# 求解常微分方程組
TensorFlow 可用于許多算法實現和過程。 TensorFlow 多功能性的一個很好的例子是實現 ODE 求解器。以數字方式求解 ODE 是一種迭代過程,可以在計算圖中輕松描述。對于這個秘籍,我們將解決 Lotka-Volterra 捕食者 - 獵物系統。
## 做好準備
該秘籍將說明如何求解常微分方程(ODE)系統。我們可以使用與前兩節類似的方法來更新值,因為我們迭代并解決 ODE 系統。
我們將考慮的 ODE 系統是著名的 Lotka-Volterra 捕食者 - 獵物系統。該系統顯示了捕食者 - 食餌系統如何在給定特定參數的情況下振蕩。
Lotka-Volterra 系統于 1920 年在一篇論文中發表(參見圖 1,標量值,我們的斜率估計,在張量板中可視化)。我們將使用類似的參數來表明可以發生振蕩系統。這是以數學上離散的方式表示的系統:
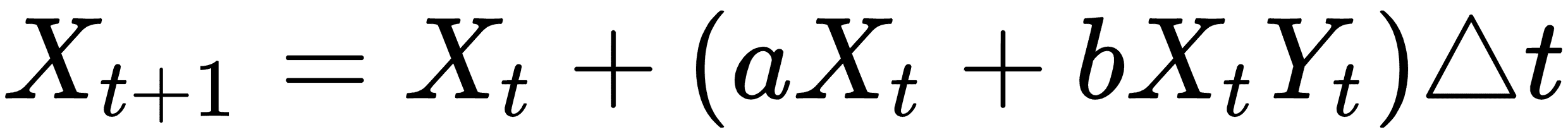
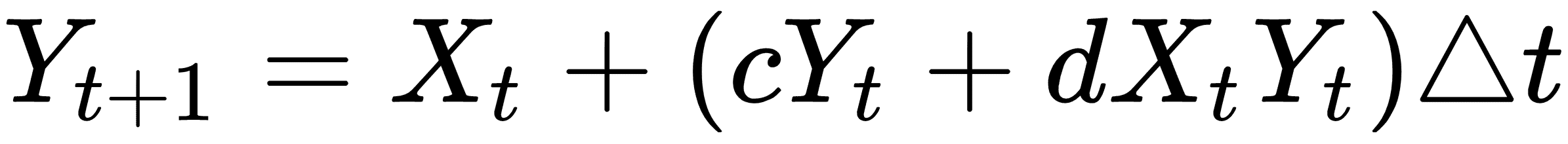
在這里,`X`是獵物,`Y`將成為捕食者。我們通過`a`,`b`,`c`和`d`的值來確定哪個是獵物,哪個是捕食者:對于獵物,`a>0`,`b<0`和捕食者,`c<0`,`d>0`。我們將在 TensorFlow 解決方案中將此離散版本實現到系統中。
## 操作步驟
1. 我們首先加載庫并開始圖會話:
```py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
sess = tf.Session()
```
1. 然后我們在圖中聲明我們的常量和變量:
```py
x_initial = tf.constant(1.0)
y_initial = tf.constant(1.0)
X_t1 = tf.Variable(x_initial)
Y_t1 = tf.Variable(y_initial)
# Make the placeholders
t_delta = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=())
a = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=())
b = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=())
c = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=())
d = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=())
```
1. 接下來,我們將實現先前引入的離散系統,然后更新`X`和`Y`群體:
```py
X_t2 = X_t1 + (a * X_t1 + b * X_t1 * Y_t1) * t_delta
Y_t2 = Y_t1 + (c * Y_t1 + d * X_t1 * Y_t1) * t_delta
# Update to New Population
step = tf.group(
X_t1.assign(X_t2),
Y_t1.assign(Y_t2))
```
1. 我們現在初始化圖并運行離散 ODE 系統,并使用特定參數來說明循環行為:
```py
init = tf.global_variables_initializer() sess.run(init) # Run the ODE prey_values = [] predator_values = [] for i in range(1000): # Step simulation (using constants for a known cyclic solution) step.run({a: (2./3.), b: (-4./3.), c: -1.0, d: 1.0, t_delta: 0.01}, session=sess) # Store each outcome temp_prey, temp_pred = sess.run([X_t1, Y_t1]) prey_values.append(temp_prey) predator_values.append(temp_pred)
```
A steady state (and cyclic) solution to this specific system, the Lotka-Volterra equations, very much depends on specific parameters and population values. We encourage the reader to try different parameters and values to see what can happen.
1. 現在,我們可以繪制捕食者和獵物的價值:
```py
plt.plot(prey_values, label="Prey")
plt.plot(predator_values, label="Predator")
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.show()
```
這個繪圖代碼將生成一個屏幕截圖,顯示掠食者和獵物的振蕩種群:
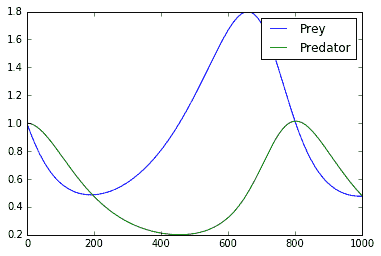
圖 6:在這里,我們繪制 ODE 解決方案的捕食者和獵物值。事實上,我們可以看到周期確實發生了
## 工作原理
我們使用 TensorFlow 逐步求解 ODE 系統的離散版本。對于特定參數,我們看到捕食者 - 食餌系統確實可以具有循環解。這在我們的系統生物學上是有意義的,因為如果有太多的捕食者,獵物開始死亡,然后掠食者的食物就會減少,所以他們會死掉,等等。
## 另見
Lotka,A。J.,關于有機系統中某些節奏關系的分析性說明。 PROC。納特。科學院。 6(1920)( [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1084562/](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1084562/) )。
- TensorFlow 入門
- 介紹
- TensorFlow 如何工作
- 聲明變量和張量
- 使用占位符和變量
- 使用矩陣
- 聲明操作符
- 實現激活函數
- 使用數據源
- 其他資源
- TensorFlow 的方式
- 介紹
- 計算圖中的操作
- 對嵌套操作分層
- 使用多個層
- 實現損失函數
- 實現反向傳播
- 使用批量和隨機訓練
- 把所有東西結合在一起
- 評估模型
- 線性回歸
- 介紹
- 使用矩陣逆方法
- 實現分解方法
- 學習 TensorFlow 線性回歸方法
- 理解線性回歸中的損失函數
- 實現 deming 回歸
- 實現套索和嶺回歸
- 實現彈性網絡回歸
- 實現邏輯回歸
- 支持向量機
- 介紹
- 使用線性 SVM
- 簡化為線性回歸
- 在 TensorFlow 中使用內核
- 實現非線性 SVM
- 實現多類 SVM
- 最近鄰方法
- 介紹
- 使用最近鄰
- 使用基于文本的距離
- 使用混合距離函數的計算
- 使用地址匹配的示例
- 使用最近鄰進行圖像識別
- 神經網絡
- 介紹
- 實現操作門
- 使用門和激活函數
- 實現單層神經網絡
- 實現不同的層
- 使用多層神經網絡
- 改進線性模型的預測
- 學習玩井字棋
- 自然語言處理
- 介紹
- 使用詞袋嵌入
- 實現 TF-IDF
- 使用 Skip-Gram 嵌入
- 使用 CBOW 嵌入
- 使用 word2vec 進行預測
- 使用 doc2vec 進行情緒分析
- 卷積神經網絡
- 介紹
- 實現簡單的 CNN
- 實現先進的 CNN
- 重新訓練現有的 CNN 模型
- 應用 StyleNet 和 NeuralStyle 項目
- 實現 DeepDream
- 循環神經網絡
- 介紹
- 為垃圾郵件預測實現 RNN
- 實現 LSTM 模型
- 堆疊多個 LSTM 層
- 創建序列到序列模型
- 訓練 Siamese RNN 相似性度量
- 將 TensorFlow 投入生產
- 介紹
- 實現單元測試
- 使用多個執行程序
- 并行化 TensorFlow
- 將 TensorFlow 投入生產
- 生產環境 TensorFlow 的一個例子
- 使用 TensorFlow 服務
- 更多 TensorFlow
- 介紹
- 可視化 TensorBoard 中的圖
- 使用遺傳算法
- 使用 k 均值聚類
- 求解常微分方程組
- 使用隨機森林
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras
