# Serverless
> 原文:[https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/project/clusters/serverless/](https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/project/clusters/serverless/)
* [Overview](#overview)
* [Knative](#knative)
* [Prerequisites](#prerequisites)
* [Installing Knative via GitLab’s Kubernetes integration](#installing-knative-via-gitlabs-kubernetes-integration)
* [Using an existing installation of Knative](#using-an-existing-installation-of-knative)
* [Supported runtimes](#supported-runtimes)
* [GitLab-managed runtimes](#gitlab-managed-runtimes)
* [OpenFaaS runtimes](#openfaas-runtimes)
* [Deploying functions](#deploying-functions)
* [`service`](#service)
* [`provider`](#provider)
* [`functions`](#functions)
* [Deployment](#deployment)
* [Runtime aliases](#runtime-aliases)
* [Secrets](#secrets)
* [CLI example](#cli-example)
* [Part of deployment job](#part-of-deployment-job)
* [Running functions locally](#running-functions-locally)
* [Deploying Serverless applications](#deploying-serverless-applications)
* [Deploy the application with Knative](#deploy-the-application-with-knative)
* [Function details](#function-details)
* [Invocation metrics](#invocation-metrics)
* [Configuring logging](#configuring-logging)
* [Prerequisites](#prerequisites-1)
* [Enable request log template](#enable-request-log-template)
* [Enable request logs](#enable-request-logs)
* [Viewing request logs](#viewing-request-logs)
* [Enabling TLS for Knative services](#enabling-tls-for-knative-services)
* [Using an older version of `gitlabktl`](#using-an-older-version-of-gitlabktl)
# Serverless[](#serverless "Permalink")
在 GitLab 11.5 中引入.
**警告:** Serverless 目前處于[alpha 狀態](https://about.gitlab.com/handbook/product/#alpha) .
## Overview[](#overview "Permalink")
無服務器架構為運營商和開發人員提供了在不配置單個服務器的情況下編寫高度可擴展的應用程序的能力.
GitLab 支持在 Kubernetes 環境和主要的云 FAAS 環境中部署無服務器應用程序的幾種方法.
目前,我們支持:
* [Knative](#knative) :在 GKE 和 EKS 上使用 Knative 和`gitlabktl`構建 Knative 應用程序.
* [AWS Lambda](aws.html) :通過無服務器框架和 GitLab CI / CD 創建無服務器應用程序.
## Knative[](#knative "Permalink")
使用[Knative](https://cloud.google.com/knative/)在 Kubernetes 上運行無服務器工作負載.
Knative 擴展了 Kubernetes 以提供一組中間件組件,這些組件對于構建現代的,以源為中心的,基于容器的應用程序很有用. Knative 通過其主要組件帶來了一些明顯的好處:
* [服務](https://github.com/knative/serving) :請求驅動的計算,可擴展為零.
* [事件](https://github.com/knative/eventing) : [事件的](https://github.com/knative/eventing)管理和交付.
有關 Knative 的更多信息,請訪問[Knative docs 資源庫](https://github.com/knative/docs) .
借助 GitLab Serverless,您可以部署功能即服務(FaaS)和無服務器應用程序.
## Prerequisites[](#prerequisites "Permalink")
要在 GitLab 上運行 Knative,您需要:
1. **現有的 GitLab 項目:**您將需要一個 GitLab 項目來關聯所有資源. 最簡單的入門方法:
* 如果您打算[部署功能](#deploying-functions) ,請克隆[功能示例項目](https://gitlab.com/knative-examples/functions)以開始使用.
* 如果您打算[部署無服務器應用程序](#deploying-serverless-applications) ,請克隆示例[Knative Ruby App](https://gitlab.com/knative-examples/knative-ruby-app)以開始使用.
2. **Kubernetes 集群:**部署 Knative 需要啟用 RBAC 的 Kubernetes 集群. 最簡單的入門方法是使用 GitLab 的[GKE 集成](../add_remove_clusters.html)添加集群. 建議的運行 Knative 的最低建議群集規格為 3 個節點,6 個 vCPU 和 22.50 GB 內存.
3. **GitLab 運行程序:**運行 CI 作業需要運行程序,該作業會將無服務器的應用程序或功能部署到您的集群上. 您可以將 GitLab Runner 安裝到現有的 Kubernetes 集群上. 有關更多信息,請參見[安裝應用程序](../index.html#installing-applications) .
4. **域名:** Knative 將使用 Istio 提供自己的負載平衡器. 它將為 Knative 服務的所有應用程序提供一個外部 IP 地址或主機名. 系統將提示您輸入一個通配符域,將在其中提供您的應用程序. 配置您的 DNS 服務器以使用該域的外部 IP 地址或主機名.
5. **`.gitlab-ci.yml` :** GitLab 使用[Kaniko](https://github.com/GoogleContainerTools/kaniko)來構建應用程序. 我們還使用[GitLab Knative 工具](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlabktl) CLI 來簡化向 Knative 部署服務和功能.
6. **`serverless.yml`** ( [僅](#deploying-functions)適用于[功能](#deploying-functions) ):使用 lessserver 部署功能時, `serverless.yml`文件將包含存儲庫中托管的所有功能的信息以及所使用的運行時的引用.
7. **`Dockerfile`** ( [僅](#deploying-serverless-applications)適用于[應用程序](#deploying-serverless-applications) ):Knative 需要`Dockerfile`才能構建您的應用程序. 它應該包含在項目存儲庫的根目錄中,并公開端口`8080` . 如果您打算使用我們的[運行時](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/serverless/runtimes)來構建無服務器功能,則不需要`Dockerfile` .
8. **Prometheus** (可選):安裝 Prometheus 可使您監視無服務器功能/應用程序的規模和流量. 有關更多信息,請參見[安裝應用程序](../index.html#installing-applications) .
9. **日志記錄** (可選):配置日志記錄可讓您查看和搜索無服務器功能/應用程序的請求日志. 有關更多信息,請參見[配置日志記錄](#configuring-logging) .
## Installing Knative via GitLab’s Kubernetes integration[](#installing-knative-via-gitlabs-kubernetes-integration "Permalink")
**注意:**運行 Knative 的最小建議群集大小是 3 節點,6 vCPU 和 22.50 GB 內存. **必須啟用 RBAC.**
1. [Add a Kubernetes cluster](../add_remove_clusters.html).
2. 選擇" **應用程序"**選項卡,然后向下滾動到" Knative 應用程序"部分. 輸入要用于您的應用程序/功能的域(例如`example.com` ),然后單擊**Install** .
[](img/install-knative.png)
3. Knative 安裝完成后,您可以等待 IP 地址或主機名顯示在**Knative Endpoint**字段中,或[手動檢索 Istio Ingress 端點](../../../clusters/applications.html#determining-the-external-endpoint-manually) .
**注意:**在集群上運行`kubectl`命令需要首先設置對集群的訪問. 對于在 GKE 上創建的集群,請參見[GKE 集群訪問](https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/how-to/cluster-access-for-kubectl) ,對于其他平臺,請[安裝 kubectl](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/install-kubectl/) .
4. 入口現在在此地址可用,并將基于請求中的 DNS 名稱將傳入請求路由到適當的服務. 為此,應為所需的域名創建通配符 DNS 記錄. 例如,如果您的 Knative 基礎域是`knative.info`則需要創建一個 A 記錄或 CNAME 記錄,其域`*.knative.info`指向 Ingress 的 IP 地址或主機名.
[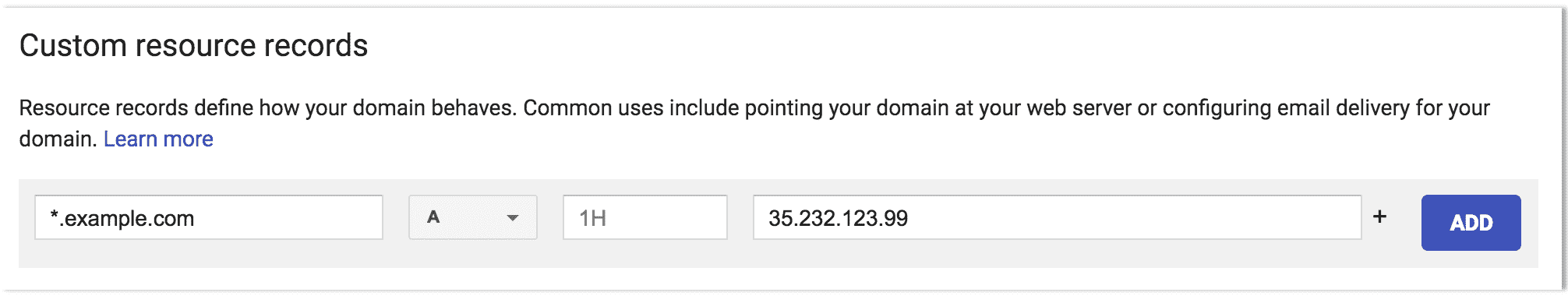](img/dns-entry.png)
**注意:**可以在給定項目上部署[功能](#deploying-functions)或[無服務器應用程序](#deploying-serverless-applications) ,但不能兩者都部署. 當前實現利用了的`serverless.yml`文件發信號 FAAS 項目.
## Using an existing installation of Knative[](#using-an-existing-installation-of-knative "Permalink")
[Introduced](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-foss/-/issues/58941) in GitLab 12.0.
**注意:**添加現有的 Knative 安裝時,GitLabless server 的"調用"監視功能將不起作用.
也可以將 GitLab Serverless 與已經安裝 Knative 的現有 Kubernetes 集群一起使用.
您必須執行以下操作:
1. 按照步驟[添加現有的 Kubernetes 集群](../add_remove_clusters.html#add-existing-cluster) .
2. 確保 GitLab 可以管理 Knative:
* 對于非 GitLab 托管群集,請確保提供的令牌的服務帳戶可以管理`serving.knative.dev` API 組中的資源.
* 對于 GitLab 托管群集,如果您在[GitLab 12.1 或更高版本中](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-foss/-/merge_requests/30235)添加了群集,則 GitLab 將已經具有所需的訪問權限,您可以繼續進行下一步.
否則,您需要手動授權 GitLab 的服務帳戶具有管理`serving.knative.dev` API 組中資源的能力. 由于每個 GitLab 服務帳戶都具有`edit`集群角色,因此最簡單的方法是通過將默認規則添加到默認`edit`集群角色的[聚合 ClusterRole](https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/rbac/#aggregated-clusterroles) :首先,將以下 YAML 保存為`knative-serving-only-role.yaml` :
```
apiVersion : rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind : ClusterRole metadata : name : knative-serving-only-role labels : rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-edit : " true" rules : - apiGroups : - serving.knative.dev resources : - configurations - configurationgenerations - routes - revisions - revisionuids - autoscalers - services verbs : - get - list - create - update - delete - patch - watch
```
然后運行以下命令:
```
kubectl apply -f knative-serving-only-role.yaml
```
如果您希望基于每個服務帳戶授予權限,則可以使用特定于服務帳戶和名稱空間的`Role`和`RoleBinding`來執行此操作.
3. 請按照以下步驟將[功能](#deploying-functions)或[無服務器應用程序](#deploying-serverless-applications)部署到群集上.
## Supported runtimes[](#supported-runtimes "Permalink")
GitLab 的無服務器功能可以使用以下命令運行:
* [GitLab-managed](#gitlab-managed-runtimes) runtimes.
* [OpenFaaS](#openfaas-runtimes) runtimes.
如果所需的編程語言無法使用運行時,請考慮部署[無服務器應用程序](#deploying-serverless-applications) .
### GitLab-managed runtimes[](#gitlab-managed-runtimes "Permalink")
當前,以下 GitLab 管理的[運行時](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/serverless/runtimes)可用:
* `go` (概念證明)
* `nodejs`
* `ruby`
如果未指定運行時,則必須提供一個`Dockerfile`來運行無服務器功能.
### OpenFaaS runtimes[](#openfaas-runtimes "Permalink")
在 GitLab 12.5 中[引入](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/issues/29253) .
[OpenFaaS 經典運行時](https://github.com/openfaas/templates#templates-in-store)可與 GitLab 無服務器一起使用.
OpenFaas 運行時可用于以下語言:
* C#
* Go
* NodeJS
* PHP
* Python
* Ruby
使用以下模式指定運行時: `openfaas/classic/<template_name>` . 下面的示例示出了如何定義一個函數`serverless.yml`使用 OpenFaaS 運行時:
```
hello:
source: ./hello
runtime: openfaas/classic/ruby
description: "Ruby function using OpenFaaS classic runtime"
```
`handler` is not needed for OpenFaaS functions. The location of the handler is defined by the conventions of the runtime.
有關使用 OpenFaaS 運行時的函數示例,請參見[`ruby-openfaas-function`](https://gitlab.com/knative-examples/ruby-openfaas-function)項目.
## Deploying functions[](#deploying-functions "Permalink")
在 GitLab 11.6 中引入.
您可以在**[功能示例項目中](https://gitlab.com/knative-examples/functions)**找到并導入此文檔中引用的所有文件.
請按照以下步驟將使用 Node.js 運行時的功能部署到您的 Knative 實例(如果您已克隆示例項目,則可以跳過以下步驟):
1. 創建一個目錄來容納該函數. 在此示例中,我們將在項目的根目錄創建一個名為`echo`的目錄.
2. 創建將包含功能代碼的文件. 在此示例中,我們的文件名為`echo.js` ,位于`echo`目錄中. 如果您的項目是:
* 公開,繼續下一步.
* 私有的,您將需要使用`gitlab-deploy-token`作為名稱和`read_registry`范圍[創建一個 GitLab 部署令牌](../../deploy_tokens/index.html#creating-a-deploy-token) .
3. `.gitlab-ci.yml` :這定義了用于部署功能的管道. 它必須包含在存儲庫的根目錄中:
```
include:
- template: Serverless.gitlab-ci.yml
functions:build:
extends: .serverless:build:functions
environment: production
functions:deploy:
extends: .serverless:deploy:functions
environment: production
```
這個`.gitlab-ci.yml`創建的作業會調用一些預定義的命令來構建功能并將其部署到集群中.
`Serverless.gitlab-ci.yml` is a template that allows customization. You can either import it with `include` parameter and use `extends` to customize your jobs, or you can inline the entire template by choosing it from **套用范本** dropdown when editing the `.gitlab-ci.yml` file through the user interface.
4. `serverless.yml` :此文件包含您的功能的元數據,例如名稱,運行時和環境.
它必須包含在存儲庫的根目錄中. 下面是一個示例`echo`函數,它顯示了文件所需的結構.
您可以在[功能示例項目中](https://gitlab.com/knative-examples/functions)找到該項目的相關文件.
```
service: functions
description: "GitLab Serverless functions using Knative"
provider:
name: triggermesh
envs:
FOO: value
secrets:
- my-secrets
functions:
echo-js:
handler: echo-js
source: ./echo-js
runtime: gitlab/runtimes/nodejs
description: "node.js runtime function"
envs:
MY_FUNCTION: echo-js
secrets:
- my-secrets
```
上面使用的字段的說明:
### `service`[](#service "Permalink")
| Parameter | Description |
| --- | --- |
| `service` | 服務該功能的 Knative 服務的名稱. |
| `description` | 在的簡短描述`service` . |
### `provider`[](#provider "Permalink")
| Parameter | Description |
| --- | --- |
| `name` | 指示使用哪個提供程序來執行`serverless.yml`文件. 在這種情況下,使用 TriggerMesh 中間件. |
| `envs` | 包括要在文件中**所有**函數的函數執行過程中傳遞的環境變量,其中`FOO`是變量名, `BAR`是變量內容. 您可以將其替換為自己的變量. |
| `secrets` | 包含 Kubernetes 機密的內容作為環境變量,可訪問該變量作為文件中**所有**函數的函數執行的一部分進行傳遞. 機密應采用 INI 格式. |
### `functions`[](#functions "Permalink")
在上面的`serverless.yml`示例中,函數名稱為`echo` ,隨后的行包含函數屬性.
| Parameter | Description |
| --- | --- |
| `handler` | 函數的名稱. |
| `source` | 具有功能源的目錄. |
| `runtime` (optional) | 用于執行功能的運行時. 這可以是運行時別名(請參閱[運行時別名](#runtime-aliases) ),也可以是自定義運行時存儲庫的完整 URL. 當未指定運行`Dockerfile` ,我們假定`Dockerfile`存在于`source`指定的函數目錄中. |
| `description` | 功能的簡短描述. |
| `envs` | 僅為特定功能設置環境變量. |
| `secrets` | 將 Kubernetes 機密的內容作為環境變量包含在內,這些變量只能作為特定函數的函數執行的一部分進行傳遞. 機密應采用 INI 格式. |
### Deployment[](#deployment "Permalink")
#### Runtime aliases[](#runtime-aliases "Permalink")
可選的`runtime`參數可以引用以下運行時別名之一(另請參閱[受支持的運行時](#supported-runtimes) ):
| 運行時別名 | 維護者 |
| --- | --- |
| `gitlab/runtimes/go` | GitLab |
| `gitlab/runtimes/nodejs` | GitLab |
| `gitlab/runtimes/ruby` | GitLab |
| `openfaas/classic/csharp` | OpenFaaS |
| `openfaas/classic/go` | OpenFaaS |
| `openfaas/classic/node` | OpenFaaS |
| `openfaas/classic/php7` | OpenFaaS |
| `openfaas/classic/python` | OpenFaaS |
| `openfaas/classic/python3` | OpenFaaS |
| `openfaas/classic/ruby` | OpenFaaS |
經過`gitlab-ci.yml`模板已添加和`serverless.yml`文件被創建,推動提交到您的項目將導致 CI 管道被執行,而部署的每個功能的 Knative 服務. 部署階段完成后,該功能的其他詳細信息將顯示在" **操作">"無服務器"下** .
[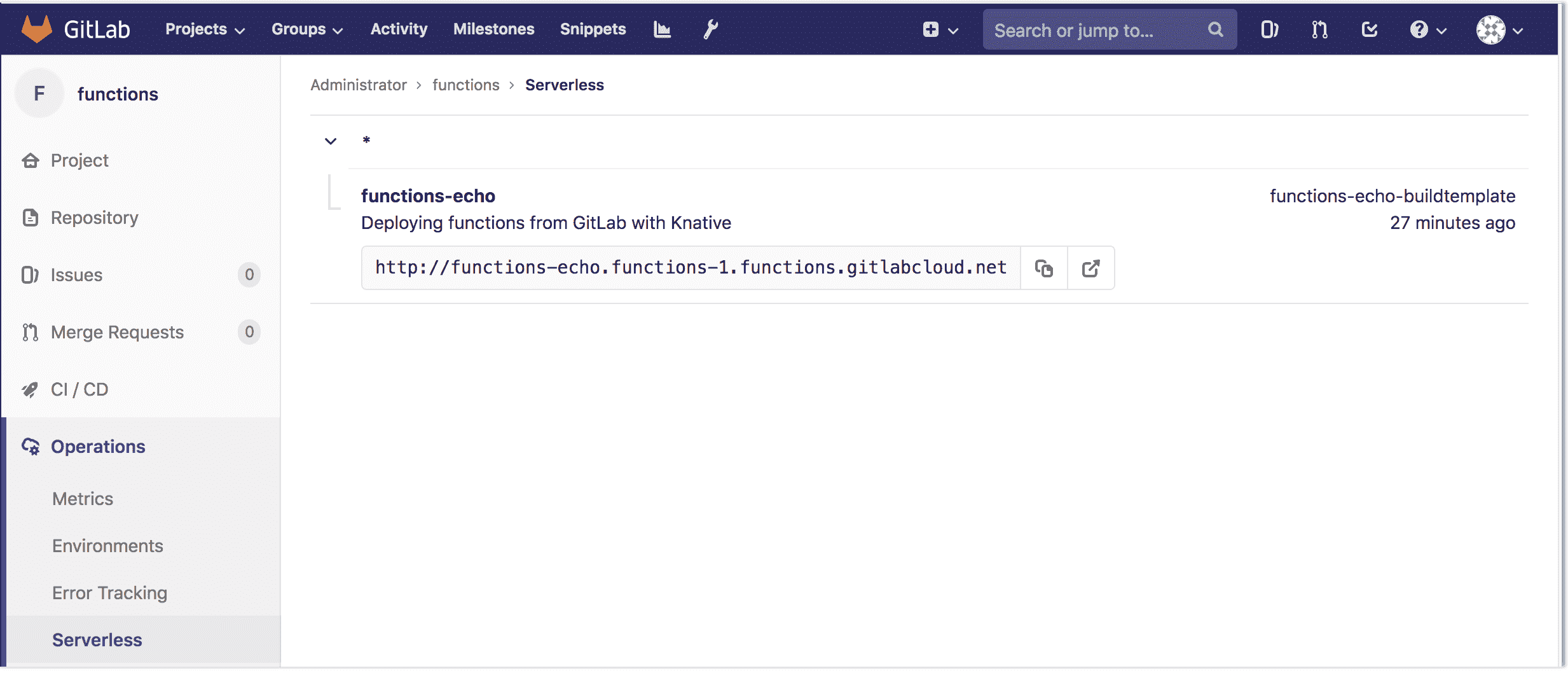](img/serverless-page.png)
該頁面包含可用于項目的所有功能,訪問功能的描述以及(如果有)功能的運行時信息. 詳細信息來自于項目的每個 Kubernetes 集群中的 Knative 安裝. 單擊每個功能以獲得詳細的規模和調用數據.
可以從集群上的 Knative 直接檢索函數詳細信息:
```
kubectl -n "$KUBE_NAMESPACE" get services.serving.knative.dev
```
現在可以使用任何簡單的`POST`調用從任何 HTTP 客戶端觸發示例函數:
1. 使用 curl(將最后一行的 URL 替換為應用程序的 URL):
```
curl \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request POST \
--data '{"GitLab":"FaaS"}' \
http://functions-echo.functions-1.functions.example.com/
```
2. 使用基于 Web 的工具(例如 Postman 或 Restlet)
[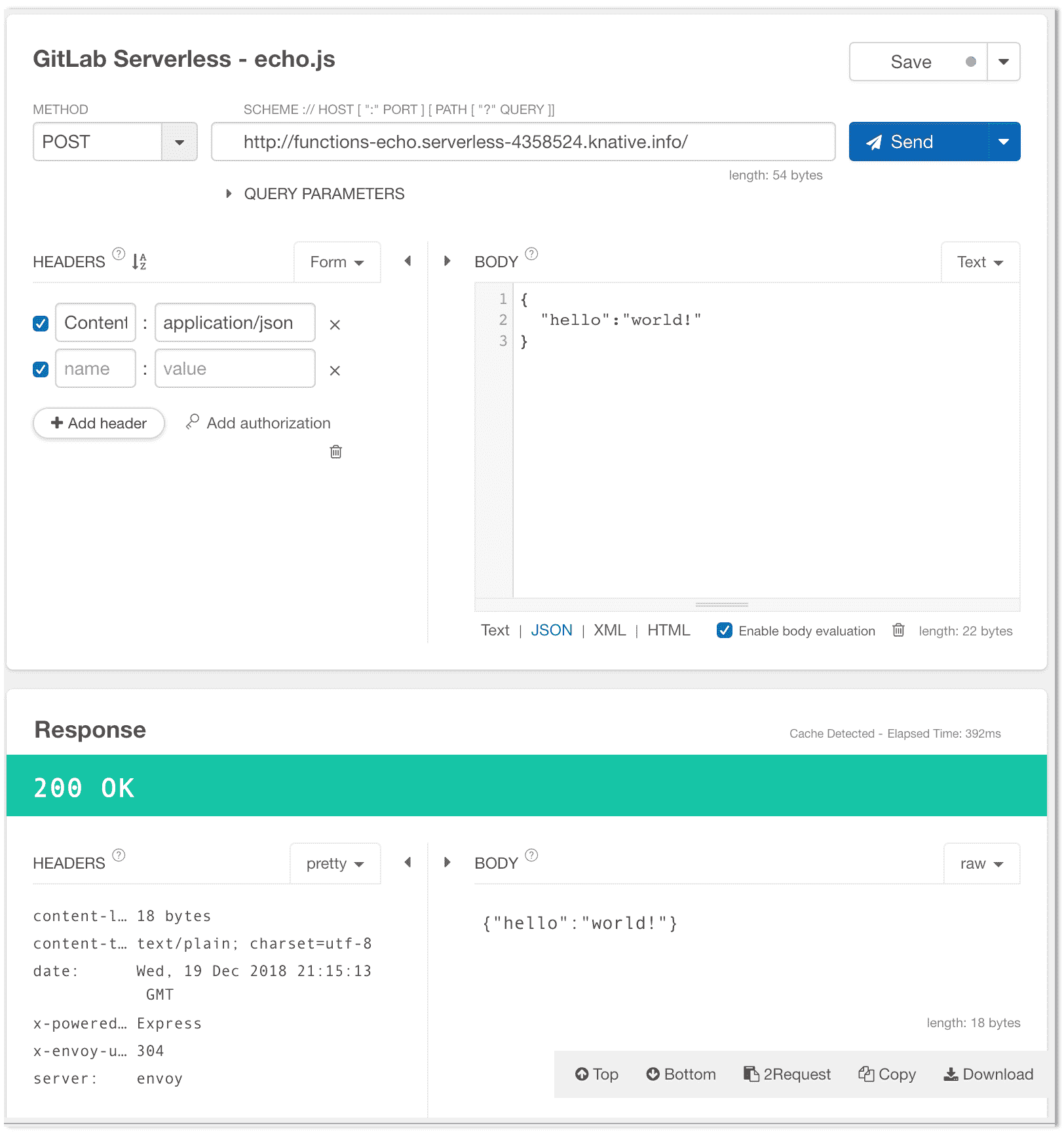](img/function-execution.png)
### Secrets[](#secrets "Permalink")
要從函數內部訪問 Kubernetes 機密,應在無服務器部署的名稱空間下創建該機密,并在上述`serverless.yml`文件中指定這些機密. 您可以通過多種方式創建機密. 以下各節顯示了一些示例.
#### CLI example[](#cli-example "Permalink")
```
kubectl create secret generic my-secrets -n "$KUBE_NAMESPACE" --from-literal MY_SECRET=imverysecure
```
#### Part of deployment job[](#part-of-deployment-job "Permalink")
您可以擴展`.gitlab-ci.yml`以在部署期間使用安全存儲在 GitLab 項目下的[環境變量](../../../../ci/variables/README.html)來創建秘密.
```
deploy:function:
stage: deploy
environment: production
extends: .serverless:deploy:functions
before_script:
- kubectl create secret generic my-secret
--from-literal MY_SECRET="$GITLAB_SECRET_VARIABLE"
--namespace "$KUBE_NAMESPACE"
--dry-run -o yaml | kubectl apply -f -
```
### Running functions locally[](#running-functions-locally "Permalink")
在本地運行功能是在開發過程中快速驗證行為的好方法.
在本地運行功能需要:
* 轉到 1.12 或更高版本.
* Docker Engine 已安裝并正在運行.
* 使用 Go 軟件包管理器安裝的`gitlabktl` :
```
GO111MODULE=on go get gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlabktl
```
要在本地運行功能:
1. 導航到您的 GitLab 無服務器項目的根目錄.
2. 將功能構建到 Docker 映像中:
```
gitlabktl serverless build
```
3. 在 Docker 中運行您的函數:
```
docker run -itp 8080:8080 <your_function_name>
```
4. 調用您的功能:
```
curl http://localhost:8080
```
## Deploying Serverless applications[](#deploying-serverless-applications "Permalink")
在 GitLab 11.5 中引入.
無服務器應用程序是[無服務器功能](#deploying-functions)的替代[方法](#deploying-functions) . 它們在現有運行時不能滿足應用程序需求的情況下很有用,例如以一種沒有可用運行時的語言編寫的應用程序. 請注意,盡管無服務器應用程序應該是無狀態的!
**注意:**您可以參考并導入示例[Knative Ruby 應用程序](https://gitlab.com/knative-examples/knative-ruby-app)以開始使用.
將以下`.gitlab-ci.yml`添加到存儲庫的根目錄中(如果您先前已經克隆了上述示例[Knative Ruby App,](https://gitlab.com/knative-examples/knative-ruby-app)則可以跳過此步驟):
```
include:
- template: Serverless.gitlab-ci.yml
build:
extends: .serverless:build:image
deploy:
extends: .serverless:deploy:image
```
`Serverless.gitlab-ci.yml`是允許自定義的模板. 您可以使用`include`參數導入它,并使用`extends`來自定義作業,或者可以通過在通過用戶界面編輯`.gitlab-ci.yml`文件時從**Apply a template**下拉列表中選擇它來內聯整個模板.
部署無服務器應用程序時,不需要`serverless.yml`文件.
### Deploy the application with Knative[](#deploy-the-application-with-knative "Permalink")
一切就緒后,下次運行 CI 管道時,將部署 Knative 應用程序. 導航到**CI / CD>管道** ,然后單擊最新的管道.
### Function details[](#function-details "Permalink")
轉到**操作>無服務器**頁面以查看功能的最終 URL.
[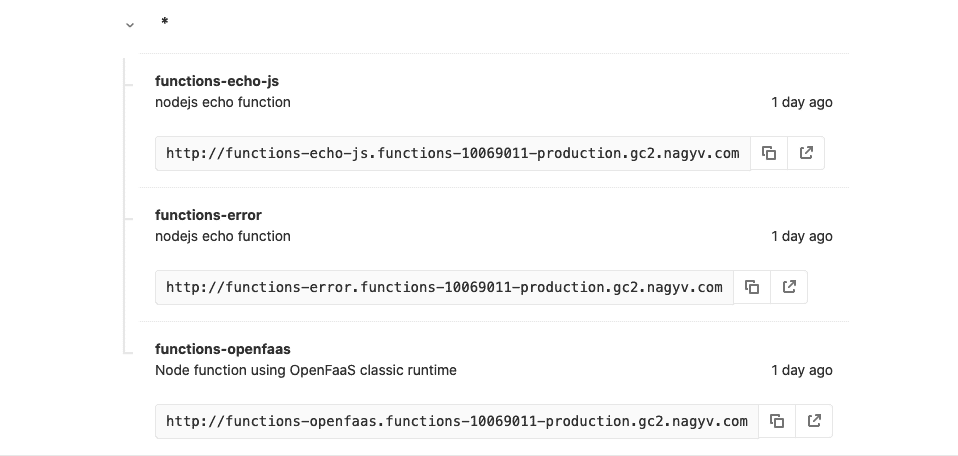](img/function-list_v12_7.png)
### Invocation metrics[](#invocation-metrics "Permalink")
On the same page as above, click on one of the function rows to bring up the function details page.
[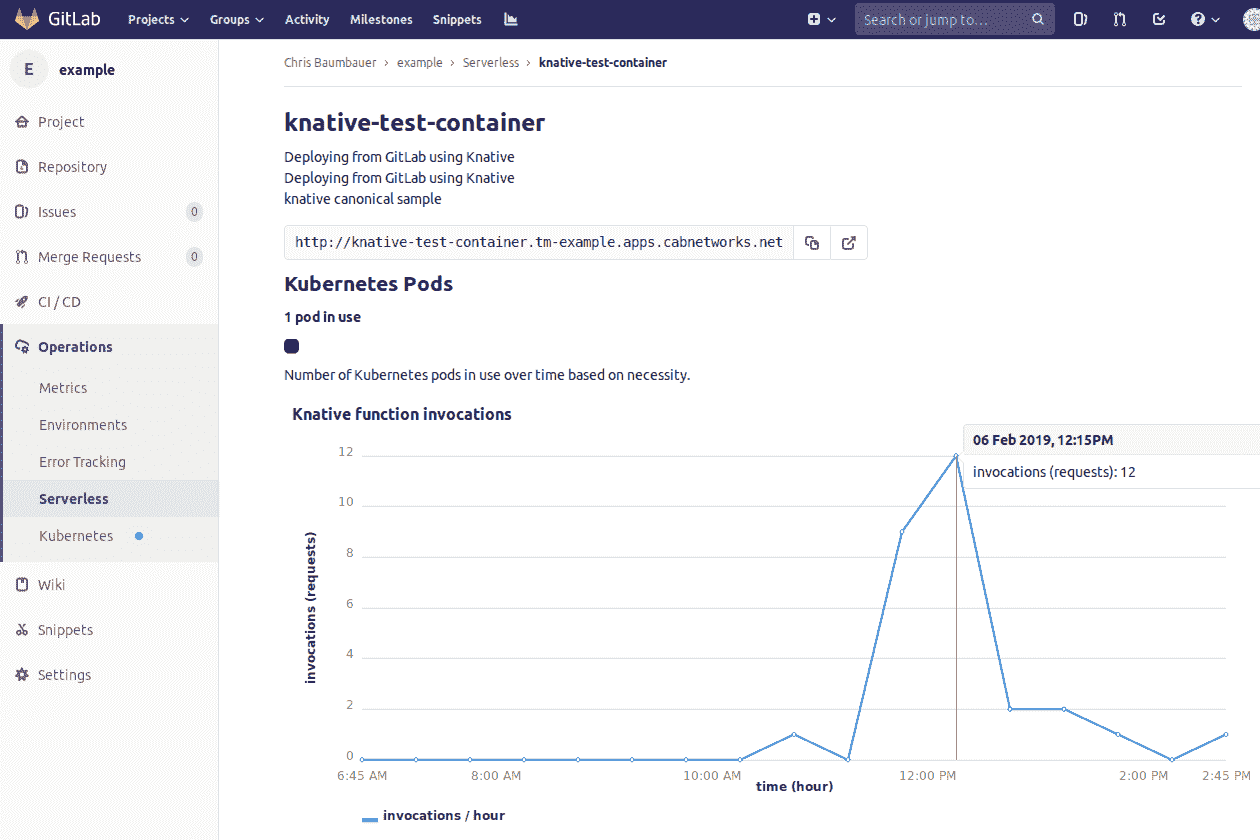](img/function-details-loaded.png)
容器數將為您提供在給定集群上運行無服務器功能實例的容器數.
為了顯示 Knative 函數調用, [必須安裝 Prometheus](../index.html#installing-applications) .
一旦安裝了 Prometheus,可能會出現一條消息,指示度量標準數據*正在加載或當前不可用.* 它會在首次訪問該頁面時顯示,但應在幾秒鐘后消失. 如果該消息沒有消失,則可能是 GitLab 無法連接到集群上運行的 Prometheus 實例.
## Configuring logging[](#configuring-logging "Permalink")
在 GitLab 12.5 中[引入](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/issues/33330) .
### Prerequisites[](#prerequisites-1 "Permalink")
* 由 GitLab 管理的集群.
* `kubectl`已安裝并正在運行.
在集群上運行`kubectl`命令需要首先設置對集群的訪問權限. 對于在以下位置創建的集群:
* GKE,請參閱[GKE 群集訪問](https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/how-to/cluster-access-for-kubectl)
* 其他平臺,請參閱[安裝和設置 kubectl](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/install-kubectl/) .
### Enable request log template[](#enable-request-log-template "Permalink")
運行以下命令以啟用請求日志:
```
kubectl edit cm -n knative-serving config-observability
```
將`logging.request-log-template`從`data._example`字段復制到層次結構中上一層的數據字段.
### Enable request logs[](#enable-request-logs "Permalink")
運行以下命令以將 Elasticsearch,Kibana 和 Filebeat 安裝到`kube-logging`命名空間中,并配置所有節點以使用 Filebeat 轉發日志:
```
kubectl apply -f https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/serverless/configurations/knative/raw/v0.7.0/kube-logging-filebeat.yaml
kubectl label nodes --all beta.kubernetes.io/filebeat-ready="true"
```
### Viewing request logs[](#viewing-request-logs "Permalink")
要查看請求日志:
1. Run `kubectl proxy`.
2. 導航到[Kibana UI](http://localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/kube-logging/services/kibana/proxy/app/kibana) .
Or:
1. 打開[Kibana UI](http://localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/kube-logging/services/kibana/proxy/app/kibana) .
2. 單擊" **發現"** ,然后從左側的下拉列表中選擇`filebeat-*` .
3. 在搜索框中輸入`kubernetes.container.name:"queue-proxy" AND message:/httpRequest/` .
## Enabling TLS for Knative services[](#enabling-tls-for-knative-services "Permalink")
默認情況下,將通過`http`提供 GitLab 無服務器部署. 為了通過`https`提供服務,您必須手動獲取并安裝 TLS 證書.
完成此操作的最簡單方法是使用[Certbot 手動獲取 Let's Encrypt 證書](https://knative.dev/docs/serving/using-a-tls-cert/#using-certbot-to-manually-obtain-let-s-encrypt-certificates) . Certbot 是一個免費的開源軟件工具,可用于在手動管理的網站上自動使用 Let's Encrypt 證書來啟用 HTTPS.
**注意:**以下說明與在安裝了 Python 3 且不能在其他操作系統或其他版本的 Python 上運行的 Linux 服務器上安裝和運行 Certbot 有關.
1. 通過運行[`certbot-auto` wrapper 腳本](https://certbot.eff.org/docs/install.html#certbot-auto)安裝 Certbot. 在服務器的命令行上,運行以下命令:
```
wget https://dl.eff.org/certbot-auto
sudo mv certbot-auto /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto
sudo chown root /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto
sudo chmod 0755 /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto
/usr/local/bin/certbot-auto --help
```
要檢查`certbot-auto`腳本的完整性,請運行:
```
wget -N https://dl.eff.org/certbot-auto.asc
gpg2 --keyserver ipv4.pool.sks-keyservers.net --recv-key A2CFB51FA275A7286234E7B24D17C995CD9775F2
gpg2 --trusted-key 4D17C995CD9775F2 --verify certbot-auto.asc /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto
```
The output of the last command should look something like:
```
gpg: Signature made Mon 10 Jun 2019 06:24:40 PM EDT
gpg: using RSA key A2CFB51FA275A7286234E7B24D17C995CD9775F2
gpg: key 4D17C995CD9775F2 marked as ultimately trusted
gpg: checking the trustdb
gpg: marginals needed: 3 completes needed: 1 trust model: pgp
gpg: depth: 0 valid: 1 signed: 0 trust: 0-, 0q, 0n, 0m, 0f, 1u
gpg: next trustdb check due at 2027-11-22
gpg: Good signature from "Let's Encrypt Client Team <letsencrypt-client@eff.org>" [ultimate]
```
2. 運行以下命令以使用 Certbot 在授權過程中使用 DNS 質詢來請求證書:
```
/usr/local/bin/certbot-auto certonly --manual --preferred-challenges dns -d '*.<namespace>.example.com'
```
其中`<namespace>`是 GitLab 為您的無服務器項目創建的名稱空間(由`<project_name>-<project_id>-<environment>` ),而`example.com`是用于項目的域. 如果不確定項目的名稱空間是什么,請導航至項目的" **操作">"無服務器"**頁面,然后檢查為功能/應用程序提供的端點.
[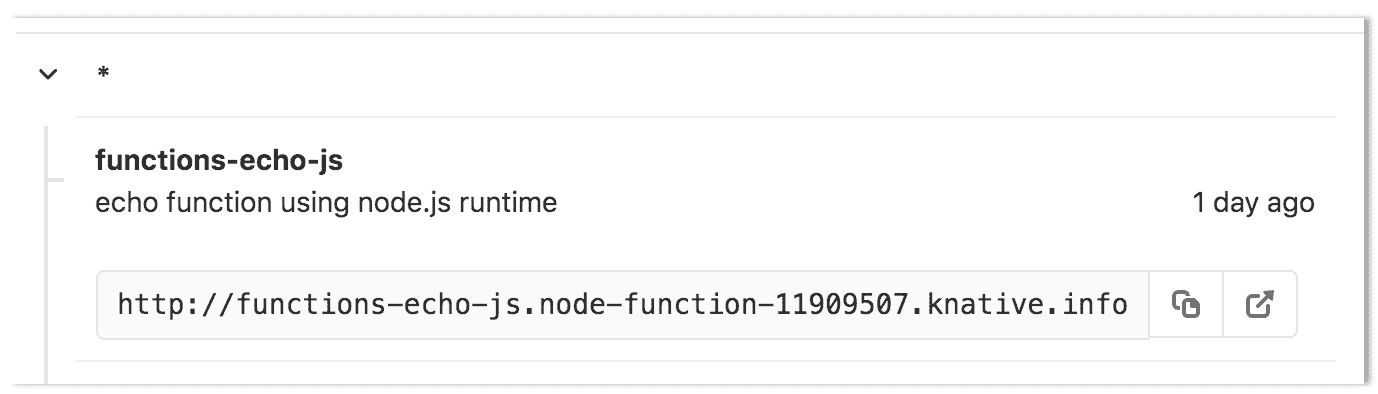](img/function-endpoint.png)
在上圖中,項目的名稱空間為`node-function-11909507` ,域為`knative.info` ,因此證書申請行如下所示:
```
./certbot-auto certonly --manual --preferred-challenges dns -d '*.node-function-11909507.knative.info'
```
Certbot 工具將引導您完成通過在這些域中創建 TXT 記錄來驗證您擁有的每個域的步驟. 此過程完成后,輸出應如下所示:
```
IMPORTANT NOTES:
- Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/namespace.example.com/fullchain.pem
Your key file has been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/namespace.example/privkey.pem
Your cert will expire on 2019-09-19\. To obtain a new or tweaked
version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot-auto
again. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run
"certbot-auto renew"
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
- Your account credentials have been saved in your Certbot
configuration directory at /etc/letsencrypt. You should make a
secure backup of this folder now. This configuration directory will
also contain certificates and private keys obtained by Certbot so
making regular backups of this folder is ideal.
```
3. 創建證書和私鑰文件. 使用 Certbot 返回的文件的內容,我們將創建兩個文件以創建 Kubernetes 機密:
運行以下命令以查看`fullchain.pem`的內容:
```
sudo cat /etc/letsencrypt/live/node-function-11909507.knative.info/fullchain.pem
```
輸出應如下所示:
```
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b4ag==
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
K2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e30Qg==
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
```
創建一個名稱為`cert.pem`的文件,其中包含整個輸出的內容.
創建`cert.pem` ,運行以下命令以查看`privkey.pem`的內容:
```
sudo cat /etc/letsencrypt/live/namespace.example/privkey.pem
```
輸出應如下所示:
```
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
2fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
04f294d1eaca42b8692017b426d53bbc8fe75f827734f0260710b83a556082df
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
fcb195768c39e9a94cec2c2e32c59c0aad7a3365c10892e8116b5d83d4096b6
4f294d1eaca42b8692017b4262==
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----
```
使用整個輸出的內容創建一個名稱為`cert.pk`的新文件.
4. 創建一個 Kubernetes 機密以保存您的 TLS 證書`cert.pem`和私鑰`cert.pk` :
**注意:**在集群上運行`kubectl`命令需要首先設置對集群的訪問. 對于在 GKE 上創建的集群,請參閱[GKE 集群訪問](https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/how-to/cluster-access-for-kubectl) . 對于其他平臺, [請安裝`kubectl`](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/install-kubectl/) .
```
kubectl create --namespace istio-system secret tls istio-ingressgateway-certs \
--key cert.pk \
--cert cert.pem
```
其中`cert.pem`和`cert.pk`是您的證書和私鑰文件. 請注意, `istio-ingressgateway-certs`秘密名稱是必需的.
5. 配置 Knative 以使用為 HTTPS 連接創建的新密碼. 運行以下命令以編輯方式打開 Knative 共享`gateway` :
```
kubectl edit gateway knative-ingress-gateway --namespace knative-serving
```
更新網關以包括以下 tls:部分和配置:
```
tls:
mode: SIMPLE
privateKey: /etc/istio/ingressgateway-certs/tls.key
serverCertificate: /etc/istio/ingressgateway-certs/tls.crt
```
Example:
```
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
# ... skipped ...
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway
servers:
- hosts:
- "*"
port:
name: http
number: 80
protocol: HTTP
- hosts:
- "*"
port:
name: https
number: 443
protocol: HTTPS
tls:
mode: SIMPLE
privateKey: /etc/istio/ingressgateway-certs/tls.key
serverCertificate: /etc/istio/ingressgateway-certs/tls.crt
```
After your changes are running on your Knative cluster, you can begin using the HTTPS protocol for secure access your deployed Knative services. In the event a mistake is made during this process and you need to update the cert, you will need to edit the gateway `knative-ingress-gateway` to switch back to `PASSTHROUGH` mode. Once corrections are made, edit the file again so the gateway will use the new certificates.
## Using an older version of `gitlabktl`[](#using-an-older-version-of-gitlabktl "Permalink")
在某些情況下,您想運行舊版本的`gitlabktl` . 這需要在`.gitlab-ci.yml`文件中設置較舊版本的`gitlabktl`映像.
要設置較舊的版本,請將`image:`添加到`functions:deploy`塊中. 例如:
```
functions:deploy:
extends: .serverless:deploy:functions
environment: production
image: registry.gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlabktl:0.5.0
```
通過更改注冊表 URL 末尾的版本標簽(格式為`registry.gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlabktl:<version>`可以使用不同的版本.
有關可用`gitlabktl`版本的完整清單,請參見`gitlabktl`項目的[容器注冊表](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlabktl/container_registry) .
- GitLab Docs
- Installation
- Requirements
- GitLab cloud native Helm Chart
- Install GitLab with Docker
- Installation from source
- Install GitLab on Microsoft Azure
- Installing GitLab on Google Cloud Platform
- Installing GitLab on Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Analytics
- Code Review Analytics
- Productivity Analytics
- Value Stream Analytics
- Kubernetes clusters
- Adding and removing Kubernetes clusters
- Adding EKS clusters
- Adding GKE clusters
- Group-level Kubernetes clusters
- Instance-level Kubernetes clusters
- Canary Deployments
- Cluster Environments
- Deploy Boards
- GitLab Managed Apps
- Crossplane configuration
- Cluster management project (alpha)
- Kubernetes Logs
- Runbooks
- Serverless
- Deploying AWS Lambda function using GitLab CI/CD
- Securing your deployed applications
- Groups
- Contribution Analytics
- Custom group-level project templates
- Epics
- Manage epics
- Group Import/Export
- Insights
- Issues Analytics
- Iterations
- Public access
- SAML SSO for GitLab.com groups
- SCIM provisioning using SAML SSO for GitLab.com groups
- Subgroups
- Roadmap
- Projects
- GitLab Secure
- Security Configuration
- Container Scanning
- Dependency Scanning
- Dependency List
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
- Secret Detection
- Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
- GitLab Security Dashboard
- Offline environments
- Standalone Vulnerability pages
- Security scanner integration
- Badges
- Bulk editing issues and merge requests at the project level
- Code Owners
- Compliance
- License Compliance
- Compliance Dashboard
- Create a project
- Description templates
- Deploy Keys
- Deploy Tokens
- File finder
- Project integrations
- Integrations
- Atlassian Bamboo CI Service
- Bugzilla Service
- Custom Issue Tracker service
- Discord Notifications service
- Enabling emails on push
- GitHub project integration
- Hangouts Chat service
- Atlassian HipChat
- Irker IRC Gateway
- GitLab Jira integration
- Mattermost Notifications Service
- Mattermost slash commands
- Microsoft Teams service
- Mock CI Service
- Prometheus integration
- Redmine Service
- Slack Notifications Service
- Slack slash commands
- GitLab Slack application
- Webhooks
- YouTrack Service
- Insights
- Issues
- Crosslinking Issues
- Design Management
- Confidential issues
- Due dates
- Issue Boards
- Issue Data and Actions
- Labels
- Managing issues
- Milestones
- Multiple Assignees for Issues
- Related issues
- Service Desk
- Sorting and ordering issue lists
- Issue weight
- Associate a Zoom meeting with an issue
- Merge requests
- Allow collaboration on merge requests across forks
- Merge Request Approvals
- Browser Performance Testing
- How to create a merge request
- Cherry-pick changes
- Code Quality
- Load Performance Testing
- Merge Request dependencies
- Fast-forward merge requests
- Merge when pipeline succeeds
- Merge request conflict resolution
- Reverting changes
- Reviewing and managing merge requests
- Squash and merge
- Merge requests versions
- Draft merge requests
- Members of a project
- Migrating projects to a GitLab instance
- Import your project from Bitbucket Cloud to GitLab
- Import your project from Bitbucket Server to GitLab
- Migrating from ClearCase
- Migrating from CVS
- Import your project from FogBugz to GitLab
- Gemnasium
- Import your project from GitHub to GitLab
- Project importing from GitLab.com to your private GitLab instance
- Import your project from Gitea to GitLab
- Import your Jira project issues to GitLab
- Migrating from Perforce Helix
- Import Phabricator tasks into a GitLab project
- Import multiple repositories by uploading a manifest file
- Import project from repo by URL
- Migrating from SVN to GitLab
- Migrating from TFVC to Git
- Push Options
- Releases
- Repository
- Branches
- Git Attributes
- File Locking
- Git file blame
- Git file history
- Repository mirroring
- Protected branches
- Protected tags
- Push Rules
- Reduce repository size
- Signing commits with GPG
- Syntax Highlighting
- GitLab Web Editor
- Web IDE
- Requirements Management
- Project settings
- Project import/export
- Project access tokens (Alpha)
- Share Projects with other Groups
- Snippets
- Static Site Editor
- Wiki
- Project operations
- Monitor metrics for your CI/CD environment
- Set up alerts for Prometheus metrics
- Embedding metric charts within GitLab-flavored Markdown
- Embedding Grafana charts
- Using the Metrics Dashboard
- Dashboard YAML properties
- Metrics dashboard settings
- Panel types for dashboards
- Using Variables
- Templating variables for metrics dashboards
- Prometheus Metrics library
- Monitoring AWS Resources
- Monitoring HAProxy
- Monitoring Kubernetes
- Monitoring NGINX
- Monitoring NGINX Ingress Controller
- Monitoring NGINX Ingress Controller with VTS metrics
- Alert Management
- Error Tracking
- Tracing
- Incident Management
- GitLab Status Page
- Feature Flags
- GitLab CI/CD
- GitLab CI/CD pipeline configuration reference
- GitLab CI/CD include examples
- Introduction to CI/CD with GitLab
- Getting started with GitLab CI/CD
- How to enable or disable GitLab CI/CD
- Using SSH keys with GitLab CI/CD
- Migrating from CircleCI
- Migrating from Jenkins
- Auto DevOps
- Getting started with Auto DevOps
- Requirements for Auto DevOps
- Customizing Auto DevOps
- Stages of Auto DevOps
- Upgrading PostgreSQL for Auto DevOps
- Cache dependencies in GitLab CI/CD
- GitLab ChatOps
- Cloud deployment
- Docker integration
- Building Docker images with GitLab CI/CD
- Using Docker images
- Building images with kaniko and GitLab CI/CD
- GitLab CI/CD environment variables
- Predefined environment variables reference
- Where variables can be used
- Deprecated GitLab CI/CD variables
- Environments and deployments
- Protected Environments
- GitLab CI/CD Examples
- Test a Clojure application with GitLab CI/CD
- Using Dpl as deployment tool
- Testing a Phoenix application with GitLab CI/CD
- End-to-end testing with GitLab CI/CD and WebdriverIO
- DevOps and Game Dev with GitLab CI/CD
- Deploy a Spring Boot application to Cloud Foundry with GitLab CI/CD
- How to deploy Maven projects to Artifactory with GitLab CI/CD
- Testing PHP projects
- Running Composer and NPM scripts with deployment via SCP in GitLab CI/CD
- Test and deploy Laravel applications with GitLab CI/CD and Envoy
- Test and deploy a Python application with GitLab CI/CD
- Test and deploy a Ruby application with GitLab CI/CD
- Test and deploy a Scala application to Heroku
- GitLab CI/CD for external repositories
- Using GitLab CI/CD with a Bitbucket Cloud repository
- Using GitLab CI/CD with a GitHub repository
- GitLab Pages
- GitLab Pages
- GitLab Pages domain names, URLs, and baseurls
- Create a GitLab Pages website from scratch
- Custom domains and SSL/TLS Certificates
- GitLab Pages integration with Let's Encrypt
- GitLab Pages Access Control
- Exploring GitLab Pages
- Incremental Rollouts with GitLab CI/CD
- Interactive Web Terminals
- Optimizing GitLab for large repositories
- Metrics Reports
- CI/CD pipelines
- Pipeline Architecture
- Directed Acyclic Graph
- Multi-project pipelines
- Parent-child pipelines
- Pipelines for Merge Requests
- Pipelines for Merged Results
- Merge Trains
- Job artifacts
- Pipeline schedules
- Pipeline settings
- Triggering pipelines through the API
- Review Apps
- Configuring GitLab Runners
- GitLab CI services examples
- Using MySQL
- Using PostgreSQL
- Using Redis
- Troubleshooting CI/CD
- GitLab Package Registry
- GitLab Container Registry
- Dependency Proxy
- GitLab Composer Repository
- GitLab Conan Repository
- GitLab Maven Repository
- GitLab NPM Registry
- GitLab NuGet Repository
- GitLab PyPi Repository
- API Docs
- API resources
- .gitignore API
- GitLab CI YMLs API
- Group and project access requests API
- Appearance API
- Applications API
- Audit Events API
- Avatar API
- Award Emoji API
- Project badges API
- Group badges API
- Branches API
- Broadcast Messages API
- Project clusters API
- Group clusters API
- Instance clusters API
- Commits API
- Container Registry API
- Custom Attributes API
- Dashboard annotations API
- Dependencies API
- Deploy Keys API
- Deployments API
- Discussions API
- Dockerfiles API
- Environments API
- Epics API
- Events
- Feature Flags API
- Feature flag user lists API
- Freeze Periods API
- Geo Nodes API
- Group Activity Analytics API
- Groups API
- Import API
- Issue Boards API
- Group Issue Boards API
- Issues API
- Epic Issues API
- Issues Statistics API
- Jobs API
- Keys API
- Labels API
- Group Labels API
- License
- Licenses API
- Issue links API
- Epic Links API
- Managed Licenses API
- Markdown API
- Group and project members API
- Merge request approvals API
- Merge requests API
- Project milestones API
- Group milestones API
- Namespaces API
- Notes API
- Notification settings API
- Packages API
- Pages domains API
- Pipeline schedules API
- Pipeline triggers API
- Pipelines API
- Project Aliases API
- Project import/export API
- Project repository storage moves API
- Project statistics API
- Project templates API
- Projects API
- Protected branches API
- Protected tags API
- Releases API
- Release links API
- Repositories API
- Repository files API
- Repository submodules API
- Resource label events API
- Resource milestone events API
- Resource weight events API
- Runners API
- SCIM API
- Search API
- Services API
- Application settings API
- Sidekiq Metrics API
- Snippets API
- Project snippets
- Application statistics API
- Suggest Changes API
- System hooks API
- Tags API
- Todos API
- Users API
- Project-level Variables API
- Group-level Variables API
- Version API
- Vulnerabilities API
- Vulnerability Findings API
- Wikis API
- GraphQL API
- Getting started with GitLab GraphQL API
- GraphQL API Resources
- API V3 to API V4
- Validate the .gitlab-ci.yml (API)
- User Docs
- Abuse reports
- User account
- Active sessions
- Deleting a User account
- Permissions
- Personal access tokens
- Profile preferences
- Threads
- GitLab and SSH keys
- GitLab integrations
- Git
- GitLab.com settings
- Infrastructure as code with Terraform and GitLab
- GitLab keyboard shortcuts
- GitLab Markdown
- AsciiDoc
- GitLab Notification Emails
- GitLab Quick Actions
- Autocomplete characters
- Reserved project and group names
- Search through GitLab
- Advanced Global Search
- Advanced Syntax Search
- Time Tracking
- GitLab To-Do List
- Administrator Docs
- Reference architectures
- Reference architecture: up to 1,000 users
- Reference architecture: up to 2,000 users
- Reference architecture: up to 3,000 users
- Reference architecture: up to 5,000 users
- Reference architecture: up to 10,000 users
- Reference architecture: up to 25,000 users
- Reference architecture: up to 50,000 users
- Troubleshooting a reference architecture set up
- Working with the bundled Consul service
- Configuring PostgreSQL for scaling
- Configuring GitLab application (Rails)
- Load Balancer for multi-node GitLab
- Configuring a Monitoring node for Scaling and High Availability
- NFS
- Working with the bundled PgBouncer service
- Configuring Redis for scaling
- Configuring Sidekiq
- Admin Area settings
- Continuous Integration and Deployment Admin settings
- Custom instance-level project templates
- Diff limits administration
- Enable and disable GitLab features deployed behind feature flags
- Geo nodes Admin Area
- GitLab Pages administration
- Health Check
- Job logs
- Labels administration
- Log system
- PlantUML & GitLab
- Repository checks
- Repository storage paths
- Repository storage types
- Account and limit settings
- Service templates
- System hooks
- Changing your time zone
- Uploads administration
- Abuse reports
- Activating and deactivating users
- Audit Events
- Blocking and unblocking users
- Broadcast Messages
- Elasticsearch integration
- Gitaly
- Gitaly Cluster
- Gitaly reference
- Monitoring GitLab
- Monitoring GitLab with Prometheus
- Performance Bar
- Usage statistics
- Object Storage
- Performing Operations in GitLab
- Cleaning up stale Redis sessions
- Fast lookup of authorized SSH keys in the database
- Filesystem Performance Benchmarking
- Moving repositories managed by GitLab
- Run multiple Sidekiq processes
- Sidekiq MemoryKiller
- Switching to Puma
- Understanding Unicorn and unicorn-worker-killer
- User lookup via OpenSSH's AuthorizedPrincipalsCommand
- GitLab Package Registry administration
- GitLab Container Registry administration
- Replication (Geo)
- Geo database replication
- Geo with external PostgreSQL instances
- Geo configuration
- Using a Geo Server
- Updating the Geo nodes
- Geo with Object storage
- Docker Registry for a secondary node
- Geo for multiple nodes
- Geo security review (Q&A)
- Location-aware Git remote URL with AWS Route53
- Tuning Geo
- Removing secondary Geo nodes
- Geo data types support
- Geo Frequently Asked Questions
- Geo Troubleshooting
- Geo validation tests
- Disaster Recovery (Geo)
- Disaster recovery for planned failover
- Bring a demoted primary node back online
- Automatic background verification
- Rake tasks
- Back up and restore GitLab
- Clean up
- Namespaces
- Maintenance Rake tasks
- Geo Rake Tasks
- GitHub import
- Import bare repositories
- Integrity check Rake task
- LDAP Rake tasks
- Listing repository directories
- Praefect Rake tasks
- Project import/export administration
- Repository storage Rake tasks
- Generate sample Prometheus data
- Uploads migrate Rake tasks
- Uploads sanitize Rake tasks
- User management
- Webhooks administration
- X.509 signatures
- Server hooks
- Static objects external storage
- Updating GitLab
- GitLab release and maintenance policy
- Security
- Password Storage
- Custom password length limits
- Restrict allowed SSH key technologies and minimum length
- Rate limits
- Webhooks and insecure internal web services
- Information exclusivity
- How to reset your root password
- How to unlock a locked user from the command line
- User File Uploads
- How we manage the TLS protocol CRIME vulnerability
- User email confirmation at sign-up
- Security of running jobs
- Proxying assets
- CI/CD Environment Variables
- Contributor and Development Docs
- Contribute to GitLab
- Community members & roles
- Implement design & UI elements
- Issues workflow
- Merge requests workflow
- Code Review Guidelines
- Style guides
- GitLab Architecture Overview
- CI/CD development documentation
- Database guides
- Database Review Guidelines
- Database Review Guidelines
- Migration Style Guide
- What requires downtime?
- Understanding EXPLAIN plans
- Rake tasks for developers
- Mass inserting Rails models
- GitLab Documentation guidelines
- Documentation Style Guide
- Documentation structure and template
- Documentation process
- Documentation site architecture
- Global navigation
- GitLab Docs monthly release process
- Telemetry Guide
- Usage Ping Guide
- Snowplow Guide
- Experiment Guide
- Feature flags in development of GitLab
- Feature flags process
- Developing with feature flags
- Feature flag controls
- Document features deployed behind feature flags
- Frontend Development Guidelines
- Accessibility & Readability
- Ajax
- Architecture
- Axios
- Design Patterns
- Frontend Development Process
- DropLab
- Emojis
- Filter
- Frontend FAQ
- GraphQL
- Icons and SVG Illustrations
- InputSetter
- Performance
- Principles
- Security
- Tooling
- Vuex
- Vue
- Geo (development)
- Geo self-service framework (alpha)
- Gitaly developers guide
- GitLab development style guides
- API style guide
- Go standards and style guidelines
- GraphQL API style guide
- Guidelines for shell commands in the GitLab codebase
- HTML style guide
- JavaScript style guide
- Migration Style Guide
- Newlines style guide
- Python Development Guidelines
- SCSS style guide
- Shell scripting standards and style guidelines
- Sidekiq debugging
- Sidekiq Style Guide
- SQL Query Guidelines
- Vue.js style guide
- Instrumenting Ruby code
- Testing standards and style guidelines
- Flaky tests
- Frontend testing standards and style guidelines
- GitLab tests in the Continuous Integration (CI) context
- Review Apps
- Smoke Tests
- Testing best practices
- Testing levels
- Testing Rails migrations at GitLab
- Testing Rake tasks
- End-to-end Testing
- Beginner's guide to writing end-to-end tests
- End-to-end testing Best Practices
- Dynamic Element Validation
- Flows in GitLab QA
- Page objects in GitLab QA
- Resource class in GitLab QA
- Style guide for writing end-to-end tests
- Testing with feature flags
- Translate GitLab to your language
- Internationalization for GitLab
- Translating GitLab
- Proofread Translations
- Merging translations from CrowdIn
- Value Stream Analytics development guide
- GitLab subscription
- Activate GitLab EE with a license
