數組
- C++ 多維數組
- 在 C++ 編程中將數組傳遞給函數
- C++ 字符串
- C++ 結構
- C++ 結構
- C++ 結構與功能
- C++ 結構指針
- C++ 枚舉
- C++ 對象和類
- C++ 類和對象
- C++ 構造器
- 如何通過 C++ 中的函數傳遞和返回對象?
- C++ 運算符重載
- C++ 指針
- C++ 指針
- C++ 指針和數組
- 通過引用進行 C++ 調用:使用指針[包含示例]
- C++ 內存管理:new和delete
- C++ 繼承
- C++ 繼承
- C++ 編程中的公共,受保護和私有繼承
- C++ 函數覆蓋
- C++ 多重,多層和層次繼承
- C++ 友元函數和友元類
- C++ 虛函數
- C++ 模板
- C++ 示例
- C++ 程序:HelloWorld
- C++ 程序:檢查數字是否為質數
- C++ 程序:創建金字塔和圖案
- C++ 程序:加兩個數字
- C++ 程序:打印用戶輸入的數字
- C++ 程序:查找商數和余數
- C++ 程序:在系統中查找int,float,double和char的大小
- C++ 程序:交換兩個數字
- C++ 程序:檢查數字是偶數還是奇數
- C++ 程序:檢查字符是元音還是輔音
- C++ 程序:查找三個數字中最大的數字
- C++ 程序:查找二次方程式的所有根
- C++ 程序:計算自然數之和
- C++ 程序:檢查閏年
- C++ 程序:查找階乘
- C++ 程序:生成乘法表
- C++ 程序:顯示斐波那契數列
- C++ 程序:查找 GCD
- C++ 程序:查找 LCM
- C++ 程序:反轉數字
- C++ 程序:計算數字的冪
- C++ 程序:遞增++和遞減--運算符重載
- C++ 程序:使用運算符重載減去復數
- C++ 程序:查找字符的 ASCII 值
- C++ 程序:將兩個數相乘
- C++ 程序:檢查數字是否為回文
- C++ 程序:顯示兩個間隔之間的質數
- C++ 程序:檢查阿姆斯特朗數
- C++ 程序:顯示兩個間隔之間的阿姆斯特朗數
- C++ 程序:顯示數字的因數
- C++ 程序:使用switch...case的簡單的加減乘除計算器
- C++ 程序:使用函數顯示兩個時間間隔之間的質數
- C++ 程序:通過創建函數來檢查質數
- C++ 程序:檢查數字是否可以表示為兩個質數之和
- C++ 程序:使用遞歸查找自然數之和
- C++ 程序:使用遞歸計算數字的階乘
- C++ 程序:使用遞歸查找 GCD
- C++ 程序:將二進制數轉換為十進制,反之亦然
- C++ 程序:將八進制數轉換為十進制,反之亦然
- C++ 程序:將二進制數轉換為八進制,反之亦然
- C++ 程序:使用遞歸來反轉句子
- C++ 程序:使用遞歸計算冪
- C++ 程序:使用數組計算數字平均值
- C++ 程序:查找數組的最大元素
- C++ 程序:計算標準差
- C++ 程序:使用多維數組相加兩個矩陣
- C++ 程序:使用多維數組將兩個矩陣相乘
- C++ 程序:查找矩陣的轉置
- C++ 程序:通過將矩陣傳遞給函數將兩個矩陣相乘
- C++ 程序:使用指針訪問數組元素
- C++ 程序:使用引用調用以循環順序交換數字
- C++ 程序:查找字符串中字符的頻率
- C++ 程序:查找字符串中元音,輔音,數字和空白的數量
- C++ 程序:刪除字符串中除字母之外的所有字符
- C++ 程序:查找字符串的長度
- C++ 程序:連接兩個字符串
- C++ 程序:復制字符串
- C++ 程序:按字典順序(字典順序)對元素進行排序
- C++ 程序:在結構中存儲學生的信息
- C++ 程序:使用結構相加兩個距離(以英寸-英尺為單位)
- C++ 程序:通過將結構傳遞給函數來添加復數
- C++ 程序:計算兩個時間段之間的差異
- C++ 程序:使用結構存儲和顯示信息
- Programiz C# 教程
- 簡介
- C# Hello World - 您的第一個 C# 程序
- C# 關鍵字和標識符
- C# 變量和(原始)數據類型
- C# 運算符
- C# 基本輸入和輸出
- C# 表達式,語句和塊(帶有示例)
- C# 注釋
- 流程控制
- C# if,if...else,if...else if和嵌套if語句
- C# for循環
- C# while和do...while循環
- C# foreach循環
- C# switch語句
- C# 三元(?:)運算符
- 其他話題
- C# 按位和移位運算符
- C# 預處理程序指令
- C# 編程中的命名空間
- C# 部分類和部分方法
- Programiz 數據結構和算法教程
- DSA 簡介
- 什么是算法?
- 為什么要學習數據結構和算法?
- 漸近分析
- 主定理
- 分治算法
- 數據結構(一)
- 棧
- 隊列
- 隊列類型
- 循環隊列
- 優先隊列
- 雙端隊列
- 數據結構(二)
- 鏈表
- 鏈表操作:遍歷,插入和刪除
- 鏈表的類型 - 單鏈,雙鏈和循環鏈
- 哈希表
- 堆數據結構
- 斐波那契堆
- 減小斐波那契堆上的鍵和刪除節點的操作
- 基于樹的 DSA(I)
- 樹數據結構
- 樹遍歷 - 中序,前序和后序
- 滿二叉樹
- 滿二叉樹
- 完美二叉樹
- 完全二叉樹
- 平衡二叉樹
- 二叉搜索樹(BST)
- AVL 樹
- 基于樹的 DSA(II)
- B 樹
- 插入 B 樹
- 從 B 樹刪除
- B+ 樹
- 在 B+ 樹上插入
- 從 B+ 樹中刪除
- 紅黑樹
- 插入紅黑樹
- 從紅黑樹中刪除
- 基于圖的 DSA
- 圖數據結構
- 生成樹和最小生成樹
- 強連通的組件
- 鄰接矩陣
- 鄰接表
- DFS 算法
- BFS 算法
- Bellman Ford 算法
- 排序和搜索算法
- 冒泡排序算法
- 選擇排序算法
- 插入排序算法
- 歸并排序算法
- 快速排序算法
- 計數排序算法
- 基數排序算法
- 桶排序算法
- 堆排序算法
- Shell 排序算法
- 線性搜索
- 二分搜索
- 貪婪算法
- 貪婪算法
- Ford-Fulkerson 算法
- Dijkstra 算法
- Kruskal 算法
- Prim 算法
- 霍夫曼編碼
- 動態規劃
- 動態規劃
- Floyd-Warshall 算法
- 最長公共子序列
- 其他算法
- 回溯算法
- Rabin-Karp 算法
- Programiz Java 教程
- Java 簡介
- Java HelloWorld 程序
- Java JDK,JRE 和 JVM
- Java 變量和(原始)數據類型
- Java 運算符
- Java 基本輸入和輸出
- Java 表達式,語句和塊
- Java 注釋
- Java 流程控制
- Java if,if...else語句
- Java switch語句
- Java for循環
- Java for-each循環(增強循環)
- Java while和do...while循環
- Java Break語句
- Java continue語句
- Java 數組
- Java 數組
- Java 多維數組
- Java 復制數組
- Java OOP(I)
- Java 類和對象
- Java 方法
- Java 構造器
- Java 字符串
- Java 訪問修飾符
- Java this關鍵字
- Java final關鍵字
- Java 遞歸
- Java instanceof
- Java OOP(II)
- Java 繼承
- Java 方法覆蓋
- Java super
- Java 抽象類和抽象方法
- Java 接口
- Java 多態
- Java 封裝
- Java OOP(III)
- Java 嵌套和內部類
- Java 靜態嵌套類
- Java 匿名類
- Java 單例
- Java 枚舉
- Java 枚舉構造器
- Java 枚舉字符串
- Java 反射
- Java 異常處理
- Java 異常
- Java 異常處理
- Java throw
- Java 捕獲多個異常
- Java try-with-resources
- Java 注解
- Java 注解類型
- Java 日志
- Java 斷言
- Java 列表
- Java 集合框架
- Java Collection接口
- Java List接口
- Java ArrayList類
- Java Vector
- Java Stack類
- Java 隊列
- Java Queue接口
- Java PriorityQueue
- Java Deque接口
- Java LinkedList
- Java ArrayDeque
- Java BlockingQueue
- Java ArrayBlockingQueue
- Java LinkedBlockingQueue
- Java 映射
- Java Map接口
- Java HashMap
- Java LinkedHashMap
- Java WeakHashMap
- Java EnumMap
- Java SortedMap接口
- Java NavigableMap接口
- Java TreeMap
- Java ConcurrentMap接口
- Java ConcurrentHashMap
- Java 集
- Java Set接口
- Java HashSet類
- Java EnumSet
- Java LinkedHashSet
- Java SortedSet接口
- Java NavigableSet接口
- Java TreeSet
- Java 算法
- Java Iterator接口
- Java ListIterator接口
- Java I/O 流
- Java I/O 流
- Java InputStream類
- Java OutputStream類
- Java FileInputStream類
- Java FileOutputStream類
- Java ByteArrayInputStream類
- Java ByteArrayOutputStream類
- Java ObjectInputStream類
- Java ObjectOutputStream類
- Java BufferedInputStream類
- Java BufferedOutputStream類
- Java PrintStream類
- Java 讀取器/寫入器
- Java Reader類
- Java Writer類
- Java InputStreamReader類
- Java OutputStreamWriter類
- Java FileReader類
- Java FileWriter類
- Java BufferedReader類
- Java BufferedWriter類
- Java StringReader類
- Java StringWriter類
- Java PrintWriter類
- 其他主題
- Java Scanner類
- Java 類型轉換
- Java 自動裝箱和拆箱
- Java Lambda 表達式
- Java 泛型
- Java File類
- Java 包裝器類
- Java 命令行參數
- Java 實例
- Java 程序:檢查數字是否為質數
- Java 程序:顯示斐波那契數列
- Java 程序:創建金字塔和圖案
- Java 程序:反轉數字
- Java 程序:打印整數(由用戶輸入)
- Java 程序:相加兩個整數
- Java 程序:將兩個浮點數相乘
- Java 程序:查找字符的 ASCII 值
- Java 程序:計算商數和余數
- Java 程序:交換兩個數字
- Java 程序:檢查數字是偶數還是奇數
- Java 程序:檢查字母是元音還是輔音
- Java 程序:在三個數字中找到最大值
- Java 程序:查找二次方程式的所有根
- Java 程序:檢查閏年
- Java 程序:檢查數字是正數還是負數
- Java 程序:檢查字符是否為字母
- Java 程序:計算自然數之和
- Java 程序:查找數字的階乘
- Java 程序:生成乘法表
- Java 程序:顯示斐波那契數列
- Java 程序:查找兩個數字的 GCD
- Java 程序:查找兩個數字的 LCM
- Java 程序:使用循環從 A 到 Z 顯示字符
- Java 程序:計算整數的位數
- Java 程序:計算數字的冪
- Java 程序:檢查數字是否為回文
- Java 程序:檢查數字是否為質數
- Java 程序:顯示兩個時間間隔之間的質數
- Java 程序:檢查阿姆斯特朗數
- Java 程序:顯示兩個間隔之間的阿姆斯特朗數
- Java 程序:使用函數顯示間隔之間的質數
- Java 程序:使用函數顯示間隔之間的阿姆斯特朗數
- Java 程序:以顯示數字的因數
- Java 程序:使用switch...case創建一個簡單的計算器
- Java 程序:檢查一個數字是否可以表示為兩個質數之和
- Java 程序:使用遞歸查找自然數之和
- Java 程序:使用遞歸查找數字的階乘
- Java 程序:使用遞歸查找 GCD
- Java 程序:將二進制數轉換為十進制,反之亦然
- Java 程序:將八進制數轉換為十進制,反之亦然
- Java 程序:將二進制數轉換為八進制,反之亦然
- Java 程序:使用遞歸來反轉句子
- Java 程序:使用遞歸來計算冪
- Java 程序:使用數組計算平均值
- Java 程序:查找數組的最大元素
- Java 程序:計算標準差
- Java 程序:使用多維數組相加兩個矩陣
- Java 程序:使用多維數組相乘矩陣
- Java 程序:通過將矩陣傳遞給函數來將兩個矩陣相乘
- Java 程序:查找矩陣轉置
- Java 程序:查找字符串中字符的頻率
- Java 程序:計算句子中元音和輔音的數量
- Java 程序:按字典順序對元素進行排序
- Java 程序:通過將對象傳遞給函數來相加兩個復數
- Java 程序:計算兩個時間段之間的差異
- Java 程序:從字符串中刪除所有空格
- Java 程序:打印數組
- Java 程序:將字符串轉換為日期
- Java 程序:將數字四舍五入到 n 個小數位
- Java 程序:連接兩個數組
- Java 程序:將字符轉換為字符串,反之亦然
- Java 程序:檢查數組是否包含給定值
- Java 程序:檢查字符串是否為空或null
- Java 程序:獲取當前日期/時間
- Java 程序:將毫秒轉換為分鐘和秒
- Java 程序:相加兩個日期
- Java 程序:連接兩個列表
- Java 程序:將列表(ArrayList)轉換為數組,反之亦然
- Java 程序:獲取當前工作目錄
- Java 程序:將映射(HashMap)轉換為列表
- Java 程序:將數組轉換為集(HashSet),反之亦然
- Java 程序:將字節數組轉換為十六進制
- Java 程序:從文件內容創建字符串
- Java 程序:將文本附加到現有文件
- Java 程序:將棧跟蹤轉換為字符串
- Java 程序:將文件轉換為字節數組,反之亦然
- Java 程序:將InputStream轉換為字符串
- Java 程序:將OutputStream轉換為字符串
- Java 程序:按字符串值查找枚舉
- Java 程序:比較字符串
- Java 程序:按值對映射進行排序
- Java 程序:按屬性對自定義對象的ArrayList進行排序
- Java 程序:檢查字符串是否為數字
- Java 程序:創建目錄
- Java 程序:重命名文件
- Java 程序:列出目錄中的文件
- Java 程序:復制文件
- Programiz Kotlin 教程
- Kotlin 簡介
- Kotlin HelloWorld - 您的 Kotlin 程序
- Kotlin 變量和原始類型
- Kotlin 運算符
- Kotlin 類型轉換
- Kotlin 表達式,語句和塊
- Kotlin 注釋
- Kotlin 基本輸入/輸出
- Kotlin 流程控制
- Kotlin if表達式
- Kotlin when表達式
- Kotlin while和do...while循環
- Kotlin for循環
- Kotlin break表達式
- Kotlin continue表達式
- Kotlin 函數
- Kotlin 函數
- Kotlin 中綴函數調用
- Kotlin 默認和命名參數
- Kotlin 遞歸(遞歸函數)和尾遞歸
- Kotlin OOP
- Kotlin 類和對象
- Kotlin 構造器
- Kotlin 獲取器和設置器
- Kotlin 繼承
- Kotlin 可見性修飾符
- Kotlin 抽象類
- Kotlin 接口
- Kotlin 嵌套和內部類
- Kotlin 數據類
- Kotlin 密封類
- Kotlin 對象聲明和表達式
- Kotlin 伴隨對象
- Kotlin 擴展函數
- Kotlin 運算符重載
- Kotlin 示例
- Kotlin 程序:獲取當前日期/時間
- Kotlin 程序:將列表(ArrayList)轉換為Array,反之亦然
- Kotlin 程序:將字符串轉換為日期
- Kotlin 程序:按屬性對自定義對象的ArrayList進行排序
- Kotlin 程序:打印整數(由用戶輸入)
- Kotlin 程序:相加兩個整數
- Kotlin 程序:將兩個浮點數相乘
- Kotlin 程序:查找字符的 ASCII 值
- Kotlin 程序:計算商數和余數
- Kotlin 程序:交換兩個數字
- Kotlin 程序:檢查數字是偶數還是奇數
- Kotlin 程序:檢查字母是元音還是輔音
- Kotlin 程序:在三個數字中找到最大的一個
- Kotlin 程序:查找二次方程的所有根
- Kotlin 程序:檢查閏年
- Kotlin 程序:檢查數字是正數還是負數
- Kotlin 程序:檢查字符是否為字母
- Kotlin 程序:計算自然數之和
- Kotlin 程序:查找數字的階乘
- Kotlin 程序:生成乘法表
- Kotlin 程序:展示斐波那契數列
- Kotlin 程序:查找兩個數字的 GCD
- Kotlin 程序:查找兩個數字的 LCM
- Kotlin 程序:使用循環從 A 到 Z 顯示字符
- Kotlin 程序:計算整數位數
- Kotlin 程序:反轉數字
- Kotlin 程序:計算數字的冪
- Kotlin 程序:檢查數字是否為回文
- Kotlin 程序:檢查數字是否為質數
- Kotlin 程序:顯示兩個間隔之間的質數
- Kotlin 程序:檢查阿姆斯特朗數
- Kotlin 程序:顯示兩個間隔之間的阿姆斯特朗數
- Kotlin 程序:使用函數顯示間隔之間的質數
- Kotlin 程序:使用函數顯示間隔之間的阿姆斯特朗數
- Kotlin 程序:顯示數字因數
- Kotlin 程序:使用switch...case制作一個簡單的計算器
- Kotlin 程序:檢查一個數字是否可以表示為兩個質數之和
- Kotlin 程序:使用遞歸找到自然數之和
- Kotlin 程序:使用遞歸查找數字的階乘
- Kotlin 程序:使用遞歸查找 GCD
- Kotlin 程序:將二進制數轉換為十進制,反之亦然
- Kotlin 程序:將八進制數轉換為十進制,反之亦然
- Kotlin 程序:將二進制數轉換為八進制,反之亦然
- Kotlin 程序:使用遞歸來反轉句子
- Kotlin 程序:使用遞歸來計算冪
- Kotlin 程序:使用數組計算平均值
- Kotlin 程序:在數組中查找最大的元素
- Kotlin 程序:計算標準差
- Kotlin 程序:使用多維數組相加兩個矩陣
- Kotlin 程序:使用多維數組乘以矩陣
- Kotlin 程序:通過將矩陣傳遞給函數來將兩個矩陣相乘
- Kotlin 程序:查找矩陣的轉置
- Kotlin 程序:查找字符串中字符的頻率
- Kotlin 程序:計算句子中元音和輔音的數量
- Kotlin 程序:按字典順序(字典順序)對元素進行排序
- Kotlin 程序:通過將類傳遞給函數來相加兩個復數
- Kotlin 程序:計算兩個時間段之間的差異
- Kotlin 程序:創建金字塔和圖案
- Kotlin 程序:從字符串中刪除所有空格
- Kotlin 程序:打印數組
- Kotlin 程序:將數字四舍五入到 n 個小數位
- Kotlin 程序:連接兩個數組
- Kotlin 程序:將字符轉換為字符串并反之
- Kotlin 程序:檢查數組是否包含給定值
- Kotlin 程序:檢查字符串是否為空或null
- Kotlin 程序:將毫秒轉換為分鐘
- Kotlin 程序:相加兩個日期
- Kotlin 程序:連接兩個列表
- Kotlin 程序:獲取當前工作目錄
- Kotlin 程序:將映射(HashMap)轉換為列表
- Kotlin 程序:將數組轉換為Set(HashSet),反之亦然
- Kotlin 程序:將字節數組轉換為十六進制
- Kotlin 程序:從文件內容創建字符串
- Kotlin 程序:將文本附加到現有文件
- Kotlin 程序:將棧跟蹤轉換為字符串
- Kotlin 程序:將文件轉換為字節數組,反之亦然
- Kotlin 程序:將InputStream轉換為字符串
- Kotlin 程序:將OutputStream轉換為字符串
- Kotlin 程序:通過字符串值查找枚舉
- Kotlin 程序:比較字符串
- Kotlin 程序:按值對映射排序
- Kotlin 程序:檢查字符串是否為數字
- Programiz Python 教程
- Python 簡介
- 如何開始使用 Python?
- Python 關鍵字和標識符
- Python 語句,縮進和注釋
- Python 變量,常量和字面值
- Python 數據類型
- Python 類型轉換
- Python 輸入,輸出和導入
- Python 運算符
- Python 命名空間和范圍
- Python 流程控制
- Python if...else語句
- Python for循環
- Python While循環
- Python break和continue
- Python pass語句
- Python 函數
- Python 函數
- Python 函數參數
- Python 遞歸
- Python 匿名/ Lambda 函數
- Python 全局,局部和非局部變量
- Python global關鍵字
- Python 模塊
- Python 包
- Python 數據類型
- Python 數字,類型轉換和數學
- Python 列表
- Python 元組
- Python 字符串
- Python 集
- Python 字典
- Python 文件
- Python 文件 I/O
- Python 目錄和文件管理
- Python 錯誤和內置異常
- Python 使用try,except和finally語句的異常處理
- Python 自定義異常
- Python 對象和類
- Python 面向對象編程
- Python 對象和類
- Python 繼承
- Python 多重繼承
- Python 運算符重載
- Python 高級主題
- Python 迭代器
- Python 生成器
- Python 閉包
- Python 裝飾器
- Python @property裝飾器
- Python 正則表達式
- Python 日期時間
- Python 日期時間
- Python strftime()
- Python strptime()
- 如何在 Python 中獲取當前日期和時間?
- Python 獲取當前時間
- Python 日期時間到時間戳,反之亦然
- Python time模塊
- Python sleep()
- Python 示例
- Python 程序:檢查質數
- Python 程序:相加兩個數字
- Python 程序:查找數字階乘
- Python 程序:制作一個簡單的計算器
- Python 程序:打印 Helloworld
- Python 程序:查找平方根
- Python 程序:計算三角形的面積
- Python 程序:求解二次方程式
- Python 程序:交換兩個變量
- Python 程序:生成隨機數
- Python 程序:將公里轉換為英里
- Python 程序:將攝氏溫度轉換為華氏溫度
- Python 程序:檢查數字是正數,負數還是 0
- Python 程序:檢查數字是奇數還是偶數
- Python 程序:檢查閏年
- Python 程序:在三個數字中找到最大的
- Python 程序:檢查質數
- Python 程序:打印一個間隔內的所有質數
- Python 程序:查找數字階乘
- Python 程序:顯示乘法表
- Python 程序:打印斐波那契序列
- Python 程序:檢查阿姆斯特朗數
- Python 程序:查找間隔內的阿姆斯特朗數
- Python 程序:查找自然數總和
- Python 程序:使用匿名函數顯示 2 的冪
- Python 程序:查找可被另一個數整除的數字
- Python 程序:將十進制轉換為二進制,八進制和十六進制
- Python 程序:查找字符的 ASCII 值
- Python 程序:查找 HCF 或 GCD
- Python 程序:查找 LCM
- Python 程序:查找數字的因數
- Python 程序:制作一個簡單的計算器
- Python 程序:打亂紙牌
- Python 程序:顯示日歷
- Python 程序:使用遞歸顯示斐波那契數列
- Python 程序:使用遞歸查找自然數之和
- Python 程序:使用遞歸查找數字的階乘
- Python 程序:使用遞歸將十進制轉換為二進制
- Python 程序:相加兩個矩陣
- Python 程序:轉置矩陣
- Python 程序:將兩個矩陣相乘
- Python 程序:檢查字符串是否為回文
- Python 程序:從字符串中刪除標點符號
- Python 程序:按字母順序對單詞進行排序
- Python 程序:演示不同的集合操作
- Python 程序:計算每個元音的數量
- Python 程序:合并郵件
- Python 程序:查找圖像的大小(分辨率)
- Python 程序:查找文件哈希
- Programiz Swift 教程
- Swift 介紹
- Swift HelloWorld 程序
- Swift 變量,常量和字面值
- Swift 數據類型
- Swift 可選項
- Swift 的字符和字符串
- Swift 基本輸入和輸出
- Swift 表達式,語句和代碼塊
- Swift 注釋
- Swift 運算符
- Swift 運算符
- Swift 運算符的優先級和關聯性
- Swift 三元條件運算符
- Swift 按位和移位運算符
- Seift 流程控制
- Swift if,if...else語句
- switch語句
- Swift for-in循環
- Swift while和repeat...while循環
- Swift 中的嵌套循環
- break語句
- continue語句
- Guard語句
- Swift 集合
- Swift 數組
- Swift 集
- Swift 字典
- Swift 函數
- Swift 函數
- Swift 函數參數和返回值
- Swift 嵌套函數
- Swift 遞歸
- Swift 范圍
- Swift 函數重載
- Swift 進階
- Swift 閉包
- Swift 類型別名
