# 使用線性 SVM
對于此示例,我們將從 iris 數據集創建線性分隔符。我們從前面的章節中知道,萼片長度和花瓣寬度創建了一個線性可分的二進制數據集,用于預測花是否是 I. setosa。
## 做好準備
要在 TensorFlow 中實現軟可分 SVM,我們將實現特定的損失函數,如下所示:
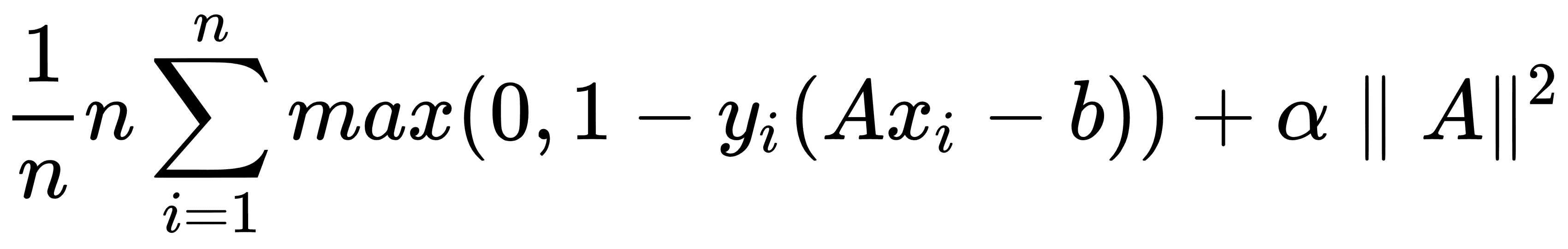
這里,`A`是部分斜率的向量,`b`是截距,`x[i]`是輸入向量,`y[i]`是實際類,(-1 或 1),`α`是軟可分性正則化參數。
## 操作步驟
我們按如下方式處理秘籍:
1. 我們首先加載必要的庫。這將包括用于訪問虹膜數據集的`scikit-learn`數據集庫。使用以下代碼:
```py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn import datasets
```
> 要為此練習設置 scikit-learn,我們只需要輸入`$pip install -U scikit-learn`。請注意,它也安裝了 Anaconda。
1. 接下來,我們啟動圖會話并根據需要加載數據。請記住,我們正在加載虹膜數據集中的第一個和第四個變量,因為它們是萼片長度和萼片寬度。我們正在加載目標變量,對于 I. setosa 將取值 1,否則為-1。使用以下代碼:
```py
sess = tf.Session()
iris = datasets.load_iris()
x_vals = np.array([[x[0], x[3]] for x in iris.data])
y_vals = np.array([1 if y==0 else -1 for y in iris.target])
```
1. 我們現在應該將數據集拆分為訓練集和測試集。我們將評估訓練和測試集的準確率。由于我們知道這個數據集是線性可分的,因此我們應該期望在兩個集合上獲得 100%的準確率。要拆分數據,請使用以下代碼:
```py
train_indices = np.random.choice(len(x_vals), round(len(x_vals)*0.8), replace=False)
test_indices = np.array(list(set(range(len(x_vals))) - set(train_indices)))
x_vals_train = x_vals[train_indices]
x_vals_test = x_vals[test_indices]
y_vals_train = y_vals[train_indices]
y_vals_test = y_vals[test_indices]
```
1. 接下來,我們設置批量大小,占位符和模型變量。值得一提的是,使用這種 SVM 算法,我們需要非常大的批量大小來幫助收斂。我們可以想象,對于非常小的批量大小,最大邊際線會略微跳躍。理想情況下,我們也會慢慢降低學習率,但現在這已經足夠了。此外,`A`變量將采用 2x1 形狀,因為我們有兩個預測變量:萼片長度和花瓣寬度。要進行此設置,我們使用以下代碼:
```py
batch_size = 100
x_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 2], dtype=tf.float32)
y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32)
A = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[2,1]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,1]))
```
1. 我們現在聲明我們的模型輸出。對于正確分類的點,如果目標是 I. setosa,則返回大于或等于 1 的數字,否則返回小于或等于-1。模型輸出使用以下代碼:
```py
model_output = tf.subtract(tf.matmul(x_data, A), b)
```
1. 接下來,我們將匯總并聲明必要的組件以獲得最大的保證金損失。首先,我們將聲明一個計算向量的 L2 范數的函數。然后,我們添加 margin 參數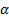。然后我們宣布我們的分類損失并將這兩個術語加在一起。使用以下代碼:
```py
l2_norm = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(A))
alpha = tf.constant([0.1])
classification_term = tf.reduce_mean(tf.maximum(0., tf.subtract(1., tf.multiply(model_output, y_target))))
loss = tf.add(classification _term, tf.multiply(alpha, l2_norm))
```
1. 現在,我們聲明我們的預測和準確率函數,以便我們可以評估訓練集和測試集的準確率,如下所示:
```py
prediction = tf.sign(model_output)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(prediction, y_target), tf.float32))
```
1. 在這里,我們將聲明我們的優化函數并初始化我們的模型變量;我們在以下代碼中執行此操作:
```py
my_opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01)
train_step = my_opt.minimize(loss)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
```
1. 我們現在可以開始我們的訓練循環,記住我們想要在訓練和測試集上記錄我們的損失和訓練準確率,如下所示:
```py
loss_vec = []
train_accuracy = []
test_accuracy = []
for i in range(500):
rand_index = np.random.choice(len(x_vals_train), size=batch_size)
rand_x = x_vals_train[rand_index]
rand_y = np.transpose([y_vals_train[rand_index]])
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y})
temp_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y})
loss_vec.append(temp_loss)
train_acc_temp = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x_data: x_vals_train, y_target: np.transpose([y_vals_train])})
train_accuracy.append(train_acc_temp)
test_acc_temp = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x_data: x_vals_test, y_target: np.transpose([y_vals_test])})
test_accuracy.append(test_acc_temp)
if (i+1)%100==0:
print('Step #' + str(i+1) + ' A = ' + str(sess.run(A)) + ' b = ' + str(sess.run(b)))
print('Loss = ' + str(temp_loss))
```
1. 訓練期間腳本的輸出應如下所示:
```py
Step #100 A = [[-0.10763293]
[-0.65735245]] b = [[-0.68752676]]
Loss = [ 0.48756418]
Step #200 A = [[-0.0650763 ]
[-0.89443302]] b = [[-0.73912662]]
Loss = [ 0.38910741]
Step #300 A = [[-0.02090022]
[-1.12334013]] b = [[-0.79332656]]
Loss = [ 0.28621092]
Step #400 A = [[ 0.03189624]
[-1.34912157]] b = [[-0.8507266]]
Loss = [ 0.22397576]
Step #500 A = [[ 0.05958777]
[-1.55989814]] b = [[-0.9000265]]
Loss = [ 0.20492229]
```
1. 為了繪制輸出(擬合,損失和精度),我們必須提取系數并將`x`值分成 I. setosa 和 Non-setosa,如下所示:
```py
[[a1], [a2]] = sess.run(A)
[[b]] = sess.run(b)
slope = -a2/a1
y_intercept = b/a1
x1_vals = [d[1] for d in x_vals]
best_fit = []
for i in x1_vals:
best_fit.append(slope*i+y_intercept)
setosa_x = [d[1] for i,d in enumerate(x_vals) if y_vals[i]==1]
setosa_y = [d[0] for i,d in enumerate(x_vals) if y_vals[i]==1]
not_setosa_x = [d[1] for i,d in enumerate(x_vals) if y_vals[i]==-1]
not_setosa_y = [d[0] for i,d in enumerate(x_vals) if y_vals[i]==-1]
```
1. 以下是使用線性分離器擬合,精度和損耗繪制數據的代碼:
```py
plt.plot(setosa_x, setosa_y, 'o', label='I. setosa')
plt.plot(not_setosa_x, not_setosa_y, 'x', label='Non-setosa')
plt.plot(x1_vals, best_fit, 'r-', label='Linear Separator', linewidth=3)
plt.ylim([0, 10])
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.title('Sepal Length vs Petal Width')
plt.xlabel('Petal Width')
plt.ylabel('Sepal Length')
plt.show()
plt.plot(train_accuracy, 'k-', label='Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(test_accuracy, 'r--', label='Test Accuracy')
plt.title('Train and Test Set Accuracies')
plt.xlabel('Generation')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.show()
plt.plot(loss_vec, 'k-')
plt.title('Loss per Generation')
plt.xlabel('Generation')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.show()
```
> 以這種方式使用 TensorFlow 來實現 SVD 算法可能導致每次運行的結果略有不同。其原因包括隨機訓練/測試集拆分以及每個訓練批次中不同批次點的選擇。此外,在每一代之后慢慢降低學習率是理想的。
得到的圖如下:
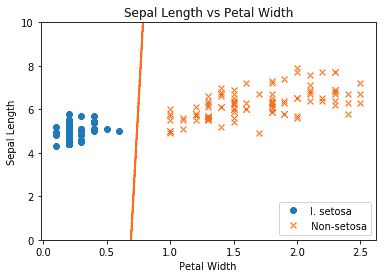
圖 2:最終線性 SVM 與繪制的兩個類別擬合
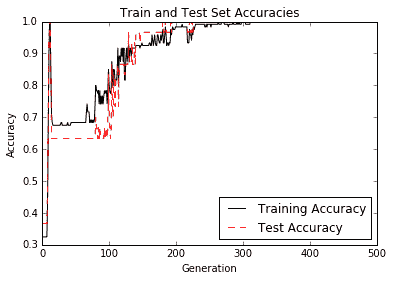
圖 3:迭代測試和訓練集精度;我們確實獲得 100%的準確率,因為這兩個類是線性可分的
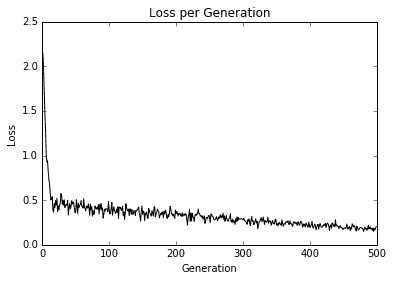
圖 4:超過 500 次迭代的最大邊際損失圖
## 工作原理
在本文中,我們已經證明使用最大邊際損失函數可以實現線性 SVD 模型。
- TensorFlow 入門
- 介紹
- TensorFlow 如何工作
- 聲明變量和張量
- 使用占位符和變量
- 使用矩陣
- 聲明操作符
- 實現激活函數
- 使用數據源
- 其他資源
- TensorFlow 的方式
- 介紹
- 計算圖中的操作
- 對嵌套操作分層
- 使用多個層
- 實現損失函數
- 實現反向傳播
- 使用批量和隨機訓練
- 把所有東西結合在一起
- 評估模型
- 線性回歸
- 介紹
- 使用矩陣逆方法
- 實現分解方法
- 學習 TensorFlow 線性回歸方法
- 理解線性回歸中的損失函數
- 實現 deming 回歸
- 實現套索和嶺回歸
- 實現彈性網絡回歸
- 實現邏輯回歸
- 支持向量機
- 介紹
- 使用線性 SVM
- 簡化為線性回歸
- 在 TensorFlow 中使用內核
- 實現非線性 SVM
- 實現多類 SVM
- 最近鄰方法
- 介紹
- 使用最近鄰
- 使用基于文本的距離
- 使用混合距離函數的計算
- 使用地址匹配的示例
- 使用最近鄰進行圖像識別
- 神經網絡
- 介紹
- 實現操作門
- 使用門和激活函數
- 實現單層神經網絡
- 實現不同的層
- 使用多層神經網絡
- 改進線性模型的預測
- 學習玩井字棋
- 自然語言處理
- 介紹
- 使用詞袋嵌入
- 實現 TF-IDF
- 使用 Skip-Gram 嵌入
- 使用 CBOW 嵌入
- 使用 word2vec 進行預測
- 使用 doc2vec 進行情緒分析
- 卷積神經網絡
- 介紹
- 實現簡單的 CNN
- 實現先進的 CNN
- 重新訓練現有的 CNN 模型
- 應用 StyleNet 和 NeuralStyle 項目
- 實現 DeepDream
- 循環神經網絡
- 介紹
- 為垃圾郵件預測實現 RNN
- 實現 LSTM 模型
- 堆疊多個 LSTM 層
- 創建序列到序列模型
- 訓練 Siamese RNN 相似性度量
- 將 TensorFlow 投入生產
- 介紹
- 實現單元測試
- 使用多個執行程序
- 并行化 TensorFlow
- 將 TensorFlow 投入生產
- 生產環境 TensorFlow 的一個例子
- 使用 TensorFlow 服務
- 更多 TensorFlow
- 介紹
- 可視化 TensorBoard 中的圖
- 使用遺傳算法
- 使用 k 均值聚類
- 求解常微分方程組
- 使用隨機森林
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras
