# 4.4.2 ContentProvider再探——Document Provider
## 本節引言:
> 學完上一節,相信你已經知道如何去使用系統提供的ContentProvider或者自定義ContentProvider了, 已經基本滿足日常開發的需求了,有趣的是,我在官方文檔上看到了另外這幾個Provider:
>
> 
>
> **Calendar Provider**:日歷提供者,就是針對針對日歷相關事件的一個資源庫,通過他提供的API,我們 可以對日歷,時間,會議,提醒等內容做一些增刪改查!
> **Contacts Provider**:聯系人提供者,這個就不用說了,這個用得最多~后面有時間再回頭翻譯下這篇文章吧!
> **Storage Access Framework(SAF)**:存儲訪問框架,4.4以后引入的一個新玩意,為用戶瀏覽手機中的 存儲內容提供了便利,可供訪問的內容不僅包括:文檔,圖片,視頻,音頻,下載,而且包含所有由 由特定ContentProvider(須具有約定的API)提供的內容。不管這些內容來自于哪里,不管是哪個應 用調用瀏覽系統文件內容的命令,系統都會用一個統一的界面讓你去瀏覽。
> 其實就是一個內置的應用程序,叫做DocumentsUI,因為它的IntentFilter不帶有LAUNCHER,所以我們并沒有 在桌面上找到這個東東!嘿嘿,試下下面的代碼,這里我們選了兩個手機來對比: 分別是4.2的Lenovo S898T 和 5.0.1的Nexus 5做對比,執行下述代碼:
```
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_OPEN_DOCUMENT); intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_OPENABLE); intent.setType("image/*"); startActivity(intent);
```
下面是運行結果:
 
右面這個就是4.4給我們帶來的新玩意了,一般我們獲取文件Url的時候就可以用到它~ 接下來簡單的走下文檔吧~
## 2.簡單走下文檔:
### 1)SAF框架的組成:
> * **Document provider**:一個特殊的ContentProvider,讓一個存儲服務(比如Google Drive)可以 對外展示自己所管理的文件。它是**DocumentsProvider**的子類,另外,document-provider的存儲格式 和傳統的文件存儲格式一致,至于你的內容如何存儲,則完全決定于你自己,Android系統已經內置了幾個 這樣的Document provider,比如關于下載,圖片以及視頻的Document provider!
> * **Client app**:一個普通的客戶端軟件,通過觸發**ACTION_OPEN_DOCUMENT** 和/或 **ACTION_CREATE_DOCUMENT**就可以接收到來自于Document provider返回的內容,比如選擇一個圖片, 然后返回一個Uri。
> * **Picker**:類似于文件管理器的界面,而且是系統級的界面,提供額訪問客戶端過濾條件的 Document provider內容的通道,就是起說的那個DocumentsUI程序!
**一些特性:**
> * 用戶可以瀏覽所有document provider提供的內容,而不僅僅是單一的應用程序
> * 提供了長期、持續的訪問document provider中文件的能力以及數據的持久化, 用戶可以實現添加、刪除、編輯、保存document provider所維護的內容
> * 支持多用戶以及臨時性的內容服務,比如USB storage providers只有當驅動安裝成功才會出現
### 2)概述:
SAF的核心是實現了DocumentsProvider的子類,還是一個ContentProvider。在一個document provider 中是以傳統的文件目錄樹組織起來的:

### 3)流程圖:
如上面所述,document provider data是基于傳統的文件層次結構的,不過那只是對外的表現形式, 如何存儲你的數據,取決于你自己,只要你對海外的接口能夠通過DocumentsProvider的api訪問就可以。 下面的流程圖展示了一個photo應用使用SAF可能的結構:
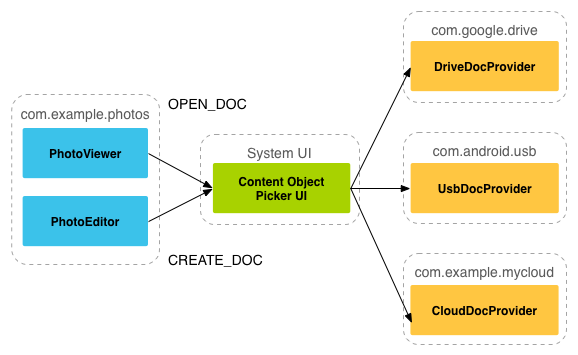
分析:
> 從上圖,我們可以看出Picker是鏈接調用者和內容提供者的一個橋梁!他提供并告訴調用者,可以選擇 哪些內容提供者,比如這里的DriveDocProvider,UsbDocProvider,CloundDocProvider。
> 當客戶端觸發了**ACTION_OPEN_DOCUMENT**或**ACTION_CREATE_DOCUMENT**的Intent,就會發生上述交互。 當然我們還可以在Intent中增加過濾條件,比如限制MIME type的類型為"image"!
