# 使用兩次遍歷收集網格中的最大點
> 原文: [https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/collect-maximum-points-in-a-grid-using-two-traversals/](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/collect-maximum-points-in-a-grid-using-two-traversals/)
給定一個矩陣,其中每個單元格代表點。 在以下條件下如何使用兩次遍歷來收集最大點?
令給定網格的尺寸為 R xC。
1)第一個遍歷從左上角即(0,0)開始并應到達左下角即(R-1,0)。 第二次遍歷從右上角開始,即(0,C-1),并且應該到達右下角,即(R-1,C-1)/
2)從點(i,j),我們可以移至(i + 1,j + 1)或(i + 1,j-1)或(i + 1,j)
3)遍歷獲取特定單元格通過的所有點。 如果一個遍歷已經收集了一個單元格的點,則另一遍歷如果再次通過該單元格則得不到任何點。
```
Input :
int arr[R][C] = {{3, 6, 8, 2},
{5, 2, 4, 3},
{1, 1, 20, 10},
{1, 1, 20, 10},
{1, 1, 20, 10},
};
Output: 73
Explanation :
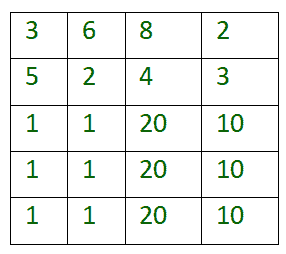
First traversal collects total points of value 3 + 2 + 20 + 1 + 1 = 27
Second traversal collects total points of value 2 + 4 + 10 + 20 + 10 = 46.
Total Points collected = 27 + 46 = 73.
```
**我們強烈建議您最小化瀏覽器,然后自己嘗試。**
這個想法是同時進行兩個遍歷。 我們首先從(0,0)開始,第二次從(0,C-1)開始遍歷。 需要注意的重要一點是,在任何特定步驟中,兩個遍歷都將在同一行中,而在所有可能的三步中,行數都會增加。 令(x1,y1)和(x2,y2)分別表示第一和第二遍歷的當前位置。 因此,由于 x1 和 x2 都向前移動,因此在任何時候 x1 都等于 x2,但是沿 y 可能會發生變化。 由于 y 的變化可能以 3 種不變的方式發生(y),因此請向左(y – 1),向右(y + 1)。 因此,y1,y2 之間總共有 9 種組合是可能的。 基本案例之后的以下 9 個案例。
```
Both traversals always move forward along x
Base Cases:
// If destinations reached
if (x == R-1 && y1 == 0 && y2 == C-1)
maxPoints(arr, x, y1, y2) = arr[x][y1] + arr[x][y2];
// If any of the two locations is invalid (going out of grid)
if input is not valid
maxPoints(arr, x, y1, y2) = -INF (minus infinite)
// If both traversals are at same cell, then we count the value of cell
// only once.
If y1 and y2 are same
result = arr[x][y1]
Else
result = arr[x][y1] + arr[x][y2]
result += max { // Max of 9 cases
maxPoints(arr, x+1, y1+1, y2),
maxPoints(arr, x+1, y1+1, y2+1),
maxPoints(arr, x+1, y1+1, y2-1),
maxPoints(arr, x+1, y1-1, y2),
maxPoints(arr, x+1, y1-1, y2+1),
maxPoints(arr, x+1, y1-1, y2-1),
maxPoints(arr, x+1, y1, y2),
maxPoints(arr, x+1, y1, y2+1),
maxPoints(arr, x+1, y1, y2-1)
}
```
上面的遞歸解決方案有很多子問題,這些子問題一次又一次地得到解決。 因此,我們可以使用動態編程更有效地解決上述問題。 以下是[記憶](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dynamic-programming-set-1/)(在動態編程中記憶可替代基于表的迭代解決方案)。 在下面的實現中,我們使用備忘錄表“ mem”來跟蹤已經解決的問題。
## C++
```cpp
// A Memoization based program to find maximum collection
// using two traversals of a grid
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define R 5
#define C 4
// checks whether a given input is valid or not
bool isValid(int x, int y1, int y2)
{
????return (x >= 0 && x < R && y1 >=0 &&
????????????y1 < C && y2 >=0 && y2 < C);
}
// Driver function to collect max value
int getMaxUtil(int arr[R][C], int mem[R][C][C], int x, int y1, int y2)
{
????/*---------- BASE CASES -----------*/
????// if P1 or P2 is at an invalid cell
????if (!isValid(x, y1, y2)) return INT_MIN;
