# 實現簡單的 CNN
在本文中,我們將開發一個四層卷積神經網絡,以提高我們預測 MNIST 數字的準確率。前兩個卷積層將各自由卷積-ReLU-Max 池操作組成,最后兩個層將是完全連接的層。
## 做好準備
為了訪問 MNIST 數據,TensorFlow 有一個`examples.tutorials`包,它具有很好的數據集加載函數。加載數據后,我們將設置模型變量,創建模型,批量訓練模型,然后可視化損失,準確率和一些樣本數字。
## 操作步驟
執行以下步驟:
1. 首先,我們將加載必要的庫并啟動圖會話:
```py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
ops.reset_default_graph()
sess = tf.Session()
```
1. 接下來,我們將加載數據并將圖像轉換為`28x28`數組:
```py
data_dir = 'temp'
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets(data_dir, one_hot=False)
train_xdata = np.array([np.reshape(x, (28,28)) for x in mnist.train.images])
test_xdata = np.array([np.reshape(x, (28,28)) for x in mnist.test.images])
train_labels = mnist.train.labels
test_labels = mnist.test.labels
```
> 請注意,此處下載的 MNIST 數據集還包括驗證集。此驗證集通常與測試集的大小相同。如果我們進行任何超參數調整或模型選擇,最好將其加載到其他測試中。
1. 現在我們將設置模型參數。請記住,圖像的深度(通道數)為 1,因為這些圖像是灰度的:
```py
batch_size = 100
learning_rate = 0.005
evaluation_size = 500
image_width = train_xdata[0].shape[0]
image_height = train_xdata[0].shape[1]
target_size = max(train_labels) + 1
num_channels = 1
generations = 500
eval_every = 5
conv1_features = 25
conv2_features = 50
max_pool_size1 = 2
max_pool_size2 = 2
fully_connected_size1 = 100
```
1. 我們現在可以聲明數據的占位符。我們將聲明我們的訓練數據變量和測試數據變量。我們將針對訓練和評估規模使用不同的批量大小。您可以根據可用于訓練和評估的物理內存來更改這些內容:
```py
x_input_shape = (batch_size, image_width, image_height, num_channels)
x_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=x_input_shape)
y_target = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=(batch_size))
eval_input_shape = (evaluation_size, image_width, image_height, num_channels)
eval_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=eval_input_shape)
eval_target = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=(evaluation_size))
```
1. 我們將使用我們在前面步驟中設置的參數聲明我們的卷積權重和偏差:
```py
conv1_weight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([4, 4, num_channels, conv1_features], stddev=0.1, dtype=tf.float32))
conv1_bias = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([conv1_features],dtype=tf.float32))
conv2_weight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([4, 4, conv1_features, conv2_features], stddev=0.1, dtype=tf.float32))
conv2_bias = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([conv2_features],dtype=tf.float32))
```
1. 接下來,我們將為模型的最后兩層聲明完全連接的權重和偏差:
```py
resulting_width = image_width // (max_pool_size1 * max_pool_size2)
resulting_height = image_height // (max_pool_size1 * max_pool_size2)
full1_input_size = resulting_width * resulting_height*conv2_features
full1_weight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([full1_input_size, fully_connected_size1], stddev=0.1, dtype=tf.float32))
full1_bias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([fully_connected_size1], stddev=0.1, dtype=tf.float32))
full2_weight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([fully_connected_size1, target_size], stddev=0.1, dtype=tf.float32))
full2_bias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([target_size], stddev=0.1, dtype=tf.float32))
```
1. 現在我們將宣布我們的模型。我們首先創建一個模型函數。請注意,該函數將在全局范圍內查找所需的層權重和偏差。此外,為了使完全連接的層工作,我們將第二個卷積層的輸出展平,這樣我們就可以在完全連接的層中使用它:
```py
def my_conv_net(input_data):
# First Conv-ReLU-MaxPool Layer
conv1 = tf.nn.conv2d(input_data, conv1_weight, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
relu1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv1, conv1_bias))
max_pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu1, ksize=[1, max_pool_size1, max_pool_size1, 1], strides=[1, max_pool_size1, max_pool_size1, 1], padding='SAME')
# Second Conv-ReLU-MaxPool Layer
conv2 = tf.nn.conv2d(max_pool1, conv2_weight, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
relu2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv2, conv2_bias))
max_pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu2, ksize=[1, max_pool_size2, max_pool_size2, 1], strides=[1, max_pool_size2, max_pool_size2, 1], padding='SAME')
# Transform Output into a 1xN layer for next fully connected layer
final_conv_shape = max_pool2.get_shape().as_list()
final_shape = final_conv_shape[1] * final_conv_shape[2] * final_conv_shape[3]
flat_output = tf.reshape(max_pool2, [final_conv_shape[0], final_shape])
# First Fully Connected Layer
fully_connected1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(tf.matmul(flat_output, full1_weight), full1_bias))
# Second Fully Connected Layer
final_model_output = tf.add(tf.matmul(fully_connected1, full2_weight), full2_bias)
return final_model_output
```
1. 接下來,我們可以在訓練和測試數據上聲明模型:
```py
model_output = my_conv_net(x_input)
test_model_output = my_conv_net(eval_input)
```
1. 我們將使用的損失函數是 softmax 函數。我們使用稀疏 softmax,因為我們的預測只是一個類別,而不是多個類別。我們還將使用一個對 logits 而不是縮放概率進行操作的損失函數:
```py
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=model_output, labels=y_target))
```
1. 接下來,我們將創建一個訓練和測試預測函數。然后我們還將創建一個準確率函數來確定模型在每個批次上的準確率:
```py
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(model_output)
test_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(test_model_output)
# Create accuracy function
def get_accuracy(logits, targets):
batch_predictions = np.argmax(logits, axis=1)
num_correct = np.sum(np.equal(batch_predictions, targets))
return 100\. * num_correct/batch_predictions.shape[0]
```
1. 現在我們將創建我們的優化函數,聲明訓練步驟,并初始化所有模型變量:
```py
my_optimizer = tf.train.MomentumOptimizer(learning_rate, 0.9)
train_step = my_optimizer.minimize(loss)
# Initialize Variables
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
```
1. 我們現在可以開始訓練我們的模型。我們以隨機選擇的批次循環數據。我們經常選擇在訓練上評估模型并測試批次并記錄準確率和損失。我們可以看到,經過 500 代,我們可以在測試數據上快速達到 96%-97%的準確率:
```py
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_acc = []
for i in range(generations):
rand_index = np.random.choice(len(train_xdata), size=batch_size)
rand_x = train_xdata[rand_index]
rand_x = np.expand_dims(rand_x, 3)
rand_y = train_labels[rand_index]
train_dict = {x_input: rand_x, y_target: rand_y}
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict=train_dict)
temp_train_loss, temp_train_preds = sess.run([loss, prediction], feed_dict=train_dict)
temp_train_acc = get_accuracy(temp_train_preds, rand_y)
if (i+1) % eval_every == 0:
eval_index = np.random.choice(len(test_xdata), size=evaluation_size)
eval_x = test_xdata[eval_index]
eval_x = np.expand_dims(eval_x, 3)
eval_y = test_labels[eval_index]
test_dict = {eval_input: eval_x, eval_target: eval_y}
test_preds = sess.run(test_prediction, feed_dict=test_dict)
temp_test_acc = get_accuracy(test_preds, eval_y)
# Record and print results
train_loss.append(temp_train_loss)
train_acc.append(temp_train_acc)
test_acc.append(temp_test_acc)
acc_and_loss = [(i+1), temp_train_loss, temp_train_acc, temp_test_acc]
acc_and_loss = [np.round(x,2) for x in acc_and_loss]
print('Generation # {}. Train Loss: {:.2f}. Train Acc (Test Acc): {:.2f} ({:.2f})'.format(*acc_and_loss))
```
1. 這導致以下輸出:
```py
Generation # 5\. Train Loss: 2.37\. Train Acc (Test Acc): 7.00 (9.80)
Generation # 10\. Train Loss: 2.16\. Train Acc (Test Acc): 31.00 (22.00)
Generation # 15\. Train Loss: 2.11\. Train Acc (Test Acc): 36.00 (35.20)
...
Generation # 490\. Train Loss: 0.06\. Train Acc (Test Acc): 98.00 (97.40)
Generation # 495\. Train Loss: 0.10\. Train Acc (Test Acc): 98.00 (95.40)
Generation # 500\. Train Loss: 0.14\. Train Acc (Test Acc): 98.00 (96.00)
```
1. 以下是使用`Matplotlib`繪制損耗和精度的代碼:
```py
eval_indices = range(0, generations, eval_every)
# Plot loss over time
plt.plot(eval_indices, train_loss, 'k-')
plt.title('Softmax Loss per Generation')
plt.xlabel('Generation')
plt.ylabel('Softmax Loss')
plt.show()
# Plot train and test accuracy
plt.plot(eval_indices, train_acc, 'k-', label='Train Set Accuracy')
plt.plot(eval_indices, test_acc, 'r--', label='Test Set Accuracy')
plt.title('Train and Test Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Generation')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.show()
```
然后我們得到以下圖:
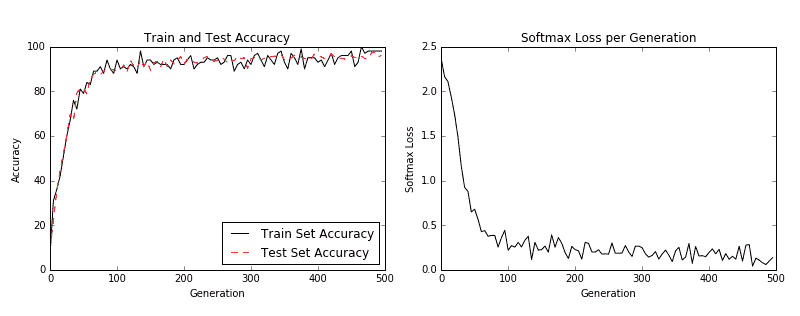
圖 3:左圖是我們 500 代訓練中的訓練和測試集精度。右圖是超過 500 代的 softmax 損失值。
1. 如果我們想要繪制最新批次結果的樣本,下面是繪制由六個最新結果組成的樣本的代碼:
```py
# Plot the 6 of the last batch results:
actuals = rand_y[0:6]
predictions = np.argmax(temp_train_preds,axis=1)[0:6]
images = np.squeeze(rand_x[0:6])
Nrows = 2
Ncols = 3
for i in range(6):
plt.subplot(Nrows, Ncols, i+1)
plt.imshow(np.reshape(images[i], [28,28]), cmap='Greys_r')
plt.title('Actual: ' + str(actuals[i]) + ' Pred: ' + str(predictions[i]), fontsize=10)
frame = plt.gca()
frame.axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
frame.axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
```
我們得到前面代碼的以下輸出:

圖 4:六個隨機圖像的繪圖,標題中包含實際值和預測值。右下圖預計是 3,而事實上它是 1
## 工作原理
我們提高了 MNIST 數據集的表現,并構建了一個模型,在從頭開始訓練時,可快速達到約 97%的準確率。我們的前兩層是卷積,ReLU 和 Max Pooling 的組合。第二層是完全連接的層。我們以 100 個批次進行了訓練,并研究了我們訓練的幾代的準確率和損失。最后,我們還繪制了六個隨機數字和每個數字的預測/實際值。
CNN 非常適合圖像識別。造成這種情況的部分原因是卷積層創建了自己的低級特征,當它們遇到重要的部分圖像時會被激活。這種類型的模型自己創建特征并將其用于預測。
## 更多
在過去幾年中,CNN 模型在圖像識別方面取得了巨大進步。正在探索許多新穎的想法,并且經常發現新的架構。該領域的一個很好的論文庫是一個名為 Arxiv.org( [https://arxiv.org/](https://arxiv.org/) )的倉庫網站,由康奈爾大學創建和維護。 Arxiv.org 包括許多領域的一些最新論文,包括計算機科學和計算機科學子領域,如計算機視覺和圖像識別( [https://arxiv.org/list/cs.CV/recent](https://arxiv.org/list/cs.CV/recent) )。
## 另見
以下列出了一些可用于了解 CNN 的優秀資源:
* 斯坦福大學有一個很棒的維基: [http://scarlet.stanford.edu/teach/index.php/An_Introduction_to_Convolutional_Neural_Networks](http://scarlet.stanford.edu/teach/index.php/An_Introduction_to_Convolutional_Neural_Networks)
* 邁克爾·尼爾森的深度學習,在這里找到: [http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/chap6.html](http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/chap6.html)
* 吳建新介紹卷積神經網絡,在此處找到: [https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/450c/a19932fcef1ca6d0442cbf52fec38fb9d1e5.pdf](https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/450c/a19932fcef1ca6d0442cbf52fec38fb9d1e5.pdf)
- TensorFlow 入門
- 介紹
- TensorFlow 如何工作
- 聲明變量和張量
- 使用占位符和變量
- 使用矩陣
- 聲明操作符
- 實現激活函數
- 使用數據源
- 其他資源
- TensorFlow 的方式
- 介紹
- 計算圖中的操作
- 對嵌套操作分層
- 使用多個層
- 實現損失函數
- 實現反向傳播
- 使用批量和隨機訓練
- 把所有東西結合在一起
- 評估模型
- 線性回歸
- 介紹
- 使用矩陣逆方法
- 實現分解方法
- 學習 TensorFlow 線性回歸方法
- 理解線性回歸中的損失函數
- 實現 deming 回歸
- 實現套索和嶺回歸
- 實現彈性網絡回歸
- 實現邏輯回歸
- 支持向量機
- 介紹
- 使用線性 SVM
- 簡化為線性回歸
- 在 TensorFlow 中使用內核
- 實現非線性 SVM
- 實現多類 SVM
- 最近鄰方法
- 介紹
- 使用最近鄰
- 使用基于文本的距離
- 使用混合距離函數的計算
- 使用地址匹配的示例
- 使用最近鄰進行圖像識別
- 神經網絡
- 介紹
- 實現操作門
- 使用門和激活函數
- 實現單層神經網絡
- 實現不同的層
- 使用多層神經網絡
- 改進線性模型的預測
- 學習玩井字棋
- 自然語言處理
- 介紹
- 使用詞袋嵌入
- 實現 TF-IDF
- 使用 Skip-Gram 嵌入
- 使用 CBOW 嵌入
- 使用 word2vec 進行預測
- 使用 doc2vec 進行情緒分析
- 卷積神經網絡
- 介紹
- 實現簡單的 CNN
- 實現先進的 CNN
- 重新訓練現有的 CNN 模型
- 應用 StyleNet 和 NeuralStyle 項目
- 實現 DeepDream
- 循環神經網絡
- 介紹
- 為垃圾郵件預測實現 RNN
- 實現 LSTM 模型
- 堆疊多個 LSTM 層
- 創建序列到序列模型
- 訓練 Siamese RNN 相似性度量
- 將 TensorFlow 投入生產
- 介紹
- 實現單元測試
- 使用多個執行程序
- 并行化 TensorFlow
- 將 TensorFlow 投入生產
- 生產環境 TensorFlow 的一個例子
- 使用 TensorFlow 服務
- 更多 TensorFlow
- 介紹
- 可視化 TensorBoard 中的圖
- 使用遺傳算法
- 使用 k 均值聚類
- 求解常微分方程組
- 使用隨機森林
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras
