# 2.2.1 LinearLayout(線性布局)
## 本節引言
本節開始講Android中的布局,Android中有六大布局,分別是: LinearLayout(線性布局),RelativeLayout(相對布局),TableLayout(表格布局) FrameLayout(幀布局),AbsoluteLayout(絕對布局),GridLayout(網格布局) 而今天我們要講解的就是第一個布局,LinearLayout(線性布局),我們屏幕適配的使用 用的比較多的就是LinearLayout的weight(權重屬性),在這一節里,我們會詳細地解析 LinearLayout,包括一些基本的屬性,Weight屬性的使用,以及比例如何計算,另外還 會說下一個用的比較少的屬性:android:divider繪制下劃線!
## 1.本節學習圖

## 2.weight(權重)屬性詳解:
### ①最簡單用法:
如圖:
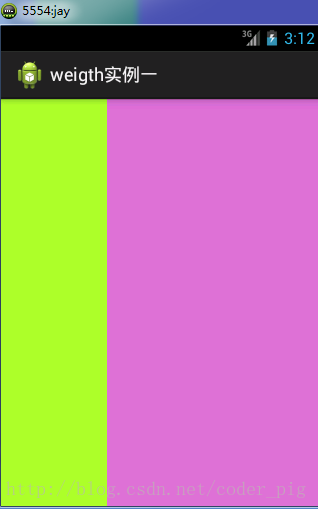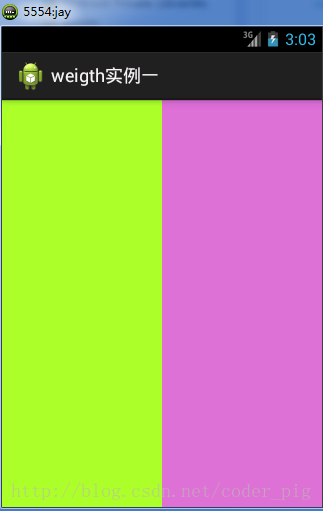
實現代碼:
```
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/LinearLayout1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal"> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:background="#ADFF2F" android:layout_weight="1"/> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:background="#DA70D6" android:layout_weight="2"/> </LinearLayout>
```
要實現第一個的1:1的效果,只需要分別把兩個LinearLayout的weight改成1和1就可以了 用法歸納: 按比例劃分水平方向:將涉及到的View的android:width屬性設置為0dp,然后設置為android weight屬性設置比例即可;類推,豎直方向,只需設android:height為0dp,然后設weight屬性即可! 大家可以自己寫個豎直方向的等比例劃分的體驗下簡單用法!
### ②weight屬性詳解:
當然,如果我們不適用上述那種設置為0dp的方式,直接用wrap_content和match_parent的話, 則要接著解析weight屬性了,分為兩種情況,wrap_content與match_parent!另外還要看 LinearLayout的orientation是水平還是豎直,這個決定哪個方向等比例劃分
**1)wrap_content比較簡單,直接就按比例的了**
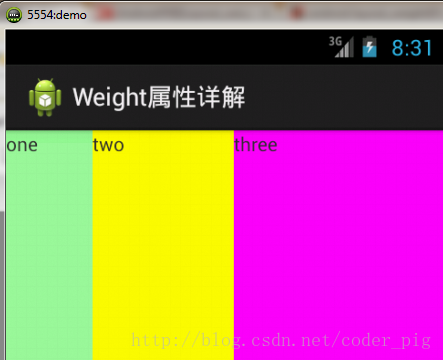
實現代碼:
```
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/LinearLayout1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" > <TextView android:layout_weight="1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:text="one" android:background="#98FB98" /> <TextView android:layout_weight="2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:text="two" android:background="#FFFF00" /> <TextView android:layout_weight="3" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:text="three" android:background="#FF00FF" /> </LinearLayout>
```
**2)match_parent(fill_parent):這個則需要計算了**
我們寫這段簡單的代碼:
```
