# 二分類
二分類是指僅有兩個不同類的問題。正如我們在上一章中所做的那樣,我們將使用 SciKit Learn 庫中的便捷函數`make_classification()`生成數據集:
```py
X, y = skds.make_classification(n_samples=200,
n_features=2,
n_informative=2,
n_redundant=0,
n_repeated=0,
n_classes=2,
n_clusters_per_class=1)
if (y.ndim == 1):
y = y.reshape(-1,1)
```
`make_classification()`的論據是不言自明的; `n_samples`是要生成的數據點數,`n_features`是要生成的特征數,`n_classes`是類的數量,即 2:
* `n_samples`是要生成的數據點數。我們將其保持在 200 以保持數據集較小。
* `n_features`是要生成的特征數量;我們只使用兩個特征,因此我們可以將它作為一個簡單的問題來理解 TensorFlow 命令。
* `n_classes`是類的數量,它是 2,因為它是二分類問題。
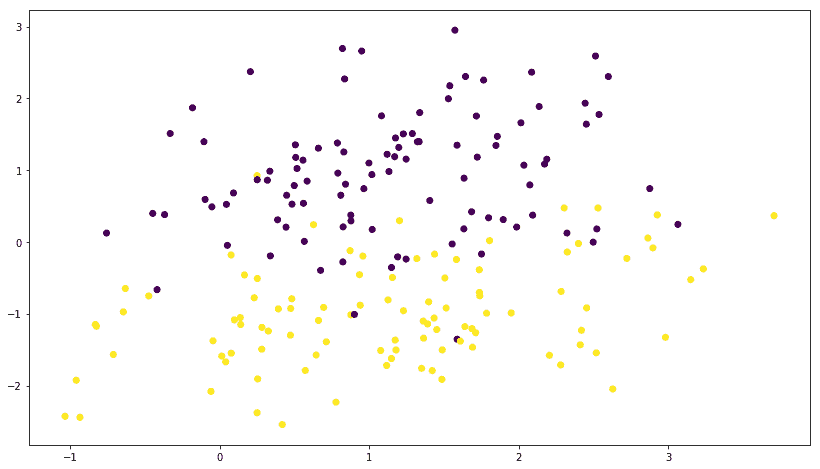
讓我們使用以下代碼繪制數據:
```py
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],marker='o',c=y)
plt.show()
```
我們得到以下繪圖;您可能會得到一個不同的圖,因為每次運行數據生成函數時都會隨機生成數據:
然后我們使用 NumPy `eye`函數將`y`轉換為單熱編碼目標:
```py
print(y[0:5])
y=np.eye(num_outputs)[y]
print(y[0:5])
```
單熱編碼目標如下所示:
```py
[1 0 0 1 0]
[[ 0\. 1.]
[ 1\. 0.]
[ 1\. 0.]
[ 0\. 1.]
[ 1\. 0.]]
```
將數據劃分為訓練和測試類別:
```py
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = skms.train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=.4, random_state=42)
```
在分類中,我們使用 sigmoid 函數來量化模型的值,使得輸出值位于范圍[0,1]之間。以下等式表示由`φ(z)`表示的 S 形函數,其中`z`是等式`w × x + b`。損失函數現在變為由`J(θ)`表示的值,其中`θ`表示參數。

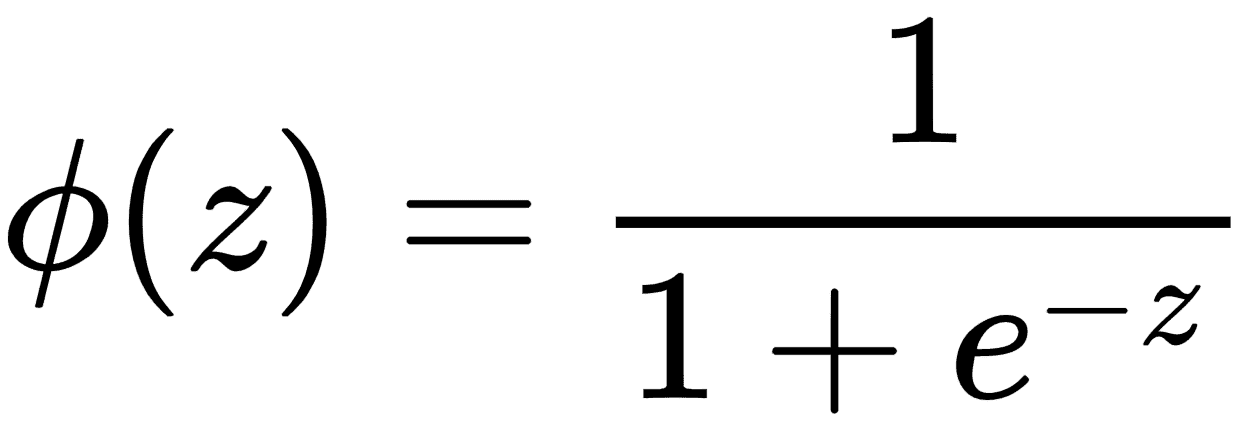
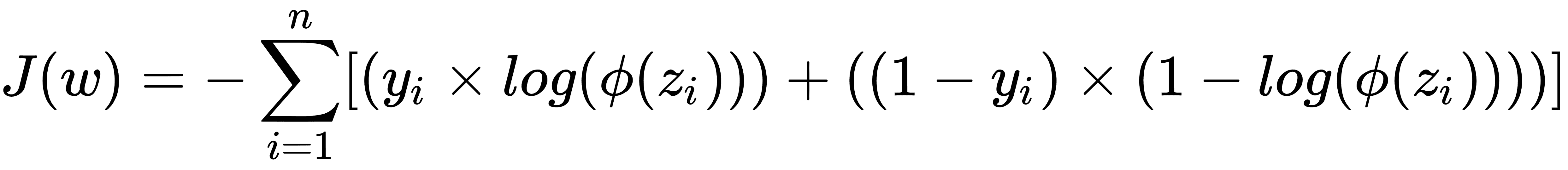
我們使用以下代碼實現新模型和損失函數:
```py
num_outputs = y_train.shape[1]
num_inputs = X_train.shape[1]
learning_rate = 0.001
# input images
x = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, num_inputs], name="x")
# output labels
y = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, num_outputs], name="y")
# model paramteres
w = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([num_inputs,num_outputs]), name="w")
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([num_outputs]), name="b")
model = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.matmul(x, w) + b)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(
(y * tf.log(model)) + ((1 - y) * tf.log(1 - model)), axis=1))
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(
learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(loss)
```
最后,我們運行我們的分類模型:
```py
num_epochs = 1
with tf.Session() as tfs:
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
tfs.run(optimizer, feed_dict={x: X_train, y: y_train})
y_pred = tfs.run(tf.argmax(model, 1), feed_dict={x: X_test})
y_orig = tfs.run(tf.argmax(y, 1), feed_dict={y: y_test})
preds_check = tf.equal(y_pred, y_orig)
accuracy_op = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(preds_check, tf.float32))
accuracy_score = tfs.run(accuracy_op)
print("epoch {0:04d} accuracy={1:.8f}".format(
epoch, accuracy_score))
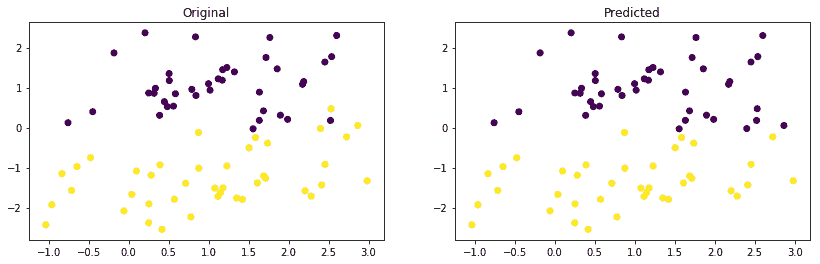
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 4))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], marker='o', c=y_orig)
plt.title('Original')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], marker='o', c=y_pred)
plt.title('Predicted')
plt.show()
```
我們獲得了大約 96%的相當好的準確率,原始和預測的數據圖如下所示:
很簡約!!現在讓我們讓我們的問題變得復雜,并嘗試預測兩個以上的類。
- TensorFlow 101
- 什么是 TensorFlow?
- TensorFlow 核心
- 代碼預熱 - Hello TensorFlow
- 張量
- 常量
- 操作
- 占位符
- 從 Python 對象創建張量
- 變量
- 從庫函數生成的張量
- 使用相同的值填充張量元素
- 用序列填充張量元素
- 使用隨機分布填充張量元素
- 使用tf.get_variable()獲取變量
- 數據流圖或計算圖
- 執行順序和延遲加載
- 跨計算設備執行圖 - CPU 和 GPU
- 將圖節點放置在特定的計算設備上
- 簡單放置
- 動態展示位置
- 軟放置
- GPU 內存處理
- 多個圖
- TensorBoard
- TensorBoard 最小的例子
- TensorBoard 詳情
- 總結
- TensorFlow 的高級庫
- TF Estimator - 以前的 TF 學習
- TF Slim
- TFLearn
- 創建 TFLearn 層
- TFLearn 核心層
- TFLearn 卷積層
- TFLearn 循環層
- TFLearn 正則化層
- TFLearn 嵌入層
- TFLearn 合并層
- TFLearn 估計層
- 創建 TFLearn 模型
- TFLearn 模型的類型
- 訓練 TFLearn 模型
- 使用 TFLearn 模型
- PrettyTensor
- Sonnet
- 總結
- Keras 101
- 安裝 Keras
- Keras 中的神經網絡模型
- 在 Keras 建立模型的工作流程
- 創建 Keras 模型
- 用于創建 Keras 模型的順序 API
- 用于創建 Keras 模型的函數式 API
- Keras 層
- Keras 核心層
- Keras 卷積層
- Keras 池化層
- Keras 本地連接層
- Keras 循環層
- Keras 嵌入層
- Keras 合并層
- Keras 高級激活層
- Keras 正則化層
- Keras 噪音層
- 將層添加到 Keras 模型
- 用于將層添加到 Keras 模型的順序 API
- 用于向 Keras 模型添加層的函數式 API
- 編譯 Keras 模型
- 訓練 Keras 模型
- 使用 Keras 模型進行預測
- Keras 的附加模塊
- MNIST 數據集的 Keras 序列模型示例
- 總結
- 使用 TensorFlow 進行經典機器學習
- 簡單的線性回歸
- 數據準備
- 構建一個簡單的回歸模型
- 定義輸入,參數和其他變量
- 定義模型
- 定義損失函數
- 定義優化器函數
- 訓練模型
- 使用訓練的模型進行預測
- 多元回歸
- 正則化回歸
- 套索正則化
- 嶺正則化
- ElasticNet 正則化
- 使用邏輯回歸進行分類
- 二分類的邏輯回歸
- 多類分類的邏輯回歸
- 二分類
- 多類分類
- 總結
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的神經網絡和 MLP
- 感知機
- 多層感知機
- 用于圖像分類的 MLP
- 用于 MNIST 分類的基于 TensorFlow 的 MLP
- 用于 MNIST 分類的基于 Keras 的 MLP
- 用于 MNIST 分類的基于 TFLearn 的 MLP
- 使用 TensorFlow,Keras 和 TFLearn 的 MLP 總結
- 用于時間序列回歸的 MLP
- 總結
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的 RNN
- 簡單循環神經網絡
- RNN 變種
- LSTM 網絡
- GRU 網絡
- TensorFlow RNN
- TensorFlow RNN 單元類
- TensorFlow RNN 模型構建類
- TensorFlow RNN 單元包裝器類
- 適用于 RNN 的 Keras
- RNN 的應用領域
- 用于 MNIST 數據的 Keras 中的 RNN
- 總結
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的時間序列數據的 RNN
- 航空公司乘客數據集
- 加載 airpass 數據集
- 可視化 airpass 數據集
- 使用 TensorFlow RNN 模型預處理數據集
- TensorFlow 中的簡單 RNN
- TensorFlow 中的 LSTM
- TensorFlow 中的 GRU
- 使用 Keras RNN 模型預處理數據集
- 使用 Keras 的簡單 RNN
- 使用 Keras 的 LSTM
- 使用 Keras 的 GRU
- 總結
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的文本數據的 RNN
- 詞向量表示
- 為 word2vec 模型準備數據
- 加載和準備 PTB 數據集
- 加載和準備 text8 數據集
- 準備小驗證集
- 使用 TensorFlow 的 skip-gram 模型
- 使用 t-SNE 可視化單詞嵌入
- keras 的 skip-gram 模型
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 中的 RNN 模型生成文本
- TensorFlow 中的 LSTM 文本生成
- Keras 中的 LSTM 文本生成
- 總結
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的 CNN
- 理解卷積
- 了解池化
- CNN 架構模式 - LeNet
- 用于 MNIST 數據的 LeNet
- 使用 TensorFlow 的用于 MNIST 的 LeNet CNN
- 使用 Keras 的用于 MNIST 的 LeNet CNN
- 用于 CIFAR10 數據的 LeNet
- 使用 TensorFlow 的用于 CIFAR10 的 ConvNets
- 使用 Keras 的用于 CIFAR10 的 ConvNets
- 總結
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的自編碼器
- 自編碼器類型
- TensorFlow 中的棧式自編碼器
- Keras 中的棧式自編碼器
- TensorFlow 中的去噪自編碼器
- Keras 中的去噪自編碼器
- TensorFlow 中的變分自編碼器
- Keras 中的變分自編碼器
- 總結
- TF 服務:生產中的 TensorFlow 模型
- 在 TensorFlow 中保存和恢復模型
- 使用保護程序類保存和恢復所有圖變量
- 使用保護程序類保存和恢復所選變量
- 保存和恢復 Keras 模型
- TensorFlow 服務
- 安裝 TF 服務
- 保存 TF 服務的模型
- 提供 TF 服務模型
- 在 Docker 容器中提供 TF 服務
- 安裝 Docker
- 為 TF 服務構建 Docker 鏡像
- 在 Docker 容器中提供模型
- Kubernetes 中的 TensorFlow 服務
- 安裝 Kubernetes
- 將 Docker 鏡像上傳到 dockerhub
- 在 Kubernetes 部署
- 總結
- 遷移學習和預訓練模型
- ImageNet 數據集
- 再訓練或微調模型
- COCO 動物數據集和預處理圖像
- TensorFlow 中的 VGG16
- 使用 TensorFlow 中預訓練的 VGG16 進行圖像分類
- TensorFlow 中的圖像預處理,用于預訓練的 VGG16
- 使用 TensorFlow 中的再訓練的 VGG16 進行圖像分類
- Keras 的 VGG16
- 使用 Keras 中預訓練的 VGG16 進行圖像分類
- 使用 Keras 中再訓練的 VGG16 進行圖像分類
- TensorFlow 中的 Inception v3
- 使用 TensorFlow 中的 Inception v3 進行圖像分類
- 使用 TensorFlow 中的再訓練的 Inception v3 進行圖像分類
- 總結
- 深度強化學習
- OpenAI Gym 101
- 將簡單的策略應用于 cartpole 游戲
- 強化學習 101
- Q 函數(在模型不可用時學習優化)
- RL 算法的探索與開發
- V 函數(模型可用時學習優化)
- 強化學習技巧
- 強化學習的樸素神經網絡策略
- 實現 Q-Learning
- Q-Learning 的初始化和離散化
- 使用 Q-Table 進行 Q-Learning
- Q-Network 或深 Q 網絡(DQN)的 Q-Learning
- 總結
- 生成性對抗網絡
- 生成性對抗網絡 101
- 建立和訓練 GAN 的最佳實踐
- 使用 TensorFlow 的簡單的 GAN
- 使用 Keras 的簡單的 GAN
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的深度卷積 GAN
- 總結
- 使用 TensorFlow 集群的分布式模型
- 分布式執行策略
- TensorFlow 集群
- 定義集群規范
- 創建服務器實例
- 定義服務器和設備之間的參數和操作
- 定義并訓練圖以進行異步更新
- 定義并訓練圖以進行同步更新
- 總結
- 移動和嵌入式平臺上的 TensorFlow 模型
- 移動平臺上的 TensorFlow
- Android 應用中的 TF Mobile
- Android 上的 TF Mobile 演示
- iOS 應用中的 TF Mobile
- iOS 上的 TF Mobile 演示
- TensorFlow Lite
- Android 上的 TF Lite 演示
- iOS 上的 TF Lite 演示
- 總結
- R 中的 TensorFlow 和 Keras
- 在 R 中安裝 TensorFlow 和 Keras 軟件包
- R 中的 TF 核心 API
- R 中的 TF 估計器 API
- R 中的 Keras API
- R 中的 TensorBoard
- R 中的 tfruns 包
- 總結
- 調試 TensorFlow 模型
- 使用tf.Session.run()獲取張量值
- 使用tf.Print()打印張量值
- 用tf.Assert()斷言條件
- 使用 TensorFlow 調試器(tfdbg)進行調試
- 總結
- 張量處理單元
