# 學習玩井字棋
為了展示適應性神經網絡的可用性,我們現在將嘗試使用神經網絡來學習井字棋的最佳動作。我們將知道井字棋是一種確定性游戲,并且最佳動作已經知道。
## 做好準備
為了訓練我們的模型,我們將使用一系列的棋盤位置,然后對許多不同的棋盤進行最佳的最佳響應。我們可以通過僅考慮在對稱性方面不同的棋盤位置來減少要訓練的棋盤數量。井字棋棋盤的非同一性變換是 90 度,180 度和 270 度的旋轉(在任一方向上),水平反射和垂直反射。鑒于這個想法,我們將使用最佳移動的候選棋盤名單,應用兩個隨機變換,然后將其輸入神經網絡進行學習。
> 由于井字棋是一個確定性的游戲,值得注意的是,無論誰先走,都應該贏或抽。我們希望能夠以最佳方式響應我們的動作并最終獲得平局的模型。
如果我們將 Xs 注釋為 1,將 Os 注釋為-1,將空格注釋為 0,則下圖說明了我們如何將棋盤位置和最佳移動視為一行數據:
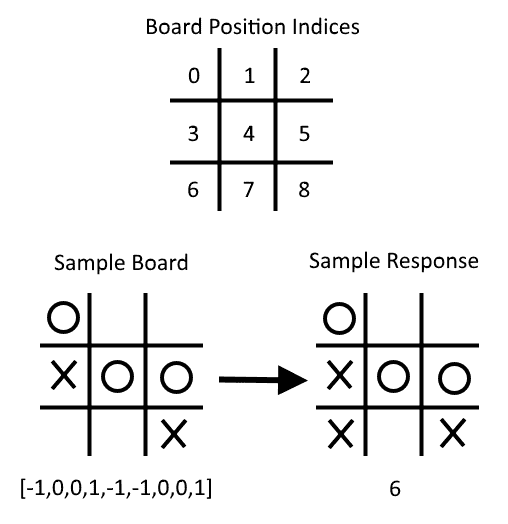Figure 9: Here, we illustrate how to consider a board and an optimal move as a row of data. Note that X = 1, O = -1, and empty spaces are 0, and we start indexing at 0
除了模型損失,要檢查我們的模型如何執行,我們將做兩件事。我們將執行的第一項檢查是從訓練集中刪除位置和最佳移動行。這將使我們能夠看到神經網絡模型是否可以推廣它以前從未見過的移動。我們將評估模型的第二種方法是在最后實際對抗它。
可以在此秘籍的 GitHub 目錄中找到可能的棋盤列表和最佳移動: [https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow_cookbook/tree/master/06_Neural_Networks/08_Learning_Tic_Tac_Toe](https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow_cookbook/tree/master/06_Neural_Networks/08_Learning_Tic_Tac_Toe) 和 Packt 倉庫: [https://github.com/PacktPublishing/TensorFlow-Machine-Learning-Cookbook-Second-Edition](https://github.com/PacktPublishing/TensorFlow-Machine-Learning-Cookbook-Second-Edition) 。
## 操作步驟
我們按如下方式處理秘籍:
1. 我們需要從為此腳本加載必要的庫開始,如下所示:
```py
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import csv
import random
import numpy as np
import random
```
1. 接下來,我們聲明以下批量大小來訓練我們的模型:
```py
batch_size = 50
```
1. 為了使棋盤更容易可視化,我們將創建一個輸出帶 Xs 和 Os 的井字棋棋盤的函數。這是通過以下代碼完成的:
```py
def print_board(board):
symbols = ['O', ' ', 'X']
board_plus1 = [int(x) + 1 for x in board]
board_line1 = ' {} | {} | {}'.format(symbols[board_plus1[0]],
symbols[board_plus1[1]],
symbols[board_plus1[2]])
board_line2 = ' {} | {} | {}'.format(symbols[board_plus1[3]],
symbols[board_plus1[4]],
symbols[board_plus1[5]])
board_line3 = ' {} | {} | {}'.format(symbols[board_plus1[6]],
symbols[board_plus1[7]],
symbols[board_plus1[8]])
print(board_line1)
print('___________')
print(board_line2)
print('___________')
print(board_line3)
```
1. 現在我們必須創建一個函數,它將返回一個新的棋盤和一個轉換下的最佳響應位置。這是通過以下代碼完成的:
```py
def get_symmetry(board, response, transformation):
'''
:param board: list of integers 9 long:
opposing mark = -1
friendly mark = 1
empty space = 0
:param transformation: one of five transformations on a board:
rotate180, rotate90, rotate270, flip_v, flip_h
:return: tuple: (new_board, new_response)
'''
if transformation == 'rotate180':
new_response = 8 - response
return board[::-1], new_response
elif transformation == 'rotate90':
new_response = [6, 3, 0, 7, 4, 1, 8, 5, 2].index(response)
tuple_board = list(zip(*[board[6:9], board[3:6], board[0:3]]))
return [value for item in tuple_board for value in item], new_response
elif transformation == 'rotate270':
new_response = [2, 5, 8, 1, 4, 7, 0, 3, 6].index(response)
tuple_board = list(zip(*[board[0:3], board[3:6], board[6:9]]))[::-1]
return [value for item in tuple_board for value in item], new_response
elif transformation == 'flip_v':
new_response = [6, 7, 8, 3, 4, 5, 0, 1, 2].index(response)
return board[6:9] + board[3:6] + board[0:3], new_response
elif transformation == 'flip_h':
# flip_h = rotate180, then flip_v
new_response = [2, 1, 0, 5, 4, 3, 8, 7, 6].index(response)
new_board = board[::-1]
return new_board[6:9] + new_board[3:6] + new_board[0:3], new_response
else:
raise ValueError('Method not implmented.')
```
1. 棋盤列表及其最佳響應位于目錄中的`.csv`文件中,可從 github 倉庫 [https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow_cookbook](https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow_cookbook) 或 Packt 倉庫獲得 [https://github.com/PacktPublishing/TensorFlow-Machine-Learning-Cookbook-Second-Edition](https://github.com/PacktPublishing/TensorFlow-Machine-Learning-Cookbook-Second-Edition)。我們將創建一個函數,它將使用棋盤和響應加載文件,并將其存儲為元組列表,如下所示:
```py
def get_moves_from_csv(csv_file):
'''
:param csv_file: csv file location containing the boards w/ responses
:return: moves: list of moves with index of best response
'''
moves = []
with open(csv_file, 'rt') as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile, delimiter=',')
for row in reader:
moves.append(([int(x) for x in row[0:9]],int(row[9])))
return moves
```
1. 現在我們需要將所有內容組合在一起以創建一個函數,該函數將返回隨機轉換的棋盤和響應。這是通過以下代碼完成的:
```py
def get_rand_move(moves, rand_transforms=2):