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/LinearLayout1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > <TextView android:layout_weight="1" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:text="one" android:background="#98FB98" /> <TextView android:layout_weight="2" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:text="two" android:background="#FFFF00" /> <TextView android:layout_weight="3" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:text="three" android:background="#FF00FF" /> </LinearLayout>
```
運行效果圖:
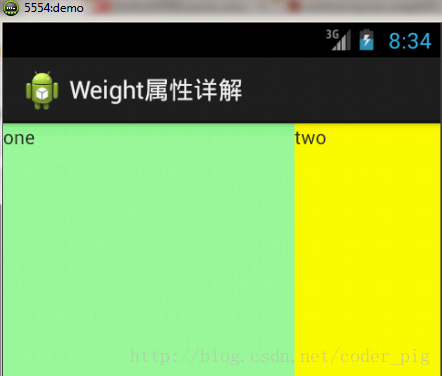
> 這個時候就會有疑問了,怎么會這樣,這比例是2:1吧,那么three去哪了?代碼里面明明有 three的啊,還設置了3的,而1和2的比例也不對耶,1:2:3卻變成了2:1:0,怎么會這樣呢? 答:這里其實沒那么簡單的,還是需要我們計算的,網上給出的算法有幾種,這里就給出筆者 覺得比較容易理解的一種: **step 1:**個個都是fill_parent,但是屏幕只有一個啦,那么1 - 3 = - 2 fill_parent **step 2:**依次比例是1/6,2/6,3/6 **step 3:**先到先得,先分給one,計算: 1 - 2 * (1/6) = 2/3 fill_parent 接著到two,計算: 1 - 2 * (2/6) = 1/3 fill_parent 最后到three,計算 1 - 2 * (3/6) = 0 fill_parent **step 4:**所以最后的結果是:one占了兩份,two占了一份,three什么都木有 以上就是為什么three沒有出現的原因了,或許大家看完還是有點蒙,沒事,我們舉多幾個例子試試就知道了!
**比例為:1:1:1**
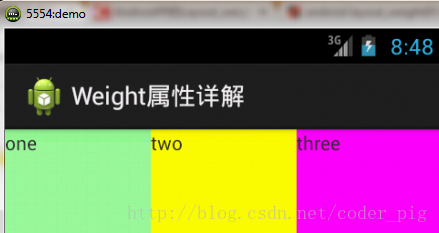
按照上面的計算方法算一次,結果是:1/3 1/3 1/3,沒錯
**接著我們再試下:2:3:4**
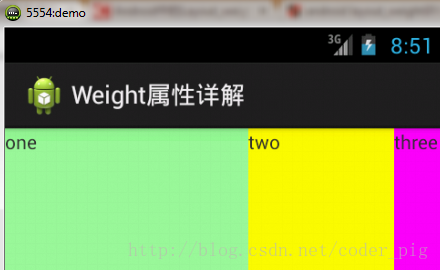
計算結果:5/9 3/9 1/9,對比效果圖,5:3:1,也沒錯,所以這個計算方法你可得mark下了!
### ③Java代碼中設置weight屬性:
```
setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, 1));
```
## 3.為LinearLayout設置分割線
很多界面開發中都會設置一些下劃線,或者分割線,從而使得界面更加整潔美觀,比如下面的酷狗 音樂的注冊頁面:
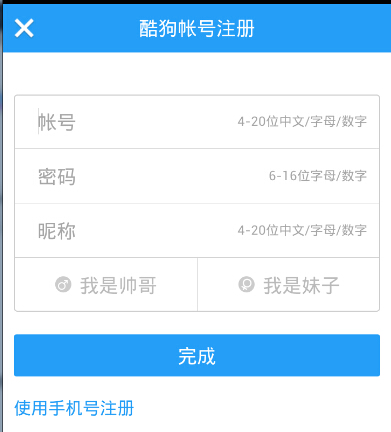
對于這種線,我們通常的做法有兩種 **①直接在布局中添加一個view**,這個view的作用僅僅是顯示出一條線,代碼也很簡單:
```
<View android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="1px" android:background="#000000" />
```
這個是水平方向上的黑線,當然你也可以改成其他顏色,或者使用圖片

**②第二種則是使用LinearLayout的一個divider屬性**,直接為LinearLayout設置分割線 這里就需要你自己準備一張線的圖片了 1)android:divider設置作為分割線的圖片 2)android:showDividers設置分割線的位置,none(無),begining(開始),end(結束),middle(每兩個組件間) 3)dividerPadding設置分割線的Padding
使用示例:
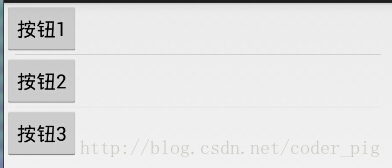
實現代碼:
```
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/LinearLayout1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:divider="@drawable/ktv_line_div" android:orientation="vertical" android:showDividers="middle" android:dividerPadding="10dp" tools:context="com.jay.example.linearlayoutdemo.MainActivity" > <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="按鈕1" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="按鈕2" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="按鈕3" /> </LinearLayout>
```
## 4.LinearLayout的簡單例子:
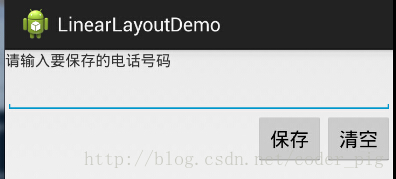
實現代碼如下:
```
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/LinearLayout1" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="請輸入要保存的電話號碼"/> <EditText android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" android:gravity="right"> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="保存"/> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="清空"/> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
```
## 5.注意事項:
使用Layout_gravity的一個很重要的問題!!! 問題內容: 在一個LinearLayout的水平方向中布置兩個TextView,想讓一個左,一個右,怎么搞? 或許你會脫口而出:"gravity設置一個left,一個right就可以啦!" 真的這么簡單?你試過嗎?寫個簡單的Layout你就會發現,事與愿違了: 代碼如下:
```
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" tools:context="com.jay.example.getscreendemo.MainActivity" > <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="200dp" android:layout_gravity="left" android:background="#FF7878" android:gravity="center" android:text="O(∩_∩)O哈哈~" /> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="200dp" android:layout_gravity="right" android:background="#FF7428" android:gravity="center" android:text="(*^__^*) 嘻嘻……" /> </LinearLayout>
```
運行結果圖:
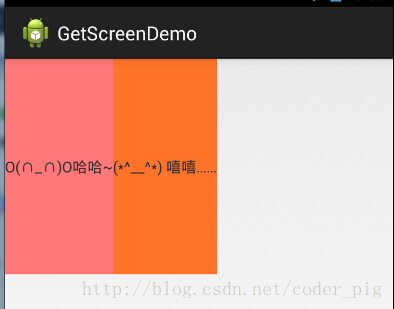
看到這里你會說:哎呀,真的不行耶,要不在外層LinearLayout加個gravity=left的屬性,然后設置第二個 TextView的layout_gravity為right,恩,好我們試一下:
```
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" android:gravity="left" tools:context="com.jay.example.getscreendemo.MainActivity" > <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="200dp" android:background="#FF7878" android:gravity="center" android:text="O(∩_∩)O哈哈~" /> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="200dp" android:layout_gravity="right" android:background="#FF7428" android:gravity="center" android:text="(*^__^*) 嘻嘻……" /> </LinearLayout>
```
結果還是一樣:
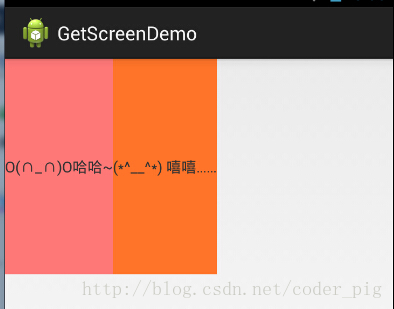
好吧,沒轍了,怎么辦好?
> **當 android:orientation="vertical" 時, 只有水平方向的設置才起作用,垂直方向的設置不起作用。 即:left,right,center_horizontal 是生效的。 當 android:orientation="horizontal" 時, 只有垂直方向的設置才起作用,水平方向的設置不起作用。 即:top,bottom,center_vertical 是生效的。**
然而,這方法好像并沒有什么卵用。比如: 如果只能豎直方向設置左右對齊的話,就會出現下面的效果:

這顯然不是我們要的結果把! 綜上,要么按照上述給出的規則來布局,不過對于這種情況還是使用相對布局RelativeLayout把! 網上沒給出具體的原因,都是說這樣改有人說這個和orientation的優先級有關 ,暫且先mark下來吧,后續如果知道原因的話再解釋!前面屏幕適配也說過了,**布局還是建議使用 RelativeLayout!**
PS:本文是之前筆者寫的布局系列文章中的一篇,自覺的寫得很贊,所以這里直接引用的原文內容, 原文鏈接如下:[New UI-布局之LinearLayout(線性布局)詳解](http://blog.csdn.net/coder_pig/article/details/42344615)
- 1.0 Android基礎入門教程
- 1.0.1 2015年最新Android基礎入門教程目錄
- 1.1 背景相關與系統架構分析
- 1.2 開發環境搭建
- 1.2.1 使用Eclipse + ADT + SDK開發Android APP
- 1.2.2 使用Android Studio開發Android APP
- 1.3 SDK更新不了問題解決
- 1.4 Genymotion模擬器安裝
- 1.5.1 Git使用教程之本地倉庫的基本操作
- 1.5.2 Git之使用GitHub搭建遠程倉庫
- 1.6 .9(九妹)圖片怎么玩
- 1.7 界面原型設計
- 1.8 工程相關解析(各種文件,資源訪問)
- 1.9 Android程序簽名打包
- 1.11 反編譯APK獲取代碼&資源
- 2.1 View與ViewGroup的概念
- 2.2.1 LinearLayout(線性布局)
- 2.2.2 RelativeLayout(相對布局)
- 2.2.3 TableLayout(表格布局)
- 2.2.4 FrameLayout(幀布局)
- 2.2.5 GridLayout(網格布局)
- 2.2.6 AbsoluteLayout(絕對布局)
- 2.3.1 TextView(文本框)詳解
- 2.3.2 EditText(輸入框)詳解
- 2.3.3 Button(按鈕)與ImageButton(圖像按鈕)
- 2.3.4 ImageView(圖像視圖)
- 2.3.5.RadioButton(單選按鈕)&Checkbox(復選框)
- 2.3.6 開關按鈕ToggleButton和開關Switch
- 2.3.7 ProgressBar(進度條)
- 2.3.8 SeekBar(拖動條)
- 2.3.9 RatingBar(星級評分條)
- 2.4.1 ScrollView(滾動條)
- 2.4.2 Date & Time組件(上)
- 2.4.3 Date & Time組件(下)
- 2.4.4 Adapter基礎講解
- 2.4.5 ListView簡單實用
- 2.4.6 BaseAdapter優化
- 2.4.7ListView的焦點問題
- 2.4.8 ListView之checkbox錯位問題解決
- 2.4.9 ListView的數據更新問題
- 2.5.0 構建一個可復用的自定義BaseAdapter
- 2.5.1 ListView Item多布局的實現
- 2.5.2 GridView(網格視圖)的基本使用
- 2.5.3 Spinner(列表選項框)的基本使用
- 2.5.4 AutoCompleteTextView(自動完成文本框)的基本使用
- 2.5.5 ExpandableListView(可折疊列表)的基本使用
- 2.5.6 ViewFlipper(翻轉視圖)的基本使用
- 2.5.7 Toast(吐司)的基本使用
- 2.5.8 Notification(狀態欄通知)詳解
- 2.5.9 AlertDialog(對話框)詳解
- 2.6.0 其他幾種常用對話框基本使用
- 2.6.1 PopupWindow(懸浮框)的基本使用
- 2.6.2 菜單(Menu)
- 2.6.3 ViewPager的簡單使用
- 2.6.4 DrawerLayout(官方側滑菜單)的簡單使用
- 3.1.1 基于監聽的事件處理機制
- 3.2 基于回調的事件處理機制
- 3.3 Handler消息傳遞機制淺析
- 3.4 TouchListener PK OnTouchEvent + 多點觸碰
- 3.5 監聽EditText的內容變化
- 3.6 響應系統設置的事件(Configuration類)
- 3.7 AnsyncTask異步任務
- 3.8 Gestures(手勢)
- 4.1.1 Activity初學乍練
- 4.1.2 Activity初窺門徑
- 4.1.3 Activity登堂入室
- 4.2.1 Service初涉
- 4.2.2 Service進階
- 4.2.3 Service精通
- 4.3.1 BroadcastReceiver牛刀小試
- 4.3.2 BroadcastReceiver庖丁解牛
- 4.4.2 ContentProvider再探——Document Provider
- 4.5.1 Intent的基本使用
- 4.5.2 Intent之復雜數據的傳遞
- 5.1 Fragment基本概述
- 5.2.1 Fragment實例精講——底部導航欄的實現(方法1)
- 5.2.2 Fragment實例精講——底部導航欄的實現(方法2)
- 5.2.3 Fragment實例精講——底部導航欄的實現(方法3)
- 5.2.4 Fragment實例精講——底部導航欄+ViewPager滑動切換頁面
- 5.2.5 Fragment實例精講——新聞(購物)類App列表Fragment的簡單實現
- 6.1 數據存儲與訪問之——文件存儲讀寫
- 6.2 數據存儲與訪問之——SharedPreferences保存用戶偏好參數
- 6.3.1 數據存儲與訪問之——初見SQLite數據庫
- 6.3.2 數據存儲與訪問之——又見SQLite數據庫
- 7.1.1 Android網絡編程要學的東西與Http協議學習
- 7.1.2 Android Http請求頭與響應頭的學習
- 7.1.3 Android HTTP請求方式:HttpURLConnection
- 7.1.4 Android HTTP請求方式:HttpClient
- 7.2.1 Android XML數據解析
- 7.2.2 Android JSON數據解析
- 7.3.1 Android 文件上傳
- 7.3.2 Android 文件下載(1)
- 7.3.3 Android 文件下載(2)
- 7.4 Android 調用 WebService
- 7.5.1 WebView(網頁視圖)基本用法
- 7.5.2 WebView和JavaScrip交互基礎
- 7.5.3 Android 4.4后WebView的一些注意事項
- 7.5.4 WebView文件下載
- 7.5.5 WebView緩存問題
- 7.5.6 WebView處理網頁返回的錯誤碼信息
- 7.6.1 Socket學習網絡基礎準備
- 7.6.2 基于TCP協議的Socket通信(1)
- 7.6.3 基于TCP協議的Socket通信(2)
- 7.6.4 基于UDP協議的Socket通信
- 8.1.1 Android中的13種Drawable小結 Part 1
- 8.1.2 Android中的13種Drawable小結 Part 2
- 8.1.3 Android中的13種Drawable小結 Part 3
- 8.2.1 Bitmap(位圖)全解析 Part 1
- 8.2.2 Bitmap引起的OOM問題
- 8.3.1 三個繪圖工具類詳解
- 8.3.2 繪圖類實戰示例
- 8.3.3 Paint API之—— MaskFilter(面具)
- 8.3.4 Paint API之—— Xfermode與PorterDuff詳解(一)
- 8.3.5 Paint API之—— Xfermode與PorterDuff詳解(二)
- 8.3.6 Paint API之—— Xfermode與PorterDuff詳解(三)
- 8.3.7 Paint API之—— Xfermode與PorterDuff詳解(四)
- 8.3.8 Paint API之—— Xfermode與PorterDuff詳解(五)
- 8.3.9 Paint API之—— ColorFilter(顏色過濾器)(1/3)
- 8.3.10 Paint API之—— ColorFilter(顏色過濾器)(2-3)
- 8.3.11 Paint API之—— ColorFilter(顏色過濾器)(3-3)
- 8.3.12 Paint API之—— PathEffect(路徑效果)
- 8.3.13 Paint API之—— Shader(圖像渲染)
- 8.3.14 Paint幾個枚舉/常量值以及ShadowLayer陰影效果
- 8.3.15 Paint API之——Typeface(字型)
- 8.3.16 Canvas API詳解(Part 1)
- 8.3.17 Canvas API詳解(Part 2)剪切方法合集
- 8.3.18 Canvas API詳解(Part 3)Matrix和drawBitmapMash
- 8.4.1 Android動畫合集之幀動畫
- 8.4.2 Android動畫合集之補間動畫
- 8.4.3 Android動畫合集之屬性動畫-初見
- 8.4.4 Android動畫合集之屬性動畫-又見
- 9.1 使用SoundPool播放音效(Duang~)
- 9.2 MediaPlayer播放音頻與視頻
- 9.3 使用Camera拍照
- 9.4 使用MediaRecord錄音
- 10.1 TelephonyManager(電話管理器)
- 10.2 SmsManager(短信管理器)
- 10.3 AudioManager(音頻管理器)
- 10.4 Vibrator(振動器)
- 10.5 AlarmManager(鬧鐘服務)
- 10.6 PowerManager(電源服務)
- 10.7 WindowManager(窗口管理服務)
- 10.8 LayoutInflater(布局服務)
- 10.9 WallpaperManager(壁紙管理器)
- 10.10 傳感器專題(1)——相關介紹
- 10.11 傳感器專題(2)——方向傳感器
- 10.12 傳感器專題(3)——加速度/陀螺儀傳感器
- 10.12 傳感器專題(4)——其他傳感器了解
- 10.14 Android GPS初涉
- 11.0《2015最新Android基礎入門教程》完結散花~
