[TOC]
# 1. 前言
貝塞爾曲線(Bézier curve),又稱貝茲曲線或貝濟埃曲線,是應用于二維圖形應用程序的數學曲線。一般的矢量圖形軟件通過它來精確畫出曲線,貝茲曲線由線段與節點組成,節點是可拖動的支點,線段像可伸縮的皮筋,我們在繪圖工具上看到的鋼筆工具就是來做這種矢量曲線的。
# 2. 介紹
## 2.1 一階貝濟埃曲線
一階貝濟埃曲線的公式如下:
```
B(t)=(1-t)P_0+tP_1,t屬于0-1
```
P0為起始點,P1為終點,t 表示當前時間,B(t)表示公式的結果值。其實也就是一條從P0到P1的直線上,勻速運動的點值。
## 2.2 二階貝塞爾曲線
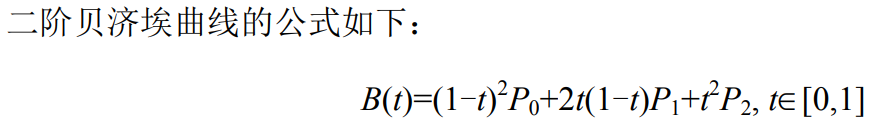

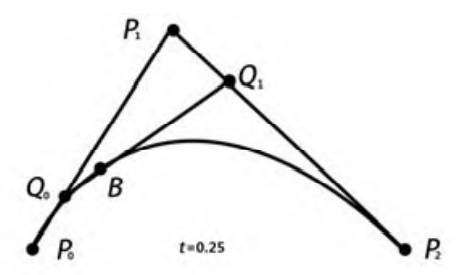
這條曲線的構成也就是每個t時刻,Q0和Q1的所屬的直線的的t時刻的距離的點,這里也就是B。不妨將上面這個圖簡單標注下:
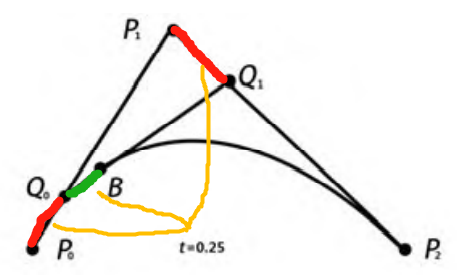
也就是在從P0到P1,進行勻速運動,在t=0.25的時刻走到Q0,類似的,從P1到P2經過勻速運動,在t=0.25的時刻走到Q1,對于Q0到Q1,經過勻速運動,在t=0.25的時刻走到B。而B也就是二階貝塞爾曲線上的點。
## 2.3 三階貝塞爾曲線
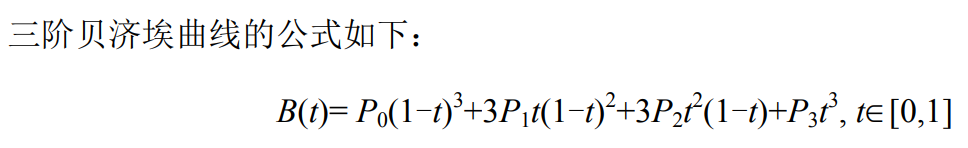
也就是說此時有兩個控制點,對應著也就是三根連著的線段,類似的我們可以得到最終的t點:
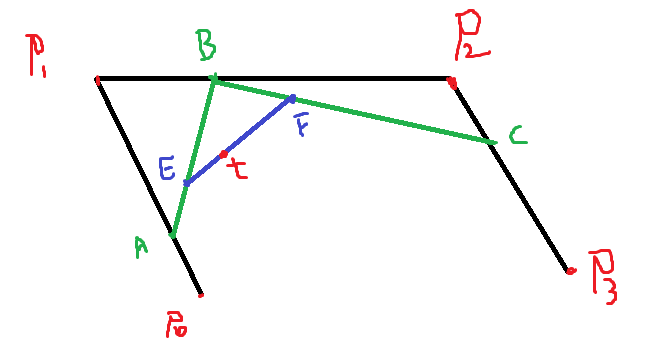
那么,根據上面的規則,我們可以自己來實現一下貝賽爾曲線的計算方式,并將曲線繪制出來。
# 3. 一、二、三階貝塞爾曲線實現
定義為:
~~~
class Point(var x: Float, var y: Float){
}
/**
* 得到貝賽爾曲線上的點集
* @param points 起始、控制和終止點坐標
* @param number 需要計算的貝賽爾曲線上的點的個數
* @return 返回路徑
*/
private fun getBezierPointsPath(points: Array<Point>, number: Int): Path{
val path = Path()
for (time in 0 until number){
val t = time * 1f / number
val point = calcPoint(points, t)
if(time == 0){
path.moveTo(point.x, point.y)
} else {
path.lineTo(point.x, point.y)
}
Log.e("TAG", "getBezierPointsPath: ${point.x} , ${point.y}", )
}
return path
}
/**
* 計算在t時刻上,位于貝賽爾曲線上的點的坐標
* @param points 點的集合
* @param t 時刻,屬于0-1
* @return 點坐標 Point
*/
private fun calcPoint(points: Array<Point>, t: Float): Point{
// 分別求任意兩個點之間的在t時刻運動的距離
// 任意兩點,按照順序分別為始和終
var index = 0
var len = points.size - 1
while (index < len){
points[index].x = getValueByTime(points[index].x, points[index + 1].x, t)
points[index].y = getValueByTime(points[index].y, points[index + 1].y, t)
index++
if(index == len){
index = 0
len--
}
}
return points[0]
}
/**
* 定義勻速運動的計算坐標
* @param start 開始的位置
* @param end 結束的位置
* @param time 運動的時間,范圍0-1
* @return time時刻的運動位置
*/
private fun getValueByTime(start: Float, end: Float, time: Float): Float{
return start + (end - start) * time
}
~~~
然后使用:
~~~
// 繪圖方法
override fun onDraw(canvas: Canvas?) {
super.onDraw(canvas)
canvas?.apply {
val points = arrayOf(Point(200f, 400f), Point(100f, 20f), Point(500f, 20f), Point(800f, 400f))
val numberOfPoint = 100
mPath = getBezierPointsPath(points, numberOfPoint)
drawPath(mPath, mPaint)
}
}
~~~
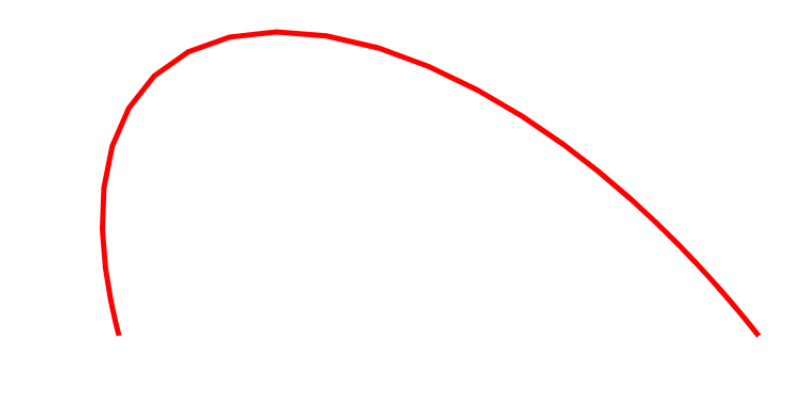

很明顯,這里細粒度不夠。可以把numberOfPoint 設置的更大些。當設置為1000的時候:
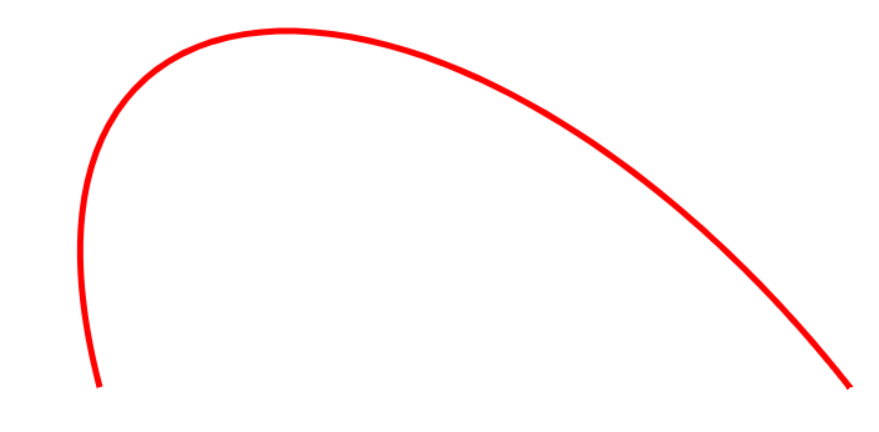

當然這里可以使用arrayOf的時候添加更多的點,以做到更加高階的貝塞爾曲線,比如簡單修改一下:
~~~
val points = arrayOf(Point(200f, 400f),
Point(100f, 20f),
Point(500f, 20f),
Point(800f, 400f),
Point(1000f, 20f)
)
~~~
也就是對應三個控制點,對應四階本塞爾曲線,對應效果:

當然,在系統中其實也提供了一、二、三階的貝賽爾曲線的API,所以通常直接調用即可。對應的如下:
* mPath.lineTo:進行直線繪制 ;
* mPath.quadTo(x1, y1, x2, y2) :生成二次貝塞爾曲線,(x1,y1) 為控制點,(x2,y2)為結束點 ;
* mPath.cubicTo(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3):生成三次貝塞爾曲線, (x1,y1) 為控制點,(x2,y2)為控制點,(x3,y3) 為結束點;
# 4. 案例
~~~
/**
* 學習波浪效果,其實也就是移動類似于正弦的連續圖像,帶來的視覺效果
* @author 夢否
* 2022年3月15日
*/
class WaterRippleView : View {
constructor(context: Context?) : super(context) {
init()
}
constructor(context: Context?, attrs: AttributeSet?) : super(context, attrs) {
init()
}
constructor(context: Context?, attrs: AttributeSet?, defStyleAttr: Int) : super(
context,
attrs,
defStyleAttr
) {
init()
}
private lateinit var mPath: Path
private lateinit var mPaint: Paint
private lateinit var points1: Array<MyPoint>
private lateinit var points2: Array<MyPoint>
class MyPoint(var x: Float, var y: Float)
/**
* 初始化方法
*/
private fun init() {
mPath = Path()
mPaint = Paint()
mPaint.isDither = true
mPaint.isAntiAlias = true
mPaint.strokeWidth = 5f
mPaint.color = Color.GRAY
mPaint.style = Paint.Style.FILL
val viewWidth = resources.displayMetrics.widthPixels
points1 = arrayOf(
MyPoint(0f * viewWidth, 200f),
MyPoint(.33f * viewWidth, 20f),
MyPoint(.66f * viewWidth, 360f),
MyPoint(1f * viewWidth, 200f)
)
points2 = arrayOf(
MyPoint(-1f * viewWidth, 200f),
MyPoint(-.66f * viewWidth, 20f),
MyPoint(-.33f * viewWidth, 360f),
MyPoint(0f * viewWidth, 200f),
)
// 三階貝塞爾曲線,傳入0,也就是初始時刻
updatePathByDistance(0f)
}
override fun onDraw(canvas: Canvas?) {
super.onDraw(canvas)
canvas?.apply {
drawPath(mPath, mPaint)
}
}
/**
* 根據距離來進行更新在貝賽爾曲線中的點的坐標值
* @param distance 傳入的距離
*/
private fun updatePathByDistance(distance: Float) {
// 重置
mPath.reset()
// 設置
mPath.moveTo(points2[0].x, points2[0].y)
mPath.cubicTo(
points2[1].x + distance,
points2[1].y,
points2[2].x + distance,
points2[2].y,
points2[3].x + distance,
points2[3].y
)
mPath.cubicTo(
points1[1].x + distance,
points1[1].y,
points1[2].x + distance,
points1[2].y,
points1[3].x + distance,
points1[3].y
)
val y = resources.displayMetrics.heightPixels
mPath.lineTo(points1[3].x, y.toFloat())
mPath.lineTo(points2[0].x + distance, y.toFloat())
mPath.lineTo(points2[0].x + distance, points2[0].y)
}
/**
* 一直移動繪制的兩個類似于正弦函數的路徑
*/
var startedMove = false
private fun startMove() {
startedMove = true
val animator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0f, resources.displayMetrics.widthPixels.toFloat())
animator.duration = 800
// 線性插值器,使之勻速運動
animator.interpolator = LinearInterpolator()
// 循環
animator.repeatCount = ValueAnimator.INFINITE
animator.addUpdateListener(object : ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener {
override fun onAnimationUpdate(animation: ValueAnimator?) {
val value = animator.getAnimatedValue()
updatePathByDistance(value as Float)
// 重繪
invalidate()
}
})
animator.start()
}
override fun onTouchEvent(event: MotionEvent?): Boolean {
super.onTouchEvent(event)
var flag = false
when (event?.action) {
MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN -> {
flag = true
if(!startedMove) startMove()
}
MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE,
MotionEvent.ACTION_UP -> {
flag = false
}
}
return flag
}
override fun onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec: Int, heightMeasureSpec: Int) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec)
val minHeight = dp2px(300)
val minWidth = dp2px(500)
val widthSize = getMeasureSize(widthMeasureSpec, minWidth.toInt())
val heightSize = getMeasureSize(heightMeasureSpec, minHeight.toInt())
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, heightSize)
}
/**
* 計算高度和寬度
*/
private fun getMeasureSize(Spec: Int, minValue: Int): Int {
var result = 0
// 獲取模式
val mode = MeasureSpec.getMode(Spec)
val size = MeasureSpec.getSize(Spec)
// 判斷一下
when (mode) {
MeasureSpec.AT_MOST -> {
result = Math.min(size, minValue)
}
MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED -> {
result = minValue
}
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY -> {
result = size
}
}
return result
}
/**
* dp轉換為px
*/
private fun dp2px(size: Int): Float {
return resources.displayMetrics.density * size
}
}
~~~
- 介紹
- UI
- MaterialButton
- MaterialButtonToggleGroup
- 字體相關設置
- Material Design
- Toolbar
- 下拉刷新
- 可折疊式標題欄
- 懸浮按鈕
- 滑動菜單DrawerLayout
- NavigationView
- 可交互提示
- CoordinatorLayout
- 卡片式布局
- 搜索框SearchView
- 自定義View
- 簡單封裝單選
- RecyclerView
- xml設置點擊樣式
- adb
- 連接真機
- 小技巧
- 通過字符串ID獲取資源
- 自定義View組件
- 使用系統控件重新組合
- 旋轉菜單
- 輪播圖
- 下拉輸入框
- 自定義VIew
- 圖片組合的開關按鈕
- 自定義ViewPager
- 聯系人快速索引案例
- 使用ListView定義側滑菜單
- 下拉粘黏效果
- 滑動沖突
- 滑動沖突之非同向沖突
- onMeasure
- 繪制字體
- 設置畫筆Paint
- 貝賽爾曲線
- Invalidate和PostInvalidate
- super.onTouchEvent(event)?
- setShadowLayer與陰影效果
- Shader
- ImageView的scaleType屬性
- 漸變
- LinearGradient
- 圖像混合模式
- PorterDuffXfermode
- 橡皮擦效果
- Matrix
- 離屏繪制
- Canvas和圖層
- Canvas簡介
- Canvas中常用操作總結
- Shape
- 圓角屬性
- Android常見動畫
- Android動畫簡介
- View動畫
- 自定義View動畫
- View動畫的特殊使用場景
- LayoutAnimation
- Activity的切換轉場效果
- 屬性動畫
- 幀動畫
- 屬性動畫監聽
- 插值器和估值器
- 工具
- dp和px的轉換
- 獲取屏幕寬高
- JNI
- javah命令
- C和Java相互調用
- WebView
- Android Studio快捷鍵
- Bitmap和Drawable圖像
- Bitmap簡要介紹
- 圖片縮放和裁剪效果
- 創建指定顏色的Bitmap圖像
- Gradle本地倉庫
- Gradle小技巧
- RxJava+Okhttp+Retrofit構建網絡模塊
- 服務器相關配置
- node環境配置
- 3D特效
