[TOC]
## 介紹
Yosys是Verilog RTL綜合的框架。它目前具有廣泛的Verilog-2005支持,并為各種應用程序領域提供了一組基本的綜合算法。所選功能和典型應用:
* 處理幾乎所有可綜合的Verilog-2005設計
* 將Verilog轉換為BLIF / EDIF / BTOR / SMT-LIB /簡單的RTL Verilog /等等
* 內置的形式檢查屬性和等效性的方法
* 映射到ASIC標準單元庫(自由文件格式)
* 映射到Xilinx 7系列和Lattice iCE40 FPGA
* 自定義流程的基礎和/或前端
通過使用合成腳本組合現有過程(算法)并根據需要通過擴展Yosys C ++代碼庫添加其他過程,可以使Yosys適于執行任何綜合工作。 <br/>
Yosys是根據ISC許可(與MIT許可或2子BSD許可類似的GPL兼容許可)許可的免費軟件。<br/>
事實上,yosys是一個解釋器,就如同python的解釋器一樣,于是從理論上我們可以在linux使用sheban來寫腳本運行!
[文檔推薦]([https://www.kutu66.com/GitHub/article\_94386](https://www.kutu66.com/GitHub/article_94386))
## 在deepin上的安裝
**首先安裝所需要的依賴項目**
```bash
sudo apt-get install build-essential clang bison flex \
libreadline-dev gawk tcl-dev libffi-dev git \
graphviz xdot pkg-config python3 libboost-system-dev \
libboost-python-dev libboost-filesystem-dev zlib1g-dev
```
**安裝yosys**
使用一下命令進行安裝
```bash
sudo apt-get install yosys
```
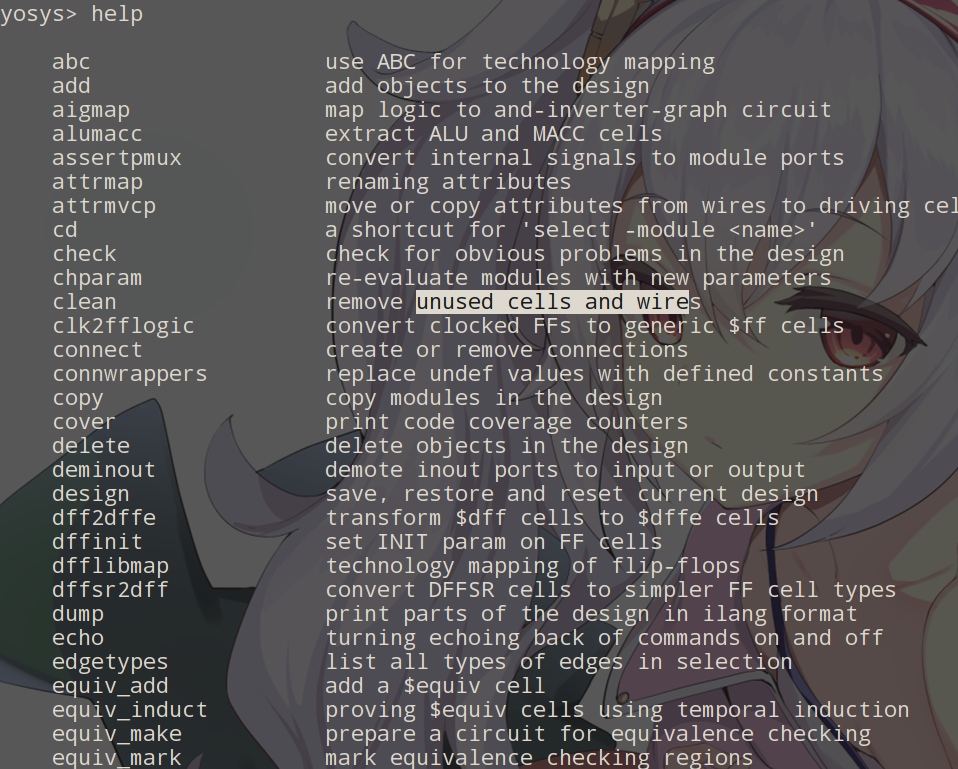
## 關于幫助
對于不同版本的yosys,有些命令可能不同,yosys是一個解釋器,可以在終端輸入`yosys`進入,然后輸入`help`查看支持的命令!
## 分步說明一個簡單的例子
**新建`foo.v`文件,文件內容如下所示**
```
module foo (
input a,
input b,
input c,
output o
);
assign o = (a & b) | c;
endmodule
```
**終端切換到yosys解釋器,終端輸入yosys即可**
```
yosys
```
**讀入待分析的verilog文件**
當然根據版本的不同可能read要換成 read_verilog.
```
yosys> read -sv foo.v
1. Executing Verilog-2005 frontend.
Parsing SystemVerilog input from `foo.v' to AST representation.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\foo'.
Successfully finished Verilog frontend.
```
**指出頂層模塊**
```
yosys> hierarchy -top foo
2. Executing HIERARCHY pass (managing design hierarchy).
2.1. Analyzing design hierarchy..
Top module: \foo
2.2. Analyzing design hierarchy..
Top module: \foo
Removed 0 unused modules.
```
**將設計以Yosys的內部格式寫入控制臺**
```
yosys> write_ilang
3. Executing ILANG backend.
Output filename: <stdout>
# Generated by Yosys 0.8 (git sha1 5706e90)
autoidx 3
attribute \top 1
attribute \src "foo.v:1"
module \foo
attribute \src "foo.v:8"
wire $and$foo.v:8$1_Y
attribute \src "foo.v:8"
wire $or$foo.v:8$2_Y
attribute \src "foo.v:2"
wire input 1 \a
attribute \src "foo.v:3"
wire input 2 \b
attribute \src "foo.v:4"
wire input 3 \c
attribute \src "foo.v:5"
wire output 4 \o
attribute \src "foo.v:8"
cell $and $and$foo.v:8$1
parameter \A_SIGNED 0
parameter \A_WIDTH 1
parameter \B_SIGNED 0
parameter \B_WIDTH 1
parameter \Y_WIDTH 1
connect \A \a
connect \B \b
connect \Y $and$foo.v:8$1_Y
end
attribute \src "foo.v:8"
cell $or $or$foo.v:8$2
parameter \A_SIGNED 0
parameter \A_WIDTH 1
parameter \B_SIGNED 0
parameter \B_WIDTH 1
parameter \Y_WIDTH 1
connect \A $and$foo.v:8$1_Y
connect \B \c
connect \Y $or$foo.v:8$2_Y
end
connect \o $or$foo.v:8$2_Y
end
```
**將流程(always塊)轉換為網表元素并執行一些簡單的優化**
```
yosys> proc; opt
4. Executing PROC pass (convert processes to netlists).
4.1. Executing PROC_CLEAN pass (remove empty switches from decision trees).
Cleaned up 0 empty switches.
4.2. Executing PROC_RMDEAD pass (remove dead branches from decision trees).
Removed a total of 0 dead cases.
4.3. Executing PROC_INIT pass (extract init attributes).
4.4. Executing PROC_ARST pass (detect async resets in processes).
4.5. Executing PROC_MUX pass (convert decision trees to multiplexers).
4.6. Executing PROC_DLATCH pass (convert process syncs to latches).
4.7. Executing PROC_DFF pass (convert process syncs to FFs).
4.8. Executing PROC_CLEAN pass (remove empty switches from decision trees).
Cleaned up 0 empty switches.
5. Executing OPT pass (performing simple optimizations).
5.1. Executing OPT_EXPR pass (perform const folding).
5.2. Executing OPT_MERGE pass (detect identical cells).
Finding identical cells in module `\foo'.
Removed a total of 0 cells.
5.3. Executing OPT_MUXTREE pass (detect dead branches in mux trees).
Running muxtree optimizer on module \foo..
Creating internal representation of mux trees.
No muxes found in this module.
Removed 0 multiplexer ports.
5.4. Executing OPT_REDUCE pass (consolidate $*mux and $reduce_* inputs).
Optimizing cells in module \foo.
Performed a total of 0 changes.
5.5. Executing OPT_MERGE pass (detect identical cells).
Finding identical cells in module `\foo'.
Removed a total of 0 cells.
5.6. Executing OPT_RMDFF pass (remove dff with constant values).
5.7. Executing OPT_CLEAN pass (remove unused cells and wires).
Finding unused cells or wires in module \foo..
removed 1 unused temporary wires.
Removed 0 unused cells and 1 unused wires.
5.8. Executing OPT_EXPR pass (perform const folding).
5.9. Finished OPT passes. (There is nothing left to do.)
```
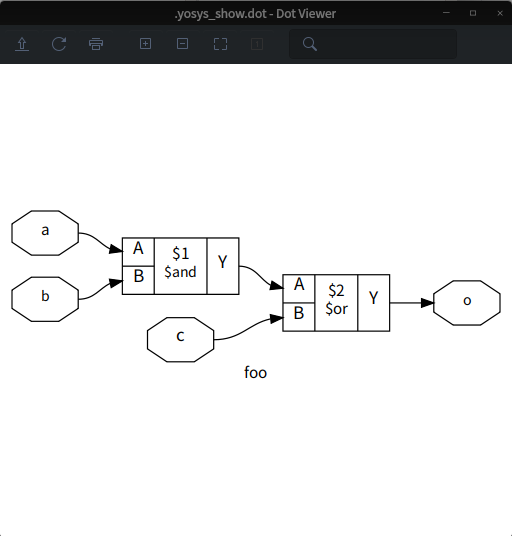
**使用xdot顯示設計網表**
```
yosys> show
```
顯示結果如下:
同樣的實現,使用gv可用以下命令實現:
```
yosys> show -format ps -viewer gv
```
**將網表轉換為門邏輯并執行一些簡單的優化**
```
yosys> techmap; opt
7. Executing TECHMAP pass (map to technology primitives).
7.1. Executing Verilog-2005 frontend.
Parsing Verilog input from `<techmap.v>' to AST representation.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\_90_simplemap_bool_ops'.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\_90_simplemap_reduce_ops'.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\_90_simplemap_logic_ops'.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\_90_simplemap_compare_ops'.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\_90_simplemap_various'.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\_90_simplemap_registers'.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\_90_shift_ops_shr_shl_sshl_sshr'.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\_90_shift_shiftx'.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\_90_fa'.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\_90_lcu'.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\_90_alu'.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\_90_macc'.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\_90_alumacc'.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\$__div_mod_u'.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\$__div_mod'.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\_90_div'.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\_90_mod'.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\_90_pow'.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\_90_pmux'.
Generating RTLIL representation for module `\_90_lut'.
Successfully finished Verilog frontend.
Mapping foo.$and$foo.v:8$1 ($and) with simplemap.
Mapping foo.$or$foo.v:8$2 ($or) with simplemap.
No more expansions possible.
8. Executing OPT pass (performing simple optimizations).
8.1. Executing OPT_EXPR pass (perform const folding).
8.2. Executing OPT_MERGE pass (detect identical cells).
Finding identical cells in module `\foo'.
Removed a total of 0 cells.
8.3. Executing OPT_MUXTREE pass (detect dead branches in mux trees).
Running muxtree optimizer on module \foo..
Creating internal representation of mux trees.
No muxes found in this module.
Removed 0 multiplexer ports.
8.4. Executing OPT_REDUCE pass (consolidate $*mux and $reduce_* inputs).
Optimizing cells in module \foo.
Performed a total of 0 changes.
8.5. Executing OPT_MERGE pass (detect identical cells).
Finding identical cells in module `\foo'.
Removed a total of 0 cells.
8.6. Executing OPT_RMDFF pass (remove dff with constant values).
8.7. Executing OPT_CLEAN pass (remove unused cells and wires).
Finding unused cells or wires in module \foo..
Removed 0 unused cells and 1 unused wires.
8.8. Executing OPT_EXPR pass (perform const folding).
8.9. Finished OPT passes. (There is nothing left to do.)
```
**將設計網表寫入新的Verilog文件**
```
yosys> write_verilog synth.v
```
這樣流程基本就結束了!
## 腳本方式執行
If ABC is enabled in the Yosys build configuration and a cell library is given in the liberty file `mycells.lib`, the following synthesis script will synthesize for the given cell library:
```
# read design
read -sv foo.v
hierarchy -top foo
# the high-level stuff
proc; fsm; opt; memory; opt
# mapping to internal cell library
techmap; opt
# mapping flip-flops to mycells.lib
dfflibmap -liberty mycells.lib
# mapping logic to mycells.lib
abc -liberty mycells.lib
# cleanup
clean
```
## 簡單腳本實現
建立foo.ys文件,內容如下:
```
#!/usr/bin/env yosys
read -sv foo.v
hierarchy -top foo
proc; opt; techmap; opt
show
write_verilog synth.v
```
執行腳本可以使用 `yosys foo.ys`執行。<br/>
前面已經說到yosys是一個解釋器,那么我們可以為foo.ys添加執行權限,使用`chmod +x foo.ys`,然后就如同在linux上執行bash腳本一樣,使用 `./foo.ys`來執行。
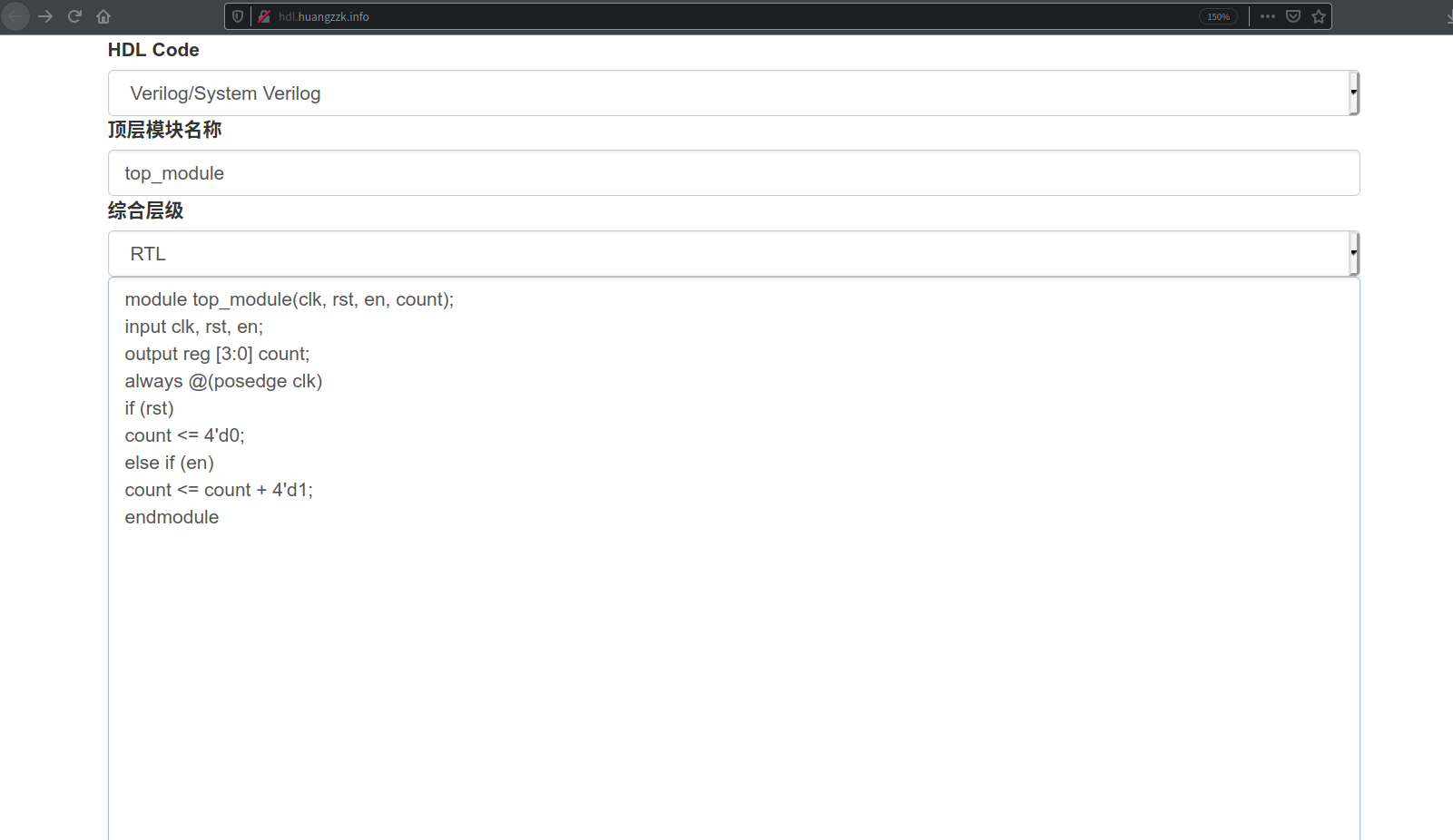
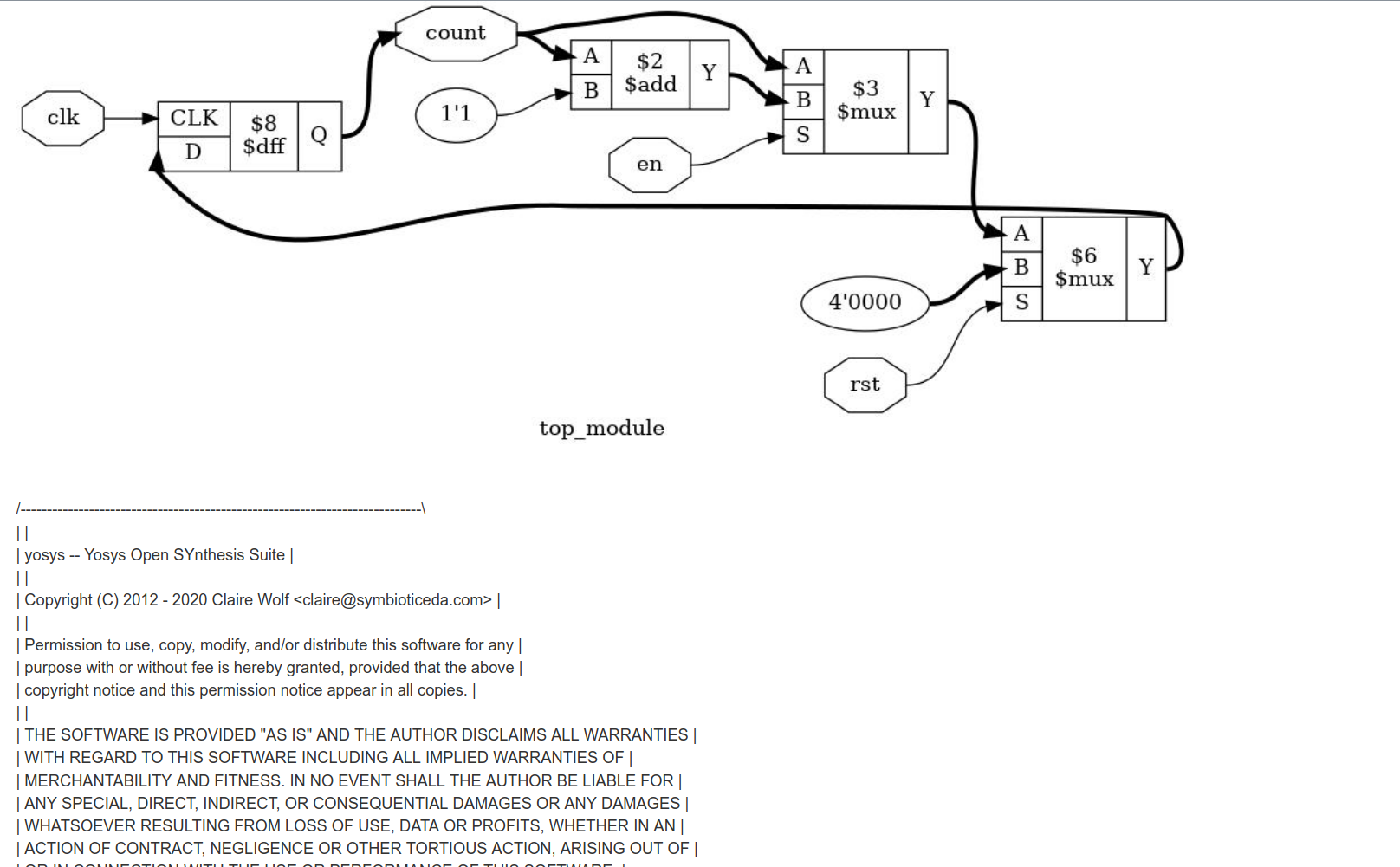
## yosys的web版本
我們有時候學習就只想很快的查看一些RTL或者GATE級的結果,安裝環境可能遇到各種問題,在這種情況下,我們可以使用yosys的web版本,鏈接地址:
[yosys的web版本](http://hdl.huangzzk.info/)
## 鏈接地址
[yosys github地址](https://github.com/YosysHQ/yosys)
[測試源碼地址](https://gitee.com/yuan_hp/yosys-test)
- 序
- 第1章 Linux下開發FPGA
- 1.1 Linux下安裝diamond
- 1.2 使用輕量級linux仿真工具iverilog
- 1.3 使用linux shell來讀寫串口
- 1.4 嵌入式上的linux
- 設備數教程
- linux C 標準庫文檔
- linux 網絡編程
- 開機啟動流程
- 1.5 linux上實現與樹莓派,FPGA等通信的串口腳本
- 第2章 Intel FPGA的使用
- 2.1 特別注意
- 2.2 高級應用開發流程
- 2.2.1 生成二進制bit流rbf
- 2.2.2 制作Preloader Image
- 2.2.2.1 生成BSP文件
- 2.2.2.2 編譯preloader和uboot
- 2.2.2.3 更新SD的preloader和uboot
- 2.3 HPS使用
- 2.3.1 通過JTAG下載代碼
- 2.3.2 HPS軟件部分開發
- 2.3 quartus中IP核的使用
- 2.3.1 Intel中RS232串口IP的使用
- 2.4 一些問題的解決方法
- 2.4.1 關于引腳的復用的綜合出錯
- 第3章 關于C/C++的一些語法
- 3.1 C中數組作為形參不傳長度
- 3.2 匯編中JUMP和CALL的區別
- 3.3 c++中map的使用
- 3.4 鏈表的一些應用
- 3.5 vector的使用
- 3.6 使用C實現一個簡單的FIFO
- 3.6.1 循環隊列
- 3.7 C語言不定長參數
- 3.8 AD采樣計算同頻信號的相位差
- 3.9 使用C實現棧
- 3.10 增量式PID
- 第4章 Xilinx的FPGA使用
- 4.1 Alinx使用中的一些問題及解決方法
- 4.1.1 在Genarate Bitstream時提示沒有name.tcl
- 4.1.2 利用verilog求位寬
- 4.1.3 vivado中AXI寫DDR說明
- 4.1.4 zynq中AXI GPIO中斷問題
- 4.1.5 關于時序約束
- 4.1.6 zynq的PS端利用串口接收電腦的數據
- 4.1.7 SDK啟動出錯的解決方法
- 4.1.8 讓工具綜合是不優化某一模塊的方法
- 4.1.9 固化程序(雙核)
- 4.1.10 分配引腳時的問題
- 4.1.11 vivado仿真時相對文件路徑的問題
- 4.2 GCC使用Attribute分配空間給變量
- 4.3 關于Zynq的DDR寫入byte和word的方法
- 4.4 常用模塊
- 4.4.1 I2S接收串轉并
- 4.5 時鐘約束
- 4.5.1 時鐘約束
- 4.6 VIVADO使用
- 4.6.1 使用vivado進行仿真
- 4.7 關于PicoBlaze軟核的使用
- 4.8 vivado一些IP的使用
- 4.8.1 float-point浮點單元的使用
- 4.10 zynq的雙核中斷
- 第5章 FPGA的那些好用的工具
- 5.1 iverilog
- 5.2 Arduino串口繪圖器工具
- 5.3 LabVIEW
- 5.4 FPGA開發實用小工具
- 5.5 Linux下繪制時序圖軟件
- 5.6 verilog和VHDL相互轉換工具
- 5.7 linux下搭建輕量易用的verilog仿真環境
- 5.8 VCS仿真verilog并查看波形
- 5.9 Verilog開源的綜合工具-Yosys
- 5.10 sublim text3編輯器配置verilog編輯環境
- 5.11 在線工具
- 真值表 -> 邏輯表達式
- 5.12 Modelsim使用命令仿真
- 5.13 使用TCL實現的個人仿真腳本
- 5.14 在cygwin下使用命令行下載arduino代碼到開發板
- 5.15 STM32開發
- 5.15.1 安裝Atollic TrueSTUDIO for STM32
- 5.15.2 LED閃爍吧
- 5.15.3 模擬U盤
- 第6章 底層實現
- 6.1 硬件實現加法的流程
- 6.2 硬件實現乘法器
- 6.3 UART實現
- 6.3.1 通用串口發送模塊
- 6.4 二進制數轉BCD碼
- 6.5 基本開源資源
- 6.5.1 深度資源
- 6.5.2 FreeCore資源集合
- 第7章 常用模塊
- 7.1 溫濕度傳感器DHT11的verilog驅動
- 7.2 DAC7631驅動(verilog)
- 7.3 按鍵消抖
- 7.4 小腳丫數碼管顯示
- 7.5 verilog實現任意人數表決器
- 7.6 基本模塊head.v
- 7.7 四相八拍步進電機驅動
- 7.8 單片機部分
- 7.8.1 I2C OLED驅動
- 第8章 verilog 掃盲區
- 8.1 時序電路中數據的讀寫
- 8.2 從RTL角度來看verilog中=和<=的區別
- 8.3 case和casez的區別
- 8.4 關于參數的傳遞與讀取(paramter)
- 8.5 關于符號優先級
- 第9章 verilog中的一些語法使用
- 9.1 可綜合的repeat
- 第10章 system verilog
- 10.1 簡介
- 10.2 推薦demo學習網址
- 10.3 VCS在linux上環境的搭建
- 10.4 deepin15.11(linux)下搭建system verilog的vcs仿真環境
- 10.5 linux上使用vcs寫的腳本仿真管理
- 10.6 system verilog基本語法
- 10.6.1 數據類型
- 10.6.2 枚舉與字符串
- 第11章 tcl/tk的使用
- 11.1 使用Tcl/Tk
- 11.2 tcl基本語法教程
- 11.3 Tk的基本語法
- 11.3.1 建立按鈕
- 11.3.2 復選框
- 11.3.3 單選框
- 11.3.4 標簽
- 11.3.5 建立信息
- 11.3.6 建立輸入框
- 11.3.7 旋轉框
- 11.3.8 框架
- 11.3.9 標簽框架
- 11.3.10 將窗口小部件分配到框架/標簽框架
- 11.3.11 建立新的上層窗口
- 11.3.12 建立菜單
- 11.3.13 上層窗口建立菜單
- 11.3.14 建立滾動條
- 11.4 窗口管理器
- 11.5 一些學習的腳本
- 11.6 一些常用的操作語法實現
- 11.6.1 刪除同一后綴的文件
- 11.7 在Lattice的Diamond中使用tcl
- 第12章 FPGA的重要知識
- 12.1 面積與速度的平衡與互換
- 12.2 硬件原則
- 12.3 系統原則
- 12.4 同步設計原則
- 12.5 乒乓操作
- 12.6 串并轉換設計技巧
- 12.7 流水線操作設計思想
- 12.8 數據接口的同步方法
- 第13章 小項目
- 13.1 數字濾波器
- 13.2 FIFO
- 13.3 一個精簡的CPU( mini-mcu )
- 13.3.1 基本功能實現
- 13.3.2 中斷添加
- 13.3.3 使用中斷實現流水燈(實際硬件驗證)
- 13.3.4 綜合一點的應用示例
- 13.4.5 使用flex開發匯編編譯器
- 13.4.5 linux--Flex and Bison
- 13.4 有符號數轉單精度浮點數
- 13.5 串口調試FPGA模板