# This function performs random transformations on a board.
(board, response) = random.choice(moves)
possible_transforms = ['rotate90', 'rotate180', 'rotate270', 'flip_v', 'flip_h']
for i in range(rand_transforms):
random_transform = random.choice(possible_transforms)
(board, response) = get_symmetry(board, response, random_transform)
return board, response
```
1. 接下來,我們需要初始化圖會話,加載數據,并創建一個訓練集,如下所示:
```py
sess = tf.Session()
moves = get_moves_from_csv('base_tic_tac_toe_moves.csv')
# Create a train set:
train_length = 500
train_set = []
for t in range(train_length):
train_set.append(get_rand_move(moves))
```
1. 請記住,我們希望從我們的訓練集中刪除一個棋盤和一個最佳響應,以查看該模型是否可以推廣以實現最佳移動。以下棋盤的最佳舉措將是在第 6 號指數進行:
```py
test_board = [-1, 0, 0, 1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1]
train_set = [x for x in train_set if x[0] != test_board]
```
1. 我們現在可以創建函數來創建模型變量和模型操作。請注意,我們在以下模型中不包含`softmax()`激活函數,因為它包含在損失函數中:
```py
def init_weights(shape):
return tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape))
def model(X, A1, A2, bias1, bias2):
layer1 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(X, A1), bias1))
layer2 = tf.add(tf.matmul(layer1, A2), bias2)
return layer2
```
1. 現在我們需要聲明我們的占位符,變量和模型,如下所示:
```py
X = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, 9])
Y = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.int32, shape=[None])
A1 = init_weights([9, 81])
bias1 = init_weights([81])
A2 = init_weights([81, 9])
bias2 = init_weights([9])
model_output = model(X, A1, A2, bias1, bias2)
```
1. 接下來,我們需要聲明我們的`loss`函數,它將是最終輸出 logits 的平均 softmax(非標準化輸出)。然后我們將聲明我們的訓練步驟和優化器。如果我們希望將來能夠對抗我們的模型,我們還需要創建一個預測操作,如下所示:
```py
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=model_output, labels=Y))
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.025).minimize(loss)
prediction = tf.argmax(model_output, 1)
```
1. 我們現在可以使用以下代碼初始化變量并循環遍歷神經網絡的訓練:
```py
# Initialize variables
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
loss_vec = []
for i in range(10000):
# Select random indices for batch
rand_indices = np.random.choice(range(len(train_set)), batch_size, replace=False)
# Get batch
batch_data = [train_set[i] for i in rand_indices]
x_input = [x[0] for x in batch_data]
y_target = np.array([y[1] for y in batch_data])
# Run training step
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={X: x_input, Y: y_target})
# Get training loss
temp_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={X: x_input, Y: y_target})
loss_vec.append(temp_loss)
```
```py
if i%500==0:
print('iteration ' + str(i) + ' Loss: ' + str(temp_loss))
```
1. 以下是繪制模型訓練損失所需的代碼:
```py
plt.plot(loss_vec, 'k-', label='Loss')
plt.title('Loss (MSE) per Generation')
plt.xlabel('Generation')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.show()
```
我們應該得到以下每代損失的繪圖:
圖 10:Tic-Tac-Toe 訓練組損失超過 10,000 次迭代
在上圖中,我們繪制了訓練步驟的損失。
1. 為了測試模型,我們需要看看它是如何在我們從訓練集中刪除的測試棋盤上執行的。我們希望模型可以推廣和預測移動的最佳索引,這將是索引號 6.大多數時候模型將成功,如下所示:
```py
test_boards = [test_board]
feed_dict = {X: test_boards}
logits = sess.run(model_output, feed_dict=feed_dict)
predictions = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict=feed_dict)
print(predictions)
```
1. 上一步應該產生以下輸出:
```py
[6]
```
1. 為了評估我們的模型,我們需要與我們訓練的模型進行對比。要做到這一點,我們必須創建一個能夠檢查勝利的函數。這樣,我們的程序將知道何時停止要求更多動作。這是通過以下代碼完成的:
```py
def check(board):
wins = [[0,1,2], [3,4,5], [6,7,8], [0,3,6], [1,4,7], [2,5,8], [0,4,8], [2,4,6]]
for i in range(len(wins)):
if board[wins[i][0]]==board[wins[i][1]]==board[wins[i][2]]==1.:
return 1
elif board[wins[i][0]]==board[wins[i][1]]==board[wins[i][2]]==-1.:
return 1
return 0
```
1. 現在我們可以使用我們的模型循環播放游戲。我們從一個空白棋盤(全零)開始,我們要求用戶輸入一個索引(0-8),然后我們將其輸入到模型中進行預測。對于模型的移動,我們采用最大的可用預測,也是一個開放空間。從這個游戲中,我們可以看到我們的模型并不完美,如下所示:
```py
game_tracker = [0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]
win_logical = False
num_moves = 0
while not win_logical:
player_index = input('Input index of your move (0-8): ')
num_moves += 1
# Add player move to game
game_tracker[int(player_index)] = 1\.
# Get model's move by first getting all the logits for each index
[potential_moves] = sess.run(model_output, feed_dict={X: [game_tracker]})
# Now find allowed moves (where game tracker values = 0.0)
allowed_moves = [ix for ix,x in enumerate(game_tracker) if x==0.0]
# Find best move by taking argmax of logits if they are in allowed moves
model_move = np.argmax([x if ix in allowed_moves else -999.0 for ix,x in enumerate(potential_moves)])
# Add model move to game
game_tracker[int(model_move)] = -1\.
print('Model has moved')
print_board(game_tracker)
# Now check for win or too many moves
if check(game_tracker)==1 or num_moves>=5:
print('Game Over!')
win_logical = True
```
1. 上一步應該產生以下交互輸出:
```py
Input index of your move (0-8): 4
Model has moved
O | |
___________
| X |
___________
| |
Input index of your move (0-8): 6
Model has moved
O | |
___________
| X |
___________
X | | O
Input index of your move (0-8): 2
Model has moved
O | | X
___________
O | X |
___________
X | | O
Game Over!
```
## 工作原理
在本節中,我們通過饋送棋盤位置和九維向量訓練神經網絡來玩井字棋,并預測最佳響應。我們只需要喂幾個可能的井字棋棋盤并對每個棋盤應用隨機變換以增加訓練集大小。
為了測試我們的算法,我們刪除了一個特定棋盤的所有實例,并查看我們的模型是否可以推廣以預測最佳響應。最后,我們針對我們的模型玩了一個示例游戲。雖然它還不完善,但仍有不同的架構和訓練程序可用于改進它。
- TensorFlow 入門
- 介紹
- TensorFlow 如何工作
- 聲明變量和張量
- 使用占位符和變量
- 使用矩陣
- 聲明操作符
- 實現激活函數
- 使用數據源
- 其他資源
- TensorFlow 的方式
- 介紹
- 計算圖中的操作
- 對嵌套操作分層
- 使用多個層
- 實現損失函數
- 實現反向傳播
- 使用批量和隨機訓練
- 把所有東西結合在一起
- 評估模型
- 線性回歸
- 介紹
- 使用矩陣逆方法
- 實現分解方法
- 學習 TensorFlow 線性回歸方法
- 理解線性回歸中的損失函數
- 實現 deming 回歸
- 實現套索和嶺回歸
- 實現彈性網絡回歸
- 實現邏輯回歸
- 支持向量機
- 介紹
- 使用線性 SVM
- 簡化為線性回歸
- 在 TensorFlow 中使用內核
- 實現非線性 SVM
- 實現多類 SVM
- 最近鄰方法
- 介紹
- 使用最近鄰
- 使用基于文本的距離
- 使用混合距離函數的計算
- 使用地址匹配的示例
- 使用最近鄰進行圖像識別
- 神經網絡
- 介紹
- 實現操作門
- 使用門和激活函數
- 實現單層神經網絡
- 實現不同的層
- 使用多層神經網絡
- 改進線性模型的預測
- 學習玩井字棋
- 自然語言處理
- 介紹
- 使用詞袋嵌入
- 實現 TF-IDF
- 使用 Skip-Gram 嵌入
- 使用 CBOW 嵌入
- 使用 word2vec 進行預測
- 使用 doc2vec 進行情緒分析
- 卷積神經網絡
- 介紹
- 實現簡單的 CNN
- 實現先進的 CNN
- 重新訓練現有的 CNN 模型
- 應用 StyleNet 和 NeuralStyle 項目
- 實現 DeepDream
- 循環神經網絡
- 介紹
- 為垃圾郵件預測實現 RNN
- 實現 LSTM 模型
- 堆疊多個 LSTM 層
- 創建序列到序列模型
- 訓練 Siamese RNN 相似性度量
- 將 TensorFlow 投入生產
- 介紹
- 實現單元測試
- 使用多個執行程序
- 并行化 TensorFlow
- 將 TensorFlow 投入生產
- 生產環境 TensorFlow 的一個例子
- 使用 TensorFlow 服務
- 更多 TensorFlow
- 介紹
- 可視化 TensorBoard 中的圖
- 使用遺傳算法
- 使用 k 均值聚類
- 求解常微分方程組
- 使用隨機森林
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras
