# 實現非線性 SVM
對于此秘籍,我們將應用非線性內核來拆分數據集。
## 做好準備
在本節中,我們將在實際數據上實現前面的高斯核 SVM。我們將加載虹膜數據集并為 I. setosa 創建分類器(與非 setosa 相比)。我們將看到各種伽馬值對分類的影響。
## 操作步驟
我們按如下方式處理秘籍:
1. 我們首先加載必要的庫,其中包括`scikit-learn`數據集,以便我們可以加載虹膜數據。然后,我們將開始圖會話。使用以下代碼:
```py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn import datasets
sess = tf.Session()
```
1. 接下來,我們將加載虹膜數據,提取萼片長度和花瓣寬度,并分離每個類的`x`和`y`值(以便以后繪圖),如下所示:
```py
iris = datasets.load_iris()
x_vals = np.array([[x[0], x[3]] for x in iris.data])
y_vals = np.array([1 if y==0 else -1 for y in iris.target])
class1_x = [x[0] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if y_vals[i]==1]
class1_y = [x[1] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if y_vals[i]==1]
class2_x = [x[0] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if y_vals[i]==-1]
class2_y = [x[1] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if y_vals[i]==-1]
```
1. 現在,我們聲明我們的批量大小(首選大批量),占位符和模型變量`b`,如下所示:
```py
batch_size = 100
x_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 2], dtype=tf.float32)
y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32)
prediction_grid = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 2], dtype=tf.float32)
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,batch_size]))
```
1. 接下來,我們聲明我們的高斯內核。這個內核依賴于伽馬值,我們將在本文后面的各個伽瑪值對分類的影響進行說明。使用以下代碼:
```py
gamma = tf.constant(-10.0)
dist = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(x_data), 1)
dist = tf.reshape(dist, [-1,1])
sq_dists = tf.add(tf.subtract(dist, tf.multiply(2., tf.matmul(x_data, tf.transpose(x_data)))), tf.transpose(dist))
my_kernel = tf.exp(tf.multiply(gamma, tf.abs(sq_dists)))
# We now compute the loss for the dual optimization problem, as follows:
model_output = tf.matmul(b, my_kernel)
first_term = tf.reduce_sum(b)
b_vec_cross = tf.matmul(tf.transpose(b), b)
y_target_cross = tf.matmul(y_target, tf.transpose(y_target))
second_term = tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(my_kernel, tf.multiply(b_vec_cross, y_target_cross)))
loss = tf.negative(tf.subtract(first_term, second_term))
```
1. 為了使用 SVM 執行預測,我們必須創建預測內核函數。之后,我們還會聲明一個準確率計算,它只是使用以下代碼正確分類的點的百分比:
```py
rA = tf.reshape(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(x_data), 1),[-1,1])
rB = tf.reshape(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(prediction_grid), 1),[-1,1])
pred_sq_dist = tf.add(tf.subtract(rA, tf.mul(2., tf.matmul(x_data, tf.transpose(prediction_grid)))), tf.transpose(rB))
pred_kernel = tf.exp(tf.multiply(gamma, tf.abs(pred_sq_dist)))
prediction_output = tf.matmul(tf.multiply(tf.transpose(y_target),b), pred_kernel)
prediction = tf.sign(prediction_output-tf.reduce_mean(prediction_output))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(tf.squeeze(prediction), tf.squeeze(y_target)), tf.float32))
```
1. 接下來,我們聲明我們的優化函數并初始化變量,如下所示:
```py
my_opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01)
train_step = my_opt.minimize(loss)
