# 使用基于文本的距離
最近鄰居比處理數字更通用。只要我們有一種方法來測量特征之間的距離,我們就可以應用最近鄰算法。在本文中,我們將介紹如何使用 TensorFlow 測量文本距離。
## 做好準備
在本文中,我們將說明如何在字符串之間使用 TensorFlow 的文本距離度量,Levenshtein 距離(編輯距離)。這將在本章后面重要,因為我們擴展了最近鄰方法以包含帶有文本的特征。
Levenshtein 距離是從一個字符串到另一個字符串的最小編輯次數。允許的編輯是插入字符,刪除字符或用不同的字符替換字符。對于這個秘籍,我們將使用 TensorFlow 的 Levenshtein 距離函數`edit_distance()`。值得說明這個函數的用法,因為它的用法將適用于后面的章節。
> 請注意,TensorFlow 的`edit_distance()`函數僅接受稀疏張量。我們必須創建我們的字符串作為單個字符的稀疏張量。
## 操作步驟
1. 首先,我們將加載 TensorFlow 并初始化圖:
```py
import tensorflow as tf
sess = tf.Session()
```
1. 然后,我們將說明如何計算兩個單詞`'bear'`和`'beer'`之間的編輯距離。首先,我們將使用 Python 的`list()`函數從我們的字符串創建一個字符列表。接下來,我們將從該列表中創建一個稀疏的 3D 矩陣。我們必須告訴 TensorFlow 字符索引,矩陣的形狀以及我們在張量中想要的字符。之后,我們可以決定是否要使用總編輯距離`(normalize=False)`或標準化編輯距離`(normalize=True)`,我們將編輯距離除以第二個單詞的長度:
```py
hypothesis = list('bear')
truth = list('beers')
h1 = tf.SparseTensor([[0,0,0], [0,0,1], [0,0,2], [0,0,3]],
hypothesis, [1,1,1])
t1 = tf.SparseTensor([[0,0,0], [0,0,1], [0,0,1], [0,0,3],[0,0,4]], truth, [1,1,1])
print(sess.run(tf.edit_distance(h1, t1, normalize=False)))
[[ 2.]]
```
> TensorFlow 的文檔將兩個字符串視為提議(假設)字符串和基礎事實字符串。我們將在這里用`h`和`t`張量繼續這個表示法。函數`SparseTensorValue()`是一種在 TensorFlow 中創建稀疏張量的方法。它接受我們希望創建的稀疏張量的索引,值和形狀。
1. 接下來,我們將說明如何將兩個單詞`bear`和`beer`與另一個單詞`beers`進行比較。為了達到這個目的,我們必須復制`beers`以獲得相同數量的可比詞:
```py
hypothesis2 = list('bearbeer')
truth2 = list('beersbeers')
h2 = tf.SparseTensor([[0,0,0], [0,0,1], [0,0,2], [0,0,3], [0,1,0], [0,1,1], [0,1,2], [0,1,3]], hypothesis2, [1,2,4])
t2 = tf.SparseTensor([[0,0,0], [0,0,1], [0,0,2], [0,0,3], [0,0,4], [0,1,0], [0,1,1], [0,1,2], [0,1,3], [0,1,4]], truth2, [1,2,5])
print(sess.run(tf.edit_distance(h2, t2, normalize=True)))
[[ 0.40000001 0.2 ]]
```
1. 在此示例中顯示了將一組單詞與另一單詞進行比較的更有效方法。我們將事先為假設和基本真實字符串創建索引和字符列表:
```py
hypothesis_words = ['bear','bar','tensor','flow']
truth_word = ['beers'']
num_h_words = len(hypothesis_words)
h_indices = [[xi, 0, yi] for xi,x in enumerate(hypothesis_words) for yi,y in enumerate(x)]
h_chars = list(''.join(hypothesis_words))
h3 = tf.SparseTensor(h_indices, h_chars, [num_h_words,1,1])
truth_word_vec = truth_word*num_h_words
t_indices = [[xi, 0, yi] for xi,x in enumerate(truth_word_vec) for yi,y in enumerate(x)]
t_chars = list(''.join(truth_word_vec))
t3 = tf.SparseTensor(t_indices, t_chars, [num_h_words,1,1])
print(sess.run(tf.edit_distance(h3, t3, normalize=True)))
[[ 0.40000001]
[ 0.60000002]
[ 0.80000001]
[ 1\. ]]
```
1. 現在,我們將說明如何使用占位符計算兩個單詞列表之間的編輯距離。這個概念是一樣的,除了我們將`SparseTensorValue()`而不是稀疏張量。首先,我們將創建一個從單詞列表創建稀疏張量的函數:
```py
def create_sparse_vec(word_list):
num_words = len(word_list)
indices = [[xi, 0, yi] for xi,x in enumerate(word_list) for yi,y in enumerate(x)]
chars = list(''.join(word_list))
return(tf.SparseTensorValue(indices, chars, [num_words,1,1]))
hyp_string_sparse = create_sparse_vec(hypothesis_words)
truth_string_sparse = create_sparse_vec(truth_word*len(hypothesis_words))
hyp_input = tf.sparse_placeholder(dtype=tf.string)
truth_input = tf.sparse_placeholder(dtype=tf.string)
edit_distances = tf.edit_distance(hyp_input, truth_input, normalize=True)
feed_dict = {hyp_input: hyp_string_sparse,
truth_input: truth_string_sparse}
print(sess.run(edit_distances, feed_dict=feed_dict))
[[ 0.40000001]
[ 0.60000002]
[ 0.80000001]
[ 1\. ]]
```
## 工作原理
在這個秘籍中,我們展示了我們可以使用 TensorFlow 以多種方式測量文本距離。這對于在具有文本特征的數據上執行最近鄰居非常有用。當我們執行地址匹配時,我們將在本章后面看到更多內容。
## 更多
我們應該討論其他文本距離指標。這是一個定義表,描述了兩個字符串`s1`和`s2`之間的其他文本距離:
| 名稱 | 描述 | 公式 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| 漢明距離 | 相同位置的相等字符的數量。僅在字符串長度相等時有效。 | 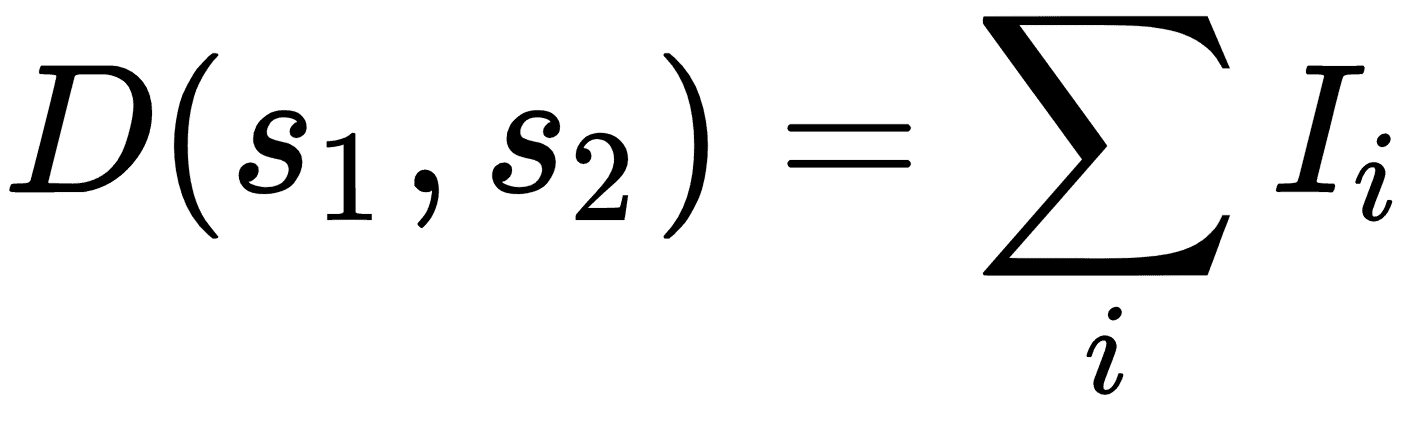,其中`I`是相等字符的指示函數。 |
| 余弦距離 | `k` - 差異的點積除以`k` - 差異的 L2 范數。 | 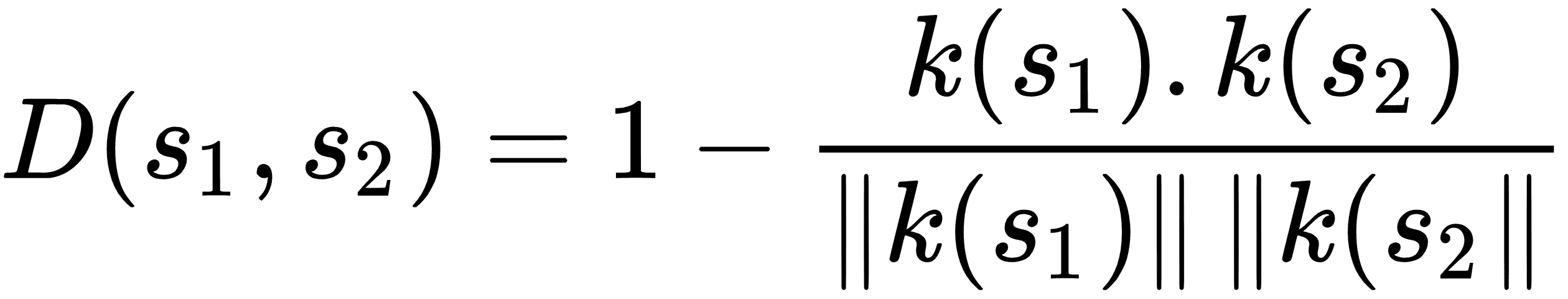 |
| 雅克卡距離 | 共同的字符數除以兩個字符串中的字符總和。 | 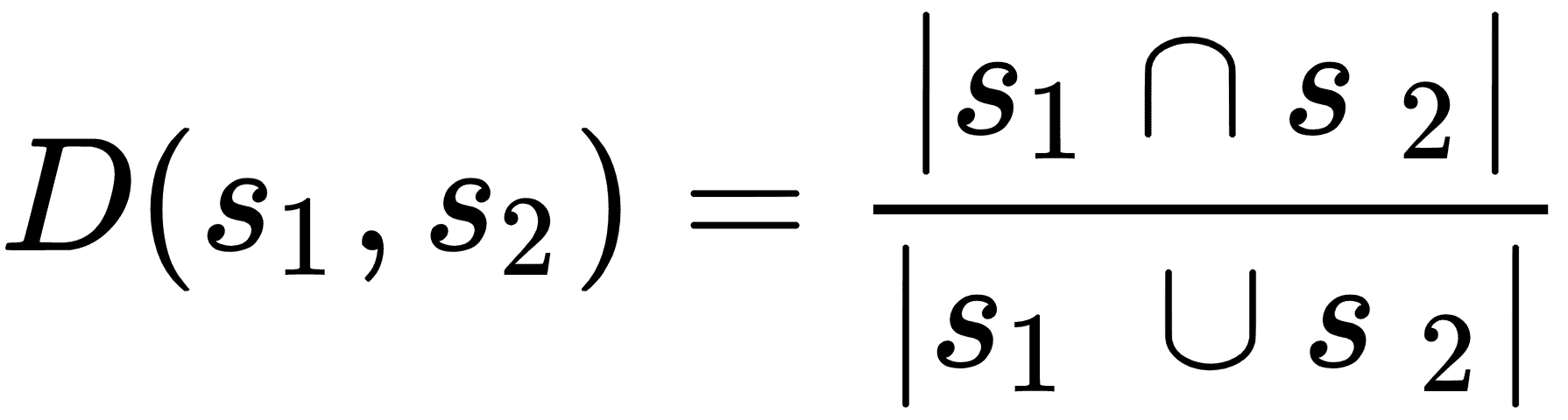 |
- TensorFlow 入門
- 介紹
- TensorFlow 如何工作
- 聲明變量和張量
- 使用占位符和變量
- 使用矩陣
- 聲明操作符
- 實現激活函數
- 使用數據源
- 其他資源
- TensorFlow 的方式
- 介紹
- 計算圖中的操作
- 對嵌套操作分層
- 使用多個層
- 實現損失函數
- 實現反向傳播
- 使用批量和隨機訓練
- 把所有東西結合在一起
- 評估模型
- 線性回歸
- 介紹
- 使用矩陣逆方法
- 實現分解方法
- 學習 TensorFlow 線性回歸方法
- 理解線性回歸中的損失函數
- 實現 deming 回歸
- 實現套索和嶺回歸
- 實現彈性網絡回歸
- 實現邏輯回歸
- 支持向量機
- 介紹
- 使用線性 SVM
- 簡化為線性回歸
- 在 TensorFlow 中使用內核
- 實現非線性 SVM
- 實現多類 SVM
- 最近鄰方法
- 介紹
- 使用最近鄰
- 使用基于文本的距離
- 使用混合距離函數的計算
- 使用地址匹配的示例
- 使用最近鄰進行圖像識別
- 神經網絡
- 介紹
- 實現操作門
- 使用門和激活函數
- 實現單層神經網絡
- 實現不同的層
- 使用多層神經網絡
- 改進線性模型的預測
- 學習玩井字棋
- 自然語言處理
- 介紹
- 使用詞袋嵌入
- 實現 TF-IDF
- 使用 Skip-Gram 嵌入
- 使用 CBOW 嵌入
- 使用 word2vec 進行預測
- 使用 doc2vec 進行情緒分析
- 卷積神經網絡
- 介紹
- 實現簡單的 CNN
- 實現先進的 CNN
- 重新訓練現有的 CNN 模型
- 應用 StyleNet 和 NeuralStyle 項目
- 實現 DeepDream
- 循環神經網絡
- 介紹
- 為垃圾郵件預測實現 RNN
- 實現 LSTM 模型
- 堆疊多個 LSTM 層
- 創建序列到序列模型
- 訓練 Siamese RNN 相似性度量
- 將 TensorFlow 投入生產
- 介紹
- 實現單元測試
- 使用多個執行程序
- 并行化 TensorFlow
- 將 TensorFlow 投入生產
- 生產環境 TensorFlow 的一個例子
- 使用 TensorFlow 服務
- 更多 TensorFlow
- 介紹
- 可視化 TensorBoard 中的圖
- 使用遺傳算法
- 使用 k 均值聚類
- 求解常微分方程組
- 使用隨機森林
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras
