# 六、TensorFlow GPU 編程和服務
在本章中,我們將介紹以下主題:
* GPU 編程
* TensorFlow 服務:
* 如何安裝 TensorFlow 服務
* 如何使用 TensorFlow 服務
* 如何加載和導出 TensorFlow 模型
# GPU 編程
在第 5 章,“深度學習”中,我們針對 NLP 應用訓練了**循環神經網絡**(**RNN**), 深度學習應用可能需要大量計算。 但是,您可以通過**圖形處理單元**(**GPU**)使用并行編程技術來減少訓練時間。 實際上,現代圖形單元的計算資源使它們能夠執行并行代碼部分,從而確保了高性能。
GPU 編程模型是一種編程策略,包括將 CPU 替換為 GPU 以加速各種應用的執行。 該策略的應用范圍非常廣泛,并且每天都在增長。 目前,GPU 能夠減少跨平臺(從汽車到手機,從平板電腦到無人機和機器人)的應用執行時間。
下圖顯示了 GPU 編程模型如何工作。 在該應用中,有一些調用告訴 CPU 放棄代碼 GPU 的特定部分,并使其運行以提高執行速度。 此類特定部分依賴兩個 GPU 的原因取決于 GPU 架構提供的速度。 GPU 具有許多**流式多處理器**(**SMP**),每個處理器都具有許多計算核心。 這些內核借助**單指令多線程**(**SIMT**)調用能夠執行 ALU 和其他操作,從而大大減少了執行時間。
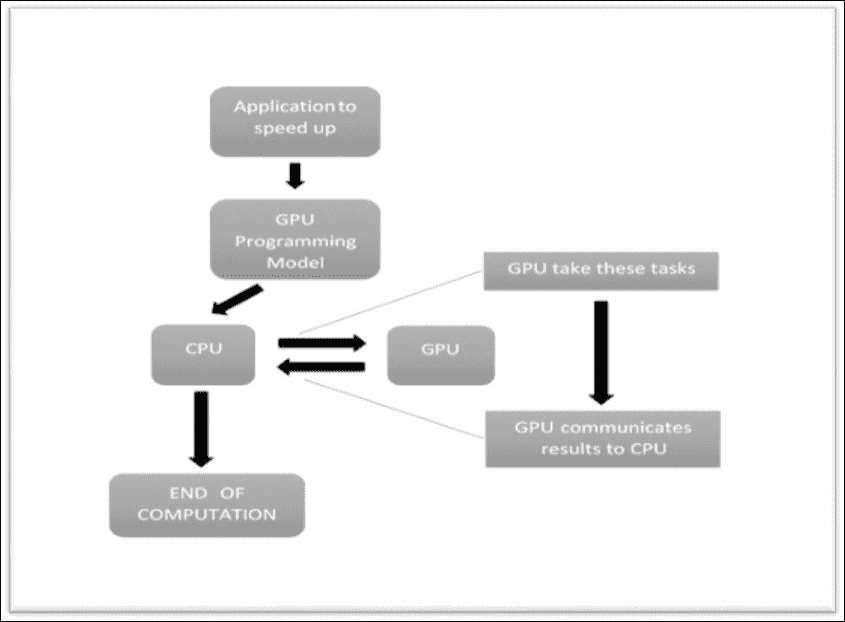
在 GPU 編程模型中,有一些代碼在 CPU 中順序執行,而某些部分則由 GPU 并行執行
TensorFlow 具有可以利用此編程模型的功能(如果您具有 NVIDIA GPU),支持 GPU 的包版本需要 Cuda Toolkit 7.0 和 6.5 CUDNN V2。
### 注意
對于 Cuda 環境的安裝,[我們建議參考 Cuda 安裝頁面](http://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-getting-started-guide-for-linux/#axzz49w1XvzNj):
TensorFlow 通過以下方式引用這些設備:
* `/cpu:0`:引用服務器 CPU
* `/gpu:0`:GPU 服務器(如果只有一個)
* `/gpu:1`:第二個 GPU 服務器,依此類推
要找出分配給我們的操作的設備,張緊器需要創建會話,并選擇將實例化的`log_device_placement`設置為`True`。
考慮以下示例。
我們創建一個計算圖; `a`和`b`將是兩個矩陣:
```py
a = tf.constant([1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0], shape=[2, 3], name='a')
b = tf.constant([1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0], shape=[3, 2], name='b')
```
在`c`中,我們將這兩個輸入張量的矩陣相乘:
```py
c = tf.matmul(a, b)
```
然后,我們將`log_device_placement`設置為`True`來建立會話:
```py
sess = tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(log_device_placement=True))
```
最后,我們啟動會話:
```py
print sess.run(c)
```
您應該看到以下輸出:
```py
Device mapping:
/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/gpu:0 -> device: 0, name: Tesla K40c, pci bus
id: 0000:05:00.0
b: /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/gpu:0
a: /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/gpu:0
MatMul: /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/gpu:0
[[ 22\. 28.]
[ 49\. 64.]]
```
如果您希望某個特定的操作在您選擇的設備上運行而不是自動為您選擇的設備,則可以使用`tf.device`創建設備上下文,以便該上下文中的所有操作將具有相同的設備分配。
讓我們使用`tf.device`指令創建相同的計算圖:
```py
with tf.device('/cpu:0'):
a = tf.constant([1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0], shape=[2, 3], name='a')
b = tf.constant([1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0], shape=[3, 2], name='b')
c = tf.matmul(a, b)
```
同樣,我們構建會話圖并啟動它:
```py
sess = tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(log_device_placement=True))
print sess.run(c)
```
您會看到`a`和`b`已分配給`cpu:0`:
```py
Device mapping:
/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/gpu:0 -> device: 0, name: Tesla K40c, pci bus
id: 0000:05:00.0
b: /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/cpu:0
a: /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/cpu:0
MatMul: /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/gpu:0
[[ 22\. 28.]
[ 49\. 64.]]
```
如果您擁有多個 GPU,則可以在創建會話時在配置選項中將`allow_soft_placement`設置為`True`來直接選擇它。
# TensorFlow 服務
服務是 TensorFlow 包,已開發該包將機器學習模型帶入生產系統。 這意味著開發人員可以使用 TensorFlow 服務的 API 來構建服務器以服務于已實現的模型。
服務的模型每次都可以根據其客戶提供的數據進行推斷和預測,從而可以改進模型。
為了與服務系統進行通信,客戶端使用 Google 開發的高性能開源**遠程過程調用**(**RPC**)接口,稱為 gRPC。
典型的管道(請參見下圖)是將訓練數據饋送到學習器,后者輸出模型。 經過驗證后,即可將其部署到 TensorFlow 服務系統。 隨著新數據的可用或模型的改進,隨著時間的推移啟動和迭代我們的模型非常普遍。
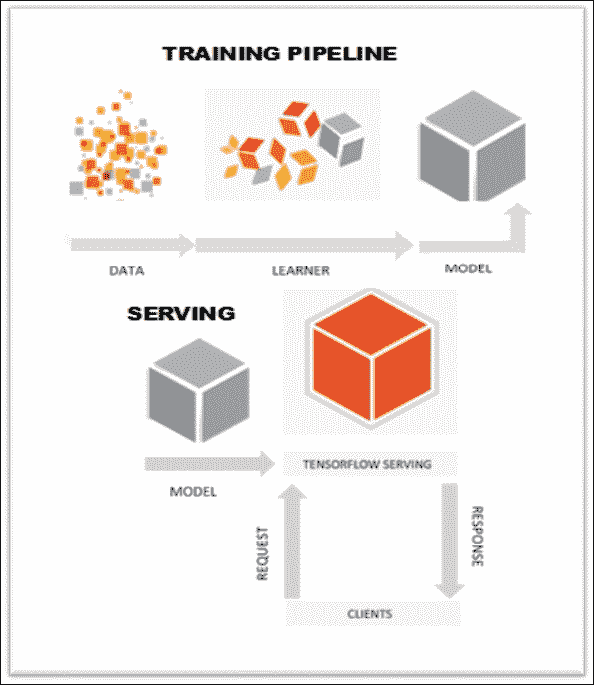
TensorFlow 服務管道
## 如何安裝 TensorFlow 服務
要編譯和使用 TensorFlow 服務,您需要設置一些先決條件。
### Bazel
TensorFlow 服務需要 [Bazel 0.2.0](http://www.bazel.io/) )或更高版本。 下載`bazel-0.2.0-installer-linux-x86_64.sh`。
### 注意
Bazel 是使軟件構建和測試自動化的工具。 支持的構建任務包括運行編譯器和鏈接器以生成可執行程序和庫,以及組裝可部署的包。
運行以下命令:
```py
chmod +x bazel-0.2.0-installer-linux-x86_64.sh
./bazel-0.2.0-installer-linux-x86_64.sh -user
```
最后,設置您的環境。 將其導出到您的`~/.bashrc`目錄中:
```py
export PATH="$PATH:$HOME/bin"
```
### gRPC
我們的教程使用 gRPC(0.13 或更高版本)作為我們的 RPC 框架。
### 注意
您可以在[這個頁面](https://github.com/grpc)上找到其他參考。
#### TensorFlow 服務依賴項
要安裝 TensorFlow 服務依賴項,請執行以下操作:
```py
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y \
build-essential \
curl \
git \
libfreetype6-dev \
libpng12-dev \
libzmq3-dev \
pkg-config \
python-dev \
python-numpy \
python-pip \
software-properties-common \
swig \
zip \
zlib1g-dev
```
然后通過運行以下命令來配置 TensorFlow:
```py
cd tensorflow
./configure
cd ..
```
#### 安裝服務
使用 Git 克隆存儲庫:
```py
git clone --recurse-submodules
https://github.com/tensorflow/serving
cd serving
```
需要`--recurse-submodules`選項來獲取 TensorFlow,gRPC 和 TensorFlow 服務所依賴的其他庫。 要構建 TensorFlow,您必須使用 Bazel:
```py
bazel build tensorflow_serving/
```
二進制文件將放置在`bazel-bin`目錄中,并且可以使用以下命令運行:
```py
/bazel-bin/tensorflow_serving/example/mnist_inference
```
最后,您可以通過執行以下命令來測試安裝:
```py
bazel test tensorflow_serving/
```
## 如何使用 TensorFlow 服務
在本教程中,我們將展示*如何導出*訓練有素的 TensorFlow 模型,以及*如何構建服務器*為導出的模型提供服務。 實現的模型是用于手寫圖像分類(MNIST 數據)的 Softmax 回歸模型。
該代碼將由兩部分組成:
* 訓練和導出模型的 Python 文件(`mnist_export.py`)
* 一個 C++ 文件(`mnist_inference.cc`),該文件加載導出的模型并運行 gRPC 服務為其提供服務
在以下各節中,我們報告使用 TensorFlow 服務的基本步驟。 對于其他參考,您可以查看[這里](https://tensorflow.github.io/serving/serving_basic)。
### 訓練和導出 TensorFlow 模型
如您在`mnist_export.py`中看到的,訓練的方法與 MNIST 中的方法相同。 對于初學者教程,請參考[以下鏈接](https://www.tensorflow.org/versions/r0.9/tutorials/mnist/beginners/index.html)。
TensorFlow 圖在 TensorFlow 會話`sess`中啟動,輸入張量(圖像)為`x`,輸出張量(Softmax 分數)為`y`。 然后我們使用 TensorFlow 服務導出器導出模型; 它構建了經過訓練的模型的快照,以便以后可以加載以進行推斷。 現在,讓我們看一下用于導出訓練后的模型的主要功能。
導入`exporter`以序列化模型:
```py
from tensorflow_serving.session_bundle import exporter
```
然后,您必須使用 TensorFlow 函數`tf.train.Saver`定義`saver`。 它的`sharded` 參數等于`True`:
```py
saver = tf.train.Saver(sharded=True)
```
`saver`用于將圖的變量值序列化為模型導出,以便以后可以正確還原它們。
下一步是定義`model_exporter`:
```py
model_exporter = exporter.Exporter(saver)
signature = exporter.classification_signature\
(input_tensor=x, scores_tensor=y)
model_exporter.init(sess.graph.as_graph_def(),
default_graph_signature=signature)
```
`model_exporter`采用以下兩個參數:
* `sess.graph.as_graph_def()`是該圖的原型。 導出會將 protobuf 序列化為模型導出,以便稍后可以正確恢復 TensorFlow 圖。
* `default_graph_signature=signature`指定模型導出簽名。 簽名指定要導出的模型類型,以及運行推理時綁定到的輸入/輸出張量。 在這種情況下,您可以使用`exporter.classification_signature`將該模型指定為分類模型。
最后,我們創建`export`:
```py
model_exporter.export(export_path,tf.constant\
(FLAGS.export_version), sess)
```
`model_exporter.export`采用以下參數:
* `export_path`是導出目錄的路徑。 如果目錄不存在,導出將創建該目錄。
* `tf.constant(FLAGS.export_version)`是一個張量,指定模型的版本。 導出同一模型的較新版本時,應指定一個較大的整數值。 每個版本將導出到給定路徑下的不同子目錄。
* `sess`是 TensorFlow 會話,其中包含您要導出的經過訓練的模型。
### 執行會話
要導出模型,請首先清除導出目錄:
```py
$>rm -rf /tmp/mnist_model
```
然后,使用`bazel`構建`mnist_export`示例:
```py
$>bazel build //tensorflow_serving/example:mnist_export
```
最后,您可以運行以下示例:
```py
$>bazel-bin/tensorflow_serving/example/mnist_export /tmp/mnist_model
Training model...
Done training!
Exporting trained model to /tmp/mnist_model
Done exporting!
```
在導出目錄中,我們應該有一個子目錄,用于導出模型的每個版本:
```py
$>ls /tmp/mnist_model
00000001
```
對應的子目錄的默認值為`1`,因為我們先前將`tf.constant(FLAGS.export_version)`指定為模型版本,而`FLAGS.export_version`的默認值為`1`。
子目錄的每個版本都包含以下文件:
* `export.meta`是模型的序列化`tensorflow::MetaGraphDef`。 它包括模型的圖定義,以及模型的元數據,例如簽名。
* `export-?????-of-?????`是保存圖的序列化變量的文件。
```py
$>ls /tmp/mnist_model/00000001
checkpoint export-00000-of-00001 export.meta
```
# 加載和導出 TensorFlow 模型
用于加載導出的 TensorFlow 模型的 C++ 代碼在`mnist_inference.cc`中的`main()`函數中。 在這里,我們報告摘錄; 我們不考慮用于批量的參數。 如果要調整最大批量大小,超時閾值或用于批量推理的后臺線程數,可以通過在`BatchingParameters`中設置更多值來進行調整:
```py
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
SessionBundleConfig session_bundle_config;
. . . Here batching parameters
std::unique_ptr<SessionBundleFactory> bundle_factory;
TF_QCHECK_OK(
SessionBundleFactory::Create(session_bundle_config,
&bundle_factory));
std::unique_ptr<SessionBundle> bundle(new SessionBundle);
TF_QCHECK_OK(bundle_factory->CreateSessionBundle(bundle_path,
&bundle));
......
RunServer(FLAGS_port, std::move(bundle));
return 0;
}
```
`SessionBundle`是 TensorFlow 服務的組件。 讓我們考慮包含文件`SessionBundle.h`:
```py
struct SessionBundle {
std::unique_ptr<tensorflow::Session> session;
tensorflow::MetaGraphDef meta_graph_def;
};
```
`session`參數是一個 TensorFlow 會話,具有原始圖和正確還原了必要變量的圖。
`SessionBundleFactory::CreateSessionBundle()`從`bundle_path`加載導出的 TensorFlow 模型,并創建一個`SessionBundle`對象以對該模型進行推理。
`RunServer`啟動了一個 gRPC 服務器,該服務器導出單個`Classify()` API。
每個推理請求將按以下步驟處理:
1. 驗證輸入。 對于每個推理請求,服務器都只需要一個 MNIST 格式的圖像。
2. 將輸入轉換為推斷輸入張量并創建輸出張量占位符。
3. 運行推斷。
要運行推理,必須鍵入以下命令:
```py
$>bazel build //tensorflow_serving/example:mnist_inference
$>bazel-bin/tensorflow_serving/example/mnist_inference --port=9000 /tmp/mnist_model/00000001
```
## 測試服務
要測試服務器,我們使用[`mnist_client.py`](https://github.com/tensorflow/serving/blob/master/tensorflow_serving/example/mnist_client.py)工具。
該客戶端下載 MNIST 測試數據,將其作為請求發送到服務器,并計算推斷錯誤率。
要運行它,請鍵入以下命令:
```py
$>bazel build //tensorflow_serving/example:mnist_client
$>bazel-bin/tensorflow_serving/example/mnist_client --num_tests=1000
--server=localhost:9000
Inference error rate: 10.5%
```
結果確認服務器成功加載并運行了經過訓練的模型。 實際上,對于 1,000 張圖像,推理錯誤率為 10.5% ,這為訓練后的 Softmax 模型提供了 91% 的準確率。
# 總結
我們在本章中描述了 TensorFlow 的兩個重要功能。 首先是使用稱為 *GPU 計算*的編程模型的可能性,通過該模型可以加快代碼的速度(例如,神經網絡的訓練階段)。 本章的第二部分專門描述框架 *TensorFlow 服務*。 這是一個用于機器學習模型的高性能,開源服務系統,專為生產環境而設計,并針對 TensorFlow 進行了優化。 這個強大的框架可以運行多個模型,這些模型可以根據現實世界的數據隨時間變化,從而可以更有效地利用 GPU 資源,并允許開發人員改善自己的機器學習模型。
- TensorFlow 1.x 深度學習秘籍
- 零、前言
- 一、TensorFlow 簡介
- 二、回歸
- 三、神經網絡:感知器
- 四、卷積神經網絡
- 五、高級卷積神經網絡
- 六、循環神經網絡
- 七、無監督學習
- 八、自編碼器
- 九、強化學習
- 十、移動計算
- 十一、生成模型和 CapsNet
- 十二、分布式 TensorFlow 和云深度學習
- 十三、AutoML 和學習如何學習(元學習)
- 十四、TensorFlow 處理單元
- 使用 TensorFlow 構建機器學習項目中文版
- 一、探索和轉換數據
- 二、聚類
- 三、線性回歸
- 四、邏輯回歸
- 五、簡單的前饋神經網絡
- 六、卷積神經網絡
- 七、循環神經網絡和 LSTM
- 八、深度神經網絡
- 九、大規模運行模型 -- GPU 和服務
- 十、庫安裝和其他提示
- TensorFlow 深度學習中文第二版
- 一、人工神經網絡
- 二、TensorFlow v1.6 的新功能是什么?
- 三、實現前饋神經網絡
- 四、CNN 實戰
- 五、使用 TensorFlow 實現自編碼器
- 六、RNN 和梯度消失或爆炸問題
- 七、TensorFlow GPU 配置
- 八、TFLearn
- 九、使用協同過濾的電影推薦
- 十、OpenAI Gym
- TensorFlow 深度學習實戰指南中文版
- 一、入門
- 二、深度神經網絡
- 三、卷積神經網絡
- 四、循環神經網絡介紹
- 五、總結
- 精通 TensorFlow 1.x
- 一、TensorFlow 101
- 二、TensorFlow 的高級庫
- 三、Keras 101
- 四、TensorFlow 中的經典機器學習
- 五、TensorFlow 和 Keras 中的神經網絡和 MLP
- 六、TensorFlow 和 Keras 中的 RNN
- 七、TensorFlow 和 Keras 中的用于時間序列數據的 RNN
- 八、TensorFlow 和 Keras 中的用于文本數據的 RNN
- 九、TensorFlow 和 Keras 中的 CNN
- 十、TensorFlow 和 Keras 中的自編碼器
- 十一、TF 服務:生產中的 TensorFlow 模型
- 十二、遷移學習和預訓練模型
- 十三、深度強化學習
- 十四、生成對抗網絡
- 十五、TensorFlow 集群的分布式模型
- 十六、移動和嵌入式平臺上的 TensorFlow 模型
- 十七、R 中的 TensorFlow 和 Keras
- 十八、調試 TensorFlow 模型
- 十九、張量處理單元
- TensorFlow 機器學習秘籍中文第二版
- 一、TensorFlow 入門
- 二、TensorFlow 的方式
- 三、線性回歸
- 四、支持向量機
- 五、最近鄰方法
- 六、神經網絡
- 七、自然語言處理
- 八、卷積神經網絡
- 九、循環神經網絡
- 十、將 TensorFlow 投入生產
- 十一、更多 TensorFlow
- 與 TensorFlow 的初次接觸
- 前言
- 1.?TensorFlow 基礎知識
- 2. TensorFlow 中的線性回歸
- 3. TensorFlow 中的聚類
- 4. TensorFlow 中的單層神經網絡
- 5. TensorFlow 中的多層神經網絡
- 6. 并行
- 后記
- TensorFlow 學習指南
- 一、基礎
- 二、線性模型
- 三、學習
- 四、分布式
- TensorFlow Rager 教程
- 一、如何使用 TensorFlow Eager 構建簡單的神經網絡
- 二、在 Eager 模式中使用指標
- 三、如何保存和恢復訓練模型
- 四、文本序列到 TFRecords
- 五、如何將原始圖片數據轉換為 TFRecords
- 六、如何使用 TensorFlow Eager 從 TFRecords 批量讀取數據
- 七、使用 TensorFlow Eager 構建用于情感識別的卷積神經網絡(CNN)
- 八、用于 TensorFlow Eager 序列分類的動態循壞神經網絡
- 九、用于 TensorFlow Eager 時間序列回歸的遞歸神經網絡
- TensorFlow 高效編程
- 圖嵌入綜述:問題,技術與應用
- 一、引言
- 三、圖嵌入的問題設定
- 四、圖嵌入技術
- 基于邊重構的優化問題
- 應用
- 基于深度學習的推薦系統:綜述和新視角
- 引言
- 基于深度學習的推薦:最先進的技術
- 基于卷積神經網絡的推薦
- 關于卷積神經網絡我們理解了什么
- 第1章概論
- 第2章多層網絡
- 2.1.4生成對抗網絡
- 2.2.1最近ConvNets演變中的關鍵架構
- 2.2.2走向ConvNet不變性
- 2.3時空卷積網絡
- 第3章了解ConvNets構建塊
- 3.2整改
- 3.3規范化
- 3.4匯集
- 第四章現狀
- 4.2打開問題
- 參考
- 機器學習超級復習筆記
- Python 遷移學習實用指南
- 零、前言
- 一、機器學習基礎
- 二、深度學習基礎
- 三、了解深度學習架構
- 四、遷移學習基礎
- 五、釋放遷移學習的力量
- 六、圖像識別與分類
- 七、文本文件分類
- 八、音頻事件識別與分類
- 九、DeepDream
- 十、自動圖像字幕生成器
- 十一、圖像著色
- 面向計算機視覺的深度學習
- 零、前言
- 一、入門
- 二、圖像分類
- 三、圖像檢索
- 四、對象檢測
- 五、語義分割
- 六、相似性學習
- 七、圖像字幕
- 八、生成模型
- 九、視頻分類
- 十、部署
- 深度學習快速參考
- 零、前言
- 一、深度學習的基礎
- 二、使用深度學習解決回歸問題
- 三、使用 TensorBoard 監控網絡訓練
- 四、使用深度學習解決二分類問題
- 五、使用 Keras 解決多分類問題
- 六、超參數優化
- 七、從頭開始訓練 CNN
- 八、將預訓練的 CNN 用于遷移學習
- 九、從頭開始訓練 RNN
- 十、使用詞嵌入從頭開始訓練 LSTM
- 十一、訓練 Seq2Seq 模型
- 十二、深度強化學習
- 十三、生成對抗網絡
- TensorFlow 2.0 快速入門指南
- 零、前言
- 第 1 部分:TensorFlow 2.00 Alpha 簡介
- 一、TensorFlow 2 簡介
- 二、Keras:TensorFlow 2 的高級 API
- 三、TensorFlow 2 和 ANN 技術
- 第 2 部分:TensorFlow 2.00 Alpha 中的監督和無監督學習
- 四、TensorFlow 2 和監督機器學習
- 五、TensorFlow 2 和無監督學習
- 第 3 部分:TensorFlow 2.00 Alpha 的神經網絡應用
- 六、使用 TensorFlow 2 識別圖像
- 七、TensorFlow 2 和神經風格遷移
- 八、TensorFlow 2 和循環神經網絡
- 九、TensorFlow 估計器和 TensorFlow HUB
- 十、從 tf1.12 轉換為 tf2
- TensorFlow 入門
- 零、前言
- 一、TensorFlow 基本概念
- 二、TensorFlow 數學運算
- 三、機器學習入門
- 四、神經網絡簡介
- 五、深度學習
- 六、TensorFlow GPU 編程和服務
- TensorFlow 卷積神經網絡實用指南
- 零、前言
- 一、TensorFlow 的設置和介紹
- 二、深度學習和卷積神經網絡
- 三、TensorFlow 中的圖像分類
- 四、目標檢測與分割
- 五、VGG,Inception,ResNet 和 MobileNets
- 六、自編碼器,變分自編碼器和生成對抗網絡
- 七、遷移學習
- 八、機器學習最佳實踐和故障排除
- 九、大規模訓練
- 十、參考文獻