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
sess.run(init)
```
1. 現在,我們可以開始訓練循環了。我們運行循環 300 次迭代并存儲損失值和批次精度。為此,我們使用以下實現:
```py
loss_vec = []
batch_accuracy = []
for i in range(300):
rand_index = np.random.choice(len(x_vals), size=batch_size)
rand_x = x_vals[rand_index]
rand_y = np.transpose([y_vals[rand_index]])
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y})
temp_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y})
loss_vec.append(temp_loss)
acc_temp = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x,
y_target: rand_y,
prediction_grid:rand_x})
batch_accuracy.append(acc_temp)
```
1. 為了繪制決策邊界,我們將創建`x`,`y`點的網格并評估我們在所有這些點上創建的預測函數,如下所示:
```py
x_min, x_max = x_vals[:, 0].min() - 1, x_vals[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = x_vals[:, 1].min() - 1, x_vals[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.02),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.02))
grid_points = np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]
[grid_predictions] = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={x_data: x_vals,
y_target: np.transpose([y_vals]),
prediction_grid: grid_points})
grid_predictions = grid_predictions.reshape(xx.shape)
```
1. 為簡潔起見,我們只展示如何用決策邊界繪制點。有關 gamma 的圖和效果,請參閱本秘籍的下一部分。使用以下代碼:
```py
plt.contourf(xx, yy, grid_predictions, cmap=plt.cm.Paired, alpha=0.8)
plt.plot(class1_x, class1_y, 'ro', label='I. setosa')
plt.plot(class2_x, class2_y, 'kx', label='Non-setosa')
plt.title('Gaussian SVM Results on Iris Data')
plt.xlabel('Petal Length')
plt.ylabel('Sepal Width')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.ylim([-0.5, 3.0])
plt.xlim([3.5, 8.5])
plt.show()
```
## 工作原理
以下是對四種不同伽瑪值(1,10,25 和 100)的 I. setosa 結果的分類。注意伽瑪值越高,每個單獨點對分類邊界的影響越大:
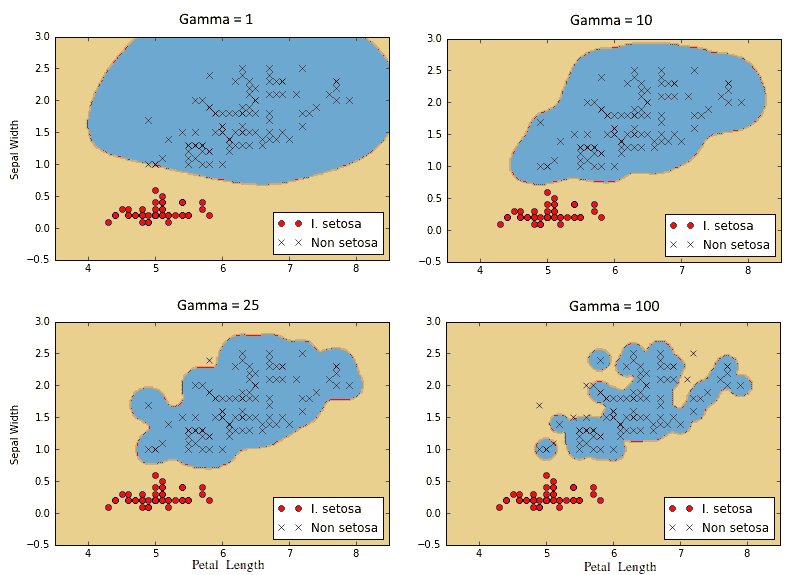
圖 9:使用具有四個不同伽馬值的高斯核 SVM 的 I. setosa 的分類結果
- TensorFlow 入門
- 介紹
- TensorFlow 如何工作
- 聲明變量和張量
- 使用占位符和變量
- 使用矩陣
- 聲明操作符
- 實現激活函數
- 使用數據源
- 其他資源
- TensorFlow 的方式
- 介紹
- 計算圖中的操作
- 對嵌套操作分層
- 使用多個層
- 實現損失函數
- 實現反向傳播
- 使用批量和隨機訓練
- 把所有東西結合在一起
- 評估模型
- 線性回歸
- 介紹
- 使用矩陣逆方法
- 實現分解方法
- 學習 TensorFlow 線性回歸方法
- 理解線性回歸中的損失函數
- 實現 deming 回歸
- 實現套索和嶺回歸
- 實現彈性網絡回歸
- 實現邏輯回歸
- 支持向量機
- 介紹
- 使用線性 SVM
- 簡化為線性回歸
- 在 TensorFlow 中使用內核
- 實現非線性 SVM
- 實現多類 SVM
- 最近鄰方法
- 介紹
- 使用最近鄰
- 使用基于文本的距離
- 使用混合距離函數的計算
- 使用地址匹配的示例
- 使用最近鄰進行圖像識別
- 神經網絡
- 介紹
- 實現操作門
- 使用門和激活函數
- 實現單層神經網絡
- 實現不同的層
- 使用多層神經網絡
- 改進線性模型的預測
- 學習玩井字棋
- 自然語言處理
- 介紹
- 使用詞袋嵌入
- 實現 TF-IDF
- 使用 Skip-Gram 嵌入
- 使用 CBOW 嵌入
- 使用 word2vec 進行預測
- 使用 doc2vec 進行情緒分析
- 卷積神經網絡
- 介紹
- 實現簡單的 CNN
- 實現先進的 CNN
- 重新訓練現有的 CNN 模型
- 應用 StyleNet 和 NeuralStyle 項目
- 實現 DeepDream
- 循環神經網絡
- 介紹
- 為垃圾郵件預測實現 RNN
- 實現 LSTM 模型
- 堆疊多個 LSTM 層
- 創建序列到序列模型
- 訓練 Siamese RNN 相似性度量
- 將 TensorFlow 投入生產
- 介紹
- 實現單元測試
- 使用多個執行程序
- 并行化 TensorFlow
- 將 TensorFlow 投入生產
- 生產環境 TensorFlow 的一個例子
- 使用 TensorFlow 服務
- 更多 TensorFlow
- 介紹
- 可視化 TensorBoard 中的圖
- 使用遺傳算法
- 使用 k 均值聚類
- 求解常微分方程組
- 使用隨機森林
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras