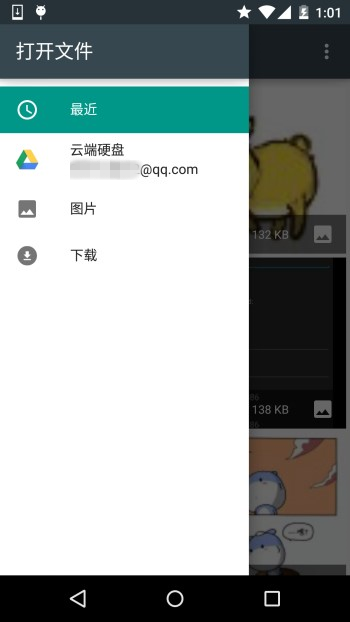
就是上面這些東西,如果你還安裝了其他看圖的軟件的話,也會在這里看到! 簡單點說就是:客戶端發送了上面兩種Action的Intent后,會打開Picker UI,在這里會顯示相關可用的 Document Provider,供用戶選擇,用戶選擇后可以獲得文件的相關信息!
### 4)客戶端調用,并獲取返回的Uri
**實現代碼如下:**
```
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener { private static final int READ_REQUEST_CODE = 42; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); Button btn_show = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_show); btn_show.setOnClickListener(this); } @Override public void onClick(View v) { Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_OPEN_DOCUMENT); intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_OPENABLE); intent.setType("image/*"); startActivityForResult(intent, READ_REQUEST_CODE); } @Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) { if (requestCode == READ_REQUEST_CODE && resultCode == Activity.RESULT_OK) { Uri uri; if (data != null) { uri = data.getData(); Log.e("HeHe", "Uri: " + uri.toString()); } } } }
```
**運行結果:** 比如我們選中那只狗,然后Picker UI自己會關掉,然后Logcat上可以看到這樣一個uri:

### 5)根據uri獲取文件參數
**核心代碼如下:**
```
public void dumpImageMetaData(Uri uri) { Cursor cursor = getContentResolver() .query(uri, null, null, null, null, null); try { if (cursor != null && cursor.moveToFirst()) { String displayName = cursor.getString( cursor.getColumnIndex(OpenableColumns.DISPLAY_NAME)); Log.e("HeHe", "Display Name: " + displayName); int sizeIndex = cursor.getColumnIndex(OpenableColumns.SIZE); String size = null; if (!cursor.isNull(sizeIndex)) { size = cursor.getString(sizeIndex); }else { size = "Unknown"; } Log.e("HeHe", "Size: " + size); } }finally { cursor.close(); } }
```
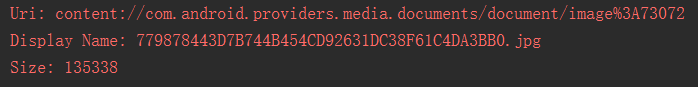
**運行結果:** 還是那只狗,調用方法后會輸入文件名以及文件大小,以byte為單位
### 6)根據Uri獲得Bitmap
**核心代碼如下:**
```
private Bitmap getBitmapFromUri(Uri uri) throws IOException { ParcelFileDescriptor parcelFileDescriptor = getContentResolver().openFileDescriptor(uri, "r"); FileDescriptor fileDescriptor = parcelFileDescriptor.getFileDescriptor(); Bitmap image = BitmapFactory.decodeFileDescriptor(fileDescriptor); parcelFileDescriptor.close(); return image; }
```
**運行結果**:
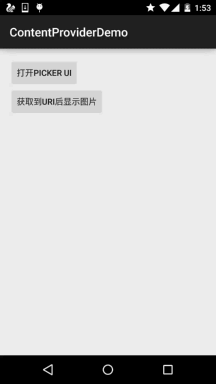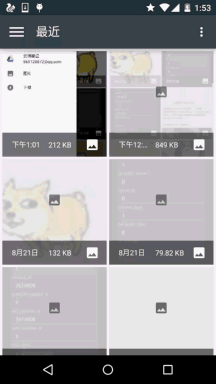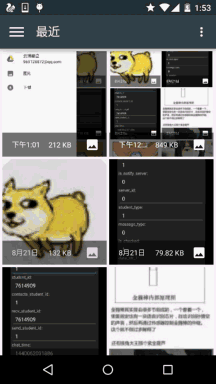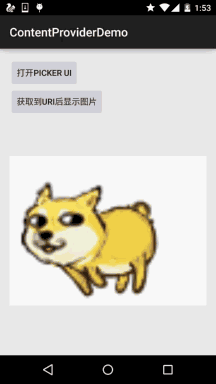
### 7)根據Uri獲取輸入流
**核心代碼如下:**
```
private String readTextFromUri(Uri uri) throws IOException { InputStream inputStream = getContentResolver().openInputStream(uri); BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader( inputStream)); StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); String line; while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) { stringBuilder.append(line); } fileInputStream.close(); parcelFileDescriptor.close(); return stringBuilder.toString(); }
```
上述的內容只告訴你通過一個Uri你可以知道什么,而Uri的獲取則是通過SAF得到的!
### 8) 創建新文件以及刪除文件:
**創建文件:**
```
private void createFile(String mimeType, String fileName) { Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_CREATE_DOCUMENT); intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_OPENABLE); intent.setType(mimeType); intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_TITLE, fileName); startActivityForResult(intent, WRITE_REQUEST_CODE); }
```
可在onActivityResult()中獲取被創建文件的uri
**刪除文件:**
前提是Document.COLUMN_FLAGS包含**SUPPORTS_DELETE**
```
DocumentsContract.deleteDocument(getContentResolver(), uri);
```
### 9)編寫一個自定義的Document Provider
如果你希望自己應用的數據也能在documentsui中打開,你就需要寫一個自己的document provider。 下面介紹自定義DocumentsProvider的步驟:
> * API版本為19或者更高
> * 在manifest.xml中注冊該Provider
> * Provider的name為類名加包名,比如: **com.example.android.storageprovider.MyCloudProvider**
> * Authority為包名+provider的類型名,如: **com.example.android.storageprovider.documents**
> * **android:exported屬性的值為ture**
下面是Provider的例子寫法:
```
<manifest... > ... <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="19" android:targetSdkVersion="19" /> .... <provider android:name="com.example.android.storageprovider.MyCloudProvider" android:authorities="com.example.android.storageprovider.documents" android:grantUriPermissions="true" android:exported="true" android:permission="android.permission.MANAGE_DOCUMENTS" android:enabled="@bool/atLeastKitKat"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.content.action.DOCUMENTS_PROVIDER" /> </intent-filter> </provider> </application> </manifest>
```
### 10 )DocumentsProvider的子類
至少實現如下幾個方法:
> * queryRoots()
> * queryChildDocuments()
> * queryDocument()
> * openDocument()
還有些其他的方法,但并不是必須的。下面演示一個實現訪問文件(file)系統的 DocumentsProvider的大致寫法。
**Implement queryRoots**
```
@Override public Cursor queryRoots(String[] projection) throws FileNotFoundException { // Create a cursor with either the requested fields, or the default // projection if "projection" is null. final MatrixCursor result = new MatrixCursor(resolveRootProjection(projection)); // If user is not logged in, return an empty root cursor. This removes our // provider from the list entirely. if (!isUserLoggedIn()) { return result; } // It's possible to have multiple roots (e.g. for multiple accounts in the // same app) -- just add multiple cursor rows. // Construct one row for a root called "MyCloud". final MatrixCursor.RowBuilder row = result.newRow(); row.add(Root.COLUMN_ROOT_ID, ROOT); row.add(Root.COLUMN_SUMMARY, getContext().getString(R.string.root_summary)); // FLAG_SUPPORTS_CREATE means at least one directory under the root supports // creating documents. FLAG_SUPPORTS_RECENTS means your application's most // recently used documents will show up in the "Recents" category. // FLAG_SUPPORTS_SEARCH allows users to search all documents the application // shares. row.add(Root.COLUMN_FLAGS, Root.FLAG_SUPPORTS_CREATE | Root.FLAG_SUPPORTS_RECENTS | Root.FLAG_SUPPORTS_SEARCH); // COLUMN_TITLE is the root title (e.g. Gallery, Drive). row.add(Root.COLUMN_TITLE, getContext().getString(R.string.title)); // This document id cannot change once it's shared. row.add(Root.COLUMN_DOCUMENT_ID, getDocIdForFile(mBaseDir)); // The child MIME types are used to filter the roots and only present to the // user roots that contain the desired type somewhere in their file hierarchy. row.add(Root.COLUMN_MIME_TYPES, getChildMimeTypes(mBaseDir)); row.add(Root.COLUMN_AVAILABLE_BYTES, mBaseDir.getFreeSpace()); row.add(Root.COLUMN_ICON, R.drawable.ic_launcher); return result; }
```
**Implement queryChildDocuments**
```
public Cursor queryChildDocuments(String parentDocumentId, String[] projection, String sortOrder) throws FileNotFoundException { final MatrixCursor result = new MatrixCursor(resolveDocumentProjection(projection)); final File parent = getFileForDocId(parentDocumentId); for (File file : parent.listFiles()) { // Adds the file's display name, MIME type, size, and so on. includeFile(result, null, file); } return result; }
```
**Implement queryDocument**
```
@Override public Cursor queryDocument(String documentId, String[] projection) throws FileNotFoundException { // Create a cursor with the requested projection, or the default projection. final MatrixCursor result = new MatrixCursor(resolveDocumentProjection(projection)); includeFile(result, documentId, null); return result; }
```
好吧,文檔中的內容大概就是這些了: 一開始是想自己翻譯的,后來在泡在網上的日子上找到了這一篇文檔的中文翻譯,就偷下懶了~
中文翻譯鏈接:[android存儲訪問框架Storage Access Framework](http://www.jcodecraeer.com/a/anzhuokaifa/androidkaifa/2014/1026/1845.html727.jpg)
## 3.Android 4.4 獲取資源路徑問題:
其實這個SAF我們用得較多的地方無非是獲取圖片的Uri而已,而從上面的例子我們也發現了: 我們這樣獲取的鏈接是這樣的:
```
content://com.android.providers.media.documents/document/image%3A69983
```
這樣的鏈接,我們直接通過上面的方法獲得uri即可!
當然,這個是4.4 或者以上版本的~!
如果是以前的版本:uri可能是這樣的:
```
content://media/external/images/media/image%3A69983
```
這里貼下在別的地方看到的一個全面的方案,原文鏈接:[Android4.4中獲取資源路徑問題](http://blog.csdn.net/huangyanan1989/article/details/17263203)
```
public static String getPath(final Context context, final Uri uri) { final boolean isKitKat = Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT; // DocumentProvider if (isKitKat && DocumentsContract.isDocumentUri(context, uri)) { // ExternalStorageProvider if (isExternalStorageDocument(uri)) { final String docId = DocumentsContract.getDocumentId(uri); final String[] split = docId.split(":"); final String type = split[0]; if ("primary".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) { return Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory() + "/" + split[1]; } // TODO handle non-primary volumes } // DownloadsProvider else if (isDownloadsDocument(uri)) { final String id = DocumentsContract.getDocumentId(uri); final Uri contentUri = ContentUris.withAppendedId( Uri.parse("content://downloads/public_downloads"), Long.valueOf(id)); return getDataColumn(context, contentUri, null, null); } // MediaProvider else if (isMediaDocument(uri)) { final String docId = DocumentsContract.getDocumentId(uri); final String[] split = docId.split(":"); final String type = split[0]; Uri contentUri = null; if ("image".equals(type)) { contentUri = MediaStore.Images.Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI; } else if ("video".equals(type)) { contentUri = MediaStore.Video.Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI; } else if ("audio".equals(type)) { contentUri = MediaStore.Audio.Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI; } final String selection = "_id=?"; final String[] selectionArgs = new String[] { split[1] }; return getDataColumn(context, contentUri, selection, selectionArgs); } } // MediaStore (and general) else if ("content".equalsIgnoreCase(uri.getScheme())) { return getDataColumn(context, uri, null, null); } // File else if ("file".equalsIgnoreCase(uri.getScheme())) { return uri.getPath(); } return null; } /**
* Get the value of the data column for this Uri. This is useful for
* MediaStore Uris, and other file-based ContentProviders.
*
* @param context The context.
* @param uri The Uri to query.
* @param selection (Optional) Filter used in the query.
* @param selectionArgs (Optional) Selection arguments used in the query.
* @return The value of the _data column, which is typically a file path.
*/ public static String getDataColumn(Context context, Uri uri, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) { Cursor cursor = null; final String column = "_data"; final String[] projection = { column }; try { cursor = context.getContentResolver().query(uri, projection, selection, selectionArgs, null); if (cursor != null && cursor.moveToFirst()) { final int column_index = cursor.getColumnIndexOrThrow(column); return cursor.getString(column_index); } } finally { if (cursor != null) cursor.close(); } return null; } /**
* @param uri The Uri to check.
* @return Whether the Uri authority is ExternalStorageProvider.
*/ public static boolean isExternalStorageDocument(Uri uri) { return "com.android.externalstorage.documents".equals(uri.getAuthority()); } /**
* @param uri The Uri to check.
* @return Whether the Uri authority is DownloadsProvider.
*/ public static boolean isDownloadsDocument(Uri uri) { return "com.android.providers.downloads.documents".equals(uri.getAuthority()); } /**
* @param uri The Uri to check.
* @return Whether the Uri authority is MediaProvider.
*/ public static boolean isMediaDocument(Uri uri) { return "com.android.providers.media.documents".equals(uri.getAuthority()); }
```
## 本節小結:
> 好的,關于本節android存儲訪問框架SAF就到這里吧,沒什么例子,后面用到再深入研究吧, 知道下就好,4.4后獲取文件路徑就簡單多了~
- 1.0 Android基礎入門教程
- 1.0.1 2015年最新Android基礎入門教程目錄
- 1.1 背景相關與系統架構分析
- 1.2 開發環境搭建
- 1.2.1 使用Eclipse + ADT + SDK開發Android APP
- 1.2.2 使用Android Studio開發Android APP
- 1.3 SDK更新不了問題解決
- 1.4 Genymotion模擬器安裝
- 1.5.1 Git使用教程之本地倉庫的基本操作
- 1.5.2 Git之使用GitHub搭建遠程倉庫
- 1.6 .9(九妹)圖片怎么玩
- 1.7 界面原型設計
- 1.8 工程相關解析(各種文件,資源訪問)
- 1.9 Android程序簽名打包
- 1.11 反編譯APK獲取代碼&資源
- 2.1 View與ViewGroup的概念
- 2.2.1 LinearLayout(線性布局)
- 2.2.2 RelativeLayout(相對布局)
- 2.2.3 TableLayout(表格布局)
- 2.2.4 FrameLayout(幀布局)
- 2.2.5 GridLayout(網格布局)
- 2.2.6 AbsoluteLayout(絕對布局)
- 2.3.1 TextView(文本框)詳解
- 2.3.2 EditText(輸入框)詳解
- 2.3.3 Button(按鈕)與ImageButton(圖像按鈕)
- 2.3.4 ImageView(圖像視圖)
- 2.3.5.RadioButton(單選按鈕)&Checkbox(復選框)
- 2.3.6 開關按鈕ToggleButton和開關Switch
- 2.3.7 ProgressBar(進度條)
- 2.3.8 SeekBar(拖動條)
- 2.3.9 RatingBar(星級評分條)
- 2.4.1 ScrollView(滾動條)
- 2.4.2 Date & Time組件(上)
- 2.4.3 Date & Time組件(下)
- 2.4.4 Adapter基礎講解
- 2.4.5 ListView簡單實用
- 2.4.6 BaseAdapter優化
- 2.4.7ListView的焦點問題
- 2.4.8 ListView之checkbox錯位問題解決
- 2.4.9 ListView的數據更新問題
- 2.5.0 構建一個可復用的自定義BaseAdapter
- 2.5.1 ListView Item多布局的實現
- 2.5.2 GridView(網格視圖)的基本使用
- 2.5.3 Spinner(列表選項框)的基本使用
- 2.5.4 AutoCompleteTextView(自動完成文本框)的基本使用
- 2.5.5 ExpandableListView(可折疊列表)的基本使用
- 2.5.6 ViewFlipper(翻轉視圖)的基本使用
- 2.5.7 Toast(吐司)的基本使用
- 2.5.8 Notification(狀態欄通知)詳解
- 2.5.9 AlertDialog(對話框)詳解
- 2.6.0 其他幾種常用對話框基本使用
- 2.6.1 PopupWindow(懸浮框)的基本使用
- 2.6.2 菜單(Menu)
- 2.6.3 ViewPager的簡單使用
- 2.6.4 DrawerLayout(官方側滑菜單)的簡單使用
- 3.1.1 基于監聽的事件處理機制
- 3.2 基于回調的事件處理機制
- 3.3 Handler消息傳遞機制淺析
- 3.4 TouchListener PK OnTouchEvent + 多點觸碰
- 3.5 監聽EditText的內容變化
- 3.6 響應系統設置的事件(Configuration類)
- 3.7 AnsyncTask異步任務
- 3.8 Gestures(手勢)
- 4.1.1 Activity初學乍練
- 4.1.2 Activity初窺門徑
- 4.1.3 Activity登堂入室
- 4.2.1 Service初涉
- 4.2.2 Service進階
- 4.2.3 Service精通
- 4.3.1 BroadcastReceiver牛刀小試
- 4.3.2 BroadcastReceiver庖丁解牛
- 4.4.2 ContentProvider再探——Document Provider
- 4.5.1 Intent的基本使用
- 4.5.2 Intent之復雜數據的傳遞
- 5.1 Fragment基本概述
- 5.2.1 Fragment實例精講——底部導航欄的實現(方法1)
- 5.2.2 Fragment實例精講——底部導航欄的實現(方法2)
- 5.2.3 Fragment實例精講——底部導航欄的實現(方法3)
- 5.2.4 Fragment實例精講——底部導航欄+ViewPager滑動切換頁面
- 5.2.5 Fragment實例精講——新聞(購物)類App列表Fragment的簡單實現
- 6.1 數據存儲與訪問之——文件存儲讀寫
- 6.2 數據存儲與訪問之——SharedPreferences保存用戶偏好參數
- 6.3.1 數據存儲與訪問之——初見SQLite數據庫
- 6.3.2 數據存儲與訪問之——又見SQLite數據庫
- 7.1.1 Android網絡編程要學的東西與Http協議學習
- 7.1.2 Android Http請求頭與響應頭的學習
- 7.1.3 Android HTTP請求方式:HttpURLConnection
- 7.1.4 Android HTTP請求方式:HttpClient
- 7.2.1 Android XML數據解析
- 7.2.2 Android JSON數據解析
- 7.3.1 Android 文件上傳
- 7.3.2 Android 文件下載(1)
- 7.3.3 Android 文件下載(2)
- 7.4 Android 調用 WebService
- 7.5.1 WebView(網頁視圖)基本用法
- 7.5.2 WebView和JavaScrip交互基礎
- 7.5.3 Android 4.4后WebView的一些注意事項
- 7.5.4 WebView文件下載
- 7.5.5 WebView緩存問題
- 7.5.6 WebView處理網頁返回的錯誤碼信息
- 7.6.1 Socket學習網絡基礎準備
- 7.6.2 基于TCP協議的Socket通信(1)
- 7.6.3 基于TCP協議的Socket通信(2)
- 7.6.4 基于UDP協議的Socket通信
- 8.1.1 Android中的13種Drawable小結 Part 1
- 8.1.2 Android中的13種Drawable小結 Part 2
- 8.1.3 Android中的13種Drawable小結 Part 3
- 8.2.1 Bitmap(位圖)全解析 Part 1
- 8.2.2 Bitmap引起的OOM問題
- 8.3.1 三個繪圖工具類詳解
- 8.3.2 繪圖類實戰示例
- 8.3.3 Paint API之—— MaskFilter(面具)
- 8.3.4 Paint API之—— Xfermode與PorterDuff詳解(一)
- 8.3.5 Paint API之—— Xfermode與PorterDuff詳解(二)
- 8.3.6 Paint API之—— Xfermode與PorterDuff詳解(三)
- 8.3.7 Paint API之—— Xfermode與PorterDuff詳解(四)
- 8.3.8 Paint API之—— Xfermode與PorterDuff詳解(五)
- 8.3.9 Paint API之—— ColorFilter(顏色過濾器)(1/3)
- 8.3.10 Paint API之—— ColorFilter(顏色過濾器)(2-3)
- 8.3.11 Paint API之—— ColorFilter(顏色過濾器)(3-3)
- 8.3.12 Paint API之—— PathEffect(路徑效果)
- 8.3.13 Paint API之—— Shader(圖像渲染)
- 8.3.14 Paint幾個枚舉/常量值以及ShadowLayer陰影效果
- 8.3.15 Paint API之——Typeface(字型)
- 8.3.16 Canvas API詳解(Part 1)
- 8.3.17 Canvas API詳解(Part 2)剪切方法合集
- 8.3.18 Canvas API詳解(Part 3)Matrix和drawBitmapMash
- 8.4.1 Android動畫合集之幀動畫
- 8.4.2 Android動畫合集之補間動畫
- 8.4.3 Android動畫合集之屬性動畫-初見
- 8.4.4 Android動畫合集之屬性動畫-又見
- 9.1 使用SoundPool播放音效(Duang~)
- 9.2 MediaPlayer播放音頻與視頻
- 9.3 使用Camera拍照
- 9.4 使用MediaRecord錄音
- 10.1 TelephonyManager(電話管理器)
- 10.2 SmsManager(短信管理器)
- 10.3 AudioManager(音頻管理器)
- 10.4 Vibrator(振動器)
- 10.5 AlarmManager(鬧鐘服務)
- 10.6 PowerManager(電源服務)
- 10.7 WindowManager(窗口管理服務)
- 10.8 LayoutInflater(布局服務)
- 10.9 WallpaperManager(壁紙管理器)
- 10.10 傳感器專題(1)——相關介紹
- 10.11 傳感器專題(2)——方向傳感器
- 10.12 傳感器專題(3)——加速度/陀螺儀傳感器
- 10.12 傳感器專題(4)——其他傳感器了解
- 10.14 Android GPS初涉
- 11.0《2015最新Android基礎入門教程》完結散花~