????// if both traversals reach their destinations
????if (x == R-1 && y1 == 0 && y2 == C-1)
???????return (y1 == y2)? arr[x][y1]: arr[x][y1] + arr[x][y2];
????// If both traversals are at last row but not at their destination
????if (x == R-1) return INT_MIN;
????// If subproblem is already solved
????if (mem[x][y1][y2] != -1) return mem[x][y1][y2];
????// Initialize answer for this subproblem
????int ans = INT_MIN;
????// this variable is used to store gain of current cell(s)
????int temp = (y1 == y2)? arr[x][y1]: arr[x][y1] + arr[x][y2];
????/* Recur for all possible cases, then store and return the
???????one with max value */
????ans = max(ans, temp + getMaxUtil(arr, mem, x+1, y1, y2-1));
????ans = max(ans, temp + getMaxUtil(arr, mem, x+1, y1, y2+1));
????ans = max(ans, temp + getMaxUtil(arr, mem, x+1, y1, y2));
????ans = max(ans, temp + getMaxUtil(arr, mem, x+1, y1-1, y2));
????ans = max(ans, temp + getMaxUtil(arr, mem, x+1, y1-1, y2-1));
????ans = max(ans, temp + getMaxUtil(arr, mem, x+1, y1-1, y2+1));
????ans = max(ans, temp + getMaxUtil(arr, mem, x+1, y1+1, y2));
????ans = max(ans, temp + getMaxUtil(arr, mem, x+1, y1+1, y2-1));
????ans = max(ans, temp + getMaxUtil(arr, mem, x+1, y1+1, y2+1));
????return (mem[x][y1][y2] = ans);
}
// This is mainly a wrapper over recursive function getMaxUtil().
// This function creates a table for memoization and calls
// getMaxUtil()
int geMaxCollection(int arr[R][C])
{
????// Create a memoization table and initialize all entries as -1
????int mem[R][C][C];
????memset(mem, -1, sizeof(mem));
????// Calculation maximum value using memoization based function
????// getMaxUtil()
????return getMaxUtil(arr, mem, 0, 0, C-1);
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
????int arr[R][C] = {{3, 6, 8, 2},
?????????????????????{5, 2, 4, 3},
?????????????????????{1, 1, 20, 10},
?????????????????????{1, 1, 20, 10},
?????????????????????{1, 1, 20, 10},
????????????????????};
????cout << "Maximum collection is " << geMaxCollection(arr);
????return 0;
}
```
- GeeksForGeeks 數組教程
- 介紹
- 數組介紹
- C/C++ 中的數組
- Java 中的數組
- Python 中的數組| 系列 1(簡介和功能)
- C# | 數組
- 回轉
- 數組旋轉程序
- 數組旋轉的逆向算法
- 數組旋轉的塊交換算法
- 程序循環旋轉一個數組
- 在經過排序和旋轉的數組中搜索元素
- 給定一個經過排序和旋轉的數組,查找是否存在一對具有給定總和的數組
- 在只允許旋轉給定數組的情況下找到Sum(i * arr[i])的最大值
- 給定數組所有旋轉中i * arr [i]的最大和
- 在旋轉排序數組中找到旋轉計數
- 快速找到數組的多個左旋轉| 系列 1
- 在經過排序和旋轉的數組中找到最小元素
- 數組右旋轉的逆向算法
- 查找具有最大漢明距離的旋轉
- 數組左右循環查詢
- 在O(n)時間和O(1)空間中打印數組的左旋轉
- 旋轉幾次后,在給定索引處查找元素
- 拆分數組并將第一部分添加到末尾
- 重排
- 重新排列數組,使arr[i] = i
- 編寫程序以反轉數組或字符串
- 重新排列數組,如果i為偶數則arr[i] >= arr[j],如果i為奇數且j < i則 arr[i] <= arr[j]
- 在O(n)時間和O(1)額外空間中重新排列正數和負數
- 重新排列數組,交替出現&個正數的負數項,多余的空間為O(1) | 系列 1
- 將所有零移動到數組末尾
- 將所有零移動到數組的末尾| 系列 2(使用單遍歷)
- 將所有小于或等于 k 的元素組合在一起所需的最小交換
- 使用內置排序功能重新排列正數和負數
- 重新排列數組,使偶數位置大于奇數
- 按順序重新排列數組-最小,最大,第二個最小,第二個最大..
- 將第一個元素加倍,然后將零移動到結尾
- 根據給定的索引對數組重新排序
- 用恒定的額外空間重新排列正數和負數
- 排列給定數字以形成最大數| 系列 1
- 重新排列數組,如果arr[i]為j,則arr[j]變為i | 系列 1
- 以最大最小形式重新排列數組| 系列 1
- 以最大最小形式重新排列數組| 系列 2(O(1)額外空間)
- 將所有負元素移動到最后,并留出足夠的空間
- 重新排列數組,使偶數索引元素較小而奇數索引元素較大
- 正數元素位于偶數位置,負數元素位于奇數位置(不保持相對順序)
- 用上一個和下一個的乘法替換每個數組元素
- 使用 Fisher-Yates 隨機播放算法隨機播放給定數組
- 分離偶數和奇數| 系列 3
- 將數組中的 0 和 1 分開
- 最長的雙子序列| DP-15
- 在線性時間內找到大小為 3 的排序子序列
- 最大數目等于 0 和 1 的子數組
- 最大產品子數組
- 用右側的最大元素替換每個元素
- 最大循環子數組總和
- 最長遞增子序列的構造(N log N)
- 按頻率對元素排序| 系列 2
- 最大化圓形數組中的連續差之和
- 根據另一個數組定義的順序對數組進行排序
- 查找索引 0 替換為 1,以獲得二進制數組中最長的連續序列 1s
- 在給定范圍內對數組進行三向分區
- 從兩個給定排序數組的備用元素生成所有可能的排序數組
- 安排彼此相鄰的線對所需的最小交換次數
- 將數組轉換為 Zig-Zag 風格
- 從給定序列中形成最小數
- 將兩個連續的相等值替換為一個更大的值
- 重新排列二進制字符串作為 x 和 y 的交替出現
- 數組中不同的相鄰元素
- 不使用多余空間將 2n 個整數隨機排列為 a1-b1-a2-b2-a3-b3-.bn
- 合并 k 個排序的數組| 系列 1
- 訂單統計
- 未排序數組中第 K 個最小/最大元素| 系列 1
- 未排序數組中第 K 個最小/最大元素| 系列 2(預期線性時間)
- 未排序數組中第 K 個最小/最大元素| 組合 3(最壞情況的線性時間)
- 使用 STL 的第 K 個最小/最大元素
- 數組中的 k 個最大(或最小)元素| 添加了最小堆方法
- 按行和按列排序的 2D 數組中的 Kth 個最小元素| 系列 1
- 程序以查找數組中的最大元素
- 查找數組中最大的三個元素
- 查找數組中至少有兩個大元素的所有元素
- 未排序數組的均值和中位數的程序
- 使用 STL 的運行整數流的中位數
- 正整數數組中 k 個整數的最小積
- 第 K 個最大和的連續子數組
- 來自兩個數組的 K 個最大和組合
- 重疊的連續子數組的 K 個最大和
- 非重疊的連續子數組的 K 個最大和
- 使用O(1)額外空間按相同順序排列 k 個最小元素
- 在兩個數組中找到具有最小和的 k 對
- 數組中兩個元素的第 k 個最小絕對差
- 在數組中查找第二大元素
- 查找給定數組中出現次數最多的 k 個數字
- 查找數組中的最小和第二個最小元素
- 尋找最小的遺失號碼
- 使得兩個元素都不相鄰的最大和
- 使用最少數量的比較的數組的最大值和最小值
- 兩個元素之間的最大差異,使得較大的元素出現在較小的數字之后
- 給定數組 arr [],找到最大 j – i,使得 arr [j] > arr [i]
- 最大滑動窗口(大小為 k 的所有子數組的最大值)
- 找到兩個數字之間的最小距離
- 在先增加然后減少的數組中找到最大元素
- 計算右側較小的元素
- 最長遞增子序列大小(N log N)
- 查找未排序數組中缺失的最小正數| 系列 1
- 在O(n)時間和O(1)多余空間中找到最大重復數
- 給定大小為 n 且數字為 k 的數組,找到出現次數超過 n / k 次的所有元素
- 找出長度為 3 且具有最大乘積的遞增子序列
- 兩個數組中的最大求和路徑
- 從兩個排序的數組中找到最接近的對
- 在未排序的數組中找到最大的對和
- 整個數組中最小的較大元素
- 刪除小于 next 或變得更小的數組元素
- 在線檢查回文的在線算法
- 刪除小于 next 或變得更小的數組元素
- 找到要翻轉的零,以使連續的 1 的數目最大化
- 計算嚴格增加的子數組
- 流中的第 K 個最大元素
- 在兩個數組中找到具有最小和的 k 對
- k 元素組與數組其余部分之間的最大差值。
- 要使中位數等于 x 的最小元素數量
- 下一個更大的元素
- 范圍查詢
- MO 的算法(查詢平方根分解)| 系列 1(簡介)
- Sqrt(或平方根)分解技術 系列 1(簡介)
- 稀疏表
- 使用稀疏表進行范圍總和查詢
- 范圍最小查詢(平方根分解和稀疏表)
- 數組元素的頻率范圍查詢
- 數組上的恒定時間范圍添加操作
- 范圍 LCM 查詢
- 數組中給定索引范圍的 GCD
- 查詢給定數組中所有數字的 GCD(給定范圍內的元素除外)
- 給定子數組中小于或等于給定數目的元素數
- 給定子數組中小于或等于給定數字的元素數| 第 2 組(包括更新)
- 查詢值在給定范圍內的數組元素的計數
- 查詢二進制數組的子數組的十進制值
- 計算將 L-R 范圍內的所有數字相除的元素
- 給定數組范圍的 XOR 之和最大的數字
- 在給定范圍內出現偶數次的數字的 XOR
- 范圍查詢中的數組范圍查詢
- 數組范圍查詢以搜索元素
- 數組范圍查詢頻率與值相同的元素
- 給定范圍內的最大出現次數
- 給定范圍內具有相等元素的索引數
- 合并排序樹以獲取范圍順序統計信息
- 范圍內沒有重復數字的總數
- 差異數組|O(1)中的范圍更新查詢
- 對數組的范圍查詢,其每個元素都是索引值與前一個元素的 XOR
- 查找子數組是否為山脈形式
- 范圍總和查詢,無更新
- 子數組中的素數(帶有更新)
- 在二進制數組中檢查子數組表示的數字是奇數還是偶數
- 用于乘法,替換和乘積的數組查詢
- 數組范圍的平均值
- 執行加減命令后打印修改后的數組
- 在給定范圍內對偶數或奇數概率的查詢
- 數組中范圍的乘積
- 計算范圍內的素數
- M 個范圍切換操作后的二進制數組
- 合并重疊間隔
- 檢查給定間隔中是否有兩個間隔重疊
- 間隔之和與除數的更新
- 多次數組范圍遞增操作后打印修改后的數組
- 范圍最大奇數的 XOR 查詢
- 查詢子數組中不同元素的數量
- 計數和切換二進制數組上的查詢
- 數組中的最小-最大范圍查詢
- 優化問題
- 最大總和連續子數組
- 通過最多買賣兩次股份獲得最大利潤
- 查找平均數最少的子數組
- 找到兩個數字之間的最小距離
- 最小化高度之間的最大差異
- 到達終點的最小跳數
- 最大總和增加子序列| DP-14
- 總和大于給定值的最小子數組
- 查找 k 個長度的最大平均子數組
- 計算最小步數以獲得給定的所需數組
- 乘積小于 k 的子集數
- 查找使數組回文的最小合并操作數
- 查找不能表示為給定數組的任何子集之和的最小正整數值
- 具有最大總和的子數組的大小
- 找出任何兩個元素之間的最小差異
- 使用位操作進行空間優化
- 兩個二進制數組中具有相同總和的最長跨度
- 排序
- 替代排序
- 對幾乎排序(或 K 排序)的數組進行排序
- 根據給定值的絕對差對數組進行排序
- 以波形形式對數組進行排序
- 將大小為 n 的數組合并為大小為 m + n 的另一個數組
- 對包含 1 到 n 個值的數組進行排序
- 通過交換相鄰元素將 1 排序為 N
- 對包含兩種類型元素的數組進行排序
- 按頻率對元素排序| 系列 1
- 計算數組中的反轉 系列 1(使用合并排序)
- 兩個元素的和最接近零
- 最短無序子數組
- 排序數組所需的最小交換次數
- 兩個排序數組的并集和交集
- 查找兩個未排序數組的并集和交集
- 對 0、1 和 2 的數組進行排序
- 找到最小長度未排序子數組,進行排序,使整個數組排序
- 中位數為整數流(運行整數)
- 計算可能的三角形數量
- 查找數組中的對數(x,y),使得 x ^ y > y ^ x
- 計算所有等于 k 的不同對
- 打印給定整數數組的所有不同元素
- 從其對和數組構造一個數組
- 合并兩個有O(1)額外空間的排序數組
- 第一個數組中的最大值與第二個數組中的最小值的乘積
- 對數(a [j] > = a [i])的對數,其中 k 個范圍在(a [i],a [j])中,可被 x 整除
- 隨機對為最大加權對的概率
- AP 數組中存在的最小解排列(算術級數)
- 對兩個數組的最小乘積之和進行重新排列
- 將數組劃分為 k 個片段,以最大化片段最小值的最大值
- 最小乘積對為正整數數組
- 計算形成最小產品三胞胎的方法
- 檢查是否反轉子數組使數組排序
- 使用另一個數組最大化元素
- 使兩個數組的元素相同,最小增減
- 檢查是否有任何間隔完全重疊
- 除子數組中的元素外,對數組進行排序
- 對除一個以外的所有數組元素進行排序
- 排序二進制數組所需的最小相鄰交換
- 按數組中出現的元素順序對鏈接列表進行排序
- 打印數組中排序的不同元素
- 可以單獨排序以進行排序的最大分區數
- 使用 STL 根據因素數量進行排序
- 每次取下最小的鋼絲繩后剩下的鋼絲繩
- 數組中所有元素的排名
- 合并 3 個排序的數組
- 使數組遞減的最小減法運算數
- 最大化 arr [i] * i 的總和
- 差異小于 K 的對
- 按排序順序合并兩個未排序的數組
- 從兩個數組最大化唯一對
- 應用給定方程后對數組排序
- 每個數組元素的最小絕對差之和
- 查找是否可以使用一個外部數字使數組元素相同
- 兩個未排序數組之間的最小差值對
- 程序檢查數組是否排序(迭代和遞歸)
- 查找大于數組中一半元素的元素
- 使兩個數組相同的最小交換
- 要添加的元素,以便數組中存在某個范圍的所有元素
- 正在搜尋
- 搜索,插入和刪除未排序的數組
- 在排序的數組中搜索,插入和刪除
- 給定數組 A []和數字 x,請檢查 A []中的對,總和為 x
- 在相鄰項最多相差 k 的數組中搜索
- 在三個排序的數組中查找共同的元素
- 在無數排序數組中查找元素的位置
- 查找 1 到 n-1 之間的唯一重復元素
- 查找在數組中一次出現的元素,其中每個其他元素出現兩次
- 排除某些元素的最大子數組總和
- 數組中的最大平衡和
- 數組的平衡指數
- 領導者數組
- 天花板排列
- 多數元素
- 檢查排序數組中的多數元素
- 檢查數組是否具有多數元素
- 兩指針技術
- 查找峰元素
- 找到給定數組中的兩個重復元素
- 在給定的數組中找到一個固定點(等于索引的值)
- 查找給定總和的子數組| 系列 1(負數)
- 數組中的最大三元組和
- 來自三個數組的最小差異三元組
- 查找一個三元組,將其總和成給定值
- 找到所有零和的三元組
- 所有合計給定值的唯一三元組
- 計算總數小于給定值的三元組
- 打印形成 AP 的排序數組中的所有三元組
- XOR 為零的唯一三元組數
- 找到一個三元組,使得兩個和等于第三元素
- 查找出現次數的奇數
- 查找丟失的號碼
- 計算排序數組中的出現次數(或頻率)
- 給定一個已排序的數組和一個數字 x,在數組中找到總和最接近 x 的對
- 在排序的二進制數組中計數 1
- 在整數數組中找到第一個重復元素
- 從重復的數組中查找丟失的元素
- 找到重復的和丟失的| 添加了 3 種新方法
- 在未排序的數組中找到出現奇數的兩個數字
- 找到具有給定差異的一對
- 找到四個總和為給定值的元素| 集合 1(n ^ 3 解)
- 找到四個總和為給定值的元素| 系列 2
- 查找是否有一個總和為 0 的子數組
- 在相鄰元素之間的差為 1 的數組中搜索元素
- 一系列不同元素中的第三大元素
- 檢查數組中是否存在兩個元素的總和等于數組其余部分的總和
- 檢查給定數組是否包含彼此之間 k 距離內的重復元素
- 使用最少的比較次數搜索未排序數組中的元素
- 連續元素排序數組中僅重復元素的計數
- 在頻率大于或等于 n / 2 的排序數組中查找元素。
- 圓形數組中相鄰元素的最小絕對差
- 在數組中找到第一個,第二個和第三個最小元素
- 程序來查找數組的最小(或最大)元素
- 每個數組元素中另一個數組中最接近的較大元素
- 計算O(1)額外空間和O(n)時間中數組中所有元素的頻率
- 與給定的總和和距末端的最大最短距離配對
- 從數組中刪除一個元素(使用兩次遍歷和一次遍歷)
- 計算給定數組中大小為 3 的反轉
- 計算給定總和的對
- 對排序向量中的二分搜索
- 困雨水
- 替換元素會使數組元素連續
- 排序數組中的第 k 個缺失元素
- O(log(min(n(n,m)))中具有不同大小的兩個排序數組的中位數
- 從兩個排序的數組中打印不常見的元素
- 非重復元素
- 數組中最頻繁的元素
- 數組中最少的元素
- m 個元素的兩個子集之間的最大差
- n 個數組中升序元素的最大和
- 配對使得一個是其他的冪倍
- 查找數組中對的數量,以使它們的 XOR 為 0
- 兩次最大出現之間的最小距離
- 如果我們在數組中每次成功搜索后加倍,則找到最終值
- 排序數組中的最后一個重復元素
- 找到一個數組元素,使所有元素都可被它整除
- 以原始順序查找數組的 k 個最大元素
- 數組中的最大值,至少是其他元素的兩倍
- 連續步驟到屋頂
- 兩個大小的組之間的最大差異
- 兩個大小的組之間的最小差異
- 未排序整數列表中最接近的數字
- 值和索引和的最大絕對差
- 數組中局部極值的數量
- 檢查數組是否具有多數元素
- 查找數組中最接近的數字
- 最大和的對數
- 按原始順序打印給定數組中的 n 個最小元素
- 查找給定數組中缺少的前 k 個自然數
- 數組中的高尚整數(大于等于的元素數等于 value)
- 兩個數組對的絕對差的最小和
- 查找數組中非重復(不同)元素的總和
- 檢查是否可以從給定數組形成算術級數
- 數組的最小乘積子集
- 計算選擇差異最大的對的方法
- 每次成功搜索后通過將元素加倍來重復搜索
- 允許負數的數組中成對乘積的最大和
- 矩陣
- 旋轉矩陣元素
- 將方形矩陣旋轉 90 度| 系列 1
- 將矩陣旋轉 90 度,而無需使用任何額外空間| 系列 2
- 將矩陣旋轉 180 度
- 用 K 元素逆時針旋轉矩陣的每個環
- 將圖像旋轉 90 度
- 檢查矩陣的所有行是否都是彼此旋轉
- 排序給定矩陣
- 查找最大數量為 1 的行
- 在按行排序的矩陣中找到中位數
- 矩陣乘法| 遞歸的
- 程序將兩個矩陣相乘
- 矩陣的標量乘法程序
- 程序打印數組的下三角和上三角矩陣
- 查找矩陣所有行共有的不同元素
- 以螺旋形式打印給定的矩陣
- 查找矩陣中每一行的最大元素
- 在矩陣中查找唯一元素
- 將矩陣元素逐行移動 k
- 矩陣的不同運算
- 以逆時針螺旋形式打印給定矩陣
- 交換方矩陣的主要和次要對角線
- 矩陣中的最大路徑總和
- 矩陣對角元素的正方形
- 沿給定方向移動矩陣元素并添加具有相同值的元素
- 按升序對矩陣行進行排序,然后按降序對列進行排序
- 矩陣中間行和列的總和
- 矩陣的按行遍歷與按列遍歷
- 向右旋轉矩陣 K 次
- 檢查冪等矩陣的程序
- 程序檢查對合矩陣
- 矩陣中第一行和最后一行的交換元素
- zag-zag 方式打印矩陣
- 二維數組中的按行排序
- 馬爾可夫矩陣程序
- 檢查對角矩陣和標量矩陣的程序
- 按行和列對矩陣進行排序
- 查找島嶼數| 系列 1(使用 DFS)
- 魔術廣場| 偶數訂單
- 魔術廣場
- 檢查給定矩陣是否為幻方
- 檢查給定矩陣是否為幻方
- 兩種矩陣的 Kronecker 積
- 計數總和可分為“ k”的子矩陣
- 對角占優矩陣
- 使矩陣的每一行和每一列相等所需的最少操作
- 計算大小為 n 的矩陣中 k 的頻率,其中 matrix(i,j)= i + j
- 給定 1、2、3……k 以之字形打印它們。
- 皇后可以在棋盤上移動的障礙物數量
- 矩陣中 4 個相鄰元素的最大積
- 使二進制矩陣對稱所需的最小翻轉
- 程序檢查矩陣是否為下三角
- 程序檢查矩陣是否為上三角
- 矩陣中偶數和奇數的頻率
- 矩陣的中心元素等于對角線的一半
- 身份矩陣程序
- 程序用矩陣的下對角元素交換上對角元素。
- 稀疏矩陣表示| 系列 3(CSR)
- 填充矩陣以使所有行和所有列的乘積等于 1 的方式
- 矩陣對角線的鏡像
- 查找二進制矩陣中是否有一個角為 1 的矩形
- 查找所有填充有 0 的矩形
- 矩陣或網格中兩個單元之間的最短距離
- 計算二進制矩陣中 1 和 0 的集合
- 搜索按行和按列排序的矩陣
- 創建具有 O 和 X 的交替矩形的矩陣
- 矩陣的鋸齒形(或對角線)遍歷
- 原位(固定空間)M x N 大小的矩陣轉置| 更新
- 排序從 0 到 n ^ 2 – 1 的數字矩陣的最低成本
- 二進制矩陣中的唯一像元
- 計算特殊矩陣中等于 x 的條目
- 檢查給定矩陣是否稀疏
- 方矩陣的兩個對角線中的行式公共元素
- 檢查矩陣中第 i 行和第 i 列的總和是否相同
- 查找最大數為 1 的二進制矩陣的行號
- 程序檢查矩陣是否對稱
- 通過遵循單元格值來查找二維數組是否被完全遍歷
- 程序以 Z 格式打印矩陣
- 在矩陣中從左上到右下打印所有回文路徑
- 騎士的可能舉動
- 有效地計算矩陣的對角線總和
- 矩陣的邊界元素
- 從點開始以螺旋形式打印矩陣
- 以蛇形圖案打印矩陣
- 矩陣對角線互換程序
- 找出兩個對角線之和之間的差
- 從給定的二叉樹構造祖先矩陣
- 從祖先矩陣構造樹
- 圓形矩陣(以螺旋方式構造數字 1 到 m * n 的矩陣)
- Sudoku Generator 程序
- 康威人生游戲計劃
- 矩陣中沙漏的最大和
- 方陣中的最大值和最小值。
- 以防螺旋形式打印矩陣
- 查找矩陣的法線和跡線的程序
- 以各種方式對矩陣進行排序
- 設置二進制矩陣的所有元素所需的最少操作
- 以反向螺旋形式打印給定的矩陣
- C 程序檢查矩陣是否傾斜對稱
- 矩陣元素的總和,其中每個元素是行和列的整數除法
- 稀疏矩陣及其表示| 系列 2(使用列表和鍵字典)
- 查找使兩個矩陣相等的變換數
- 形成矩陣線圈
- 每個元素是其行號和列號的絕對差的矩陣總和
- 檢查二進制矩陣中的水平和垂直對稱性
- 每個值為 0 或 n 的矩陣的最大行列式
- 螺旋奇數階方陣的兩個對角線之和
- 在二進制矩陣中找到具有最大位差的行對
- 查找矩陣中給定行的所有置換行
- 在二進制矩陣中查找以 1s 形成的形狀的周長
- 在矩陣中打印具有相同矩形和的單元格
- 以對角線圖案打印矩陣
- 矩陣中兩行元素之和的最大差
- 查找具有給定總和的對,以便該對的元素位于不同的行中
- 二進制矩陣中所有零的總覆蓋率
- 用行或列的最大 GCD 替換每個矩陣元素
- 計算矩陣中所有排序的行
- 矩陣查詢
- 矩陣中的最大 XOR 值
- 可以從下到右傳輸光線的最大反射鏡
- 最后一個方塊的方向
- 以矩陣的螺旋形式打印第 K 個元素
- 查找給定的矩陣是否為 Toeplitz
- 在按行和按列排序的矩陣中計數零
- 在列明智和行明智排序矩陣中計算負數
- 在二進制矩陣中查找所有位形成的最大“ +”的大小
- 返回擴展矩陣中的前一個元素
- 使用O(1)額外空間打印 n x n 螺旋矩陣
- 二進制迷宮中的最短路徑
- 查找矩陣中圖案的方向
- 在矩陣中查找特定對
- 打印給定大小的最大和平方子矩陣
- 給定矩陣的所有行中的公共元素
- 按特定順序就地轉換矩陣
- 布爾矩陣問題
- 給定布爾矩陣,找到 k,使第 k 行中的所有元素均為 0,第 k 列為 1。
- 在給定的布爾矩陣中打印唯一行
- 找到 1 的最大矩形,并允許交換列
- 給定井字棋盤配置的有效性
- 子矩陣總和查詢
- 矩陣排名程序
- 全為 1 的最大尺寸矩形二進制子矩陣
- 全為 1 的最大尺寸正方形子矩陣
- 查找矩陣中除給定單元格的行和/或列中的元素以外的所有元素的總和?
- 計算每個島按行和列分隔的島數
- 在給定的按行排序的矩陣的所有行中找到一個公共元素
- 給定矩陣“ O”和“ X”,如果被“ X”包圍,則將“ O”替換為“ X”
- 給定矩陣“ O”和“ X”,找到被“ X”包圍的最大子正方形
- 洪水填充算法–如何在 paint 中實現 fill()?
- 從行和列的排序矩陣中按排序順序打印所有元素
- 給定一個 n x n 方陣,求出大小為 k x k 的所有子方和
- 查找矩陣轉置的程序
- 用于添加兩個矩陣的程序
- 矩陣減法程序
- 使用兩次遍歷收集網格中的最大點
- 在死胡同之前收集最多硬幣
- 正好有 k 個硬幣的路徑數
- 查找從給定起始字符開始的最長連續路徑的長度
- 在給定約束條件下找到矩陣中的最長路徑
- 到達目的地的最低初始點
- 分而治之| 第 5 組(Strassen 的矩陣乘法)
- 2D 矩陣中的最大和矩形| DP-27
- 雜項
- 子數組/子字符串與子序列以及生成它們的程序
- 產品數組難題
- 具有給定乘積的子數組數
- 鏈表與數組
- 檢查數組元素是否連續 新增方法 3
- 查找一個數組是否是另一個數組的子集 新增方法 3
- 在一個數組中實現兩個堆棧
- 查找兩個排序數組的相對補碼
- 通過 k 次運算的最小增量以使所有元素相等
- 最小化三個不同排序數組的(max(A [i],B [j],C [k])– min(A [i],B [j],C [k]))
